Hydrocarbons
Get insights from 111 questions on Hydrocarbons, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Hydrocarbons
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
CH3 group is electron-donating while -NO2 group is electron-withdrawing. Therefore, maximum electron density will be in toluene, followed by benzene and least in m-dinitrobenzene. Therefore, the ease of nitration decreases in the order: toluene > benzene > m-dinitrobenzene.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) The typical reactions of benzene are electrophilic substitution reactions. Higher the electron-density in the benzene ring, more reactive is the compound towards thesereactions. Since NO2 is a more powerful electron-withdrawing group than Cl, therefore, more the number of nitro groups, less reactive is the compound. Thus, the overall reactivity decreases in the order:Chlorobenzene > p-nitrochlorobenzene > 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene
(b) Here, CH3 group is electron donating but NO2 group is electron-withdrawing. Therefore, the maximum electron-density will be in toluene, followed by p-nitrotoluene followed by p-dinitrobenzene. Thus,
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
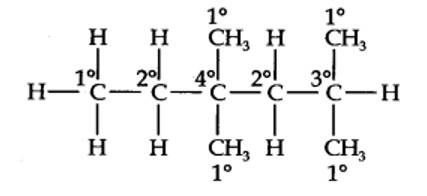
The basic skeleton structure of 2-methylbutane is
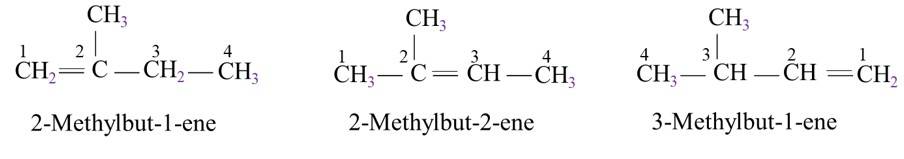
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Benzene is a rich source of electrons because of the presence of an electron cloud containing 6 n-electrons above and below the plane of the ring. Consequently, it attracts the electrophiles (electron-deficient) reagents towards it and repels nucleophiles (electron- rich) reagents. As a result, benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The hybridization state of carbon in these three compounds is:
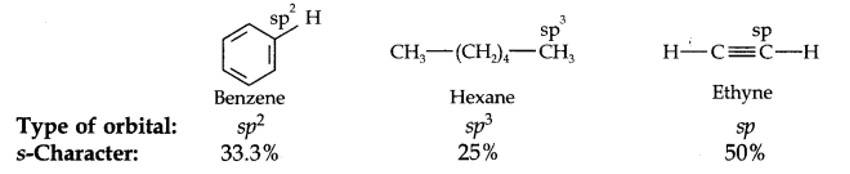
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
o-Xylene may be regarded as a resonance hybrid of the following two Kekule structures. Ozonolysis of each one of these gives two products as shown below:
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
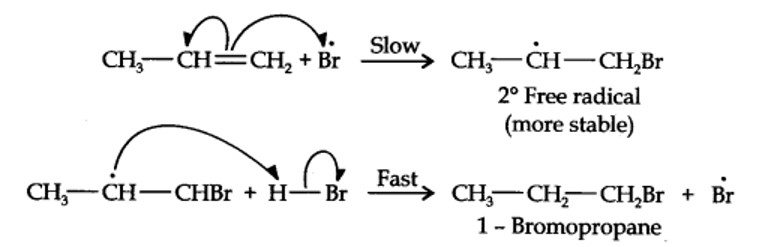
Addition of HBr to propene is an ionic electrophilic addition reaction in which the electrophile, i.e., H+ first adds to give a more stable 2° carbocation. In the 2nd step, the carbocation is rapidly attacked by the nucleophile Br~ ion to give 2-bromopropane.
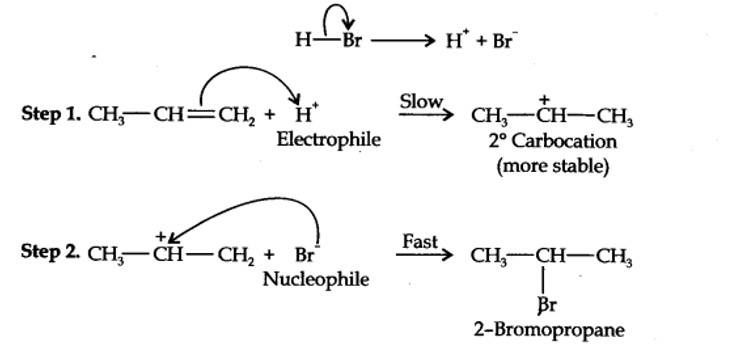
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Branching of carbon atom chain decreases the boiling point of alkane.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers