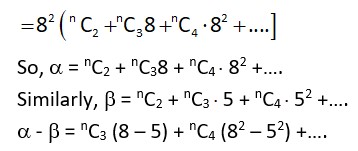Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four Determinants offers practice questions for Class 12 students who are preparing for the CBSE Board exams and other competitive exams like JEE. The exemplar questions take you beyond the NCERT Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four Determinants, and help you deepen your understanding of the concepts and formulas. It gives extra questions for practice, which include Multiple Choice Questions, Short Answer, and long-answer-type questions.
Students can download the Class 12 Determinants PDF and practice the questions to score high in the examinations. These solutions are given in a step-by-step format, which helps students to understand each step and hence improves their problem-solving skills. Math requires practice, and when one solves the exemplar questions, they are more confident in solving the most complex problems in exams.
Related Links
| NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths | NCERT Notes |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths | NCERT Class 12 Notes |
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Maths Chapter Four Determinants
- Class 12 Maths Determinants NCERT Exemplar Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Maths Chapter Four Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Maths Determinants Objective Type Questions
- 29th June 2022 (Second Shift)
- Important Formulas Related to Maths Chapter Four NCERT Exemplar
- 02 November 2025
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Maths Chapter Four Determinants
The PDF of the Maths Class 12 Determinants here gives a curated collection of high-quality questions. It follows the CBSE syllabus and exam pattern, and hence it is ideal for exam preparation. Once the student downloads the PDF, they can study it from anywhere and at any time, even without the need for an internet connection. The Maths PDF includes the Short Answer, Long Answer, and MCQ questions, which help students to prepare for the various examinations.
The PDF questions will help students to think logically and deepen their understanding of topics like Cofactors and Minors, Properties of Determinants, Cramer's Rule for solving equations, and Adjoint and Inverse of a Matrix. The students can rely on these solutions and it is available free of cost. They can also take a printout and practice questions on paper.
Also read:
NCERT Solutions
Class 12 Maths Determinants NCERT Exemplar Short Answer Type Questions
SA Questions
Kindly Consider the following
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Commonly asked questions
Kindly Consider the following
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
=0
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
= 4
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
= (a – 1)3
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
If , then prove that
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
If the coordinates of the vertices of an equilateral triangle with sides of length ‘a’ are , , , then
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

Kindly Consider the following
Find the value of satisfying
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
If then find values of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
If are in G.P., then prove that the determinant is
independent of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
Show that the points , , and do not lie on a straight line for any value of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
Show that the is an isosceles triangle if the determinant
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
Find if and show that
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Maths Chapter Four Long Answer Type Questions
LA Questions
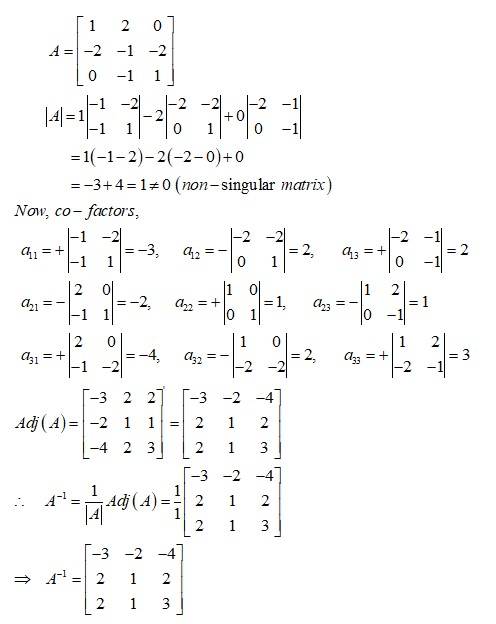
| Q1. If find . Using , solve the system of linear equations
|
| Sol: |
Commonly asked questions
Using matrix method, solve the system of equations
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
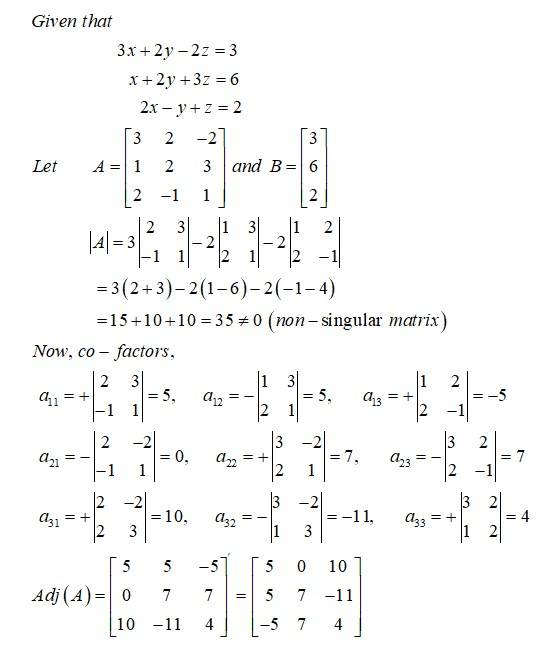
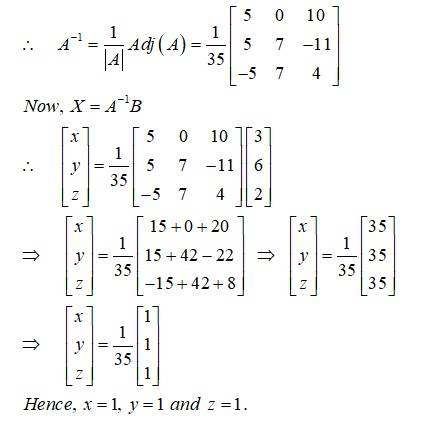
Given find and use this to solve the system of equations:
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

If and then prove that .
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
Prove that is divisible by and find the quotient.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , prove that
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Maths Determinants Objective Type Questions
Objective Type Questions
| Choose the correct answer from given four options in each of the Exercises from 1 to 14. Q1. If then the value of is (A) 3 (B) ±3 (C) ±6 (D) 6 |
| This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Sol:
|
| Q2. The value of determinant is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of these |
| This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
The area of a triangle with vertices , , and is 9 sq. units. The value of will be
(A) 9
(B) 3
(C) –9
(D) 6
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The determinant equals
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The number of distinct real roots of in the interval is
(A) 0
(B) 2
(C) 1
(D) 3
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let f(t|) then is equal to
(A) 0
(B) –1
(C) 2
(D) 3
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The maximum value of = is ( is real number)
(A)
(B) √3/2
(C) √2
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , then
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , then exists if
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If and are invertible matrices, then which of the following is not correct?
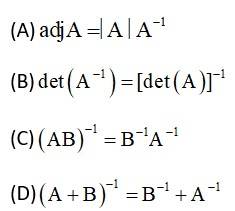
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If are all different from zero and then value of
x–1 + y–1 + z–1 is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The value of the determinant
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
There are two values of which make the determinant then the sum of these numbers is
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) -4
(D) 9
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
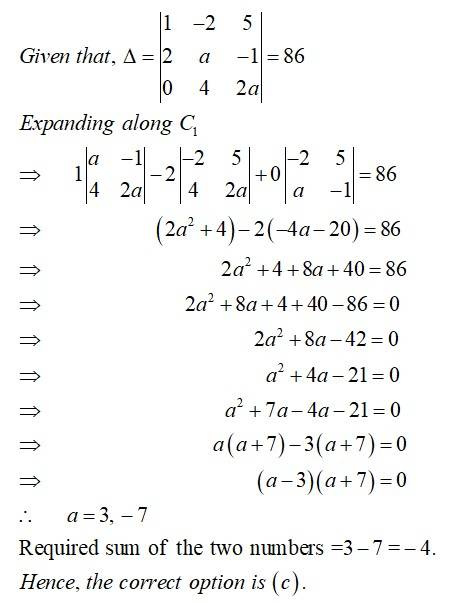
If is a matrix of order , then ___.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If is an invertible matrix of order , then = ___.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , then ___. ___________
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
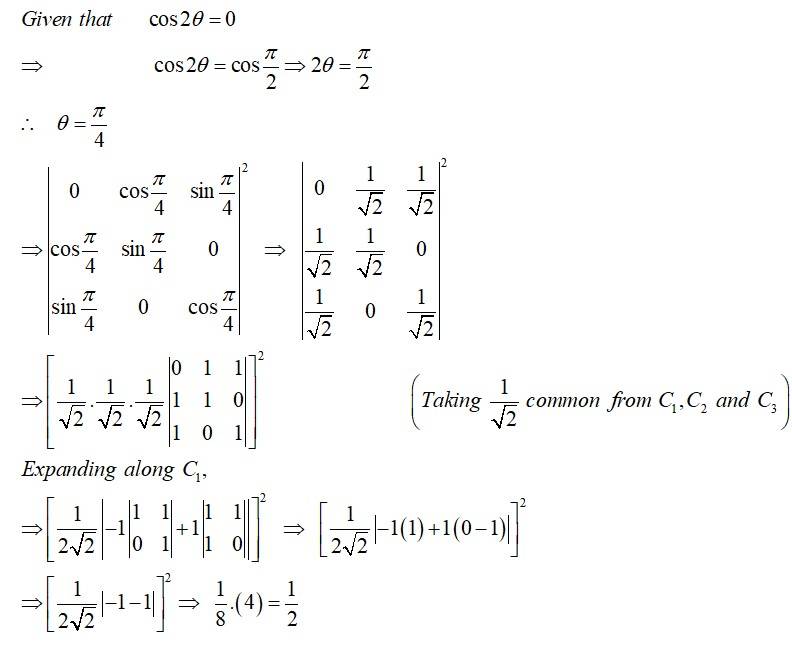
If is a matrix of order , then ____.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If is a matrix of order , then the number of minors in the determinant of is ____.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The sum of the products of elements of any row with the cofactors of corresponding elements is equal to ___.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If is a root of then the other two roots are ____.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly Consider the following
=____.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If then ____.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
, where is a square matrix and .
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
, where is any real number and is a square matrix.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
, where is a non-singular matrix.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If and are matrices of order 3 and , , then
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If the value of a third-order determinant is 12, then the value of the determinant formed by replacing each element by its cofactor will be 144.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
where are in A.P.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
, where is a square matrix of order two.
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The determinant
This is a Fill in the blanks as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
29th June 2022 (Second Shift)
29th June 2022 (Second Shift)
Commonly asked questions
Let α be root of the equation 1 + x2 + x4 = 0. Then the value of α1011 + α2022 - α3033 is equal to
x4 + x2 + 1 = 0
x4 + 2x2 + 1 – x2 = 0
Now, =
=
= 1 + 1 – 1 = 1
Let arg(z) represent the principal argument of the complex number z. Then and art(z – 1) – arg(z + 1) = intersect
circle with radius = 3
arg part of a circle (with radius ). no common points
Let If then the sum of all elements of the matrix B is
B = (I – adjA)5
fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff
The sum of the infinite series is equal to
Let S = 1
The value of is equal to
= 2
Let f : R → R be a function defined by f(x) = Then which of the following is NOT true?
option (C) is incorrect, there will be minima.
Let f be a real valued continuous function on [0, 1] and f(x) = Then, which of the following points (x, y) lies on the curve y = f(x)?
Let
So, f (x) = αx – β
Now,
f (x) = αx – β
option (D) satisfies
If
If y = y(x) is the solution of the differential equation
then is equal to
x = 0, y = 0
now at x =
Let P : y2 = 4ax, a > 0 be a parabola with focus S. Let the tangents to the parabola P make an angle of with the line y = 3x + 5 touch the parabola P at A and B. Then the value of a for which A, B and S are collinear is
Tangents making angle with y = 3x + 5.
So, these tangents are . So ASB is a focal chord.
Let a triangle ABC be inscribed in the circle such that If the length of side AB is then the area of the is equal to
here AB = , BC = 2, AC =
area =
Let lie on the plane px – qy + z = 5, for some The shortest distance of the plane form the origin is
Line to the normal
⇒ 3p + 2q – 1 = 0
lies in the plane 2p + q = 8
From here p = 15, q = -22
Equation of plane 15x – 22y + z – 5 = 0
Distance from origin = √5/142
The distance of the origin from the centroid of the triangle whose two sides have the equations x – 2y + 1 = 0 and 2x – y – 1 = 0 and whose orthocenter is
Let AB
AC
So vertex A = (1, 1)
altitude from B is perpendicular to AC and passing through orthocentre.
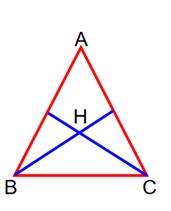
So, BH = x + 2y – 7 = 0
CH = 2x + y – 7 = 0
now solve AB & BH to get B (3, 2) similarly CH and AC to get C (2, 3) so centroid is at (2, 2)
Let Q be the mirror image of the point P(1, 2, 1) with respect to the plane x + 2y +2z = 16. Let T be a plane passing through the point Q and contains the line Then, which of the following points lies on T?
(x, y, z) = (3, 6, 5)
now point Q and line both lies in the plane.
So, equation of plane is
2x – z = 1
option (B) satisfies.
Let A, B, C be three points whose position vectors respectively are
If is the smallest positive integer for which are noncollinear, then the length of the median, in through A is
Mid point of BC is
For = 1, and will be collinear. So for non collinearity
= 2
The probability that a relation R from is both symmetric and transitive, is equal to
Total number of possible relation =
Favourable relations =
Probability =
The number of values of such that the variance of 3, 7, 12, a, 43 a is a natural number is
Variance =
Let 2a2 – a + 1 = 5x
D = 1 – 4 (2) (1 – 5n)
= 40n – 7, which is not
As each square form is
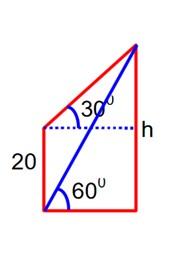
From the base of a pole of height 20 meter, the angle of elevation of the top of tower is 60°. The pole subtends an angle 30° at the top of the tower. Then the height of the tower is
Let base = b
Negation of the Boolean statement is equivalent to
pva ⇒
its negation as asked in question
=
=
Let be an integer. If 9n – 8n – 1 = 64α and 6n – 5n – 1 = 25β, then α - β is equal to
Let be a vector such that Then, the value of is equal to
Data contradiction.
Let y = y(x), x > 1, be the solution of the differential equation
If y(3) = , then the value of α+β is equal to
IF
=
y =
y (2) =
y (3) =
Let 3, 6, 9, 12,…. upto 78 terms and 5, 9, 13, 17,…. upto 59 terms be two series. Then, the sum of the terms common to both the series is equal to
First common term to both AP’s is 9
t78 of
t59 of
nth common term
9 + (n – 1) 12 234
n <
Now sum of 19 terms with a = 9, d = 12
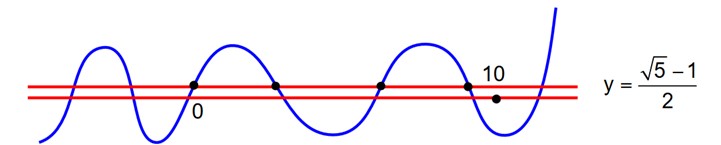
The number of solutions of the equation sin x = cos2 x in the interval (0, 10) is
sin x = 1 – sin2 x
sin x =
draw y = sin x
y = find their pt. of intersection.
For real numbers a, b(a > b > 0), let
Then the value of (a – b)2 is equal to
Given a > b
Area common to x2 + y2
is
Similarly
Equation (i) and equation (ii)
Equation (i) + equation (ii)
a2 = 75, b2 = 27
Let f and g be twice differentiable even functions on (2, 2) such that and
Then, the minimum number of solutions of is equal to
f (x) is an even function
So, f (x) has at least four roots in (-2, 2)
So, g (x) has at least two roots in (2, 2)
now number of roots of f (x)
It is same as number of roots of will have atleast 4 roots in (2, 2)
Let the coefficients of x-1 and x-3 in the expansion of be m and n respectively. If r is a positive integer such that mn2 = 15Cr . 2r, then the value of r is equal to
= 15Cr
Coefficient of x-1 ⇒ r = 10 ⇒ m = 15C10
now mn2 = 15Cr
⇒ r = 5
The total number of four digit numbers such that each of first three digits is divisible by the last digit, is equal to
Fix the unit place, find the chances for the first three digits
unit digit as 1, total ways = 9.102
unit digit as 2, total ways = 4.52
unit digit as 3 total ways = 3.42
unit digit as 4 total ways = 2.32
unit digit as 5 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 6 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 7 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 8 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 9 total ways = 1.22
Let where is a non-zero real number an If (I – M2)N = 2I, then the positive integral value of is
N =
N =
Now
? α100 + α2 = 2
? α =
Let f(x) and g(x) be two real polynomials of degree 2 and 1 respectively. If and then the value of f(2) + g(2) is
g (x) = px + q
Compare 8 = ap2 …………… (i)
-2 = a (2pq) + bp
0 = aq2 + bq + c
? 4x2 + 6x + 1 = apx2 + bpx + cp + q
? Andhra Pradesh = 4 ……………. (ii)
6 = bp
1 = cp + q
From (i) & (ii), p = 2, q = -1
? b = 3, c = 1, a = 2
f (x) = 2x2 + 3x + 1
f (2) = 8 + 6 + 1 = 15
g (x) = 2x – 1
g (2) = 3
Important Formulas Related to Maths Chapter Four NCERT Exemplar
These are the important formulas of the determinant chapter:
Determinant of a 2×2 Matrix
Determinant of a 3×3 Matrix
Cofactor
Adjoint of a Matrix
Inverse of a Matrix
Cramer’s Rule
02 November 2025
02 November 2025
Commonly asked questions
Let a, b, c be the roots of the equation x³ – 9x² + 15x + 2 = 0. The volume of a parallelopiped with nonparallel sides aî + bĵ + ck̂, bî + cĵ + ak̂ and cî + aĵ + bk̂ is
Volume = |a b c; b c a; c a b| = |3abc – a³ – b³ – c³|
= | (a + b + c) (a² + b² + c² – ab – bc – ca)| = | (a + b + c) (a + b + c)² – 3 (ab + bc + ca)|
= |9 (81-3 × 15)| = 324
There are two sets A = {a: a ∈ N and –3 ≤ a ≤ 5} and B = {b: b ∈ Z and 0 ≤ b ≤ 4}. The number of elements common in A × B and B × A are
A = {1,2,3,4,5} B = {0,1,2,3,4}
No. of elements common in A&B = 4.
∴ No. of elements common in A × B and B × A = 4 × 4 = 16
If x&y are real numbers satisfying the relation x2 + y2 – 6x + 8y + 24 = 0 then minimum value of log2(x2 + y2) is
x² + y² – 6x + 8y + 24 = 0 is circle having centre (3, −4) & r = √ (9+16-24) = 1
√x² + y² min. is min. distance from origin = 4
∴ minimum value of log? (x² + y²) = log? 16 = 4
Let f(x) =
{ (sin(2x²/a) + cos(3x²/b))^(ab/x²), x ≠ 0
{ e^(2x+3), x = 0
is a continuous function at x = 0, ∀b ∈ R, then 1/a_min is
RHL&LHL lim (x→0) (sin (2x²/a) + cos (3x/b)^ (ab/x²)
= e^ (lim (x→0) (sin (2x²/a) + cos (3x/b) - 1) (ab/x²) = e^ (4b²-9a)/2b)
f (0) = e³
For continuity at x = 0
Limit = f (0)
(4b² - 9a)/2b = 3 ⇒ 4b² – 6b – 9a = 0∀b ∈ R
⇒ D ≥ 0 ⇒ a ≥ -1/4
a? = -1/4
⇒ |1/a? | = 4.
A vertical pole PS has two marks at Q and R such that portions PQ, PR and PS subtends angle α, β, γ respectively at a point on the ground which is at distance x from the bottom of pole P. If PQ = 1, PR = 2, PS = 3 and α + β + γ = 180°, then x² is
tan α = 1/x, tan β = 2/x, tan γ = 3/x
Now α + β + γ = 180°
⇒ tan α + tan β + tan γ = tan α tan β tan γ
1/x + 2/x + 3/x = (123)/ (xxx)
⇒ x² = 1
The product of real roots of the equation |x|6/5 – 26|x|3/5 – 27 = 0 is –3k where k is
|x|³/? = y
⇒ y² – 26y – 27 = 0 ⇒ y = −1 or 27
⇒ y = 27 ⇒ |x|³/? = 3³
|x| = 3? ⇒ x = ±3?
Product of roots = (3? ) (−3? ) = −3¹?
In a hurdle race, a runner has probability p of jumping over a specific hurdle. Given that in 5 trials, the runner succeeded 3 times, the conditional probability that the runner has succeeded in the first trial is
A: runner succeeded exactly 3 times out of 5.
B: runner succeeds on the first trial.
P (B/A) = P (B ∩ A) / P (A) = (p (? C? p² (1−p)²) / (? C? p³ (1-p)²) = 3/5 = 0.6
If tan x + tan(x + π/3) + tan(x + 2π/3) = 3 then value of tan 3x is
tanx + tan (x+π/3) + tan (x-π/3) = 3
tanx + (tanx+√3)/ (1-√3tanx) + (tanx-√3)/ (1+√3tanx) = 3
tanx + (8tanx)/ (1-3tan²x) = 3
(tanx (1-3tan²x) + 8tanx)/ (1-3tan²x) = 3
(3 (3tanx – tan³x)/ (1-3tan²x) = 3
⇒ 3tan3x = 3
tan3x = 1
Let n(A) = 4 and n(B) = 6, then the number of one- one functions from A to B is
? P? = 6!/2! = 360
Let ∫ (x¹/²)/(√1-x³) dx = ⅔ gof(x) + c and f(x) = x³/², then the value of g(0) is) + c and f(x) = x³/², then the value of g(0) is
Put x³/² = t
√xdx = (2/3)dt
⇒ (2/3) ∫ dt/√ (1-t²) = (2/3)sin? ¹t + c
= (2/3)sin? ¹x³/² + c
⇒ g (x) = sin? ¹x
g (0) = 0
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four Exam