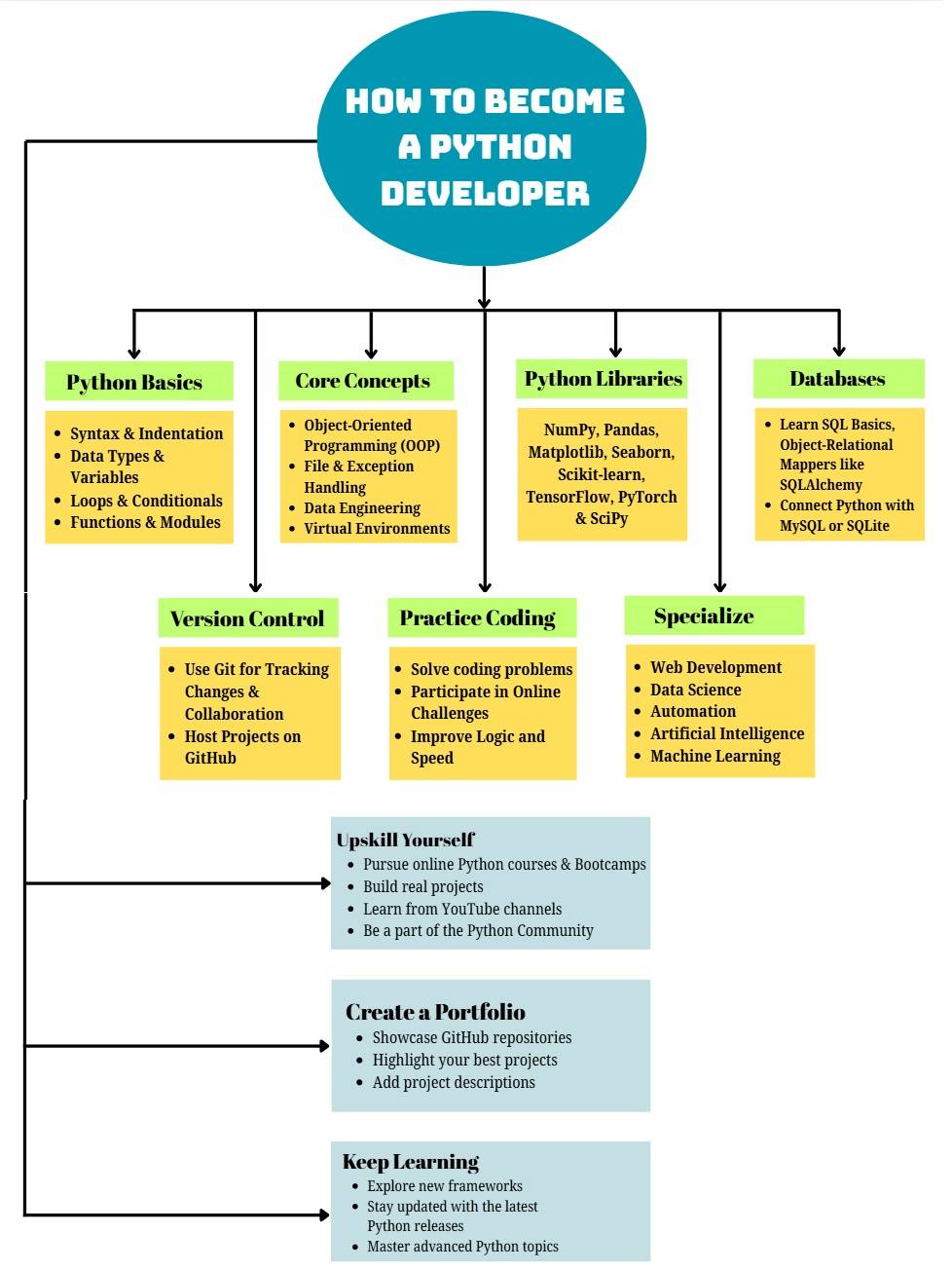
How to Become a Python Developer: Top Skills to Learn
Python is an easy-to-use, readable, and intuitive language. Over the last couple of years, Python has evolved from "the language for beginners" to a development language of choice. According to the TIOBE index, it is the most used language in the world. Why? Because it is very simple, very versatile, and very useful. Companies of all sizes use it, while developers swear by Python in building intuitive web applications. If these pointers have you hooked and you are keen to learn how to become a Python Developer, then you are at the right place. Go on!
Eligibility to Become a Python Developer
Worth noting is that there is no specific educational qualification for becoming a Python Developer. Focus on some essential skills to start your career.
| Criteria |
Details |
| Minimum Qualification |
No formal degree required |
| Preferred Degree |
|
| Who Can Learn Python |
Anyone interested in learning Python |
| Core Skills Required |
Python programming, data structures & algorithms, object-oriented programming, file handling, etc. |
| Experience Requirement |
Not mandatory. Although internships, projects, and GitHub contributions can boost your profile |
Core Skills for Python Developers
As a Python programmer, you need specific skills, discussed below.
Python is simple and easy to learn. Go for the basics first.
| Concept |
Description |
| Variables and data types to classify items |
Integers, tuples, strings, lists, floats, dictionaries, sets |
| Control structures |
|
| Functions and modular code |
Defining reusable code blocks for organisational purposes |
| Reading and writing txt, csv, and json files |
|
| Error handling |
Try, except, and finally blocks to handle errors, also known as exceptions |
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
OOP principles keep your code neat and reusable. It further makes it easier to structure your projects professionally. Here are some essential concepts that you should learn:
- Classes and objects: Creation of blueprints for objects.
- Inheritance & polymorphism: Reusing and extending code efficiently.
- Encapsulation & abstraction: Internal code structures are hidden, and their complexities are not revealed.
Web Development with Python
Python provides robust frameworks to create websites and web applications. Some of those are listed below-
| Framework |
Description |
| Feature-rich Python framework with a full-featured toolkit. It is helpful for large, high-scalability web applications |
|
|
|
| Web service interface design with Django REST Framework or FastAPI |
|
| Database management |
Storing and retrieving data by using SQLAlchemy or Django ORM |
| Web security basics |
Security against SQL injection and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
| FastAPI |
High-performance API framework |
| Pyramid |
Flexible, scalable web framework |
| CherryPy |
Minimalistic web server framework |
| Web2Py |
Full-stack web framework |
| Tornado |
Asynchronous networking framework |
| SQLAlchemy |
Python SQL toolkit and Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) |
Data Science and Machine Learning
Python is the best programming language for data science and analytics domains. If you want to have a career with a specialisation in data science, AI, analytics, or research, it would be a great idea to learn the following:
| Python library |
Task |
| Numerical computing |
|
| Data manipulation & analysis |
|
| Matplotlib and Seaborn |
Data visualization |
| Machine Learning Models & Algorithms |
|
| Deep learning projects |
|
| SciPy |
Scientific and technical computing |
| Plotly and Bokeh |
Interactive data visualization |
| Keras |
High-level deep learning API written in Python |
5. Automation and Scripting
Python is widely used to automate repetitive tasks and boost efficiency. You can write scripts to:
- Automatically rename or relocate files
- Web scraping using tools like Beautiful Soup, Scrapy or Selenium
- Interact with web services and APIs to retrieve or process information
- Schedule system jobs or monitor logs
6. Version Control with Git
Using version control to track changes and facilitate collaboration with other developers isone of the best practices of using Python. Git is a distributed version control system that has achieved industry-standard status for source code management. To manage Python projects, learn to:
- Create and manipulate repositories
- Basic Committing, Branching and Merging
- Use GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps or Bitbucket for collaboration
7. Virtual Environments
Python projects normally use many libraries and different versions. In order to avoid conflicts between versions and to isolate our projects totally from other projects, a virtual environment is very useful. Learn to use:
- venv
- env
- .venv
- .env
- pip or poetry
8. Soft Skills
Apart from technical stuff, you should also work on your business skills, also popularly called soft skills.
- Communication skills
- Logic building
- Problem solving
- Adaptability
- Teamwork & Collaboration
- Time management
- Critical thinking
- Willingness to learn
- Project management
- Empathy
- Active listening

 Call 8585951111
Call 8585951111

Rashmi Karan is a writer and editor with more than 15 years of exp., focusing on educational content. Her expertise is IT & Software domain. She also creates articles on trending tech like data science,