GD Topic - Global Food and Hunger Crisis: India Ranks 105 at Global Hunger Index 2024
Candidates planning to get admission to top B-schools and pursue MBA programme must start preparing for the Group Discussion Round. Candidates are often asked to discuss topics related to current affairs, business trends, or abstract concepts. Read the below article for information on the Global Hunger Index and India's position at the Global Hunger Index 2024.
Reasons for the Food and Hunger Crisis:
- Conflicts and Political Stability: The food production and supply chain are seriously affected during wars and conflicts. Millions of people do not get food and other essential resources during these crises.
- Climate Change: The agricultural productivity is reduced during extreme climate changes such as floods and droughts. This results in food shortages and hunger crises.
- Population Growth: In countries like India, the population keeps increasing every year. This increase in population puts a strain on the food production and distribution systems.
- Economic Inequality: As we all know, there is an unequal distribution of wealth among the people. This limits the food access to the low-income population.
- Poor Agricultural Practices: Even though there have been advancements in agricultural techniques, many countries still have inefficient farming techniques. Besides, inadequate infrastructure also plays a major role in poor food production and storage facilities.
- Pandemic: Global pandemics like COVID-19 completely disrupt the food supply chain. These pandemics also give rise to increased unemployment and poverty.
- What is the Global Hunger Index (GHI)?
- Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024
- India’s Ranking on the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024
- Causes of Hunger in India
- Top GD Topics for MBA GD/PI Round
What is the Global Hunger Index (GHI)?
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool that measures the hunger level at regional, national, and global levels. The GHI report is published annually by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe. To calculate GHI, countries are given scores on a 100-point scale. In the scale, 0 means no hunger and 100 means extreme hunger.
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) uses the following four indicators to measure the hunger level:
- Undernourishment: It is the percentage of the population with insufficient caloric intake. This is measured against the standard intake defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- Child Wasting (low weight for height): It is the percentage of children under five years of age who have low weight required for their height. These children show acute undernutrition.
- Child Stunting (low height for age): It includes the percentage of children under five years of age who have low height for their age. These children show chronic undernutrition.
- Child Mortality: The last indicator determines the percentage of children who die before they reach five years of age. These children show a mix of inadequate nutrition and an unhealthy environment.
Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024
The Global Hunger Index report aims to compare hunger levels of different countries and regions, and raise awareness in areas with higher hunger levels. In 2024, the Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV) at Ruhr-University Bochum joined as an academic partner for the GHI report. From 2024, the institute will be responsible for calculating and developing the index. To determine the GHI report 2024, data from 136 countries were taken for assessment. Sufficient data was not found for nine countries. So, the Global Hunger Index 2024 report consists of rankings for 127 countries.
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024 states that:
- 51 countries fall under Low GHI Scores
- 27 countries fall under Moderate GHI Scores
- 36 countries fall under Serious GHI Score
- 6 countries fall under Alarming GHI Scores
- 0 countries fall under Extremely Alarming GHI Score
The Global Hunger Index 2024 Score for the world is moderate, i.e., 18.3. This score is slightly less than the GHI 2016 Score; i.e., 18.8. If we compare this data with that of the 2016 GHI Report, we can see little progress in hunger reduction since 2016. However, as 42 countries still experience alarming or serious hunger, the government's aim of achieving Zero Hunger by 2030 seems difficult. According to the experts, if the hunger pace remains the same, then it is impossible to reach a low hunger level globally until 2160.

India’s Ranking on the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024
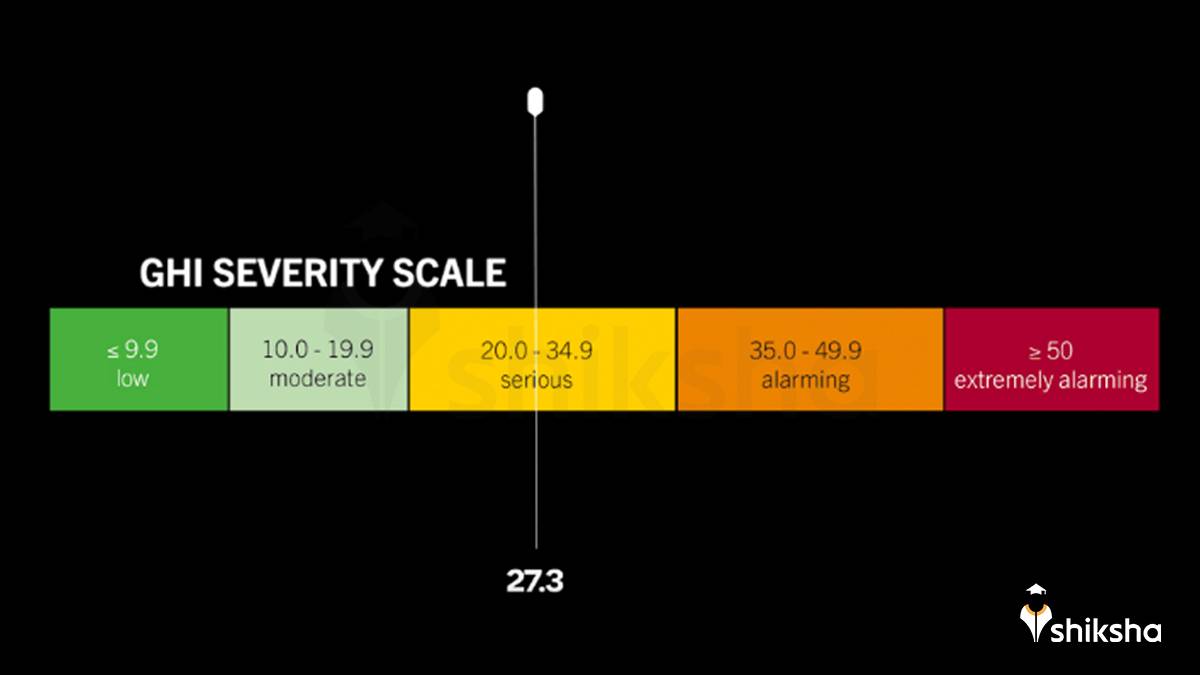
India ranks 105th out of the 127 countries in the Global Hunger Index 2024. On the severity level, India is at the Serious Level with a GHI Score of 27.3
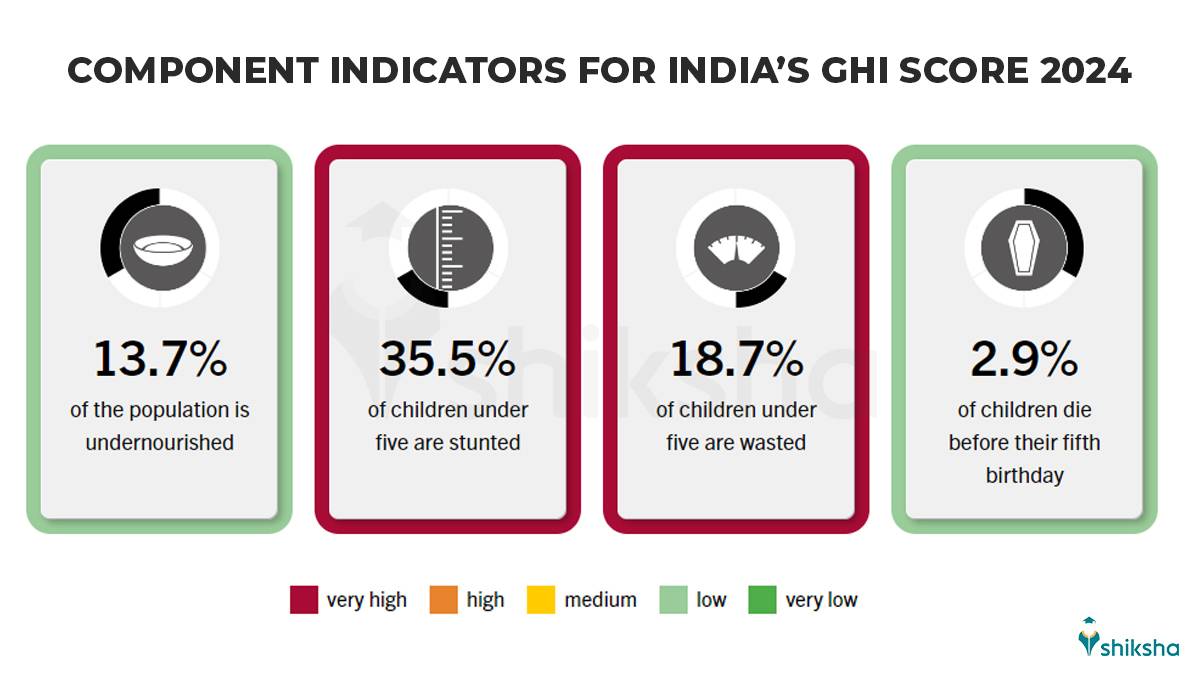
As discussed above, the GHI score is calculated based on the four component indicators: undernourishment, child wasting, child stunting, and child mortality. India scored 27.3 GHI Score based on the following percentage of these indicators:
These figures can be summarized as follows:
- 13.7% of India’s population is undernourished. It shows the lack of access to adequate food.
- 35.5% of children under the age of five are stunted. It shows chronic undernutrition and its long-term impact on growth and development.
- 18.7% of children under five experience wasting. It indicates acute malnutrition and severe health risks.
- 2.9% of children do not reach their fifth birthday. This reflects hunger and malnutrition.
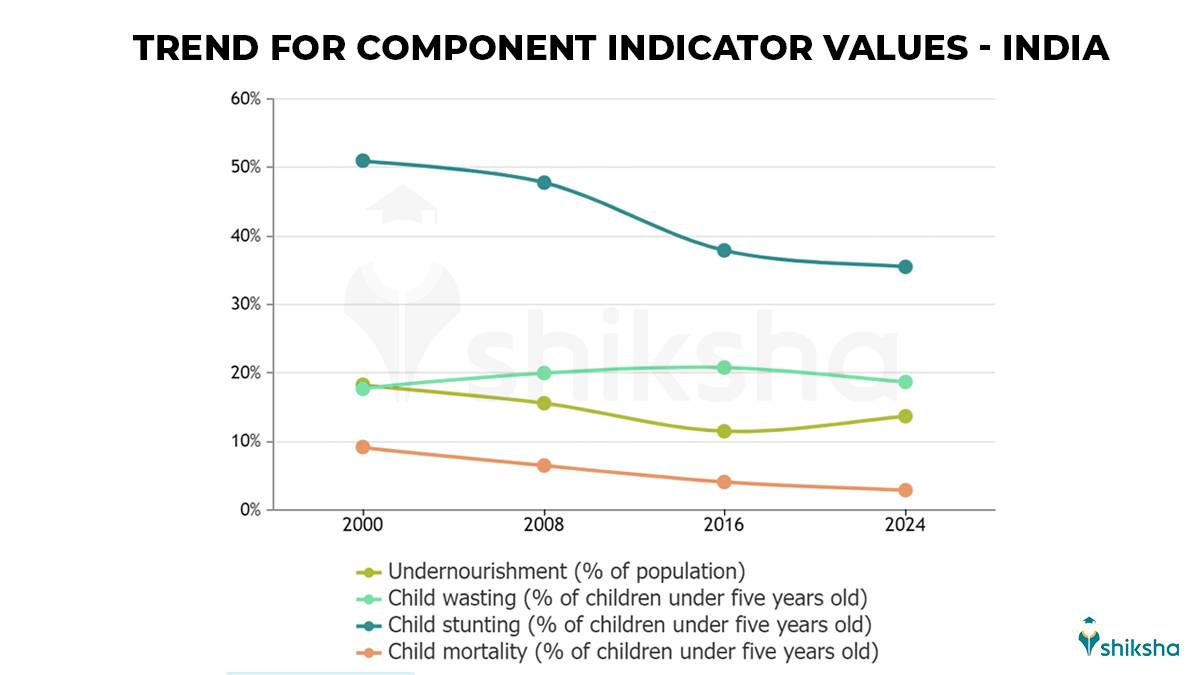
In addition to India’s 2024 GHI indicators, check out the graph below for the change in the percentage of indicators from 2000 to 2008 to 2016 to 2024.
The above graph shows the following changes in the percentage of population:
- Undernourishment: 18.3 (in 2000), 15.6 (in 2008), 11.5 (in 2016), and 13.7 (in 2004).
- Child Wasting: 17.7 (in 2000), 20.0 (in 2008), 20.8 (in 2016), and 18.7 (in 2024).
- Child Stunting: 51.0 (in 2000), 47.8 (in 2008), 37.9 (in 2016), and 35.5 (in 2024).
- Child Mortality: 9.2 (in 2000), 6.5 (in 2008), 4.1 (in 2016), and 2.9 (in 2024)
These figures show a good drop in undernourishment, child stunting, and child mortality percentage. However, India needs more improvement when it comes to child wasting.
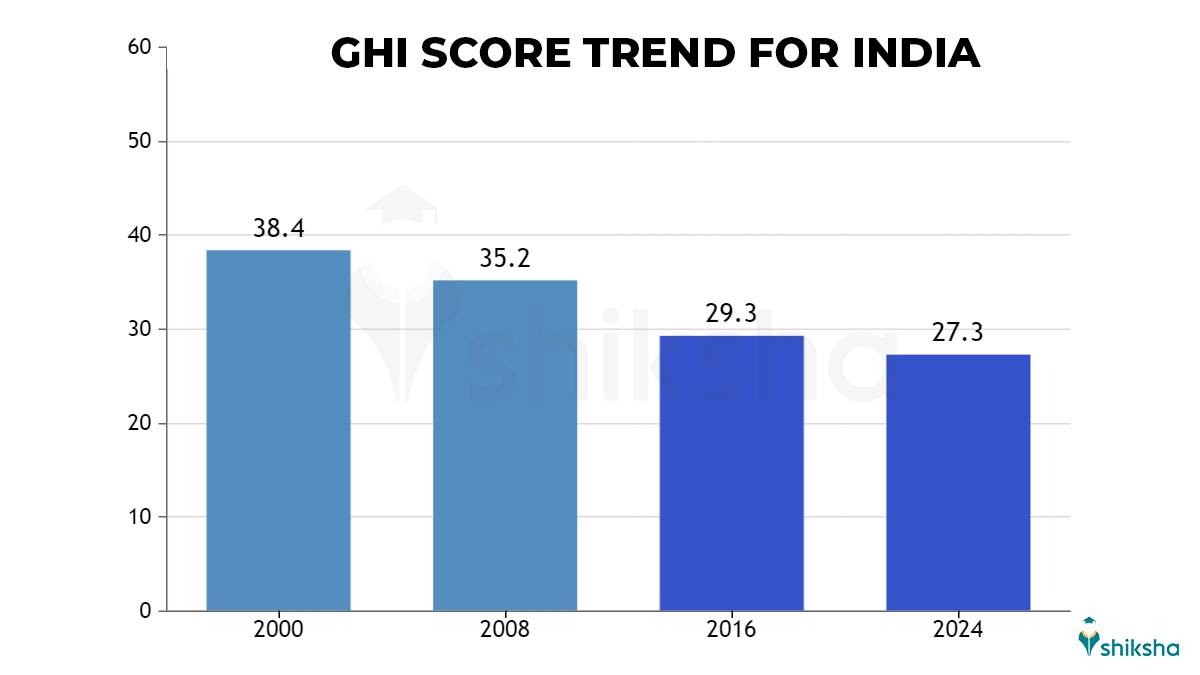
Despite the serious figures, India’s condition has gradually improved if we compare its GHI 2024 Score with the alarming score of 38.4 in 2000.
Causes of Hunger in India
India faces hunger due to several social, economic, and political factors. Some of the primary causes behind Hunger in India are:
- Poverty
- Unemployment
- Inefficient Distribution System
- Agricultural Challenges
- Climate Change
- Population Growth
Top GD Topics for MBA GD/PI Round
Below listed are some of the important GD Topics for reference.
- Importance of Statue of Unity
- Citizenship Amendment Act - What and Why
- Making Aadhaar mandatory is not a good idea- for or against
- Implications of CAA-NCR
- Cashless Economy – Is India ready for it?
- All you need to know about Right To Information
- How can we control banking frauds to reduce NPAs?
- Statue of Unity - Symbol of Pride or Wastage of Public Money?
- Rural vs Urban India
- Environment and us
- Self Motivation
- First impression is the last impression
- Funding Democracy: Are Electoral Bonds a Boon or Bane?
- Quick Commerce: A Step Toward Progress or a Wasteful Luxury?
- Crime Against Women in India: Who Bears the Responsibility?
- Innovation Vs Invention: What does the world need?
- PM Internship Scheme: How Effective is it in Enhancing Youth Employability?
- Job Reservation in Private Sector: A Boon or a Barrier?
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS): Reforming Criminal Law for Better or Worse?
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) in India: Dream or Reality?
- India’s Historic Performance at the Paris Paralympics 2024
- Global Innovation Index 2024: India Jumps from 81st to 39th Rank in 9 Years
- UCPMP 2024: Strengthening Ethical Standards in Pharmaceutical Marketing

 Call 8585951111
Call 8585951111
Nupur Jain started with a passion for educational content writing, which soon grew into a meaningful journey of helping students through reliable guidance. A commerce graduate from Delhi University, she has spent ov
Read Full Bio