Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.5
Ammonia on reacting with Cu2+ acts as a Lewis base and donates its electron pair to the metal ion and forms a linkage with the metal ion.

Here, colour of Cu2+ is blue whereas the colour of [Cu (NH3)4]2+ is deep blue.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.4
Ammonia (NH3) is generally prepared through a many numbers of processes out of which Haber's process is the most important one. Following the Le Chatlier's principle and taking into considerations the reaction conditions of the Haber's process, the yield of ammonia can be maximized by
High pressure (~ 200 atm)
High temperature (~ 700K)
A mixture of Iron oxide with small amounts of K2O and Al2O3 used as a catalyst. (This mixture acts as a positive catalyst in the Haber's process)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.3
N2 (Dinitrogen) is formed by sharing three electron pairs between two nitrogen atoms, which are joined by a triple bond as shown below:

Due to a complete octet of the nitrogen atoms and bonded by strong triple bonds, due to which its bond dissociation energy is very high. Due to this reason, N2 is very less reactive at room temperature.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.2
Atomic size increases down the group and thus the stability of the hydrides of Group-15 elements decreases. Now, the least stable hydride is the one which is more reactive and possessing higher reducing strength.
The reducing character of hydrides increases on moving from NH3 to BiH3. Hence, BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent among hydrides of Group-15 elements.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.1
Pentahalides (like MX5) means the compounds in which metal is bonded with five halogen atoms. Thus, the oxidation state of metal here is +5. Similarly, trihalides (like MX3) means the compounds in which metal is bonded with three halogen atoms.
Thus, the oxidation state of metal here is +3. Now, as the polarizing power is directly proportional to the charge, the metals with the higher charge will have higher polarizing power. Hence, Pentahalides are more covalent than trihalides.
Note: Polarizing power is the ability of a cation to distort an anion.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.15 For answering this question, we can compare the electronic configuration of standard elements and then write their corresponding oxidation
S. No | Electronic configurations in ground state | Stable oxidation states |
1 | 3d3 Vanadium | +2, +3, +4, +5 |
2 | 3d5 Chromium | +3, +4, +6 |
3 | 3d5 Manganese | +2, +4, +6, +7 |
4 | 3d8 Nickel | +1, +2, +3, +4 |
5 | 3d4 | 3d4 configuration is not stable at ground state |
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The best test for distinguishing methyl amine and dimethylamine is the Carbylamines test.
Carbylamine Test: Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide form foul-smelling isocyanides or carbylamines.
In this case, Methylamine (which is an aliphatic primary amine) gives a positive carbylamine test while dimethylamine wont.
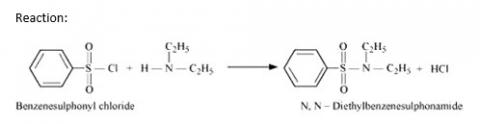
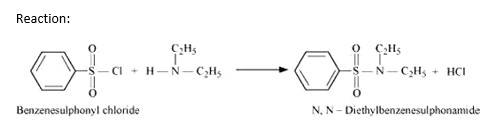
Hinsberg's reagent (benzenesulphonyl chloride, C6H5SO2Cl). can be used to distinguish secondary and tertiary amines.
Hinsberg Test: Secondary amines react with Hinsberg's reagent to form a product that is insoluble in an alkali. For example, N, N? diethylamine reacts
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.14 The elements in the first-half of the transition series exhibit many oxidation states with Mn exhibiting a maximum number of oxidation states (+2 to +7). The stability of +2 oxidation state increases with the increase in atomic number. This happens as more electrons are getting filled in the d-orbital.
However, Sc ( [Ar] 3d14s2) does not show +2 oxidation state, instead, it loses all the three valence electrons to form Sc3+. The +3 oxidation state of Sc is very stable as it attains stable configuration.
For Mn ( [Ar] 3d54s2), +2 oxidation state is very stable because after losing two electrons, it attains stable half-filled str
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers