Chemistry
Get insights from 6.9k questions on Chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Due to the larger size of the Cl-atom, the addition of an electron in the outermost orbit produces less electronic repulsion with respect to the F-atom. The following are the electron gain enthalpies in (KJ) of halogens:
F → -328, Cl → -349, Br → -325, I → -295
New question posted
4 months agoNew question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
A central atom having two lone pairs and three bond pairs reflects sp³d hybridization and a corresponding T-shaped geometry.
New answer posted
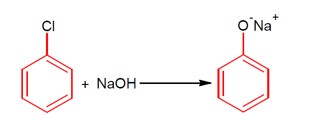
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
This describes a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Aryl halides are very less reactive toward this reaction, so the reaction takes place at a high temperature, i.e., 623K, and high pressure of 300 atm.
New question posted
4 months agoNew question posted
4 months agoNew question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
As you know, electrovalent bonds result very strong electrostatic attraction force. All the factors that help maximize this electrostatic attraction are important for the formation of the ionic bond. Here are the important factors;
- Low ionization energy Metal
- High electron affinity Non Metal
- Large-sized cations
- Small-sized anions
- Electronegativity equal to or greater than 1.7
New answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Covalent and electrovalent bonding are the two major chemical bonding processes. These two bonds are different from each other in multiple aspects. Check the table below to know a concise summary of the differences.
| Particular | Covalent Bond | Ionic Bond |
| Formation | Due to the complete transfer of electrons | Due to the sharing of electron pairs |
| Ion formation | No ions formed | Cations and Anions formed. |
| Nature | Electrostatic attraction between ions | Electrostatic attraction between nuclei and shared electrons |
| Strength | Strong | Less strong |
| Melting/Boiling point | High due to a strong bond | lower due to weaker bond |
| Polarity | Highley Polar | Non-Polar |
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers