Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Chapter Six Electromagnetic Induction offers you solutions for all the questions of the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics book. They include all kinds of questions from Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) to Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, and Very Short Answer Type Questions, covering all key topics of Chapter 6 Class 12 Physics. Practicing these questions will not only help you deepen your understanding of the key topics but will also improve your problem-solving skills.
Class 12 science students can download the Magnetic Induction Class 12 PDF from here and read it offline from anywhere. The PDF includes the well-structured solutions given in a step-by-step methodology. This helps students to understand in each step how and why formulas or concepts have been used, and it gives them a clear understanding of how to solve complex problems. The Exemplar practice also adds to the preparation of entrance exams like JEE and NEET.
Students must also refer to the NCERT solutions given on the Shiksha's page. Moreover, for a better understanding of Chapter Six, refer to Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 6 NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Six Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Objective Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Very Short Answer Type Questions
- 26th June 2022
- JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
The PDF includes all questions from Chapter 6 of the exemplar book. Students can read this from anywhere and at any time. There is no need for an internet connection, hence one can even read in areas with poor connectivity, during travel, and during power cuts. It offers you organized and structured content containing the MCQs, short/long answer questions, and solutions focusing on topics like Eddy Currents, Lenz’s Law, and Faraday’s Laws. The PDF can also be used for last-minute preparation just before the exams. One can also print the PDF and practice on paper.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 6 NCERT Exemplar
Following are the important formulas of Class 12 Physics Chapter 6:
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Magnetic Flux
Induced EMF in a Rotating Coil (AC Generator)
Motional EMF
Self-Induced EMF
Mutual Inductance EMF
Energy Stored in an Inductor
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Short Answer Type Questions
See below the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
There are two coils A and B separated by some distance. If a current of 2 A flows through A, a magnetic flux of 10-2Wb passes through B (no current through B). If no current passes through A and a current of 1A passes through B, what is the flux through A ?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Mutual inductance of coil A with respect to B
M21=N2 2/I1 = = 5mH
N1 1= M12I2= 5mH (1A)= 5mWb
A magnetic field in a certain region is given by B = Bocos(ωt) k and a coil of radius a with resistance R is placed in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin in the magnetic field. Find the magnitude and the direction of the current at (a, 0, 0) at t = π/2ω, t = π/ω and t = 3π/2ω
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
But according to faraday’s law e= Bo
So the current will be I=B0
For t=
I= along j
Sinwt= sin(w ) = sin =1
T= , I=
Sinwt=sinw = sin
T=
I=
So it become sin =-1
Consider a closed loop C in a magnetic field (figure). The flux passing through the loop is defined by choosing a surface whose edge coincides with the loop and using the formula ? = B1dA1, B2dA2…. Now, if we choose two different surfaces S1 and S2 having C as their edge, would we get the same answer for flux. Justify your answer.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The magnetic flux linked with the surface can considered as the number of magnetic field lines passing through the surface. So, let dφ = BA represents magnetic lines in an area to. By the concept of continuity of lines cannot end or start in space, therefore the number of lines passing through surface S1 must be the same as the number of lines passing through the surface S2.Therefore, in both the cases we gets the same answer for flux.

Find the current in the wire for the configuration shown in figure. Wire PQ has negligible resistance. B, the magnetic field is coming out of the paper. θ is a fixed angle made by PQ travelling smoothly over two conducting parallel wires separated by a distance d
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The motional emf along PQ = length PQ × field along PQ
= length PQ × vBsin
= vB sin = vBd
So emf make the flow of current in the circuit with resistance R
I= dvB/R

A (current versus time) graph of the current passing through a solenoid is shown in figure. For which time is the back electromotive force (u) a maximum. If the back emf at t = 3 s is e, find the back emf at t = 7 s, 15 s and 40 s. OA, AB and BC are straight line segments.

This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The back emf in solenoid force in solenoid is U a maximum rate of change of current . so maximum back emf will be obtained between 5s Since the back emf at t = 3s also the rate of change of current at t= 3s, s= slope of OA from t=0s to t= 5s=1/5 A/sec So we have if u= L1/5 (for t= 3s, dI/dt=1/5) (L is a constant). Applying e=-LdI/dt For 5s At t= 7s, u1=-3e For 10s For t>30s, u2=0 Thus back emf at t=7s,15s and 40s are -3e, e/2 and 0 respectively.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Six Long Answer Type Questions
These are the questions:
Commonly asked questions
A magnetic field B = B0sin (ωt)k covers a large region where a wire AB slides smoothly over two parallel conductors separated by a distance d (figure). The wires are in the x-y plane. The wire AB (of length d) has resistance R and the parallel wires have negligible resistance. If AB is moving with velocity v, what is the current in the circuit. What is the force needed to keep the wire moving at constant velocity?

This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let us assume that parallel wires at are y=0 i.e along x-axis and y=d.at t=0, AB has x=0 i.e along y-axis and moves with a velocity v
Motional emf across AB is = (B0sinwt)vd (-j)
Emf due to change in field along OBAC = -B0wcoswt x (t)d
Total emf in the circuit = emf due to change in field (along OBAC)+ the motional emf across AB= - B0d {wx coswt+v sinwt}
Electric current in clockwise direction is given by = (wxcoswt+vsinwt)
The force acting on the conductor is given by F= iLbsin90=iLb
Substituting the values
F= (wx coswt+v sinwt) × d × B0sinwt
= (wx coswt+v sinwt)sinwt
A conducting wire XY of mass m and negligible resistance slides smoothly on two parallel conducting wires as shown in figure. The closed circuit has a resistance R due to AC. AB and CD are perfect conductors. There is a magnetic field B = B(t) k

(i) Write down an equation for the acceleration of the wire XY
(ii) If B is independent of time, obtain v(t), assuming v(0) = u0
(iii) For (ii), show that the decrease in kinetic energy of XY equals the heat lost in
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let us assume that the parallel wires at are y= 0, i.e., along x-axis and y= l. At t= 0, XY has x = 0 i.e., along y-axis.
(i) Let the wire be at x x = (t) at time t.
The magnetic flux linked with the loop is given by
φ = B.A= Bacos0= BA
magnetic flux = B(t)(lx(t))
total emf = emf due to change in field along XYAC+ the motional emf across XY
E= - = - lx(t)- B(t)lv(t)
Electric current in clockwise direction is I= E/r
So force is F= ilBsin90=ilB
Force = [- ]i
Applying newton 2nd law
m = -
(ii) =0
Substituting in eqn 1
+ =0
=o
V= Aexp )=0
(iii) p= I2R= exp(-2I2B2tlmR)
This proves decrease in kinetic energy.
ODBAC is fixed rectangular conductor of negligible resistance (CO is not connected) and OP is a conductor which rotates clockwise with an angular ve1locity omega Fig. The entire system is in a uniform magnetic field B whose direction in along the normal to the surface of the rectangular conductor ABDC. The conductor OP is in electric contact with ABDC. The rotating conductor has a resistance of per unit length. Find the current in the rotating conductor, as it rotates by 180
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
At t=o t=T/8= the rod will make contact with side BD.at any time 0
So magnetic flux through area ODQ is
=B

I=e/R
And R= so I=
Same result for other side too
Consider an infinitely long wire carrying a current I(t), with dI/dt=λ =constant. Find the current produced in the rectangular loop of wire ABCD if its resistance is R (figure).

This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
B= (ouside the paper)
Flux= = in
Induced emf= e/R=I
Induced current = = = in
A rectangular loop of wire ABCD is kept close to an infinitely long wire carrying a current I(t) = I0(I – t/T) for 0 ≤ t ≤ T and I(0) = 0 for t >T(figure). Find the total charge passing through a given point in the loop, in time T. The resistance of the loop is R.

This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
applying ohm’s law
I=E/R=d
I= dQ/dt or dQ/dt= d
Q (t1)-Q (t2)= [ t1- t2]
t1= L1 t1
= I1in [ ]
A magnetic field B is confined to a region r ≤ a and points out of the paper (the z-axis), r = 0 being the centre of the circular region. A charged ring (charge = Q) of radius b, b> a and mass m lies in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The ring is free to rotate and is at rest. The magnetic field is brought to zero in time Δt. Find the angular velocity ω of the ring after the field vanishes.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since, the magnetic field is brought to zero in time? t, the magnetic flux linked with the ring also reduces from maximum to zero. This, in turn, induces an emf in ring by the
phenomenon of EMI. The induces emf causes the electric field E generation around the
ring.
The induced emf= electric field E (2 πb) (Because V =E d ) . (i)
By Faraday'slaw of EMI
The induced emf= rate of change of magnetic flux
=rate of change of magnetic field × area= ……. (ii)
From (i) and (ii)
2 =emf=
Since, the charged ring experienced a electric force= QE
This force try to rotate the coil, and the torque is given by
Torque = b (Force)
= Qeb= Q { }b
= Q
dL= torque (dt)= Q
as intital momentum is zero
so final momentum is = mb2w= QBa2/2
w= QBa2/2mb2
A rod of mass m and resistance R slides smoothly over two parallel perfectly conducting wires kept sloping at an angle θ with respect to the horizontal (Fig). The circuit is closed through a perfect conductor at the top. There is a constant magnetic field B along the vertical direction. If the rod is initially at rest, find the velocity of the rod as a function of time.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The component of magnetic field perpendicular the plane = Bcosθ
But when there is a motional emf then it is e = Blv=vBcosθd
And current Is I= but when discuss about force F= llB
And component of force which only act is fcosθ
So force is IBd(cosθ) = where v=dx/dt
Also component of weight is mg cosθ
So by applying newton second law of motion
m
On solving this equation we get
V=
Find the current in the sliding rod AB (resistance = R) for the arrangement shown in figure. B is constant and is out of the paper. Parallel wires have no resistance, v is constant. Switch S is closed at time t = 0.

This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The conductor of length d moves with speed v, perpendicular to magnetic field B as shown in figure. This produces motional emf across two ends of rod, which is given by= vB d.
Since, switch S is closed at time t= 0. capacitor is charged by this potential difference. Let
Q ( t) is charge on the capacitor and current flows from A to B.
Now, the induced current I= -
On rearranging = + dQ/dt =
On solving differential equation we get I= e-t/RC
Find the current in the sliding cod AB (resistance = R) for the arrangement shown in figure. B is constant and is out of the paper. Parallel wires have no resistance, v is constant. Switch S is closed at time t = 0.

This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The conductor of length d moves with speed v, perpendicular to magnetic field B as shown in figure. This produces motional emf across two ends of rod, which is given by= vBd.
Since, switch S is closed at time t= 0. current start growing in inductor by the potential
Difference due to motional emf.
Applying Kirchhoff’s voltage rule, we have
-L +vBd=IR
On solving differential equation we get I= + Ae-Rt/2
At t=0 I=0
A= -vBd/R
I= (1-e-Rt/L)
A metallic ring of mass m and radius l (ring being horizontal) is falling under gravity in a region having a magnetic- field. If z is the vertical direction, the z-component of magnetic field is Bz=B0(1+ z). If R is the resistance of the ring and if the ring falls with a velocity v, find the energy lost in the resistance. If the ring has reached a constant velocity, use the conservation of energy to determine v in terms of m, B, and acceleration due to gravity g.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
According to faraday’s law e= - and also ohm’s law V=IR
So by equating these two
We get Bo( )
I=
And energy lost/second = I2R=
As change in PE=mg but if we compare both energy then
Mgv= or v= ![]()
A long solenoid S has n turns per meter, with a radius of a. At the center of this coil, we place a smaller coil of N turns and radius b (where ). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil? Plot a graph showing the nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt2+c
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar

NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Objective Type Questions
Find below the questions with solutions:
Commonly asked questions
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by B=B0(2i+3j+4k)T, where Bo is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is
(a) 2 Bo L2
(b) 3 Bo L2 Wb
(c) 4 Bo L2 Wb
(d) B0L2 Wb
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) =B.A= B0 (2i+3j+4k)= 4B0L2wb
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0,0,0),B(L,0,0),C(L,L,O),D(0,L,0),E(0,L,L)and F(0,0,L). A magnetic field B =Bo(i+K)T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is

This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
And A= A1+A2= (L2k+L2i)
B= Bo (i+k)T
= Bo (i+k) (L2k+L2i)
= 2BoL2Wb
A cylindrical bar magnet is Rotated about its axis. A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then,
(a) A direct current flows in the ammeter A
(b) No current flows through the ammeter A
(c) An alternating sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A with a time period 2π/ω
(d) A time varying non-sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) When cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis, no change in flux linked with the circuit takes place, consequently no emf induces and hence, no current flows through the ammeter A.

There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counter clockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that
(a) There is a constant current in the clockwise direction in A
(b) There is a varying current in A
(c) There is no current in A
(d) There is a constant current in the counter clockwise direction in A

This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) When the A stops moving the current in B become zero, it is possible only if the current in A is constant. If the current in A would be variable, there must be an induced emf (current) in B even if the A stops moving.
Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counter-clockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is
(a) Constant current clockwise
(b) Varying current clockwise
(c) Varying current counter clockwise
(d) Constant current counter clockwise
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) When the current in B (at t= 0) is counter-clockwise and the coil A is considered above to it. The counterclockwise flow of the current in B is equivalent to north pole of magnet and magnetic field lines are emanating upward to coil A. When coil A start rotating at (t= 0), the current in A is constant along clockwise direction by Lenz's rule.
The self inductance L of a solenoid of length l and area of cross-section A, with a fixed number of turns N increases as
(a) l and A increase
(b) l decreases and A increases
(c) l increases and A decreases
(d) both l and A decrease
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) The self-inductance of a long solenoid of cross-sectional area A and length l, having n turns per unit length, filled the inside of the solenoid with a material of relative
permeability (e g. ., soft iron, which has a high value of relative permeability) is given by the relation L = n2A/l
A metal plate is getting heated. It can be because
(a) A direct current is passing through the plate
(b) It is placed in a time varying magnetic field
(c) It is placed in a space varying magnetic field, but does not vary with time
(d) A current (either direct or alternating) is passing through the plate
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, d) A metal plate is getting heated when a DC or AC current is passed through the plate, known as heating effect of current. Also, when metal plate is subjected to time varying magnetic field, the magnetic flux linked with the plate changes and eddy currents comes into existence which make the plate hot.
An emf is produced in a coil, which is not connected to an external voltage source. This can be due to
(a) The coil being in a time varying magnetic field
(b) The coil moving in a time varying magnetic field
(c) The coil moving in a constant magnetic field
(d) The coil is stationary in external spatially varying magnetic field, which does not change with time
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, c) Here, magnetic flux linked with the isolated coil change when the coil being in a time varying magnetic field, the coil moving in a constant magnetic field or in time varying magnetic field.
The mutual inductance M12of coil 1 with respect to coil 2
(a) Increases when they are brought nearer
(b) Depends on the current passing through the coils
(c) Increases when one of them is rotated about an axis
(d) Is the same as M21 of coil 2 with respect to coil 1
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, d) Mutual inductance of a coil increases when they came closer also the relation for the same will be given by
M21= n1n2 r12l= M12
M21= M12=M

A circular coil expands radially in a region of magnetic field and no electromotive force is produced in the coil. This can be because
(a) The magnetic field is constant
(b) The magnetic field is in the same plane as the circular coil and it may or may not vary
(c) The magnetic field has a perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) component whose magnitude is decreasing suitably
(d) There is a constant magnetic field in the perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) direction
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, d) When circular coil expands radially in a region of magnetic field such that the magnetic field is in the same plane as the circular coil or the magnetic field has a perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) component whose magnitude is decreasing suitably in such a way that the cross product of magnetic field and surface area of plane of coil remain constant at every instant.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction Very Short Answer Type Questions
Find below the VSA questions:
Commonly asked questions
Consider a magnet surrounded by a wire, with an on/off switch S (figure). If the switch is thrown from the off position (open circuit) to the on position (closed circuit), will a current flow in the circuit? Explain

This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the switch is thrown from the off position (open circuit) to the on position (closed circuit), then neither B, nor A nor the angle between B and A change. Thus, no change in magnetic flux linked with coil occur, hence no electromotive force is produced and consequently no current will flow in the circuit.
A wire in the form of a tightly wound solenoid is connected to a DC source, and carries a current. If the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil i.e., the wires are pulled apart which lead to the flux leak through the gaps.
According to Lenz's law, the emf produced must oppose this decrease, which can be done by an increase in current. So, the current will increase.
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the iron core is inserted in the current carrying solenoid, the magnetic field increase due to the magnetisation of iron core and consequently the flux increases.
According to Lenz's law, the emf produced must oppose this increase in flux, which can be done by making decrease in current. So, the current will decrease.
Consider a metal ring kept on the top of a fixed solenoid (say on a cardboard) (figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain.

This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the current is switched on, magnetic flux is linked through the ring. Thus, increase in flux takes place. According to Lenz's law, this increase in flux will be opposed and it can happen if the ring moves away from the solenoid.
This happen because the flux increases will cause a counter clockwise current (as seen from the top in the ring in figure.) i.e., opposite direction to that in the solenoid. This makes the same sense of flow of current in the ring (when viewed from the bottom of the ring) and solenoid forming same magnetic pole in front of each other. Hence, they will repel each other and the ring will move upward.
Consider a metal ring kept (supported by a cardboard) on the top of a fixed solenoid carrying a current I (see figure of Question 14). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is switched off, what will happen to the ring?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the current is switched on, magnetic flux is linked through the ring. Thus, increase influx takes place. According to Lenz's law, this increase in flux will be opposed and it can happen if the ring moves away from the solenoid.
This happen because the flux increases will cause a counter clockwise current (as seen From the top in the ring in figure.) i.e., opposite direction to that in the solenoid. This makes the same sense of flow of current in the ring (when viewed from the bottom of the ring) and solenoid forming same magnetic pole in front of each other. Hence, they will repel each other and the ring will move upward.
Consider a metallic pipe with ah inner radius of 1 cm. If a cylindrical bar magnet of radius 0.8 cm is dropped through the pipe, it takes more time to come down than it takes for a similar un-magnetised cylindrical iron bar dropped through the metallic pipe. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When cylindrical bar magnet of radius 0.8 cm is dropped through the metallic pipe with an inner radius of 1 cm, flux linked with the cylinder changes and consequently eddy currents are produced in the metallic pipe. According to Lenz's law, these currents will oppose the (cause) motion of the magnet.
Therefore, magnet's downward acceleration will be less than the acceleration due to gravity g. On the other hand, an non magnetised iron bar will not produce eddy currents and will fall with an acceleration due to gravity g.
Thus, the magnet will take more time to come down than it takes for a similar unmagnetized Cylindrical iron bar dropped through the metallic pipe.
26th June 2022
26th June 2022
Commonly asked questions
An expression for a dimensionless quantity P is given by where α and β are constants, x is distance; k is Boltzmann constant and t is the temperature. Then the dimensions of will be
= Dimensionless
dimensionless
= dimensionless of
= MLT2
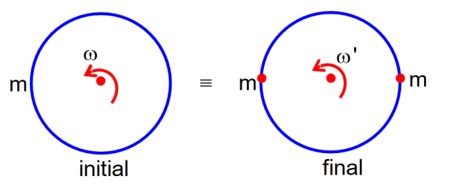
A thin circular ring of mass M and radius R is rotating with a constant angular velocity 2 rads-1 in a horizontal plane about an axis vertical to its plane and passing through the centre of the ring. If two objects each of mass m be attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of ring, the will then rotate with an angular velocity (in rads-1).
By conservation of Angular momentum
Li = Lf
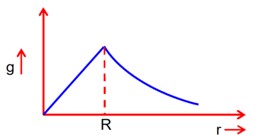
The variation of acceleration due to gravity (g) with distance (r) from the centre of the earth is correctly represented by: (Given R = radius of earth)
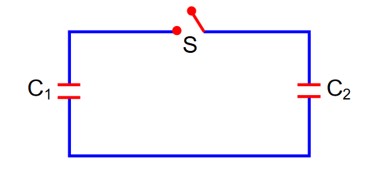
Two capacitors having C1 and C2 respectively are connected as shown in figure. Initially, capacitor C1 is charged to a potential difference V volt by a battery. The battery is then removed and the charged capacitor C1 is not connected to uncharged capacitor C2 by closing the switch S. The amount of charge on the capacitor C2, after equilibrium, is
After switch ‘S’ is closed
- (1)
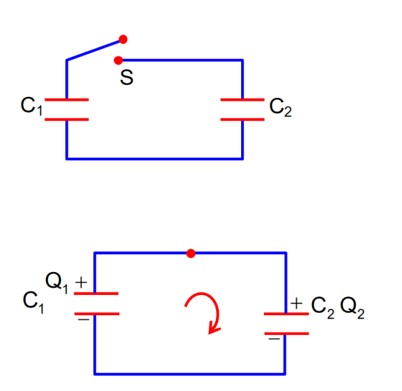
Using KVL
- (2)
from (1) & (2)
Given below two statements : One is labeled as Assertion (A) and other is labeled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Non-polar materials do not have any permanent dipole moment.
Reason (R) : When a non-polar material is placed in an electric field, the centre of the positive charge distribution of it’s individual atom or molecule coincides with the centre of the negativne charge distribution .
In the light of above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
In non-polar molecules, centre of +ve charge coincides with centre of –ve charge, Hence, net dipole moment becomes zero.
When non-polar material is placed in external field, centre of charge does not coincide, hence give non-zero moment.
If Electric field intensity of a uniform plane electro magnetic wave is given as
Then, magnetic intensity ‘H’ of this wave in Am-1 will be:
[Given : Speed of light in vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1, Permeability of vacuum ]
Since
for option D
An electron with speed and a photon with speed c have the same de-Broglie wavelength. If the kinetic energy and momentum of electron are Ee and pe and that of photon are Eph and pph respectively. Which of the following is correct?
- (1)
- (2)
A/C to question
- (3)
- (4)
= mc c
q = PPh c- (5)
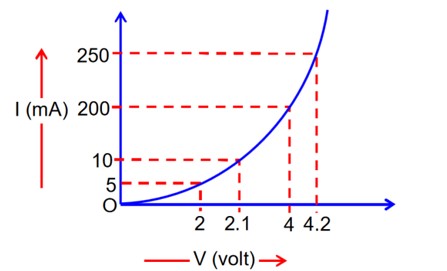
The I-V characteristics of p-n junction diode in forward bias is shown in the figure. The ration of dynamic resistance, corresponding to forward bias voltage of 2 V and 4 V respectively, is
Dynamic Resistance at 2v
=
Dynamic Resistance at 4 v
=
A ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from the height of 10m. The height, at which the magnitude of velocity becomes equal to the magnitude of acceleration due to gravity, is __________m.
[Use g = 10m/s2]
Let ‘h’ be the height at which velocity becomes equal to magnitude of Acceleration
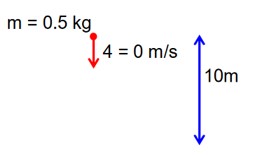
v = g = 10
v = u + at
10 = 0 + 10t
t = 1 sec
= 5m
A 20 mH coil carrying constant current is connected to a battery of 20 V through a switch. Now after switch is opened current becomes zero in 100 The average e.m.f. induced in the coil is__________V.
Decay of current in Inductor is given by,
At t = 100
i = 0
i.e. i = i0 -(1)
e.m.f induced
=
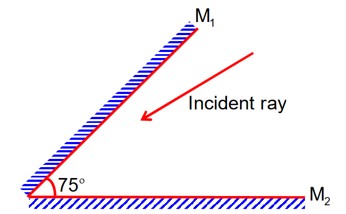
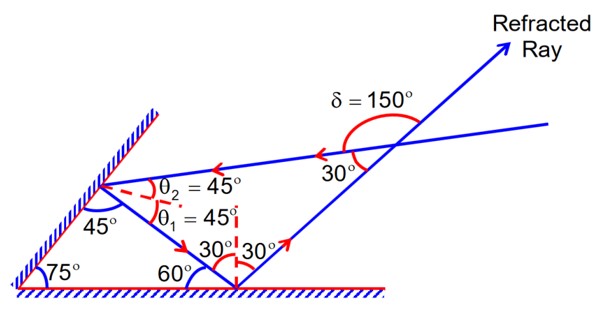
A light ray is incident, at an incident angle q1, on the system of two plane mirrors M1 and M2 having an inclination angle 75° between them (as shown in figure). After reflecting from mirror M1 it gets reflected back by the mirror M2 with an angle of reflection 30°. The total deviation of the ray will be ___________ degree.
= 360 – 2 × 75° = 210°
Total deviation =
In a vernier calipers, each cm on the main scale is divided into 20 equal parts. If tenth vernier scale division coincides with nineth main scale division. Then the value of vernier constant will be__________× 10-2mm.
Let ‘x’ he the value of one division of main scale
Let y be value of one division on venire scale given
10 y = 9 x
Least count =
= 0.005 cm
= 5 × 10-2 mm
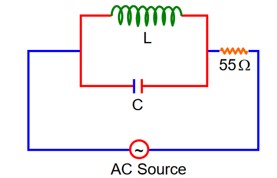
A 110 V, 50Hz, AC source is connected in the circuit (as shown in figure). The current through the resistance at resonance in the circuit, will be__________A.
At Resonance
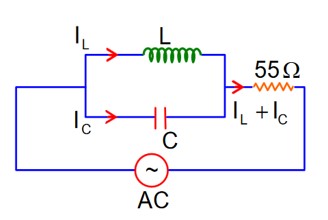
XL = XC
then lL = lC
Now phasor diagram
for L & C
So, Net current = zero
Therefore current through R circuit at resonance will be zero
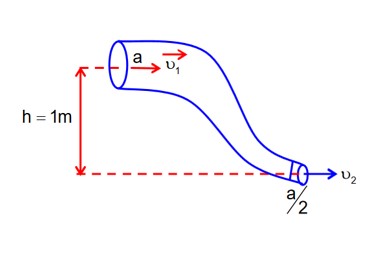
An ideal fluid of density 800kgm-3, flows smoothly through a bent pipe (as shown in figure) that tapers in cross-sectional area from a to The pressure difference between the wide and narrow sections of pipe is 4100 Pa. At wider section, the velocity of fluid is for x =________. (Given g = 10 ms-2)
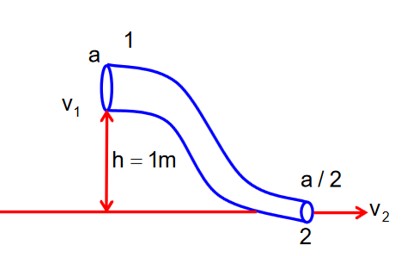
P1 – P2 = 4100 Pa
Bernoulli’s question b/w (1) & (2)
-(1)
Equation of continuity
A1v1 = A2v2
v2 = 2v1-(2)
from (1) & (2)
x = 363
A person is standing in an elevator. In which situation, he experiences weight loss?
F.B.D of person w.r.t. elevator
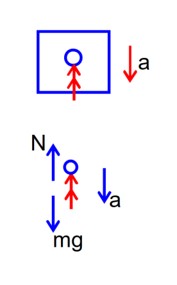
mg – N = ma
N = mg – ma
N decreases so, person experiences weight loss.
An object is thrown vertically upwards. At its maximum height, which of the following quantity becomes zero?
At maximum height velocity (v) = 0
So, momentum = mv = m × 0 = 0
The efficiency of a Carnot’s engine, working between stem point and ice point, will be
Steam point (T1) = 100°C = 273 + 100 = 373 K
Ice point (T2) = 0°C = 273 K
Time period of a simple pendulum in a stationary lift is ‘T’. If the lift accelerated with vertically upwards then the time period will be:
(Where g = acceleration due to gravity)
A thermally insulated vessel contains an ideal gas of molecular mass M and ratio of specific heats 1.4. Vessel is moving with speed and is suddenly brought to rest. Assuming no heat is lost to the surrounding and vessel temperature of the gas increases by:
(R = universal gas constant)
The magnetic flux through a coil perpendicular to its plane is varying according to the relation Weber. If the resistance of the coil is 5 ohm, then the induced current through the coil at t = 2s will be
at t = 2 sec, V = (15 × 4 + 8 × 2 + 2)
= 78 V
An aluminium wire is stretched to make its length, 0.4% larger. The percentage change in resistance is
Volume = constant
= 0.4 (0.4)
= 0.8 %
A proton and an alpha particle of the same velocity enter in a uniform magnetic field which is acting perpendicular to their direction of motion. The ratio of the radii of the circular paths described by the alpha particle and proton is
In free space, an electromagnetic wave of 3 GHz frequency strikes over the edge of an object of size where is the wavelength of the wave in free space. The phenomenon, which happens there will be
If size of object is very small as compare to wave length of EM wave in free space then, scattering will happen.
Choose the correct statement for amplitude modulation
In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the career signal is varied in according with the modulating signal.
A fighter jet is flying horizontally at a certain with a speed of 200ms-1. When it passes directly overhead ad anti-aircraft gun, a bullet is fired from the gun, at an angle q with the horizontal, to hit the jet. If the bullet speed is 400m/s, the value of q will be _____________.
B fighter jet
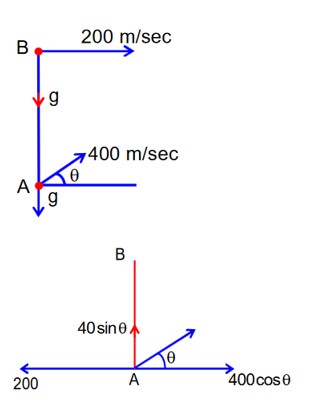
A anti-Air craft gun
Draw velocity diagram of A w.r.t. B
If A hits B
Then Relative velocity perpendicular to the line joining A to B will be zero.
That means 400 cos = 200
The elongation of a wire on the surface of the earth is 10-4m. The same wire of same dimensions is elongated by 6 × 10-5 m on another planet. The acceleration due to gravity on the planet will be__________ms-2. (Take acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth = 10 ms-2)
(change in length)
6 m/sec2
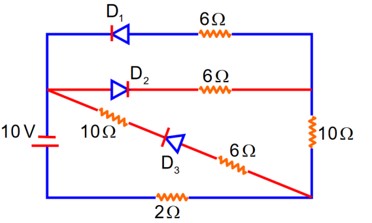
As per the given circuit, the value of current through the battery will be__________A.
Forward biased offer zero Resistance
D2} Reversed biased offers Infinite Resistance
JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
Commonly asked questions
Two small spheres each of mass 10mg are suspended from a point by threads 0.5m long. They are equally charged and repel each other to a distance of 0.20m. The charge on each of the sphere is The value of ‘a’ will be…….. [Given g = 10 ms-2]
Using the above equation find the value of ‘q’
Two particles having masses 4g and 16g respectively are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momentum is n : 2. The value of n will be………..
n = 1
A reversible heat engine converts one-fourth of the heat input into work. When the temperature of the sink is reduced by 52K, its efficiency is doubled. The temperature is Kelvin of the source will be…………
Efficiency in the Carnot engine is defined as :
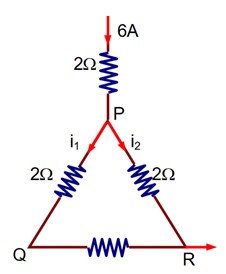
A current of 6 A enters one corner P of an equilateral triangle PQR having 3 wires of resistance each and leaves by the corner R. The currents i1 in ampere is………
i2 = 2i1
i1 + i2 = 6
i1 = 2A.
The percentage increase in the speed of transverse waves produced in a stretched string if the tension is increased by 4%, will be………….%.
new v’ =
% change =
= 2%
The wavelength of an X-ray beam is The mass of a fictitious particle having the same energy as that of the X-ray photons is The value of x is………. (h = Planck’s constant)
Energy corresponding to a particle is mc2
=
The initial velocity vi required to project a body vertically upward from the surface of the earth to reach a height of 10R, where R is the radius of the earth, may be described in terms of escape velocity ve such that The value of x will be………
Using conservation of energy :
Escape velocity is defined as
If the angle between The value of ‘θ’ will be………
If angle between them is 180° then
Two identical conducting spheres with negligible volume have 2.1 nC and 0.1 nC charges, respectively. They are brought into contact and then separated by a distance of 0.5m. The electrostatic force acting between the spheres is …………….× 10-9N.
After contact, charges an each sphere will be
The peak electric field produced by the radiation coming from the 8W bulb at a distance of 10m is The efficiency of the bulb is 10% and it is a point source. The value of x is……..
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Six Exam