Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Get insights from 261 questions on Alcohol Phenol And Ethers, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(III) 3° > 2° > 1°
Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary by lucas reagent which is a mixture of concentrated HCl and dry anhydrous ZnCl2. The carbocation is formed as the intermediate during the lucas test of alcohol.More the stability of intermediate carbocation, more will be the reactivity of alcohol.
Tertiary carbocation is most stable then the secondary alcohol is stable due to hyperconjugation and the primary alcohol is the least stable.
Stability of intermediate carbocation:
3° > 2° > 1°
Reactivity of alcohol:
3° > 2° >
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(I) The alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is butanol has 4 isomers, these are:
(a) CH3-CH2CH2-CH2OH (Butane-1-ol)
(b) CH3-C*H-CH2-CH3 (Butane-2-ol)
|
OH
(c) CH3-CH-CH2-OH (2-methylpropane-1-ol)
|
CH3
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(IV) Benzyl alcohol
The chlorine atom is substituted by the hydrogen atom of methyl hydrocarbon present in toluene to form benzyl chloride on monochlorination of toluene in presence of sunlight by free radical pathway.
C6H5CH3 + Cl2 ![]() C6H5CH2Cl
C6H5CH2Cl
Toluene Benzyl Chloride
Benzyl chloride (monochlorinated toluene product) on hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields benzyl alcohol by substituting the chloride ion by OH- ion by nucleophilic substitution reaction.
C6H5CH2Cl ![]() C6H5CH2OH
C6H5CH2OH
Benzyl &
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Increasing order of acidity is: ethanol < water < phenol.
This is because the phenoxide ion obtained after the removal of H+ is resonance stabilised, while the ethoxide ion obtained after the removal of H+ is destabilised by +1 effect of ethyl group. Thus phenol is a stronger acid than ethanol.
Now, ethanol is a weaker acid than water because the electron releasing ethyl group increases the ethanol density on oxygen and consequently the proton will not be released easily. There is no such effect is water.
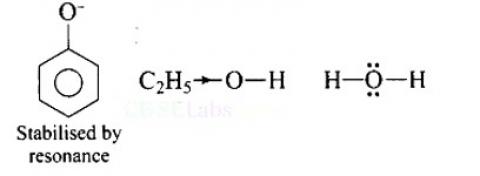
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
This can be explained as under:
(i) In phenol, the conjugation of unshared electron pairs over oxygen with aromatic ring results in partial double bond character in C – O bond.
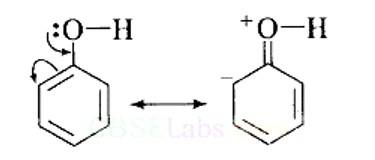
In methanol, no such conjugation (resonance) is possible.
(ii) In phenol, oxygen is attached to sp2 hybridised carbon while in methanol, oxygen attached to sp2 hybridised carbon. An sp2 hybridised carbon is more electronegative (because of greater 5-character) than sp3 hybridised carbon atom. Therefore, the bond between oxygen and sp2 hybridised carbon is more stable than the bond between oxyge
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to the presence of intermolecular H- bonds in alcohol the energy required to break H – bonds is more than the energy required to break simple dipole bonds present in ethers . Thus, the boiling point of alcohol is higher than the boiling point of ethers.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electron withdrawing group (-NO2), withdraws electrons and disperses the negative charge. Therefore, -NO2 group stabilizes the phenoxide ion. Hence p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The occurrence of intermolecular hydrogen bonds due to the H- bonds in alcohol compounds play a major role . With the increasing number of alkyl groups the molecular mass increases due to which the polar nature of these compounds get suppressed . Hence, the solubility factor of alcohols is indirectly proportional to the molecular mass.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The bond angle C—O—H in alcohols is less than tetrahedral angle because of the repulsion between the lone pairs present on the oxygen atom, which pushes the bond C—O—H closer. Therefore, C—O—H bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
In ethers, the lone pairs on oxygen atoms are also present but the two bulky alkyl groups also have repulsive force which increases the C—O—C bond angle. Therefore, the C—O—C bond angle in ether is slightly greater than tetrahedral angle .
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
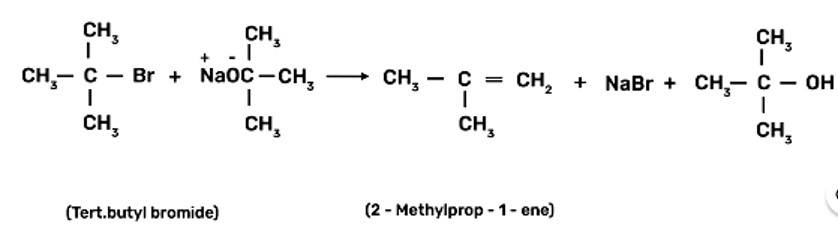
Ethers are prepared by Williamson synthesis by the reaction of alkyl halide with the stadium alkoxide. But this is not possible in case of di-tert-butyl ether. In case of preparation of di-tert-butyl ether, tert-butyl halide must react with sodium tert-butoxide. Alkoxides are nucleophiles but they are strong bases as well, due to which elimination is favoured instead of substitution and leads to the formation of 2-methylprop-1-ene.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
