Which course is the best alternative to B.Ed Course: Shiksha Poll revealed
Education is one of the most rewarding and respected career fields, especially for those who want to shape young minds. For aspiring teachers in India, choosing the right course can be overwhelming. While B.Ed (Bachelor of Education) is the most popular degree for teaching in middle and high schools, many students explore alternative teaching programs like D.El.Ed, D.Ed, NTT, and BA in Education, based on their goals, eligibility, and career plans. A poll run by Shiksha.com has revealed that 34% of students think that D.El.Ed and D.Ed are the best alternatives to B.Ed course. Read the article below to know more.
This article provides a brief overview of B.Ed, D.Ed, and D.El.Ed courses. Though all these courses are teacher training programs, they cater to different levels of education and have different eligibility criteria. This article compares B.Ed, D.El.ED, D.Ed, NTT, B.A in Education and explains why many students see these courses as worthy alternatives to B.Ed.
- B.Ed. vs. D.El.Ed: Key Differences
- B.Ed. vs. D.Ed: Key Differences
- B.Ed. vs. NTT: Key Differences
- B.Ed. vs. B.A in Education: Key Differences
- Shiksha's Poll Analysis
B.Ed. vs. D.El.Ed: Key Differences
The D.El.Ed and B.Ed are both teacher training programs but differ in level, eligibility, and career focus. Students can check the table below for more information:
| Particulars |
B.Ed. |
D.El.Ed. |
|---|---|---|
| Course Name |
Bachelor of Education |
Diploma in Elementary Education |
| Course Duration |
2 years |
2 year |
| Objective of the course |
The objective of the BEd course is to make students prepare for Teaching jobs at secondary and senior secondary levels (Classes 6-12) |
The main objective of the D.El.Ed course is to train teachers to teach students of primary and upper primary levels (Classes 1-8) |
| Eligibility |
Graduation with 50% marks in any stream. |
10+2 with 50% marks from any stream. |
| Focus subjects |
Pedagogy, subject-specific teaching, educational psychology |
Child development, pedagogy of languages, environmental studies |
| Career Opportunities |
TGT/PGT Teacher, Subject teacher, Educational Consultant |
Primary school teacher, Elementary tutor |
| Average Salary |
INR 3 - 6 Lakhs per annum |
INR 2-4 lakhs per annum |
Note- This information is sourced from the official website and may vary.
B.Ed. vs. D.Ed: Key Differences
D.Ed is another diploma-level course designed specifically for teaching Classes 1–5, often offered by state education boards. In contrast, B.Ed is a professional degree aimed at teaching Classes 6 -12. Candidates can check the table below for a detailed comparison:
The following topics are taught in NTT Course:
- Child Care and Health
- Basics of the pre-primary education
- Teaching Methodology
- History and Philosophy of pre-primary education
- Child Psychology
- Nursery school organization, Child Health, and Nutrition and community
- Practical: Viva Voice
- Practical: Arts and Crafts
IPU MBA elective courses differs depending upon the chosen MBA specialisation. Mentioned below are some of the specialisation-wise elective courses:
| Specialisation | Electives |
|---|---|
| Marketing |
|
| Finance |
|
| HR |
|
| International Business |
|

| Particulars |
B.Ed. |
D.Ed. |
|---|---|---|
| Course Name |
Bachelor of Education |
Diploma in Education |
| Course Duration |
2 years |
2 years |
| Objective of the course |
The objective of the B.Ed. course is to make students prepare for Teaching jobs at secondary and senior secondary levels (Classes 6-12) |
This course prepares educators for foundational level education (Classes 1-5) |
| Eligibility |
Graduation with 50% marks in any stream. |
10+2 with 50% marks. |
| Focus subjects |
Pedagogy, subject-specific teaching, educational psychology |
Child psychology, Early education methods, Basic pedagogy |
| Career Opportunities |
TGT/PGT Teacher, Subject teacher, Educational Consultant |
Govt./private primary teacher, Tutor, NGO Educator |
| Average Salary |
INR 3 - 6 Lakhs per annum |
INR 2.5 - 5 Lakhs per annum |
Note- This information is sourced from the official website and may vary.
B.Ed. vs. NTT: Key Differences
NTT is focused on early childhood education (ages 3 - 6), making it ideal for preschool and kindergarten teaching. Whereas, B.Ed qualifies you for teaching higher grades, especially from Class 6 onwards. Here's a comparison of both courses:
| Particulars |
B.Ed. |
NTT |
|---|---|---|
| Course Name |
Bachelor of Education |
Nursery Teacher Training |
| Course Duration |
2 years |
1-2 years |
| Objective of the course |
The objective of the B.Ed course is to make students prepare for teaching jobs at secondary and senior secondary levels (Classes 6-12) |
The main objective of the programme is to train the teachers in childhood care and nursery level teaching |
| Eligibility |
Graduation with 50% marks in any stream. |
10+2 in any stream. |
| Focus subjects |
Pedagogy, subject-specific teaching, educational psychology |
Child development, rhymes, storytelling, craft, classroom activities. |
| Career Opportunities |
TGT/PGT Teacher, Subject teacher, Educational Consultant |
Nursery Teacher, Daycare teacher, Montessori educator |
| Average Salary |
INR 3 - 6 Lakhs per annum |
INR 2- 4.5 Lakhs per annum |
Note- This information is sourced from the official website and may vary.
B.Ed. vs. B.A in Education: Key Differences
BA in Education is an academic degree that explores education as a subject of study—focusing on its theoretical and philosophical aspects. On the other hand, B.Ed is a professional teaching degree required to work as a school teacher. Candidates can check the table below for more information:
| Particulars |
B.Ed. |
BA in Education |
|---|---|---|
| Course Name |
Bachelor of Education |
Bachelor of Arts in Education |
| Course Duration |
2 years |
3 years |
| Objective of the course |
The objective of the B Ed course is to make students prepare for Teaching jobs at secondary and senior secondary levels (Classes 6-12) |
This course builds academic foundation in educational theories and systems |
| Eligibility |
Graduation with 50% marks in any stream. |
10+2 from any stream. |
| Focus subjects |
Pedagogy, subject-specific teaching, and educational psychology |
Education philosophy, history, sociology, psychology |
| Career Opportunities |
TGT/PGT Teacher, Subject teacher, Educational Consultant |
Education Assistant, Content developer |
| Average Salary |
INR 3 - 6 Lakhs per annum |
INR 2.5 – 4.5 Lakhs per annum |
Note- This information is sourced from the official website and may vary.
Shiksha's Poll Analysis
According to the recent poll conducted by Shiksha, students are exploring a variety of academic paths as alternatives to the B.Ed program. The results show a diverse preference: 34% of students opted for D.El.Ed Course, An equal 34% chose D.Ed, reflecting a growing inclination towards teaching Primary and Pre-Primary level students. 26% of respondents selected B.A in Education, pointing to the appeal of studying educational theories and systems, while a smaller group of 6% chose NTT, indicating a modest preference for teaching Nursery classes.
| Relevant Information: |
|||

Pallavi is a graduate in BJMC which is popularly known as Bachelor of Journalism and Mass Communication with a strong passion for writing. She basically specializes in creating insightful and very well researched SE
Read Full Bio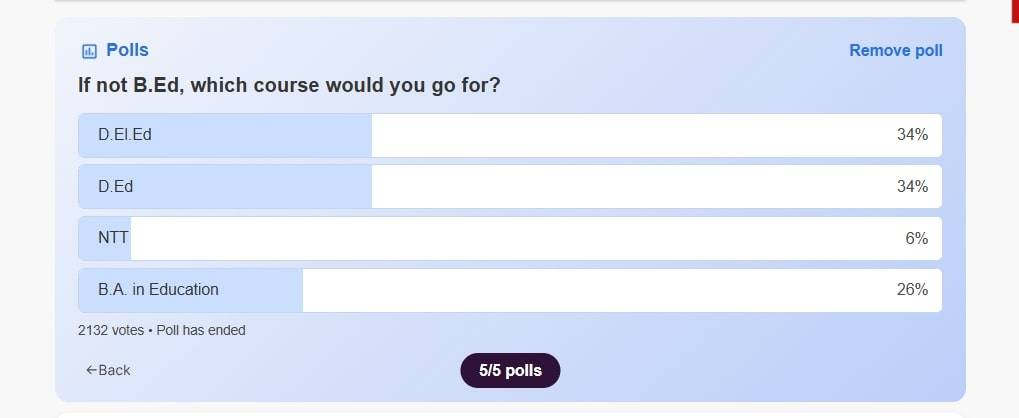

After this course, you can start working as an elementary teacher or a preschool teacher. Other than that you can go for the job of assistants or day-care facilitators across primary schools or play schools.
Besides working, you have the option to pursue higher degrees in the field of teaching and education such as D.El.Ed or B.Ed or M.Ed.
You can even work in Anganbadi and other rural educational initiatives for providing inclusive and accessible education to all young children.