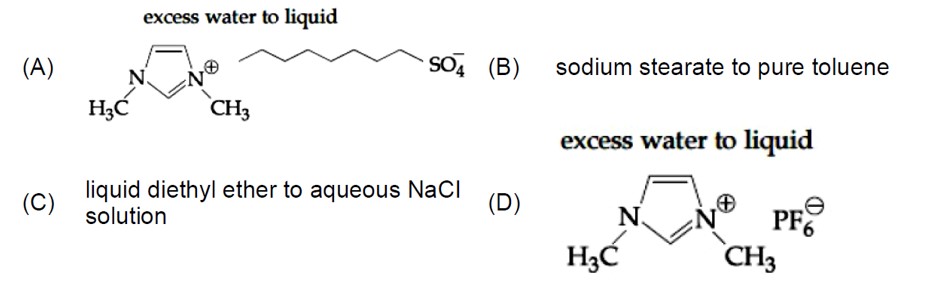Surface Chemistry
Get insights from 216 questions on Surface Chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Surface Chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
The diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of the light used. The intensity of scattered light depends on the difference between the refractive indice of the D.P and D.M., In lyophobic colloids, this difference is appreciable and therefore the tyndal effect is quite well defined but in lyophilic sols the difference is very small and the tyndal effect is very weak. So, to show Tyndall effect the refractive indices of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium differ greatly in magnitude.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
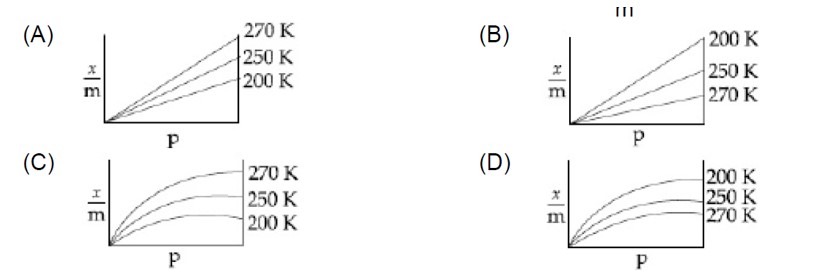
Sol. (x/m) = k (P)¹/?
log (x/m) = logk + 1/n logP
Slope = 1/n = 2 So n = 1/2
Intercept ⇒ logk = 0.477 So k = Antilog (0.477) = 3
So (x/m) = k (P)¹/? = 3² = 48
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
Bredig's Arc Method is used for preparation of colloidal sol's of less reactive metal like Au, Ag, Pt.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Gas + Solid? GS? H = -ve
Adsorbed gas
Adsorption of gas is an exothermic process. Increase in temperature reduces the extent of adsorption.
x/m = Kp¹/? (n > 1)
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
(x/m) = k (p)¹/? (1)
64 (x/m) = k (2p)¹/? (2)
From equation (1) and (2)
64 = 2¹/?
2? = 2¹/?
1/n = 6
n = 1/6
⇒ n = 0.167
= 16.7 * 10? ²
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers