Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Get insights from 261 questions on Alcohol Phenol And Ethers, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In phenol, the electron pairs on oxygen atom of -OH group are in conjugation (or resonance) with phenyl ring which decreases the polarity of the C-OH bond whereas in methanol the polarity of C-OH bond is more due to electron releasing group of -CH3.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Phenoxide ion is more reactive than phenol to electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction due to the more in electron density of phenoxide ion and hence, phenoxide ion easily undergoes the electrophilic substitution reaction than phenol by the weak CO2 electrophile.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The nitration of aromatic compounds occurs by using HSO4 and HNO3 which leads to the formation of NO2+ (nitronium ion) electrophile.
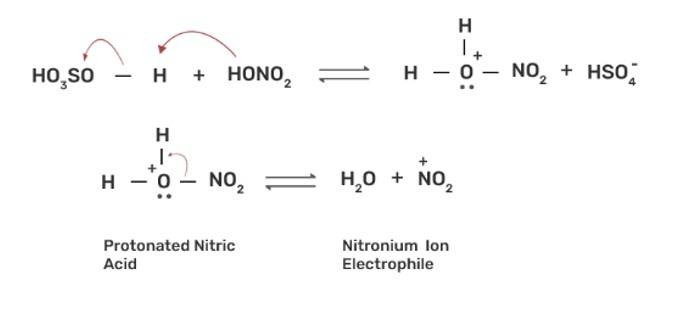
Due to the formation of NO2+ electrophile, we can say that nitration is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution. The electron releasing group on the benzene ring increases the rate of nitration and vice-versa.
Phenol is more easily nitrated than benzene as the hydroxyl (-OH) group on the benzene ring is an electron releasing group which increases the electron density at the ortho and para position due to +R effect of -
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
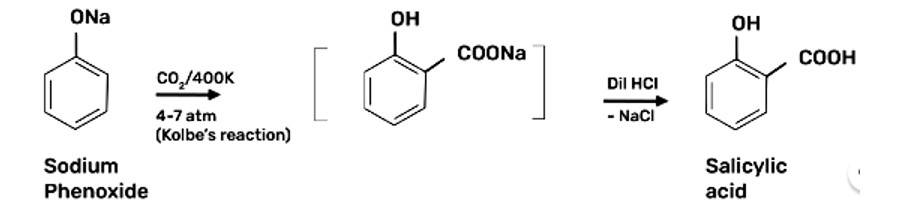
Step 1: Addition of NaOH to obtain sodium phenoxide
Step 2: Sodium Phenoxide undergoes Kolbe's reaction at high temperature and pressure in presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. The product is further hydrolysed to obtain salicylic acid.
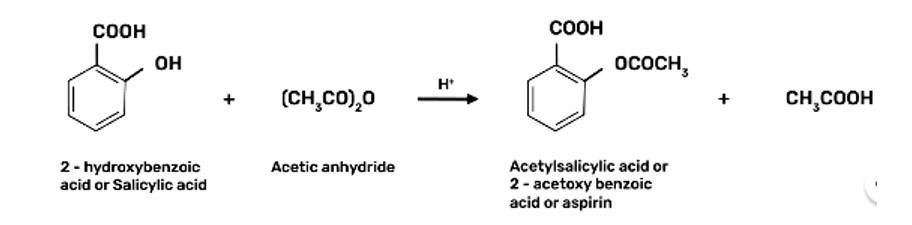
Step 3: Acetylation of salicylic acid occur when it is treated with acetic anhydride

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction of alcohol with the conc. HCl and ZnCl2 (Lucas reagent) leads to the formation of a carbocation through SN1 mechanism. The more stable the carbocation, the faster the reaction will be.
Tertiary carbocation is the most stable due to hyperconjugation and inductive effect then is the secondary alcohol and the primary alcohol is the least stable.
Stability of carbocation:
Tertiary carbocation > Secondary carbocation > Primary carbocation
According to stability of carbocation, the reactivity order of the alcohol is:
Tertiary alcohol > Secondary alc
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In O? C? O, the dipole moment is zero, hence non-polar while in R—O—R the dipole moment is non-zero due to which it is polar.
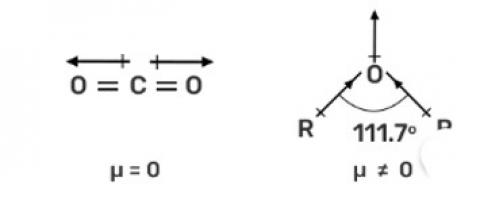
The CO2 is a linear molecule and the dipole moment is equal and in the opposite direction due to which the dipole moment is zero. While in R—O—R, has bent structure and lone pair of electrons due to which the net dipole moment is nonzero and hence, it is a polar molecule.
The CO2 is a linear molecule and the dipole moment is equal and in the opposite direction due to which the dipole moment is zero. While in R—O—R, has bent
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
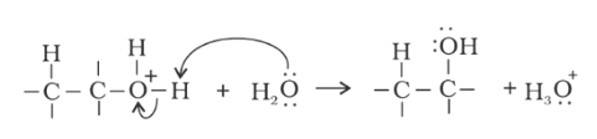
Step 1: Protonation of alkene due to the presence of double bond which attacks the H3O+ ion and forms carbocation.
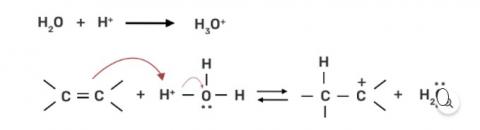
Step 2: Water molecule act as nucleophile and attack the carbocation.

Step 3: Deprotonation occur to get the alcohol and hydronium ion forms
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The C-OH bond in phenols has double bond character due to resonance of electron pairs of oxygen atom with the pi electrons of phenyl ring, which makes the C-OH bond strong and hence, the nucleophilic substitution of a nucleophile with the -OH group of alcohol is not possible as the C-OH does not break easily.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electron pairs of oxygen atom of hydroxyl (-OH) group in phenols are in conjugation with the pi electrons of phenyl ring and hence, the bond C-OH bond has double bond character due to which OH group in phenols more strongly held as compared to OH group in alcohols.
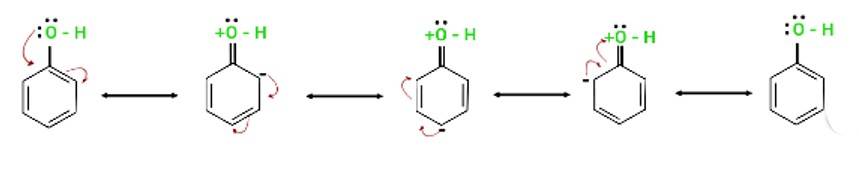
Resonance in phenol
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is butanol has 4 isomers, these are:
(a) CH3-CH2CH2-CH2OH (Butane-1-ol)
(b) CH3-C*H-CH2-CH3 (Butane-2-ol)
|
OH
(c) CH3-CH-CH2-OH (2-methylpropane-1-ol)
|
CH3
CH3
&nbs
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
