Polymers
Get insights from 154 questions on Polymers, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Polymers
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
10 months agoNew answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.20
Monomeric units of nylon-6 is Caprolactam and for Nylon-6,6 is adipoyl chloride and hexamethylene diamine.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.19
Vulcanization of natural rubber is done to improve upon all these properties. In this process, a mixture of raw rubber with sulphur and appropriate additive is heated at a temperature range between 373 K and 415 K.
This is a slow process; therefore, some additives like zinc oxide etc. are used to accelerate the process. During this process, sulphur cross links are formed which makes rubber hard, tough with greater tensile strength .The vulcanized rubber has excellent elasticity, low water absorption, resistance to oxidation & organic solvents.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.18
Natural rubber is a linear cis-1, 4-polyisoprene in which double bonds are present between C2& C3. It increases the elasticity of the rubber, as the chains are held together by weak van there waals forces and have coiled structure. Therefore, the natural rubber has coiled structure & shows elasticity & is non-crystalline.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.17 One of the common initiators used in free radical addition polymerization is Benzoyl peroxide. Its structure is
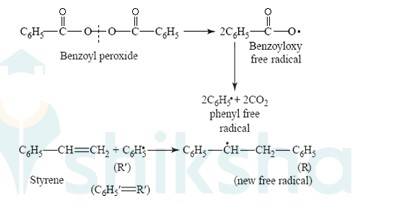
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.16
(i) Ethylene dichloride
(ii) Tetrafluoroethene
(iii) Phenol and formaldehyde
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.15
Thermoplastic Polymers: They are linear or slightly branched long chain molecules capable of repeatedly softening on heating and hardening on cooling. They possess intermolecular forces of attraction intermediate between elastomers and Some common thermoplastics are polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyl, etc.
Thermosetting Polymers: They are cross-linked or heavily branched molecules, which on heating undergo extensive cross-linking in moulds and again become infusible. Some common examples are Bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resins, etc.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.14
The chain is initiated by free radicals, Ra•, produced by the reaction between some of the ethene and the oxygen initiator.
Chain propagation
Each time a free radical hits an ethene molecule a new longer free radical is formed.
Ra• + CH2 = CH2→ RaCH2CH2•
RaCH2CH2• + CH2 = CH2→ RaCH2CH2CH2CH2 •
Chain termination
Eventually two free radicals hit each other producing a final molecule. The process stops here because no new free radicals are formed.
Ra(CH2)m• + •(CH2)n Ra → Ra(CH2)m(CH2)nRa
Because chain termination is a random process, polyethene will be made up of chains of all sorts of different lengths.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.13
Copolymers are those polymers that consist of more than one monomeric repeating unit. Copolymerisation is a process of reacting a mixture of more than one monomeric species and form a copolymer. The copolymer can be made not only by chain growth polymerisation but by step growth polymerisation also. For example, a mixture of 1, 3 – butadiene and styrene forms Buna-S and 1-3 – butadiene and acrylonitrile form Buna-N.
New answer posted
10 months agoContributor-Level 10
15.12
In Addition polymerisation, monomers generally join together to form saturated There are three steps to chain reaction to form addition polymer, they are initiation, propagation and termination. In condensation polymerisation, functional groups of two monomers react together to release a small molecule to form a polymer. Generally, small molecules like water or HCl are released as by-products.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
