Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Get insights from 261 questions on Alcohol Phenol And Ethers, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
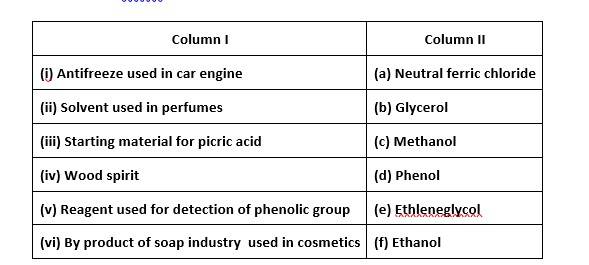
(i)- (e) ; (ii)- (f) ; (iii)- (d) ; (iv)- (c); (v)- (a); (vi)- (b)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
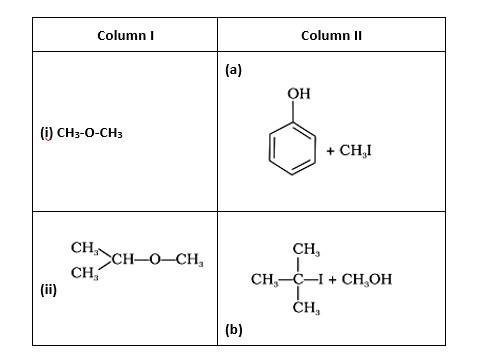
(i)- (d) (ii)- (e); (iii)- (b); (iv)- (a)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
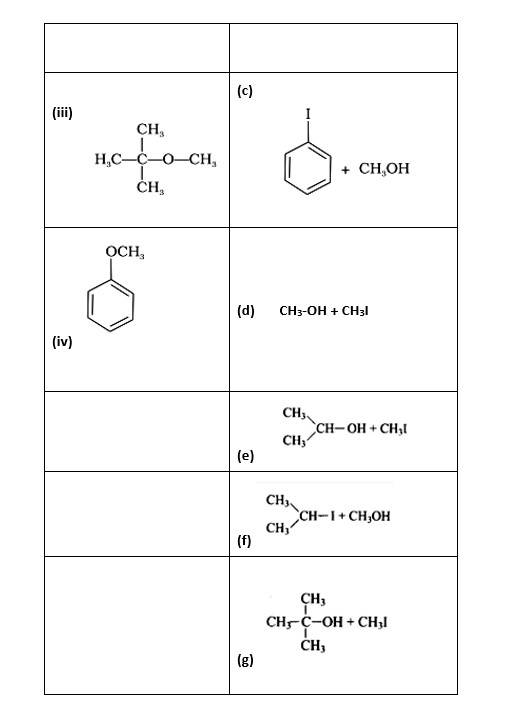
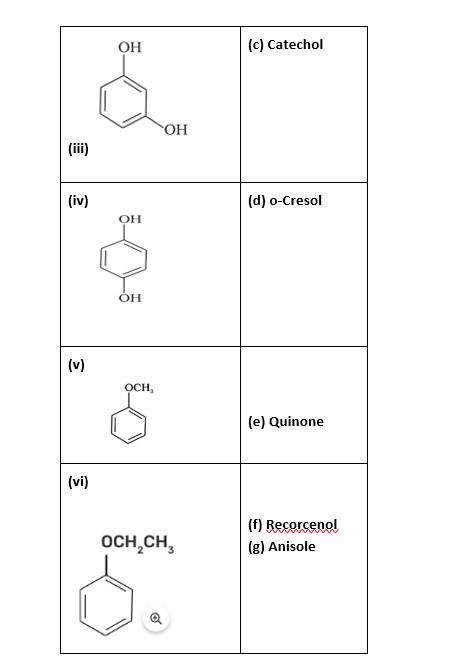
(i)- (d); (ii)- (c); (iii)- (f); (iv)- (a); (v)- (g); (vi)- (b)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
II. C6H5—CH2—OH
III. C6H5—CH—OH
|
CH3
Benzylic alcohol are those alcohols which have phenyl group attached to the alpha carbon of alcohol.
R—CαH2—OH : Benzylic Alcohol
The compound II and III have phenyl group attached at the Cα of the alcohol and thence they are benzylic alcohols
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
I. Br2/water
III. Neutral FeCl3
Phenol does not give the bromine water (Br2/water ) test whereas ethanol gives the bromine water.
Phenol on reaction with neutral FeCl3 forms a colored complex with Fe3+ ion whereas ethanol does not form the colored complex with neutral FeCl3.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
I. CrO3 in anhydrous medium.
II. Pyridinium chlorochromate.
III. Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K.
KMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent and oxidises the primary alcohol to ketone. Hence cannot be used as a reagent to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
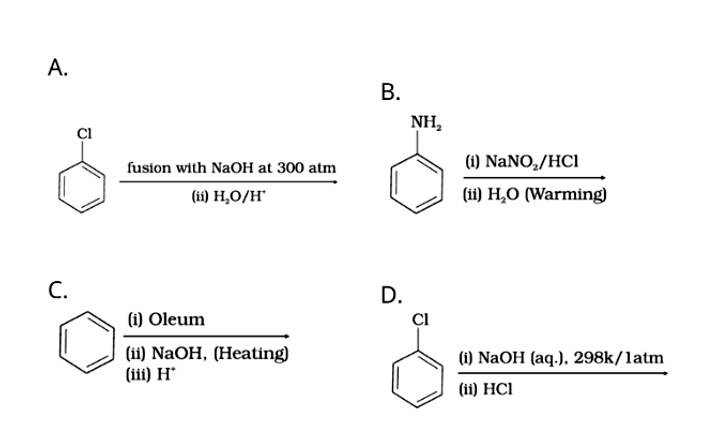
Phenol is prepared by:
Dow's process: The chlorobenzene on heating with NaOH, form sodium phenoxide which on hydrolysis with water of acid from phenol.
Diazotization of aniline: Aniline on reacting with nitrous acid at 0-5o C followed by hydrolysis with water form phenol.
Benzene undergoes sulphonation on reacting with oleum to form benzene sulphonic acid which on heating with sodium hydroxide forms sodium phenoxide and then phenol on hydrolysis.
The nucleophilic substitution of haloarenes such as chlorobenzene requires drastic conditions for conversion to phenol so chlorobenz
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
I. H2/Pd
II. LiA1H4
III. NaBH4
Aldehydes and ketones are converted to alcohols by catalytic hydrogenation.The reagents used to convert the aldehydes to alcohol are by H2/Pd, lithium aluminium hydride (LiA1H4), and sodium borohydride (NaBH4).
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(I) Propan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1-ol. pentan- 1-ol
The compounds Propan-l-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, pentan-1-ol belong to the alcohol family. The structure of the given alcohols are as shown below:
With increase in the molecular weight, the boiling points of alcohols increase. Hence, butan-1-ol has higher boiling point than propan-1-ol. Similarly, pentan-1-ol has higher boiling point than butan-1-ol.
Hence, the increasing order of the boiling points of alcohols is propan-1-ol < butan-1-ol < pentan-1-ol.
With increase in the branching of alkyl groups, the boiling point of alcohols dec
Contributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
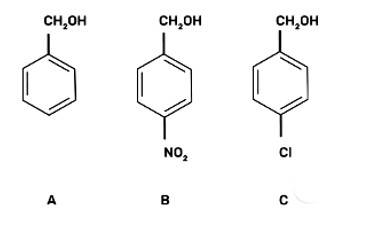
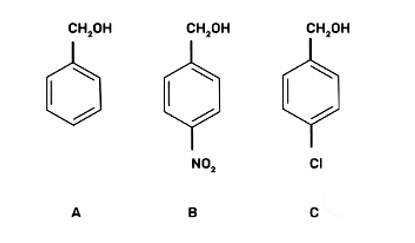
(III) b < c < a
The reaction will proceed by SN1 mechanism to form the carbocation intermediate, more the stability of carbocation more will be the reactivity of the given compound with HBr/HC1.
-NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group and due to the -M effect, increases the stability of carbocation. Cl group at para position shows + M effect due to it, carbocation is least stable and hence, the compound (c) is the least reactive.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers