- Three-Dimensional Geometry Long Answer Type Questions
- Three-Dimensional Geometry Short Answer Type Questions
- Three-Dimensional Geometry Objective Type Questions
- Three-Dimensional Geometry Fill in the blanks Type Questions
- Three-Dimensional Geometry True or False Type Questions
Three-Dimensional Geometry Long Answer Type Questions
| 1. Find the foot of the perpendicular from the point (2, 3, –8) to the line Also, find the perpendicular distance from the given point to the line. |
| Ans. |
| 2. Find the distance of the point (2, 4, –1) from the line |
| Ans. |
Commonly asked questions
Find the foot of the perpendicular from the point (2, 3, –8) to the line Also, find the perpendicular distance from the given point to the line.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the distance of the point (2, 4, –1) from the line
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the length and the foot of the perpendicular from the point ( ) to the plane .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equations of the line passing through the point (3, 0, 1) and parallel to the planes and .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equation of the plane through the points (2, 1, –1) and (–1, 3, 4), and perpendicular to the plane .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the shortest distance between the lines and
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equation of the plane which is perpendicular to the plane and contains the line of intersection of the planes and .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The plane is rotated about its line of intersection with the plane through an angle . Prove that the equation of the plane in its new position is
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equation of the plane through the intersection of the planes whose perpendicular distance from the origin is unity.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Show that the points and 3 are equidistant from the plane and lie on opposite sides of it.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
AB = 3 - + and = -3 + 2 + 4 are two vectors. The position vectors of the points A and C are 6 + 7 + 4 and -9 + 2 + respectively. Find the position vector of a point P on the line AB and a point Q on the line CD such that is perpendicular to both and both.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Show that the straight lines whose direction cosines are given by are at right angles.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If ; , and are the direction cosines of three mutually perpendicular lines, prove that the line whose direction cosines are proportional to , , and makes equal angles with them.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Three-Dimensional Geometry Short Answer Type Questions
| 1. Find the position vector of a point A in space such that is inclined at 60º to OX and at 45° to OY and = 10 units. |
| Ans. |
| 2. Find the vector equation of the line which is parallel to the vector and which passes through the point (1, –2, 3). |
| Ans. |
Commonly asked questions
Find the position vector of a point A in space such that is inclined at 60º to OX and at 45° to OY and = 10 units.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Show that the lines and intersect. Also, find their point of intersection.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the vector equation of the line which is parallel to the vector and which passes through the point (1, –2, 3).
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the angle between the lines and
Prove that the line through A(0, –1, –1) and B(4, 5, 1) intersects the line through C(3, 9, 4) and D(–4, 4, 4).
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Prove that the lines and are perpendicular if
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equation of a plane which bisects perpendicularly the line joining the points A(2, 3, 4) and B(4, 5, 8) at right angles.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equation of a plane which is at a distance of units from the origin and the normal to which is equally inclined to coordinate axes.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the line drawn from the point (–2, –1, –3) meets a plane at right angles at the point (1, –3, 3), find the equation of the plane.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equation of the plane through the points (2, 1, 0), (3, –2, –2), and (3, 1, 7).
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the equations of the two lines through the origin which intersect the line at angles of each.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the angle between the lines whose direction cosines are given by the equations
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If a variable line in two adjacent positions has direction cosines and ,show that the small angle between the two positions is given by
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
O is the origin and A is (a, b, c). Find the direction cosines of the line OA and the equation of the plane through A at right angles to OA.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Two systems of rectangular axes have the same origin. If a plane cuts them at distances a, b, c and a′, b′, c′, respectively, from the origin, prove that
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Three-Dimensional Geometry Objective Type Questions
| 1. The distance of the point from the y-axis is (A) (B) (C) (D) |
| Ans. |
| 2. If the direction cosines of a line are , then: (A) (B) (C) (D) or - |
| Ans. |
Commonly asked questions
The distance of the point from the y-axis is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the direction cosines of a line are , then:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) or -
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The distance of the plane from the origin is:
(A) 1
(B) 7
(C)
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The sine of the angle between the straight line and the plane is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reflection of the point in the xy-plane is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
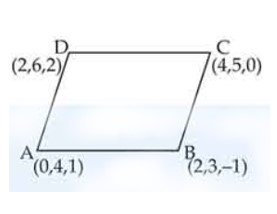
The area of the quadrilateral ABCD, where A(0, 4, 1), B(2, 3, –1), C(4, 5, 0) and D(2, 6, 2), is equal to:
(A) 9 sq. units
(B) 18 sq. units
(C) 27 sq. units
(D) 81 sq. units
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The locus represented by is:
(A) A pair of perpendicular lines
(B) A pair of parallel lines
(C) A pair of parallel planes
(D) A pair of perpendicular planes
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The plane makes an angle with the x-axis. The value of is equal to:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Three-Dimensional Geometry Fill in the blanks Type Questions
| 1. A plane passes through the points (2, 0, 0), (0, 3, 0), and (0, 0, 4). The equation of the plane is __________. |
| Ans. |
| 2. The direction cosines of the vector are __________. |
| Ans. |
Commonly asked questions
A plane passes through the points (2, 0, 0), (0, 3, 0), and (0, 0, 4). The equation of the plane is __________.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The direction cosines of the vector are __________.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The vector equation of the line is __________.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The vector equation of the line through the points (3, 4, –7) and (1, –1, 6) is __________.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The cartesian equation of the plane is __________.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Three-Dimensional Geometry True or False Type Questions
| 1. The unit vector normal to the plane is |
| Ans. |
| 2. The intercepts made by the plane on the coordinate axis are . |
| Ans. |
Commonly asked questions
The unit vector normal to the plane is
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The intercepts made by the plane on the coordinate axis are .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The angle between the line + and the plane + 5 = 0 is . .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The angle between the planes is .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The line lies in the plane
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The vector equation of the line is
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The equation of a line, which is parallel to and passes through the point (5, –2, 4), is
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to a plane is (5, –3, –2), then the equation of the plane is
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven Exam