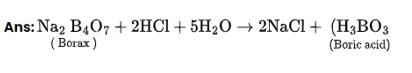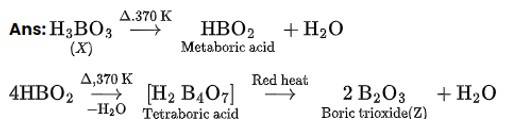Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven
Get insights from 115 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
C
Gallium generally exists as solid at room temperature but melts on slight heating (melting point: 20? C ).
Whereas the boiling point of Gallium is very high around 2400? C. Gallium has large cohesive forces that hold its structure together and it is stable for a wide range of temperatures and can be used for measuring high temperatures.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
4BF3 + 3LiAlH4? 2 B2H6 + 3LiF + 3AlF3
(Z) (X)
B2H6 + 6H2O?2H3BO3 + 6H2
(X) (Y)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) When moving down the periodic table within a group, ionization enthalpy generally decreases due to increased atomic radius. However, in the case of gallium (Ga) and aluminum (Al), gallium experiences a higher effective nuclear charge due to less shielding from its inner electrons, resulting in a higher ionization enthalpy compared to aluminum.
(ii) As boron is smaller in size and the sum of its first three ionization enthalpies i.e. ΔH1+ΔH2+ΔH3 is very large so boron does not allow to lose its all three valence electrons and exist as +3
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The following reaction takes place in the test tube
- i) When Aluminium is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Al + HCl -à AlCl3
ii) When Aluminium is treated with dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
Al + NaOH -àNaAlO2 + H2
In both the cases, the Hydrogen atoms are evolved. So, when a burning match stick is brought near the test tube we hear a pop sound.
Aluminium does not react with concentrated nitric acid. A "layer" of "Aluminium Oxide" is formed, when aluminium reacts with the nitric acid because "nitric acid" is an oxidising agent. Due t
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
BCl3+3H2O→B (OH)3+3HCl
B (OH)3+2H2O→ [B (OH)4]−+H3O+
B (OH)3 due to its incomplete octet accepts an electron pair (OH)- to give has configucation [B (OH)4]−.
Boron in this ion involves one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals. Thus, hybridization of B in [B (OH)4]− is sp3
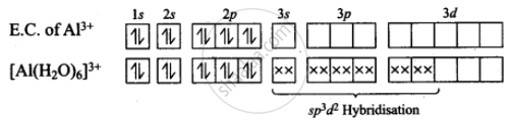
AlCl3 + 6H2O [Al (H2O)6]3+ +3Cl-
Hence, hybridization of Al is sp3d2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When a trivalent atom is added to the crystal of SiO2, it substitutes silicon atoms which result in generation of holes. These holes make the crystal conductor of electricity. The overall Crystal is electrically neutral and is called the p-type conductor.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As compared to carbon, silicon is bigger in size and is less electronegative. It shows resistance in forming p−p multiple bonding which is easily done by carbon. Thus, SiO2 is a 3−D network where each silicon is linked covalently to 4 oxygen atoms while in CO2, Carbon is linked with two oxygen atoms with double bond in a linear manner.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answers Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As we move down the group in group 13 and 14 the participation of s-electrons in bond formation decreases the primary reason behind this is the inert pair effect.
In this the p-electrons take part in bond formation and more energy is required to unpack the valence electrons to make them participate in bonding. Due to this the lower oxidation state of elements becomes stable done the hire oxidation state. As for group 13, +1 oxidation state is more stable than +3 and for group 14, +2 oxidation state is more stable than +4.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers