
NCERT Class 12 Physics Exemplar for Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields is an important study tool for this chapter. The Exemplar given here is prepared by Shiksha's subject matter experts and is highly reliable for exam preparation. The Class 12 NCERT Physics exemplar includes questions from the Class 12 Physics book along with the sample papers and previous years' question papers.
The students can also download Physics Class 12 Chapter 1 PDF from here and practice all the questions. The important concepts covered in this chapter are electric fields, Coulomb's Law, the nature of the electric charge, electric dipoles, Gauss's Law, and electric flux. The exemplar questions are designed to challenge you to think critically, apply concepts, and develop a deeper understanding of the subject.
The solutions are given in a step-by-step manner with clear explanations. It is created to clarify underlying assumptions and principles, and it also helps in preparing for the CBSE Board examinations and competitive entrance exams like NEET and JEE. Students can also read Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and Fields.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
- Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Physics Exemplar Chapter 1
- Electric Charges and Fields Questions and Answers
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 1 NCERT Exemplar
- JEE Mains paper
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
The students can download the Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 PDF from here. Shiksha's subject matter experts have created these exemplary solutions. It is as per the latest CBSE and NCERT updates. The PDF offers high-quality practice questions, conceptual clarity, and exam-oriented preparation. The PDF offers students an opportunity to study offline on a computer, tablet, or mobile device.
Refer To Table Below For Related Links
| NCERT Solutions for Maths, Physics, Chemistry | NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics |
| NCERT Solutions Physics Class 11th | NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 |
Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Physics Exemplar Chapter 1
Some of the common mistakes are the following:
- The students misunderstand the vector nature of the electric field. They often treat the electric field as a scalar. To avoid this mistake, they always need to consider the vector nature.
- Another mistake is the incorrect application of Coulomb’s Law.
- The students also get confused between electric force and electric field.
- They make errors in the superposition principle and ignore the sign of charges.
Some tips to avoid the mistakes are:
- Master units and constants, and practice diagram-based questions.
- Revise the conceptual theory because most of the exemplar questions test the concepts and not the formulas.
Read more:
Class 11 Physics Notes
Electric Charges and Fields Questions and Answers
| 1. Five charges,q each are placed at the comers of a regular pentagon of side a. |
| Explanation- (a) (i) the electric field at the center of pentagon is zero because the distance from the center is same. (ii) the field through one charge is Kq/r2 (iii) when one charge is positive and other is negative then net force towards negative charge. So net force is Kq/r2+ Kq/r2= 2Kq/r2 (b) it doesn’t depend upon the number of sides increasing the net electric field is zero. |
| 2. In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the Universe could be explained if matter carried a net charge. Suppose that the Universe is made up of hydrogen atoms with a number density N, which is maintained a constant. Let the charge on the proton be: ep=−(1+y)e where e is the electronic charge. Find the critical value of y such that expansion may start |
| Explanation- let us consider that universe is of radius R And we know that hydrogen is made up one electron and proton so net charge is -(1+y)e+e = -ye Now the number of hydrogen atom in the universe = N So total charge is = -ye N According to gauss theorem So E E= -NRye/3 And we know electrostatic force F=qE = -ye(-NRye/3 ) by using the value of E and q F= force is positive which shows that force is repulsive. But the gravity is g= and gravitational force is F= But M= N where is mass of proton So using this mass in above eqn so force = But her masses of proton and hydrogen are equal so take as m F= So calculate its critical value electrostatic force and gravitational force both are equal. So, So y2= 4 after using standard values we get value of y= approx. 10-18 |
| 3. Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as ρ (r ) = kr for r ≤ R for r > R . |
| Explanation- (i) when r
= and we know that V = = 4 = E(4 ) = = so it is clear that E is radially outwards. When r>R = E= again field is outwards (ii) When two protons are there then they must be on opposite sides or we can say along the end of diameter So q= .q= 4 If protons 1 and 2 are embedded at distance r from the center of the sphere then force will be F=eE=- but the force applied by proton F= By adding these F= - If F=0 then so after solving r= |
| 4. Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α &β ) , each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d . The third plate is released and collides with the plate β . Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β &γ . (a) Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision. (b) Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
|
| Explanation- net electric field at plate γ due to two other plate From plate 1 ,E1= From plate 2 ,E2= Total electric field E= E1 + E2 = to the left , if Q>q electric field at o due to plate α = electric field at o due to plate β = electric field at o due to plate γ = as the electric field at o is zero therefore As there is no loss of charge on collision Q+q= On solving these q1= (Q+q/2)= charge on plate β q2= (q/2)= charge on plate γ |
a
Commonly asked questions
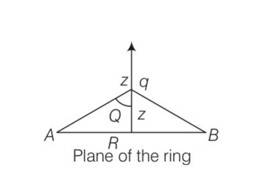
A positive charge Qis uniformly distributed along a circular ring of radius R. A small test charge q is placed at the centre of the ring as shown in figure. Then
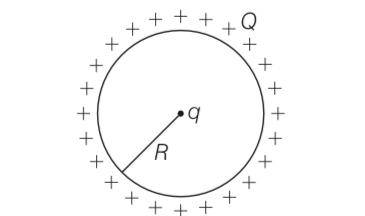
(a) If q>0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring it will be pushed back towards the centre
(b) If q<0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring, it will never return to the centre an will continue moving till it hits the ring
(c) If q<0 , it will perform SHM for small displacement along the axis.
(d) Q at the centre of the ring is in an unstable equilibrium within the plalne of the ring for q>O
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b, c
Explanation- the positive charge Q is uniformly distributed at the outer surface of the enclosed sphere thus electric field inside the sphere is zero. So the effect of electric field on charge q due to positive charge Q is zero.
Now the only attractive and repulsive force between Q and q
Case 1 q>0 this creates repulsive force
Case 2 q<0 this creates attractive force
If q is shifted from the centre then the positive charges nearer to this charge will attract it towards itself and charge q will never return to its centre.
A point positive charge is brought near an isolated conducting sphere. The electric field is best given by.
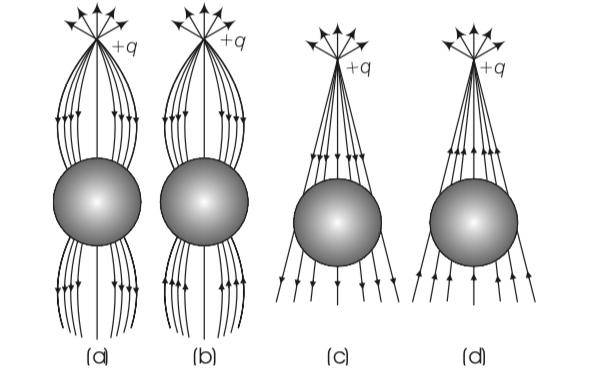
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a)
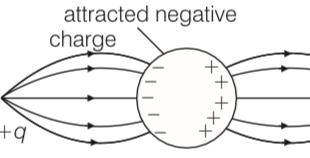
Explanation- when a positive point charge is brought near an isolated conducting sphere without touching the sphere, then the free electron in the sphere are attracted towards the positive charge. This leaves an excess positive charge on right side of sphere . And also by induction the negative charge is setup across left side. So field lines first goes from positive charge (+q) to negative charge of sphere then from positive charge of sphere to negative charge anywhere in the universe.
Figure shows electric field lines in which an electric dipole P is placed as shown. Which of the following statements is correct?
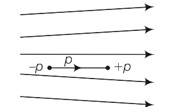
(a) The dipole will not experience any force
(b) The dipole will experience a force towards right
(c) The dipole will experience a force towards left
(d) The dipole will experience a force upwards
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (c)
Explanation- As the space is increasing towards right means electric field is decreasing so as force is also decreasing . so force on -p is more than the force on +p
Multiple Choice Questions
(One or More than One Correct Answer Type)
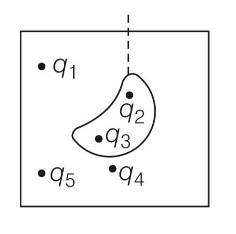
If Фs E . dS = 0 over a surface, then
(a) The electric field inside the surface and on it is zero
(b) The electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform
(c) The number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal tothe number of flux lines leaving it
(d) All charges must necessarily be outside the surface
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (c), (d)
Explanation- It is only possible when charges must be outside the surface or field line entering or leaving the surface are equal.
Figure shows the electric field lines around three point charges A, B and C.
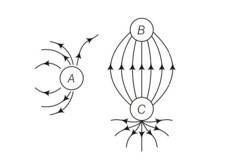
(i) Which charges are positive?
(ii) Which charge has the largest magnitude? Why?
(iii) In which region or regions of the picture could the electric field be zero? Justify your answer.
(a) Near A (b) Near B
(c) Near C (d) Nowhere
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-The electric lines of forces always starts from a positive charge and ends at a negative charge. In case of a single isolated charge, electric lines of force start from positive charge ends at infinity.
(i) Here, in the figure, the electric lines of force starts from A and C. Therefore, charges A and C must be positive.
(ii) The number of electric lines of forces starting from charge C are maximum, so C must have the largest magnitude.
(iii) From the figure we see that a neutral point exists between charges A and
Here, more number of electric lines of forces shows higher strength of charge C than A. Thus, electric field is zero near charge A hence neutral point lies near A.
Five charges q1, q2, q3, q4 and q5 are fixed at their positions as shown in figure, S is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss’ law is given by
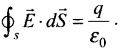
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from q1 ,q5 and q1, q5 and q3 while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q1 and q4 only
(b) E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all charges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q2 and q4 only
(c) E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all ch arges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q1, q3 and q5 only
(d) Both E on the LHS and q on the RHS will have contributions from q2 and q4 only
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (b)
Explanation-The charges may be located anywhere inside the surface, if the surface is so chosen that there are some charges inside and some outside, the electric field on the left side of equation is due to all charges, both inside and outside S.
Consider a region inside which there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region,
(a) The electric field is necessarily zero
(b) The electric field is due to the dipole moment of the charge distribution only
(c) The dominant electric field is ∝ 1/r3, for large r, where r is the distance from an origin in this regions r
(d) The work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the region, will be zero
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (c), (d)
Explanation- electric field is not necessarily zero may it become zero by their algeabric sum. For dipole the electric field is always ∝ 1/r3 and it is also conservative.
Refer to the arrangement of arrangement of charges in figure and a gaussian surface of radius R with Q charge at the center. Then
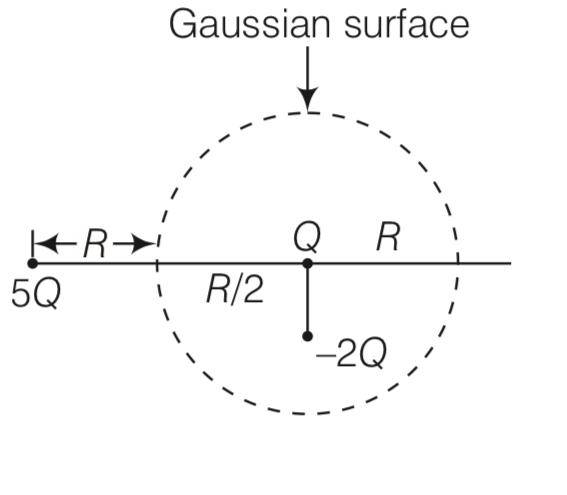
(a) Total flux through the surface of the sphere is .
(b) Field on the surface of the sphere of the sphere is -Q/4 0R2.
(c) Flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
(d) Field on the surface of sphere due to -2Q is same everywhere
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a, c)
Explanation- Gauss's law states that the total electric flux of an enclosed surface is given by q/? 0, where q is the charge enclosed by the surface.
So total charge inside the surface is = Q-2Q = -Q
Therefore total flux through the surface of the sphere = -Q/? 0
Now, charge 5Q is lies outside the surface, thus it makes no contribution to electric flux through the given surface. So both option a and c are true.
A positive charge Q is uniformly distributed along a circular ring of radius R. A small test charge q is placed at the centre of the ring figure. Then,
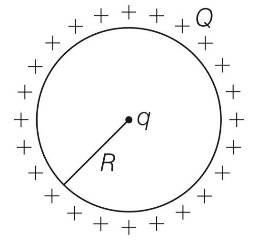
(b) If q < 0 and is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring, it will never return to the centre and will continue moving till it hits the ring
(c) If q < 0, it will perform SHM for small displacement along the axis
(d) Q at the centre of the ring is in an unstable equilibrium within the plane of the ring for q > 0
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (a), (b), (c), (d)
Explanation- The positive charge Q is uniformly distributed along the circular ring then electric field at the centre of ring will be zero, hence no force is experienced by the charge if it is placed at the centre of the ring.
Now the charge is displaced away from the centre in the plane of the ring. There will be net electric field opposite to displacement will push back the charge towards the centre of the ring if the charge is positive. If charge is negative, it will experience net force in the direction of displacement and the charge will continue moving till it hits the ring. Also this negative charge is in an unstable equilibrium. Also when a negative charge is shifted away from the center it will move back to center and show SHM for a very short distance
Consider a coin of Question 20. ft is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charge of magnitude 34.8 kC. Suppose that these equal charges were concentrated in two point charges separated by
(i) 1 cm — (1/2 x diagonal of the one paisa coin)
(ii) 100 m (~ length of a long building)
(iii) 106 m (radius of the earth). Find the force on each such point charge in each of the three cases. What do you conclude from these results?
Explanation- (i) F= = 9 109 (34.8 103)2/ (10-2)2=1.09 1023N
(ii) F= = 9 109 (34.8 103)2/ (100)2=1.09 1015N
(iii) F= = 9 109 (34.8 103)2/ (106)2=1.09 107N
Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as ρ (r ) = kr for r ≤ R for r > R .
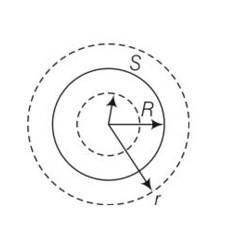
(a) Find the electric field at all points r.
(b) Suppose the total charge on the sphere is 2e where e is the electron charge. Where can two protons be embedded such that the force on each of them is zero. Assume that the introduction of the proton does not alter the negative charge distribution.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
(i) when r
= and we know that V =
= 4
=
E(4 ) = = so it is clear that E is radially outwards.
When r>R
=
E= again field is outwards
(ii) When two protons are there then they must be on opposite sides or we can say along the end of diameter
So q=
.q= 4
If protons 1 and 2 are embedded at distance r from the center of the sphere then force will be
F=eE=- but the force applied by proton F=
By adding these F= -
If F=0 then so after solving r=
The electric flux through the surface
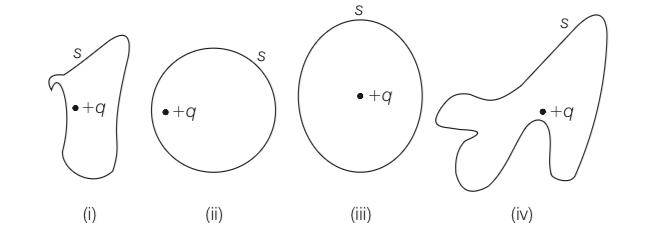
(a) In Fig. (iv) is the largest
(b) In Fig. (iii) is the least
(c) In Fig. (ii) is same as Fig. (iii) but is smaller than Fig. (iv)
(d) Is the same for all the figures
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (d)
Explanation- Total flux inside a conducting sphere is depend upon the algeabric sum of total charge inside that surface, which is same for all fig. As it does not depend upon shape of a body
A point charge +q is placed at a distance d from an isolated conducting plane. The field at a point P on the other side of the plane is
(a) Directed perpendicular to the plane and away from the plane
(b) Directed perpendicular to the plane but towards the plane
(c) Directed radially away from the point charge
(d) Directed radially towards the point charge
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (a)
Explanation- when a point positive charge brought near an isolated conducting plane, some negative charge develops on the surface of the plane towards the charge and an equal positive charge develops on opposite side of the plane. By process called induction.
Two charges –q each are fixed separated by distance 2d. A third charge q of mass m placed at the mid-point is displaced slightly by x (x<
T=[8π3ɛo md3/q2]1/2
Explanation- two charge -q at A and B
AB=AO+OB=2d and x= small distance perpendicular to O
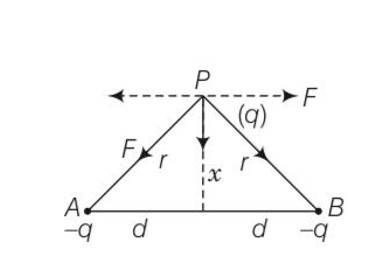
When x
F=qq/4 where AP=BP=r but horizontal components gets cancel out each other and vertical components gets add .
If angle APO=O the net force on q along PO is F’= 2Fcos
= =
When x
K= ,F
Force on charge q is proportional to its displacement from the center O and it is directed towards O
Hence we can say that motion of charge would be simple harmonic
Where w= and T=
T= 2 = 2 = [8π3?o md3/q2]1/2
Five charges,q each are placed at the comers of a regular pentagon of side a.
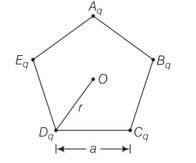
i) What will be the electric field at O, the centre of the pentagon?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the comers (say A) is removed?
(iii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by – q?
(b) How would your answer to (a) be affected if pentagon is replaced by n-sided regular polygon with charge q at each of its comers?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- (a)
(i) The electric field at the center of pentagon is zero because the distance from the center is same.
(ii) The field through one charge is Kq/r2
(iii) When one charge is positive and other is negative then net force towards negative charge. So net force is Kq/r2+ Kq/r2= 2Kq/r2
(b) It doesn't depend upon the number of sides increasing the net electric field is zero.
A paisa coin is made up of Al-Mg alloy and weight 0.75 g. It has a square shape and its diagonal measures 17 mm. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- 1 molar mass of Al has NA (Avogadro number)= 6.023 1023
M= m= 6.023 1023/27 0.75 = 1.6 1022
Magnitude of positive and negative charges in one paisa coin = Nze
As aluminium has 13 electron and 13 protons so
= 1.6 1022 13 1.6 10-19=33.28 103C.
A metallic spherical shell has an inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A charge Q is placed at the centre of the spherical cavity. What will be the surface charge density on
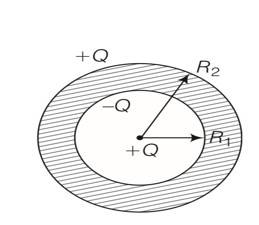
(i) The inner surface
(ii) The outer surface?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – (i) surface density=charge/area= -Q/4 12
(ii) surface density=charge/area= +Q/4 22
If the total charge enclosed by a Surface is zero, does it imply that the electric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- if the total charge inside a surface is zero it does not mean that electric field is zero may it will flow from inside to outside or vice versa. But if electric field is zero then charge must be zero .
A hemisphere is uniformly charged positively. The electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed .
(a) Perpendicular to the diameter
(b) Parallel to the diameter
(c) At an angle tilted towards the diameter
(d) At an angle tilted away from the diameter
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (a)
Explanation- field lines are always perpendicular to the surface.
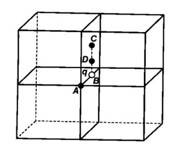
What will be the total flux through the faces of the cube (Fig. 1.9) with a side of length an if a charge q is placed at
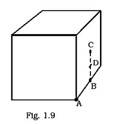
(a) A: a corner of the cube.
(b) B: mid-point of an edge of the cube.
(c) C: centre of the face of the cube.
(d) D: mid-point of B and C.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – in these type of question imagine another cube along the charge is kept in 3 dimensional aspects.
- In this part the charge is situated at the corner of cube here we can placed 7 more cube joining the corner of that cube . so charge is being shared by 8 cubes.
Therefore, the total flux through the faces of the cube= q/8 ε0
Two charges q and -3q are placed fixed on x-axis separated by distance d. where should a third charge 2q be placed such that it will not experience any force?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer = (1+ ) towards left.
Explanation -lets consider 2q charge is placed in between q and -3q, here it will definitely experience some force q charge repel 2q charge and -3q charge will attract 2q charge. So 2q charge will move towards -3q charge.
Now lets consider it to the left of q at some distance x, here the force experience by q is repulsive and force experience by -3q is attractive . so they cancel out each other and no net force is experience by 2q.
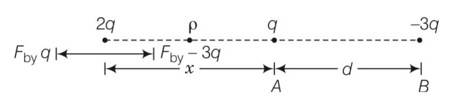
Thus, force of attraction by -3q = force of repulsion by q
k 2q q/x2 = k 2q 3q/ (x+d)2
(x+d)2 = 3x2
x2 + d2 + 2xd = 3x2
2x2 - 2dx – d2 = 0
x = +
x= (1+ ) towards left.
Total charge -Q is uniformly spread along the length of a ring of radius R. A small test charge +q of mass m is kept at the centre of the ring and is given a gentle push along the axis of the ring.
(a) Show that the particle executes a simple harmonic oscillation.
(b) Obtain its time period.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- electric field at the axis of the ring is E=KQy/ (R2+z2)3/2 where z is distance .
F=qE=KQqy/ (R2+z2)3/2
When z<
F= = -Kz
So force is directly proportional to – distance that is completely defined that is follows S.H.M
(b)w=
T=2 w=2
T=2
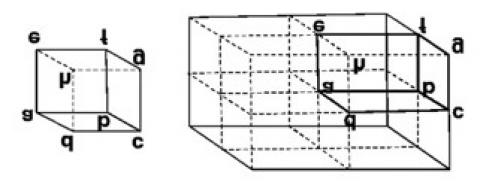
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atohis, represented by open circles are situated at the comers of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at
the centre of the Cube. The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
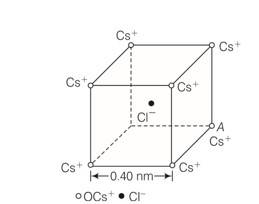
(i) What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
(ii) Suppose that the Cs atom at the comer A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- (i)The cesium atoms, are situated at the corners of a cube and Cl atom is situated at the centre of the cube. From the given figure, we can analyse that the chlorine atom is at equal distance from all the eight comers of cube where cesium atoms are placed. Thus, due to symmetry the electric field due to all Cs atoms, on Cl atom will cancel out. Hence net electric field at the centre of cube is zero.
(ii) we know, f=qE E= Kq/r2= Ke/r2
F= e (E)=e (ke/r2)=ke2/r2
Distance= = 10-9m
F=8.99 109 (1.6 10-16)2/ (0.346 10-9)2=1.92 10-9N
The electric field at a point is
(a) Always continuous
(b) Continuous if there is no charge at that point
(c) Discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point (d) discontinuous if there is a charge at that point
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (b), (d)
Explanation- if we place a charge then we must experience some forces but if there would be no charge so field is continuous
In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the Universe could be explained if matter carried a net charge. Suppose that the Universe is made up of hydrogen atoms with a number density N, which is maintained a constant. Let the charge on the proton be: ep=−(1+y)e where e is the electronic charge. Find the critical value of y such that expansion may start
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- let us consider that universe is of radius R
And we know that hydrogen is made up one electron and proton so net charge is
-(1+y)e+e = -ye
Now the number of hydrogen atom in the universe = N
So total charge is = -ye N
According to gauss theorem
So E
E= -NRye/3
And we know electrostatic force F=qE = -ye(-NRye/3 ) by using the value of E and q
F= force is positive which shows that force is repulsive.
But the gravity is g= and gravitational force is F=
But M= N where is mass of proton
So using this mass in above eqn so force =
But her masses of proton and hydrogen are equal so take as m
F=
So calculate its critical value electrostatic force and gravitational force both are equal.
So,
So y2= 4 after using standard values we get value of y= approx. 10-18
There is another useful system of units, besides the SI/mks A system, called the cgs (centimeter-gram-second) system. In this system Coloumb’s law is given by F=Qq/r2 vector r where the distance r is measured in cm (= 10–2 m), F in dynes (=10–5 N) and the charges in electrostatic units (es units), where 1es unit of charge=1/[3]x10-9C The number [3] actually arises from the speed of light in vaccum which is now taken to be exactly given by c = 2.99792458 × 108m/s. An approximate value of c then is c = [3] × 108 m/s. (i) Show that the coloumb law in cgs units yields 1 esu of charge = 1 (dyne)1/2 cm. Obtain the dimensions of units of charge in terms of mass M, length L and time T. Show that it is given in terms of fractional powers of M and L. (ii) Write 1 esu of charge = x C, where x is a dimensionless number. Show that this gives
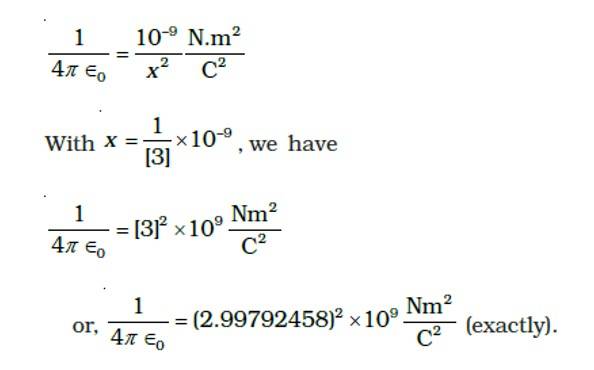
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as we know F= Qq/r2= 1dyne = 1esu of charge2/1cm2
1 esu of charge = M1/2L3/2T—1
- Q=xC where x is dimensionless quantity
So F= =1 dyne = 10-5N
Taking x= 1/3 9
After solving we get 1/4
The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus, there must be large electric fields between the protons and electrons. Why then is the electrostatic field inside a conductor zero?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- In any neutral atom, the number of electrons and protons are equal, and the protons and electrons are bound into an atom with distinct and independent existence. Electrostatic fields are caused by the presence of excess charges. But there can be no excess charge of an isolated conductor. So, the electrostatic fields inside a conductor is zero
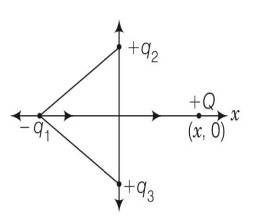
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the +x-direction on a charge q1, fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1
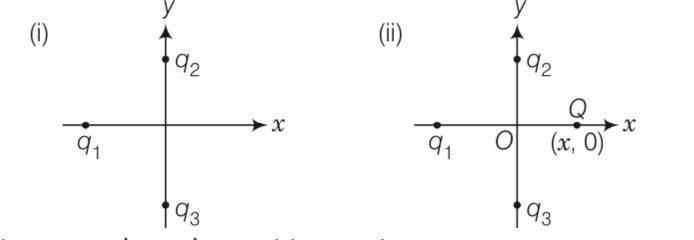
(b) Shall decrease along the positive x-axis
(c) Shall point along the negative x-axis
(d) Shall increase but the direction changes because of the intersection of Q with q2 and q3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (a)
Explanation-The force between (q1, q2) and (q1, q3) is must be attractive to net forces act in positive direction of x . so q1 must be negative. But if we place a positive charge Q in positive direction of x then it must be attractive towards along x-axis. So it will be attractive towards positive x axis.
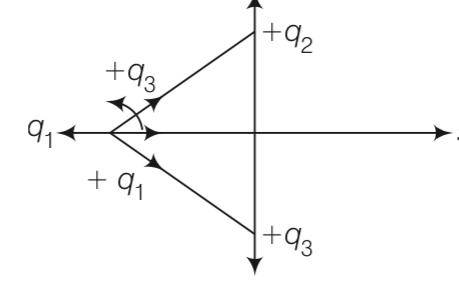
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α &β ) , each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d . The third plate is released and collides with the plate β . Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β &γ . (a) Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision. (b) Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
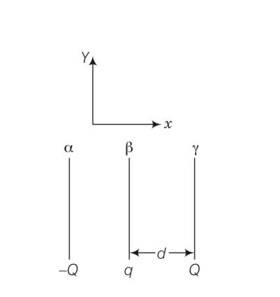
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- net electric field at plate γ due to two other plate
From plate 1 ,E1=
From plate 2 ,E2=
Total electric field E= E1 + E2 = to the left , if Q>q
electric field at o due to plate α =
electric field at o due to plate β =
electric field at o due to plate γ =
as the electric field at o is zero therefore
As there is no loss of charge on collision
Q+q=
On solving these
q1= (Q+q/2)= charge on plate β
q2= (q/2)= charge on plate γ
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Electric flux through a dipole is always zero, because the positive and negative charges cancel each other out
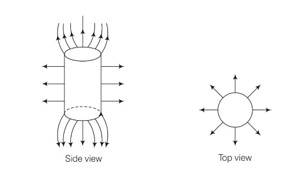
Sketch the electric field lines for a uniformly charged hollow cylinder shown in figure
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- No field inside a hollow body because if we give charge to a hollow body whole charge is distributed outside its surface. This phenomenon is called electrostatic shielding which is used to protect things from electric field or electric shock.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 1 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas related to Electric Charges and Fields:
Coulomb’s Law (Force Between Two Point Charges)
Electric Field Due to a Point Charge
Electric Field Due to an Electric Dipole (Axial Line)
Electric Field Due to an Electric Dipole (Equatorial Line)
Torque on an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field
Electric Flux (Φ)
Gauss’s Law
For topic-wise revision of Class 12 Physics, read NCERT Class 12 Physics Notes for CBSE.
JEE Mains paper
JEE Mains paper
physics ncert exemplar solution class 12th chapter one Exam
