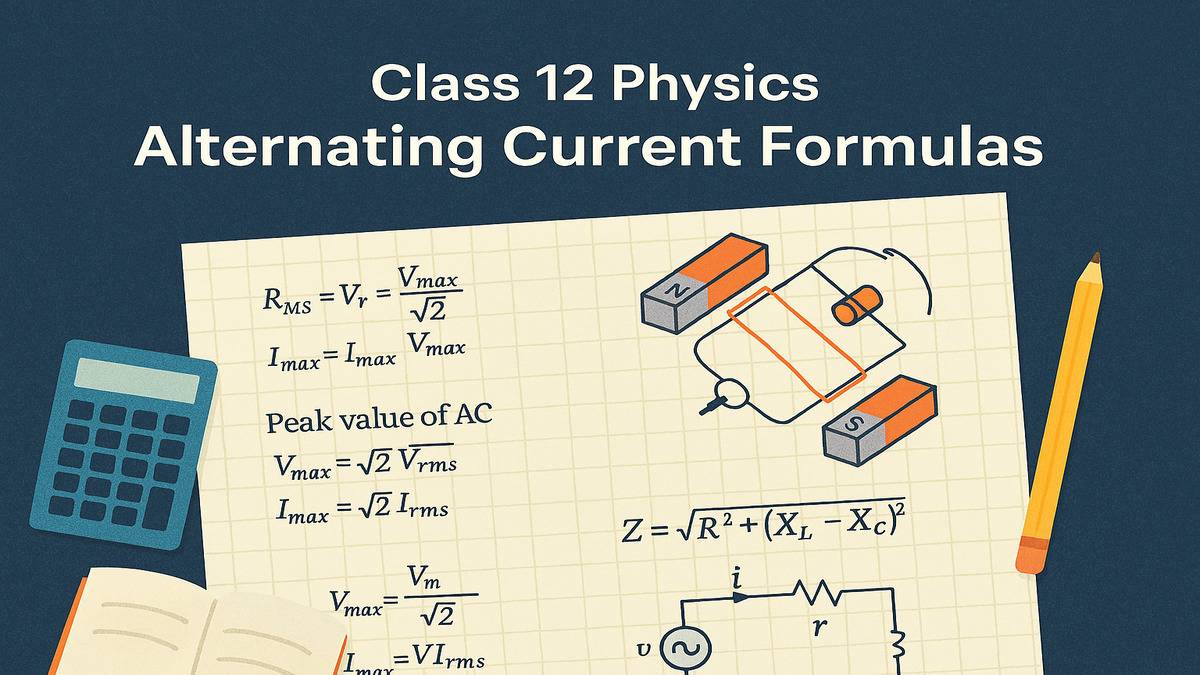
Alternating Current Class 12 Formulas
AC is one of the most important chapters for the Board and competitive exams. Find the Alternating Current Formulas for quick revision and numerical practice of the chapter.
Class 12 Physics Alternating Current includes very important concepts such as AC voltage, Power in AC Circuit, Impedance, and many other concepts. Learn all the important formulas of the Class 12 AC chapter 7.
Practice numerical problems and revise effectively using our Class 12 Chapter 7 formulas provided by Shiksha. We also provide NCERT Notes and the solution of the NCERT exercise.
- Alternating Current Basic Formulas
- AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
- AC Voltage Applied to a Capacitor
- AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor
- LCR Circuit
Alternating Current Basic Formulas
- AC Voltage:
- Peak Value of AC:
- Average Value of AC:
- RMS Value of AC:
AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
- Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule for an AC circuit with a Resistor
- Current in the AC Circuit with a Resistor
- Amplitude (Peak Value) of Current
- Instantaneous Power in a Resistive Circuit
- Phase Difference Between V and Ir
It means both will reach the respective peak values at the same time.
.
AC Voltage Applied to a Capacitor
- Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule for an AC circuit with a Capacitor
- Current in the AC Circuit with a Capacitor
- Amplitude (Peak Value) of Current
- Capacitive Reactance
- Instantaneous Power in a Capacitive Circuit
- Average Power in a Capacitive Circuit
In a full cycle, energy is stored in the first cycle and the same energy is returned in the next half cycle. So
- Phase Difference Between V and Ic
Current lags behind the voltage by 90° in a capacitive circuit:
AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor
- Kirchhoff’s Loop Rule for an AC circuit with an Inductor
- Current in the AC Circuit with An Inductor
- Amplitude (Peak Value) of Current
- Instantaneous Power in Circuit
- Average Power in Circuit
For a full cycle, the average power is zero.
- Phase Difference Between V and IL
The current phase is ahead of the voltage phase.
| Relatable Study Material for Chapter 7 |
|---|
| Class 12 Alternating Current NCERT Solutions |
| Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 NCERT Notes |
| Alternating Current Quick Revision Notes |
| Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 NCERT Exemplar Solutions |
LCR Circuit
- Current in LCR Circuit
- Impedance
- If there is no resistance
- If there is no Inductive Reactance
- If there is no capacitive reactance
- If inductive and capacitive reactance are equal, It behaves like a circuit with a resistor only. It is called resonance.
- Resonant Frequency
- Phase Angle
- Quality Factor