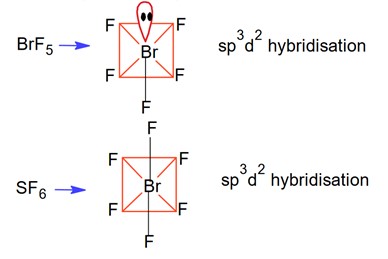
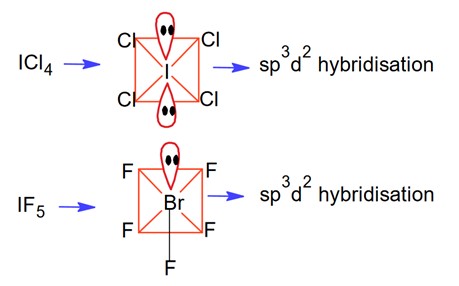
Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Get insights from 133 questions on Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Molecules usually form chemical bond through either sharing or through rtransfering the electrons. During covalent bonding the electron pairs shared between atoms to form covalent bond are called shared pair or bond pair. At the same time, the electron pair which is not involved in sharing is called lone pair of electrons.
For example: CH4 has 4 bond pairs but H2O has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs.

New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is an algorithm developed to predict the molecular geometry of the compounds. The VSEPR theory predict the molecular shape based on the repulsion between electron pairs (bonding and lone) around the central atom. As per the NCERT Textbooks:
“According to this theory, the shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs around the central atom. Electron pairs repel each other and try to remain as far apart as possible to minimise repulsion, thus determining the geometry of the molecule.”
You can use this theory in primarily explaining the molecular str
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
VSEPR theory predicts the shape of molecule based on postulate (assmptions). here are the important postulates as per the NCERT textbooks.
- The molecular geometry shape depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded and non-bonded) around the central atom.
- The electron pairs (bonded and lone pairs) in the valence shell repel each other since their electron clouds are negatively charged.
- These electron pairs arrange themselves to minimize repulsion so that the molecule attains a stable structure with minimum energy.
- All electron pair repulsion doesn't repel each other equally, Electron pairs follows this order:
Lone pai
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetic molecules are
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Number of electrons in
are e- deficient molecules. B2H6 is dimer of BH3, both compound has 6e- only.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Bond strength Bond order
NO Number of electron = 7 + 8 = 15
B.O. Similar to
B.O. of N2 = 3B.O of C2 =
Removal of e form antibonding molecular orbital increases bond order.
In NO & O2 has valance e in orbital.
New answer posted
6 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The name of covalent and ionic bonds tell their formation story in small detail. Co- means sharing or coexisting, so whenever there is bond fromation due to sharing of valence electron, it is known as covalent bond. Similerly, ionic bonds suggest that when a bond formation takes place due to ions, which attract each other, it is considered as ionic bond. Ionic bonds are also known as electrovalent bonds. There are some major differences between Electrovalent and covalent bonds. Chekc the table below:
| Aspect | Covalent Bond | Ionic Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Reason of Formation | sharing of electrons between atoms | transfer of electrons from one atom to another |
| Elements | Usually non-metals with non-metals | Usually metals with non-metals |
| Strength | Moderate | the strongest |
| Nature | Directional Bond & Poor conductors of electricity | Non-directional Bond & Conducts electricity in aqueous state |
| Electronegativity Difference | Small (generally < 1.7) | Large (generally > 1.7) |
| Physical State | Usually Gases, liquids, and soft solids | Hard crystalline solids |
| Melting & Boiling Points | low to moderate | high |
| Solubility | Non-polar solvents | Polar solvents like water |
| Examples | H? , O? , CH? , HCl, NH? | NaCl, KBr, CaCl? , MgO |
For more detail related to the chemical bonding in class 11 chemistry read our notes.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Bond order of
Bond order of
Bond order of
NB = No. of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals.
NA = No. of electron is Anti bonding molecular orbitals
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers