Surface Chemistry
Get insights from 216 questions on Surface Chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Surface Chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Tyndall effect is the optical characteristics of light in which comparable particle size of colloids and bombarded light wavelength can produce this type of effect. For scattering effect of light in Tyndall effect refractive index of dispersed phase and dispersion medium should be greatly different.
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
ln
Hence; sum of oxidation state = 2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 9
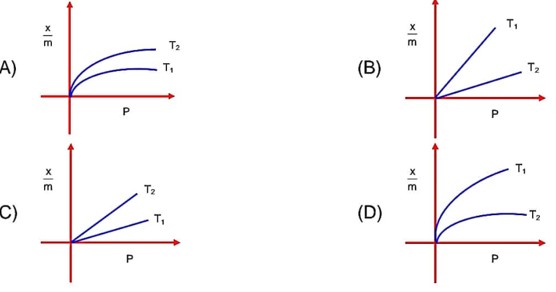
By increases in temperature absorption decreases, T1 > T2 means higher absorption at T2 temperature.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
In the lyophilic colloids, the colloidal particles are extremely solvated.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
FeCl3 + K4 [Fe (CN)6] (Potassium ferrocyanide)
excess
|
K Fe [Fe (CN)6]
(colloidal species)
Prussian Blue coloured
colloidal complex
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Tyndall effect is more effectively shown by lyophobic colloidal solution.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
During adsorption of a gas on solid surface, process is exothermic i.e. and entropy decreased, because gas particle resides on solid surface. Hence
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
When AgNO3 added to Kl solution, it form precipitate of Agl (s) which absorb I- ions from Kl and colloidal particles become negatively charged.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers