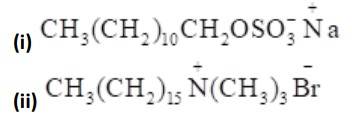Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.5
Different types of polymers have different intermolecular forces of attraction. Elastomers or rubbers have the weakest while fibres have the strongest intermolecular forces of attraction. Plastics have intermediate intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, the increasing order of the intermolecular forces of the given polymers is as follows:
Buna? S < polythene < Nylon 6, 6
Neoprene < polyvinyl chloride < Nylon 6
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.4
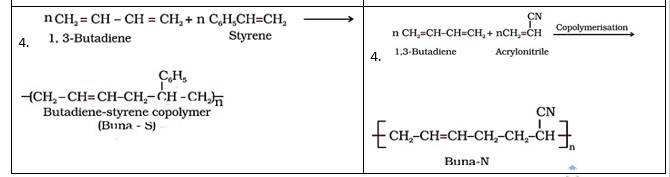
Buna-S | Buna-N |
1. It is formed from 1,3- butadiene and styrene in presence of sodium. | It is formed from 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile in presence of sodium. |
2. Bu refers Butadiene, Na refers Sodium and S refers Styrene | Bu refers Butadiene, na refers Sodium and N refers acrylonitrile |
3. It is used for making automobile tyres, rubber belts, etc. | It is used for manufacturing of tank linings, protective gloves etc. |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.3
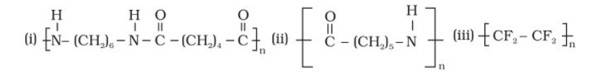
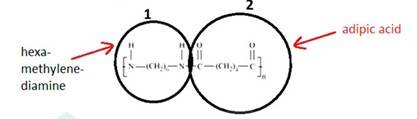
The monomer is OC- (CH2)5-NH known as Caprolactam. The cyclic structure of the monomer changes to linear to form the polymer, as shown below:
The monomer is Tetrafluroethene (CF2= CF2), the double bond breaks to form the polymeric
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.2
Polymers are classified based on structure, into 3 types:
Linear Polymer: They have a long and straight chain of Ex: high-density Polythene, Polyvinyl chloride

Branched-chain Polymers: They have linear molecular chains along with some Ex: less density polythene.
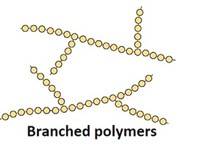
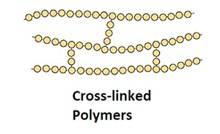
Cross-linked or network Polymers: In these polymers, strong covalent bonds are between the linear chains. Generally, they contain 2 or 3 types of functional groups. Ex: Bakelite, melamine.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.1
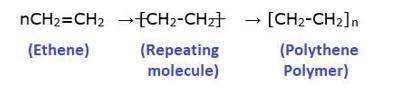
Polymer=Poly + Mer
Poly means “many” and “Mer” means unit or part. A polymer is a large molecule which is formed by linking repeating structural units. The structural units are generally simple molecules and they are linked by a covalent bond to form a polymer.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given,
Volume of water, V = 450 mL = 0.45 L
Temperature, T= (37 + 273)K = 310 K
1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000
Number of moles of polymer, n = 1 / 185,000 mol
We know that,
Osmotic pressure? = nRT/V
= 1 X 8.314 X 103 X 310 / 185000 X 0.45
= 30.98 Pa
= 31 Pa (approx)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given
Mass of acetic acid, w1 = 75 g
Lowering of melting point? Tf = 1.5 K
Kf = 3.9 K kg/mol
Molar mass of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6), M2 6 * 12 + 8 * 1 + 6 * 16 = 176 g/mol
We know that,

= 5.08 g
Hence,
5.08 g of ascorbic acid is needed to be dissolved.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.32
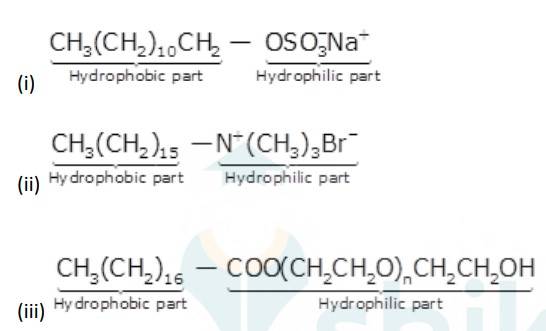
Alkyl groups are water hating groups that is they do not get assimilated in water easily whereas on the other hand functional groups like sulphonates, alcohol etc. are water liking groups that is these groups dissolve in water easily. Therefore hydrophobic part in the above detergents is the long chain alkyl group and the hydrophilic part is the alcohol group, sulphonates group etc.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given,
Mass of water, wl = 500 g
Boiling point of water = 99.63°C (at 750 mm Hg).
Molal elevation constant, Kb = 0.52 K kg/mol
Molar mass of sucrose (C12H22O11), M2 (11 * 12 + 22 * 1 + 11 * 16) = 342 g/mol
Elevation of boiling point ΔTb = (100 + 273) - (99.63 + 273) = 0.37 K
We know that,
ΔTb = Kb X 1000 X W2 / M2 X W1
0.37 = 0.52 X 1000 X W2 / 340 X 500
w2 = 0.37 X 342 X 500 / 0.52 X 1000
w2 = 121.67 g
Hence,
121.67 g (approx) Sucrose is added to 500g of water so that it boils at 100°C.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given,
Vapour pressure of water, PIo = 23.8 mm of Hg
Weight of water, w1 = 850 g
Weight of urea, w2 = 50 g
Molecular weight of water, M1 = 18 g/mol
Molecular weight of urea, M2 = 60 g/mol
n1 = w1/M1 = 850/18 = 47.22 mol
n2 = w2/M2 = 50/60 = 0.83 mol
We have to calculate vapour pressure of water in the solution p1
By using Raoult's therom,

PI = 23.4 mm of Hg Hence,
The vapour pressure of water in the solution is 23.4mm of Hg and its relative lowering is 0.0173.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers