Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
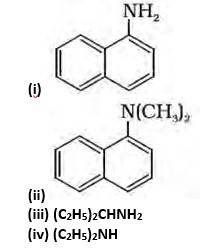
1- Alkyl group contribute inductive effect which increases the basic strength of
NH3
Then C6H5NH2 is having –I effect that reduces strength. And C6H5CH2NH2 increases the basic strength but not as much as C2H5 group.
Hence final order will be C6H5NH2<
2- By taking into consideration –R effect and steric hindrance of groups we can arrange them in the order
C6H5NH2< C2H5NH2< (C2H5)3N< (C2H5)2NH.
Because (C2H5)3N has a lot of steric hindrances that reduces the basic strength.
3- In C6H5NH2, N is directly attached to the ring that causes delocalization of electrons of the benzene ring. Whereas in case of C6H5CH2NH2 it is not directly connected to benze
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Benzene into aniline
When Benzene is treated with HNO3/H2SO4 it forms nitrobenzene. When Nitrobenzene reduced with Sn/HCL it forms Aniline because Sn/HCl is a reducing Mixture.
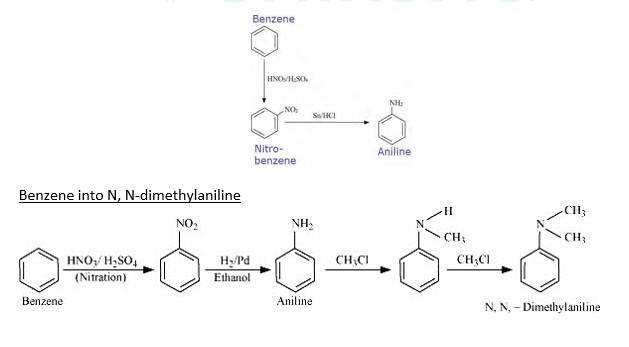
When Benzene is reacted with nitrating mixture it forms nitrobenzene. When it Reduced H2/Pd in ethanol or Sn/HCl, it forms Aniline. When Aniline reacts 2 times with CH3Cl It forms N, N- dimethylaniline.
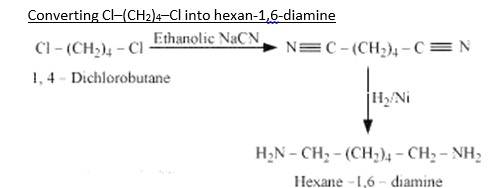
When 1,4-dichlorobutane reacts with NaCN it forms Di cyanide compound, After Hydrogenation it forms the Hexane 1,6-Diamine.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.27
Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide in the presence of
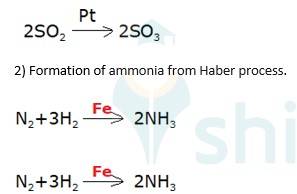
(3) Oxidation of ammonia into nitric acid in presence of platinum gauze in Ostwald's process
→ 4NH3 (g)+ 5O2 (g) Pt (s) 4NO +6H2O
(4) Hydrogenation of vegetable oils in presence of Nickel as catalyst
Vegetable oil (l)+H2 (g) Ni → Vegetable ghee (s)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.8 Given, Z=atomic number = 27 = [Ar]3d7 4s2
⇒ M2+ = [Ar]3d7
Hence, 3 unpaired electrons are present.
The spin only magnetic moment μ= √n(n+2)
Where n is the number of unpaired electrons.
Hence, μ =√(3*(3+2))
μ = √15 BM or μ = 3.87 BM
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) & (ii) There are total 8 geometrical isomers of the given compound.
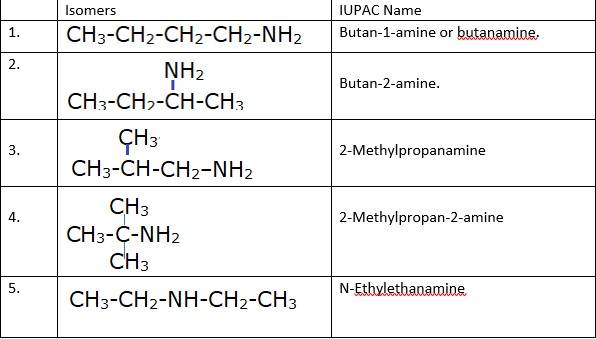
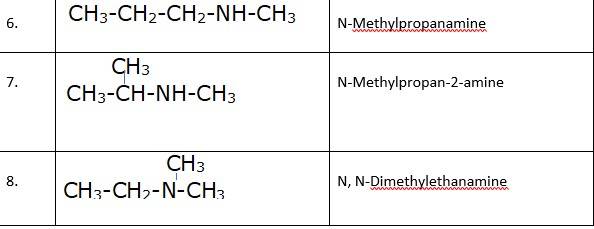
(iii) a) Pairs 1,2,6,7 Exhibit Position isomerism; means the change in position of the substituent.
b) Pairs 1,3 and 1,4 and 2,3 and 2,4 exhibit chain isomerism i.e. in this type of isomerism the different structures can be produced by changing the chain of the
c) Pairs 5,6 and 5,7 exhibit metamerism; e. different group on either side of the central atom.
d) All Primary amines exhibit functional isomers. All secondary amines share functional isomerism and same for The functional isomerism means same functional group.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.7 The following reactions are involved when Cr2+ and Fe2+ act as reducing
Cr2+ = Cr3+ ( E? Cr3+/ Cr2+ = - 0.41 V)
Fe2+⇒ Fe3+ (E? Fe3+/ Fe2+ = +0.77 V)
Since, Cr has less potential value, Cr2+ gets oxidised easily than Fe2+. Therefore, Cr2+ is a better reducing agent that Fe3+.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(ii) Tertiary, because the Nitrogen atom is attached to the 3 carbon atoms.
(iii) Primary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon atom.
(iv) Secondary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.26
Soap is sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids (long chain). Represented as RCOO–Na+. When dissolved in Water it dissociates in the RCOO– and Na+. In first ion there are two parts R and COO–. R is hydrophobic tail and COO– Hydrophilic head. RCOO– ions present at the surface with COO– group inside and R group outside.
Increasing concentration to critical micelle concentration anions are pulled inside the bulk and Form a spherical shape of hydrocarbon chain pointing towards the centre and COO– pointing outside this are called as micelle.
Cleansing action of soap: Soap molecules form micelle around oil droplets. So
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.6 The oxidation state increases when an atom loses its Example: When Fe loses 2 electrons, its oxidation state becomes +2 from 0.
Oxygen (O) and fluorine (F) are very strong oxidizing agents. Both oxide and fluoride ions are highly electronegative and have a very small size, so they attract the electrons from metal atoms. Hence, they oxidize the metal to its the highest oxidation state.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.25
Emulsifiers form an interfacial film between the suspended particles and medium. It provide coating to every drop of suspended particle and prevent it from coagulating. And it remain suspended in medium. Ex- Proteins, gums, alcohols, Lampblack etc.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers