Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven
Get insights from 115 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eleven
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A
A compound X, of boron, reacts with NH3 on heating to give another compound Y which is called inorganic benzene.
3H2H6 x + 6NH3 → 3 [BH2 (NH3)2]+ [BH4]− 2 B3N3H6 + &n
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
B
The four terminal hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms are all in the same plane.
There are two bridging hydrogen atoms above and below this plane.
The four terminal B-H bonds are regular two-centre-two-electron bonds, whereas the two bridge (B-H-B) bonds are unique and can be described as three-centre-two-electron bonds, as shown in figure:
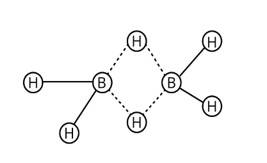
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
D
In group 13, the standardised trend of decrease of ionization enthalpy is not monitored.
As we move from Boron to Aluminium the atomic size increases and jonjation enthalpy decreases but when we move ahead from Aluminum to Gallium, the screening effect of 3 d electrons comes into play. The poor shielding effect of the electrons lead to the increase in nuclear charge on the valence electrons and results in increase of jopisation enthalpy.
Moving from gallium to Indium, due to the shielding effect of 4 d electrons the ionization enthalpy decreases.
The decre
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
C
Me3SiCl is a soleuless liquid That has a major application in the formation of silicones. On its addition in the process, it blocks the end and controls the chain length of the polymer.
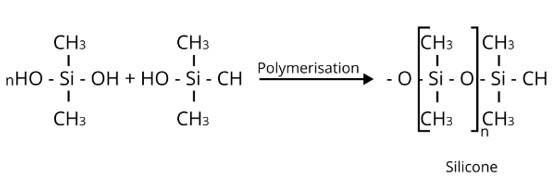
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
B
In group 14, as we move down from C to Sn, the size increases and electronegativity decreases. This results in the decrease in M-M bond energy. Hence the catenation property decreases.
Bond energy is the amount of energy required to fragment the atoms combined in a molecule are born into separate atoms. Carbon has maximum bond energy as compared to its other group elements. Therefore, shows maximum catenation property.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
C
Boric acid is Lewis acid, having six electrons in its valence shell. It combines with water, accepts electrons
from OH−of water molecule and complete it octet to 8 and releases H+
Reaction: B (OH)3 + OH − H→ [B (OH)4]− + H+
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A
Number of items/molecules bonded to the central atom is termed as coordination number. In the given MF63−
Coordination number of metal is six and boron can have topmost coordination number of four as it consists of s and p orbital only and lacks d-orbital. Therefore, boron cannot be compared in the form of MF63−.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A
The B2O3 reacts with water to form boric acid hence it is an acidic oxide. As we move down the group electronegativity decreases and the tendency to donate electrons increases therefore basic character increases or acidic character decreases. So, from the given options, the most acidic oxide is B2O3.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A
Central atom in [B (OH)4 ]− no lone pair. Electronic conf In ground state: 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py0 2pz0
In excited state, One Electron from 2s shifts to 2py orbital and the configuration becomes:
1s2 2s2 2p1 x2 p1 y2 pz0
Now, one s and three p orbitals combined to give sp3 hybridisation and tetrahedral shape.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A
Lewis acids are the species in which the state is not complete and ready to accept electrons. Because Al is surrounded by 6 electrons in AlCl3 and all three Cl atoms are surrounded by 8 electrons, AlCl3 is an electron acceptor. It is a covalent compound.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
