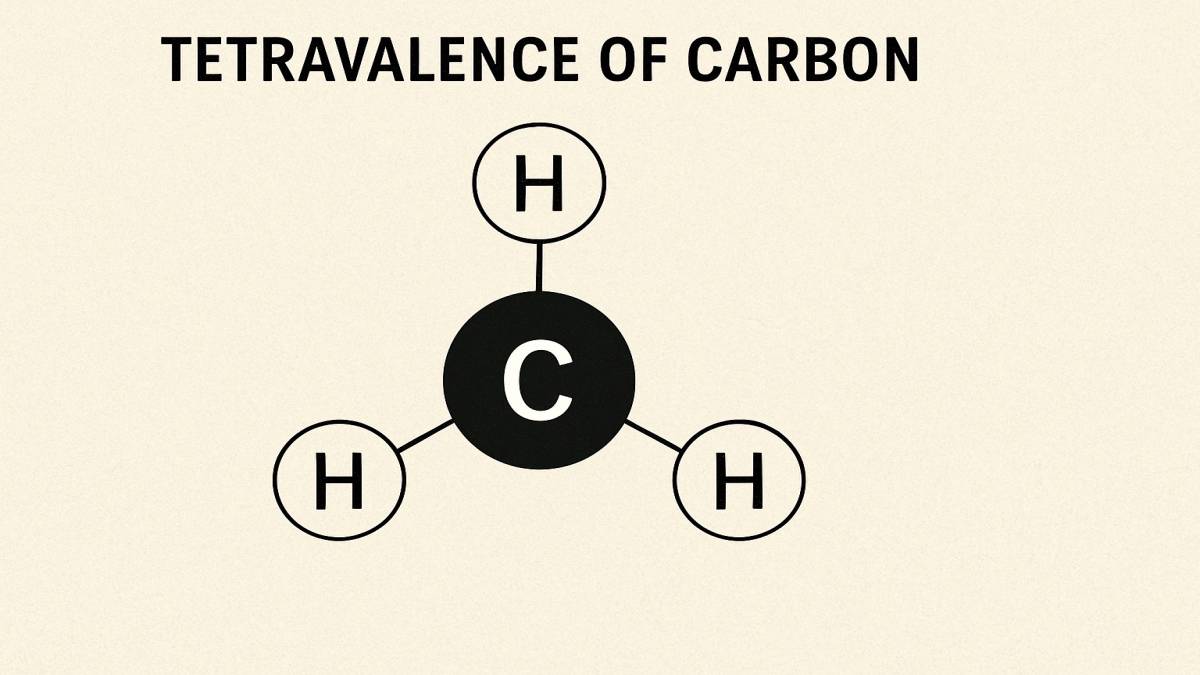
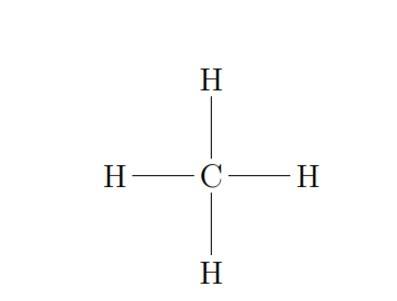
To get started with Organic Chemistry in Class 11, we should start with the tetravalence of carbon. We must know how it affects the shapes of organic compounds.
Why should we consider Carbon? It's because Carbon can form four bonds with other atoms. In the language of Chemistry, we call that tetravalence of carbon.
Tetravelence of carbon is essential to help us understand how molecules are structured, their reactions, and their properties. Chains, rings, and even 3D structures are formed by it. And that's what is required at a conceptual level to tackle JEE Mains later.
- What Does Tetravalence Mean?
- How Tetravalence Leads to Different Shapes
- Why Are Shapes Important in Organic Chemistry
- Lets Try Some Examples
What Does Tetravalence Mean?
Tetravalence of carbon is a characteristic that tells that carbon has four electrons in its outer shell. That allows the carbon electrons to form four covalent bonds. By forming these bonds, it can connect with up to four other atoms.
One common example of tetravalence of carbon is methane, . Here one carbon bonds with four hydrogen atoms.
One quick fact: Carbon can also form bonds with other elements, including oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), or even itself. This ability lets carbon create millions of organic compounds with different shapes and structures.
How Tetravalence Leads to Different Shapes
As carbon is tetravalent, it can form bonds in specific directions. That decides the shape of the molecule. The shape depends on the number and type of bonds (single, double, or triple) and the atoms attached to the carbon.
Tetrahedral Shape (spş Hybridisation)
When carbon forms 4 single bonds, it uses a special arrangement called spş hybridisation.
This means carbons electrons mix to form 4 identical bonds that point in a 3D shape called a tetrahedron. The bond angle between each bond is 109.5r.
For instance,
In methane , carbon is bonded to four hydrogens. The shape is tetrahedral, with carbon in the centre and the four hydrogens at the corners of the tetrahedron.
Why Are Shapes Important in Organic Chemistry
The shape of a molecule affects its properties and reactions. Here are some reasons to look at.
- Reactivity: The shape decides how a molecule reacts. For example, the flat shape of ethene makes its double bond easy to attack in addition reactions.
- Polarity: Shapes affect whether a molecule is polar or non-polar. Methane is non-polar because its tetrahedral shape is symmetrical.
- Isomerism: Different shapes can lead to isomers (same formula, different structures).
Lets Try Some Examples
1. Question: What is the shape of the carbon in (ethane)?
Answer: Each carbon in ethane has 4 single bonds ( 3 to H, 1 to C), so its tetrahedral (spş hybridization, 109.5ř bond angles).
2. Question: What is the shape around each carbon in (ethyne)?
Answer: Each carbon has a triple bond and a single bond, so its linear (sp hybridization, 180ř bond angle).
Chemistry Organic Chemistry Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Classification of Organic Compounds
- Tetravalence of Carbon Shapes of Organic Compounds
- Structural Representations of Organic Compounds
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Isomerism
- Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism
- Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds
- Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds
- Quantitative Analysis
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics