Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Twelve Atoms includes solutions to all questions of the NCERT Exemplar Book. There are various types of questions, including Multiple-Choice Questions, Short Questions, Very Short Questions, and Long Questions. All these questions cover all key concepts of Chapter Twelve of Class 12 Physics. Solving these questions deepens your understanding of the concepts and formulas and also improves your problem-solving skills, which in turn boosts your exam confidence.
Students will also find the NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Physics Atoms PDF on Shiksha's page. They must download it to read from anywhere, be it during travel or from a remote distance. You need not have an internet connection to access this PDF. It has well-structured solutions created by Shiksha's experts. Practicing from the PDF will prepare you well for your CBSE Board examination as well as for entrance exams. The solutions are reliable and accurate, hence the exemplar offers a great preparation tool for various examinations.
For a better understanding of Chapter 12 of Class 12 Physics, students can also read Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Atoms NCERT Solutions. They should also read the NCERT solutions page given on the Shiksha’s website.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Atoms
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 12 NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12th Chapter Twelve Atoms Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12th Chapter Twelve Atoms Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Twelve Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Atoms Objective Type Questions
- Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Physics Exemplar Chapter 12
- JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, physics, second shift
- JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, physics, First shift
- 25th June 2022 first shift
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Atoms
NCERT Exemplar Physics Class 12 PDF offers a valuable study tool to students that they can download and study from anywhere. The PDF includes solutions for MCQs, VSA, SA, and LA Questions of the NCERT Exemplar book. The PDF follows the NCERT curriculum, hence it prepares you well for the board exam and entrance tests like NEET and JEE. The exemplar goes beyond the textbook and helps students grasp complex ideas like energy levels, Bohr’s theory, Rutherford’s model, and spectral series. PDF includes the application-based and HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions, which are mostly asked in board papers and entrance exams. You can also take printouts if you want to practice on paper, make notes, and solve problems by hand.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 12 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of Chapter 12 Atoms:
Energy of Electron in the nth Orbit
Radius of the nth Orbit
Velocity of Electron in the nth Orbit
Bohr's Formula for Wavelength
Energy of Photon
Centripetal Force Balance
Quantization of Angular Momentum
NCERT Exemplar Class 12th Chapter Twelve Atoms Short Answer Type Questions
See Below The Short-Answer Type Questions
The short-answer type questions need answers slightly longer than the VSA. It requires explanations, derivations and calculations, but not in a lengthy way as in the case of Long Answer type questions. It assesses students' ability to apply basic reasoning and formulas. The SA common topics include electron orbit calculations, energy transitions in hydrogen atoms, and the significance of quantum numbers in Bohr's model.
| 1. The mass of a H-atom is less than the sum of the masses of a proton and electron. Why is this? |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- the reason behind this is the binding energy or we can say the mass defect. BE= mass defect (931MeV ). So whatever energy is liberated in fission and fusion changes the mass slightly. That's why there is a defect in mass |
| 2. Imagine removing one electron from He4 and He3. Their energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close. Explain why. |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- On removing one electron from He4 and He3, the energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close as both the nuclei are very heavy as compared to electron mass.Also after removing one electron from He4 and He3 atoms contain one electron and are hydrogen like atoms. |
| 3. When an electron falls from a higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why cannot it be emitted as other forms of energy? . |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- The transition of an electron from a higher energy to a lower energy level can appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation because electrons interact only electromagnetically. |
| 4. Would the Bohr formula for the H-atom remain unchanged if proton had a charge (+ 4/3)e and electron a charge (-3/4)e, where e = 1.6 x 10-19 Give reasons for your answer. |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- If proton had a charge (+4/3)e and electron a charge (-3/4)e, then the Bohr formula for the H-atom remain same, since the Bohr formula involves only the product of the charges which remain constant for given values of charges. |
| 5. Consider two different hydrogen atoms. The electron in each atom is in an excited state. Is it possible for the electrons to have different energies but the same orbital angular momentum according to the Bohr model? |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- According to Bohr model electrons having different energies belong to different levels having different values of n. So, their angular momenta will be different, as L=nh/2 n |
| 6. Positronium is just like a H-atom with the proton replaced by the positively charged anti-particle of the electron (called the positron which is as massive as the electron). What would be the ground state energy of positronium? |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- The total energy of the electron in the stationary states of the hydrogen atom is given by En = - where signs are as usual and the m that occurs in the Bohr formula is the reduced mass of electron and proton. Also, the total energy of the electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is−13.6 eV. For H-atom reduced mass me . Whereas for positronium, the reduced mass is m=me/2 Hence, the total energy of the electron in the ground state of the positronium atom is -13.6/2=-6.8eV |
| 7. Assume that there is no repulsive force between the electrons in an atom but the force between positive and negative charges is given by Coulomb’s law as usual. Under such circumstances, calculate the ground state energy of a He-atom. |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- For a He -nucleus with charge 2e and electrons of charge− e, the energy level in ground state is E=-13.6Z2/n2= -54.4eV Thus, the ground state will have two electrons each of energy E and the total ground state energy would be -(4×13.6)eV = -54.4eV. |
| 8. Using Bohr model, calculate the electric current created by the electron when the H-atom is in the ground state. |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- The electron in Hydrogen atom in ground state revolves on a circular path whose radius is equal to the Bohr radius (an) . Let the velocity of electron is v ∴ Number of revolutions per unit time= The electric current is given by i=q/t , if q charge flows in time t. Here, q=e The electric current is given by i= |
| 9. Show that the first few frequencies of light that is emitted when electrons fall to nth level from levels higher than n, are approximate harmonics (i.e., in the ratio 1:2:3 …) when n >> 1. |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- The frequency of any line in a series in the spectrum of hydrogen like atoms corresponding to the transition of electrons from (n+ p) level to nth level can be expressed as a difference of two terms; From the formula we can say that v=cRZ2{ } Where p =1,2,3,… R os rydberg constant When p<
V=cRZ2{ } V=cRZ2{ By binomial theorem V=cRZ2{ Thus, the first few frequencies of light that is emitted when electrons fall to the nth level from levels higher than n , are approximate harmonic (i.e., in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 …) when n >> 1 . |
| 10. What is the minimum energy that must be given to a H-atom in ground state so that it can emit an HґLine in Balmer series? If the angular momentum of the system is conserved, what would be the angular momentum of such Hґ photon? |
| This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- Hγ in Balmer series corresponds to transition n= 5 to n= 2. So, the electron in ground state i.e., from n= 1must first be placed in state n= 5. Energy required for the transition from n= 2 to n= 5 is given by E1-E5=13.6-0.54=13.06eV Since, angular momentum is conserved, angular momentum corresponding to Hg photon= change in angular momentum of electron so L5-L2=5h-2h= 3h = 3 =3.18 kgm2/s |
Commonly asked questions
Positronium is just like a H-atom with the proton replaced by the positively charged anti-particle of the electron (called the positron which is as massive as the electron). What would be the ground state energy of positronium?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The total energy of the electron in the stationary states of the hydrogen atom is given by En = -
where signs are as usual and the m that occurs in the Bohr formula is the reduced mass of
electron and proton. Also, the total energy of the electron in the ground state of the
hydrogen atom is−13.6 eV. For H-atom reduced mass me . Whereas for positronium, the
reduced mass is m=me/2
Hence, the total energy of the electron in the ground state of the positronium atom is
-13.6/2=-6.8eV
Assume that there is no repulsive force between the electrons in an atom but the force between positive and negative charges is given by Coulomb’s law as usual. Under such circumstances, calculate the ground state energy of a He-atom.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- For a He -nucleus with charge 2e and electrons of charge− e, the energy level in ground state is
E=-13.6Z2/n2= -54.4eV
Thus, the ground state will have two electrons each of energy E and the total ground state
energy would be - (4×13.6)eV = -54.4eV.
Using Bohr model, calculate the electric current created by the electron when the H-atom is in the ground state.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The electron in Hydrogen atom in ground state revolves on a circular path whose radius is equal to the Bohr radius (an) . Let the velocity of electron is v
∴ Number of revolutions per unit time=
The electric current is given by i=q/t, if q charge flows in time t. Here, q=e
The electric current is given by i=
Show that the first few frequencies of light that is emitted when electrons fall to nth level from levels higher than n, are approximate harmonics (i.e., in the ratio 1:2:3 …) when n >> 1.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The frequency of any line in a series in the spectrum of hydrogen like atoms corresponding to the transition of electrons from (n+ p) level to nth level can be expressed as a difference of two terms;
From the formula we can say that v=cRZ2 { }
Where p =1,2,3, … R os rydberg constant
When p<
V=cRZ2 { }
V=cRZ2 {
By binomial theorem
V=cRZ2 {
Thus, the first few frequencies of light that is emitted when electrons fall to the nth level
from levels higher than n, are approximate harmonic (i.e., in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 …) when
n >> 1 .
What is the minimum energy that must be given to a H-atom in ground state so that it can emit an H?Line in Balmer series? If the angular momentum of the system is conserved, what would be the angular momentum of such H? photon?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Hγ in Balmer series corresponds to transition n= 5 to n= 2. So, the electron in ground state i.e., from n= 1must first be placed in state n= 5.
Energy required for the transition from n= 2 to n= 5 is given by E1-E5=13.6-0.54=13.06eV
Since, angular momentum is conserved,
angular momentum corresponding to Hg photon= change in angular momentum of electron
so L5-L2=5h-2h= 3h = 3
=3.18 kgm2/s
NCERT Exemplar Class 12th Chapter Twelve Atoms Very Short Answer Type Questions
Following are VSA Questions
VSA questions are designed to test the basic understanding of the key atomic concepts and students' quick recall of these concepts. Typically, these are given in one or two sentences and sometimes also in one word or one formula. VSA focuses on naming laws or principles like Bohr’s quantization rule, definitions of atomic terms like ionization energy and energy levels, identifying features of atomic models like Rutherford vs. Bohr, and concept checks on formula usage such as frequency of emitted radiation.
Commonly asked questions
The mass of a H-atom is less than the sum of the masses of a proton and electron. Why is this?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the reason behind this is the binding energy or we can say the mass defect.
BE= mass defect (931MeV ). So whatever energy is liberated in fission and fusion changes the mass slighthly. That why there is a defect in mass
Imagine removing one electron from He4 and He3. Their energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close. Explain why.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- On removing one electron from He4 and He3, the energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close as both the nuclei are very heavy as compared to electron mass.Also after removing one electron from He4 and He3 atoms contain one electron and are hydrogen like atoms.
When an electron falls from a higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why cannot it be emitted as other forms of energy? .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The transition of an electron from a higher energy to a lower energy level can appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation because electrons interact only electromagnetically.
Would the Bohr formula for the H-atom remain unchanged if proton had a charge (+ 4/3)e and electron a charge (-3/4)e, where e = 1.6 x 10-19 Give reasons for your answer.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- If proton had a charge (+4/3)e and electron a charge (-3/4)e, then the Bohr formula for the H-atom remain same, since the Bohr formula involves only the product of the charges which remain constant for given values of charges.
Consider two different hydrogen atoms. The electron in each atom is in an excited state. Is it possible for the electrons to have different energies but the same orbital angular momentum according to the Bohr model?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- According to Bohr model electrons having different energies belong to different levels having different values of n. So, their angular momenta will be different, as
L=nh/2 n
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Twelve Long Answer Type Questions
See Below Long Answer Type Questions
The Long Answer Type Questions include in-depth conceptual or numerical problems. It may involve detailed reasoning, derivations, and multi-step solutions. LA may contain deriving expressions for explaining the hydrogen spectrum, radius, or energy of electron orbits, or critically analyzing the limitations of classical atomic models.
| 1. The first four spectral in the Lyman series of a H-atom are λ= 1218 Å, 1028 Å, 974.3 Å and 951.4 Å. If instead of Hydrogen, we consider deuterium, calculate the shift in the wavelength of these lines. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- as we know total energy in stationary orbit is En=- where sign have usual meaning. According to bohr third postulate h -
Where is the reduced mass Reduced mass for H=H=;me(1-me/M) D= D; me(1-me/2M) =me(1-me/2M)(1+me/2M) If for hydrogen deuterium, the wavelength = (1+ )-1= (1- ) so lines emitted are 1217.7A0,1027.7A0,974.04A0 |
| 2. Deutrium was discovered in 1931by Harold Urey by measuring the small change in wavelength for a particular transition in 1H and 2 This is because, the wavelength of transition depends to a certain extent on the nuclear mass. If nuclear motion is taken into account, then the electrons and nucleus revolve around their common centre of mass. Such a system is equivalent to a single particle with a reduced mass μ , revolving around the nucleus at a distance equal to the electron-nucleus separation. Here μ = meM / ( me + M ) where M is the nuclear mass and me is the electronic mass. Estimate the percentage difference in wavelength for the 1st line of the Lyman series in . 1H and 2H . (Mass of 1H nucleus is 1.6725 × 10-27kg , mass of 1H nucleus is 3.3374 × 10-27kg 3.3374 × 10-27 𝑘g , Mass of electron = 9.109 × 10-31 kg ). |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- total energy of electron E= The frequency hv= = = = = When me<
after solving we get 2.714 |
| 3. If a proton had a radius R and the charge was uniformly distributed, calculate using Bohr theory, the ground state energy of a H-atom when (i) R = 0.1 Å and (ii) R = 10 Å . |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- in this type of situation centripetal force is balanced by electrostatic force So mv2/r= -ke2/r2 According to bohr postuates Mvr = h when n=1 On solving n So after solving r= 0.51A0 So potential energy = -27.2eV , KE= mv2/2 = But if R If R>>r the electron moves inside the sphere with radius r’ Charge inside r’4=e So r’ = So r’4= 0.51A0R3 = 510(A0)4 |
| 4. In the Auger process, an atom maizes a transition to a lower state without emitting a photon. The excess energy is transferred to an outer electron which may be ejected by the atom (This is called an Auger electron). Assuming the nucleus to be massive, calculate the kinetic energy of an n = 4 Auger electron emitted by Chromium by absorbing the energy from a n – 2 to n = 1 transition. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- the energy of nth state En=-Z2R where R is constant and Z=24 The energy release ina transition from 2 to 1 The energy required to eject a n=4 electron is E4= Z2R1/16 So kinetic energy of auger electron is , KE= Z2R(3/4-1/16)=1/16Z2R = |
| 5. The inverse square law in electrostatics is F= for the force between an electron and proton . the (1/r) dependence of F can be understood in quantum theory as being due to fact the particles of light photon is massless. If photon had a mass mp. force would be modified to F= where and n= h/2 estimate the change in the ground state energy of H atom if mp were 10-6 times the mass of electron. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- mp= 10-6 Mpc2=10-6 = 0.8 Wavelength associated with both of them is same
U(r)=- Mvr=h V=h/mr Mv2/r=( ) ( )
13.6 |
| 6. The Bohr model for the H-atom relies on the Coulomb ’s law of electrostatics. Coulomb’s law has not directly been verified for very F= r>R0 =
(
r
Calculate in such vase the ground state energy of a H atom , if E= 0.1 R0= 1A0 |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Explanation- when r
Let F= Where = ( Let p= Electrostatic force is balanced by centripetal force Mv2/r or v2= |
Commonly asked questions
The Bohr model for the H-atom relies on the Coulomb ’s law of electrostatics. Coulomb’s law has not directly been verified for very
short distances of the order of angstroms. Supposing Coulomb’s law between two opposite charge +q1, – q2modified to
F= r>R0
= ( r
Calculate in such vase the ground state energy of a H atom , if E= 0.1 R0= 1A0
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- when r
Let
F=
Where = (
Let p=
Electrostatic force is balanced by centripetal force
Mv2/r or v2=
The first four spectral in the Lyman series of a H-atom are λ= 1218 Å, 1028 Å, 974.3 Å and 951.4 Å. If instead of Hydrogen, we consider deuterium, calculate the shift in the wavelength of these lines.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as we know total energy in stationary orbit is
En=- where sign have usual meaning.
According to bohr third postulate h
-
Where is the reduced mass
Reduced mass for H=H=;me(1-me/M)
D= D; me(1-me/2M)
=me(1-me/2M)(1+me/2M)
If for hydrogen deuterium, the wavelength
= (1+ )-1= (1- )
so lines emitted are 1217.7A0,1027.7A0,974.04A0
Deutrium was discovered in 1931by Harold Urey by measuring the small change in wavelength for a particular transition in 1H and 2 This is because, the wavelength of transition depends to a certain extent on the nuclear mass. If nuclear motion is taken into account, then the electrons and nucleus revolve around their common centre of mass. Such a system is equivalent to a single particle with a reduced mass μ , revolving around the nucleus at a distance equal to the electron-nucleus separation. Here μ = meM / ( me + M ) where M is the nuclear mass and me is the electronic mass. Estimate the percentage difference in wavelength for the 1st line of the Lyman series in . 1H and 2H . (Mass of 1H nucleus is 1.6725 × 10-27kg , mass of 1H nucleus is 3.3374 × 10-27kg 3.3374 × 10-27 ?g , Mass of electron = 9.109 × 10-31 kg ).
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- total energy of electron
E=
The frequency hv=
=
= =
=
When me<
after solving we get 2.714
If a proton had a radius R and the charge was uniformly distributed, calculate using Bohr theory, the ground state energy of a H-atom when (i) R = 0.1 Å and (ii) R = 10 Å .
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- in this type of situation centripetal force is balanced by electrostatic force
So mv2/r= -ke2/r2
According to bohr postuates
Mvr = h when n=1
On solving n
So after solving r= 0.51A0
So potential energy = -27.2eV , KE= mv2/2
=
But if R
If R>>r the electron moves inside the sphere with radius r’
Charge inside r’4=e
So r’ =
So r’4= 0.51A0R3
= 510(A0)4
In the Auger process, an atom maizes a transition to a lower state without emitting a photon. The excess energy is transferred to an outer electron which may be ejected by the atom (This is called an Auger electron). Assuming the nucleus to be massive, calculate the kinetic energy of an n = 4 Auger electron emitted by Chromium by absorbing the energy from a n – 2 to n = 1 transition.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the energy of nth state En=-Z2R where R is constant and Z=24
The energy release ina transition from 2 to 1
The energy required to eject a n=4 electron is E4= Z2R1/16
So kinetic energy of auger electron is, KE= Z2R (3/4-1/16)=1/16Z2R
=
The inverse square law in electrostatics is F= for the force between an electron and proton . the (1/r) dependence of F can be understood in quantum theory as being due to fact the particles of light photon is massless. If photon had a mass mp. force would be modified to F= where and n= h/2 estimate the change in the ground state energy of H atom if mp were 10-6 times the mass of electron.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- mp= 10-6
Mpc2=10-6
= 0.8
Wavelength associated with both of them is same
U(r)=-
Mvr=h
V=h/mr
Mv2/r=( ) ( )
13.6
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Atoms Objective Type Questions
Following Are Multiple-Choice Questions
The objective-type questions include true/false, multiple-choice, and assertion-reason-type questions. Objective questions are important for entrance exam preparation. It is designed to test identification of correct principles, conceptual clarity, and the ability to apply theoretical models to practical situations quickly. The topics covered in the LA questions include energy levels, atomic spectra, and differences between various atomic models.
| 1. Taking the Bohr radius as a0= 53 pm, the radius of Li++ ion in its ground state, on the basis of Bohr’s model, will be about (b) 27 pm (c) 18 pm (d) 13 pm |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(c) Explanation- The atomic number of lithium is 3, therefore, the radius of Li+ + ion in its ground state, on the basis of Bohr’s model, will be about 1/3 times to that of Bohr radius. Therefore, the radius of lithium ion is near 53/3=18≈ pm. |
| 2. The binding energy of a H-atom, considering an electron moving around a fixed nuclei (proton), is B= . If one decides to work in a frame of reference where the electron is at rest,the proton would be moving around it.by similar arguments, the binding energy would be B= (M=proton mass) This last expression is not correct. (a) N would not be integral (b) Bohr-quantisation applies only two electron (c) The frame in which the electron is at rest is not inertial (d) The motion of the proton would not be in circular orbits, even approximately. |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer- c Explanation- when one decides to work in a frame of reference where the electron is at rest, the given expression is not true as it the non-inertial frame of reference. |
| 3. The simple Bohr model cannot be directly applied to calculate the energy levels of an atom with man electrons. This is because |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(a) Explanation-The simple Bohr model cannot be directly applied to calculate the energy levels of an atom with many electrons. This is because of the electrons not being subject to a central force. |
| 4. For the ground state, the electron in the H-atom has an angular .momentum = h, according to the simple Bohr model. Angular momentum is a vector and hence there will be infinitely many orbits with the vector pointing in all possible directions. In actuality, this is not true, |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer –(a) Explanation- In the simple Bohr model, only the magnitude of angular momentum is kept equal to some integral multiple of h/2 π, where, h is Planck’s constant and thus, the Bohr model gives incorrect values of angular momentum. |
| 5. 02 molecule consists of two oxygen atoms. In the molecule, nuclear force between the nuclei of the two atoms |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(a) Explantion- in the molecules, nuclear force between the nuclei of the two atoms is not important because nuclear forces are short-ranged. |
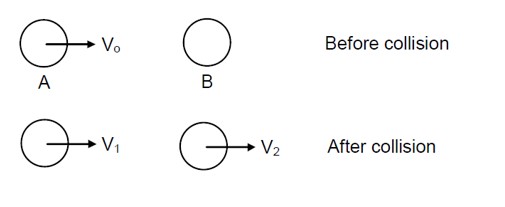
| 6. Two H atoms in the ground state collide inelastically. The maximum amount by which their combined kinetic energy is reduced is (b) 20.40eV (c) 13.6 eV |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(a) Explanation -Total energy in ground state collide elastically Is 213.6eV= 27.2eV When a electron excite from ground state to first excited state then Energy is =-13.6/22= 3.4eV+13.6(ground state energy) eV = 17.0 eV So net energy is 27.2-17 =10.2eV |
| 7. A set of atoms in an excited state decays |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(a) Explanation-A set of atoms in an excited state decays in general to any of the states with lower energy. |
| 8. An ionised H-molecule consists of an electron and two protons. The protons are separated by a small distance of the order of angstrom. In the ground state, |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer- (a,c) Explantion- The protons are separated by a small distance of the order of angstrom. In the ground state the electron would not move in circular orbits the electrons, orbit would go around the protons. |
| 9. Consider aiming a beam of free electrons towards free protons. When-they scatter, an electron and a proton cannot combine to produce a H-atom. |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(a,b) Explantion- When beam of free electrons is aiming towards free protons. Then, they scatter but an electron and a proton cannot combine to produce a H-atom because of energy conservation and without simultaneously releasing energy in the form of radiation. |
| 10. The Bohr model for the spectra of a H-atom |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(a,b) Explantion- The Bohr model for the spectra of a H-atom will not be applicable to hydrogen in the Molecular form. And also, it will not be applicable as it is for a He-atom. |
| 11. The Balmer series for the H-atom can be observed (a) If we measure the frequencies of light emitted when an excited atom falls to the ground state (b) If we measure the frequencies of light emitted due to transitions between excited states and the first excited state (c) In any transition in a H-atom . (d) As a sequence of frequencies with the higher frequencies getting closely |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer- (b,d) Explantion- Balmer series for the H-atom can be observed if we measure the frequencies of light emitted due to transitions between higher excited states and the first excited state and as a sequence of frequencies with the higher frequencies getting closely packed. |
| 12. Let En= be the energy of the nth level of H atom. If all the H-atoms are in the ground state and radiation of frequency falls on it (a) It will not be absorbed at all (b) Some of atoms will move to first excited state (c) All atoms will be excited to the n= 2 state (d) No atoms will make a transition to then n=3 state |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(b,d) Explanation- when a radiation of energy fall on it some atoms would be excited but not all would be excite also no atom will go to 3 level some go to 2 level also but not all excite to 2 level. So by considering these facts we can say b and d option are correct |
| 13. The simple Bohr model is not applicable to He4atom because |
| This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Answer-(c,d) Explanation- The simple Bohr model is not applicable to He4 atom because He4 has one more electron and electrons are not subject to central forces. |
Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Physics Exemplar Chapter 12
These are the common mistakes by the students while studying Chapter 12, Atoms:
They get confused between Bohr’s and Rutherford’s models. Students often confuse features like orbit vs. orbitals or energy quantization.
They make errors in applying Bohr's Formula or they misunderstand how transitions work (initial vs. final energy level). The formula is:
- Students also get confused in labeling the spectral series, such as the Balmer, Lyman, and Paschen series.
- They also ignore units in calculations involving energy and wavelength.
- Sometimes students also lack understanding about why Bohr’s model succeeded and Rutherford’s model failed.
- They forget that the energy of an emitted/absorbed photon = the difference between the initial and final energy levels.
See some of the tips below to avoid common mistakes while solving questions in Chapter 12, Atoms:
- Practice diagram-based questions and be comfortable interpreting photon emission/absorption pathways and energy level diagrams.
- Memorize key constants and formulas and know key values like Bohr radius, Rydberg constant, and Planck’s constant.
- Students should use mnemonics to remember the series.
- They should solve numerical problems step-by-step to avoid skipping steps in energy calculations. Also, include units.
- Compare models like Rutherford vs. Bohr to clarify distinctions.
Students should also check NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics and NCERT Solutions Physics Class 11th.
JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, physics, second shift
Commonly asked questions
A capacitor is fully charged with voltage . After disconnecting the voltage source, it is connected in parallel with another uncharged capacitor of capacitance. . The energy loss in the process after the charge is distributed between the two capacitor is:
Sol.
Let,
In photoelectric effect experiment, the graph of stopping potential versus reciprocal of wavelength obtained is shown in the figure. As the intensity of incident radiation is increased:
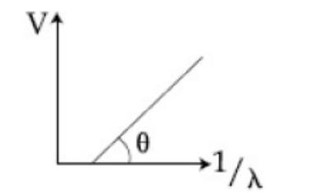
Sol.
Consider two uniform discs of the same thickness and different radii and made of the same material. If the ratio of their moments of inertia and , respectively, about their axes is then the value of is:

A circular coil has moment of inertia around any diameter and is carrying current to produce a magnetic moment of . The coil is kept initially in a vertical position and it can rotate freely around a horizontal diameter. When a uniform magnetic field of is applied along the vertical, it starts rotating around its horizontal diameter. The angular speed the coil acquires after rotating by will be:
Sol.
Find the binding energy per neucleon for . Mass of proton , mass of neutron and mass of tin nucleus . (take )
Sol.
A quantity is given by in terms of moment of inertia , force , velocity , work and Length . The dimensional formula for is same as that of:
Sol.
.
For a uniform rectangular sheet shown in the figure, the ratio of moments of inertia about the axes perpendicular to the sheet and passing through (the centre of mass) and (corner point) is:
Sol.
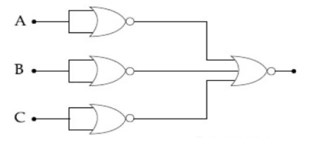
Identify the operation performed by the circuit given below:
Kindly go through the solution
A particle of charge and mass is subjected to an electric field in the -direction, where and are constants. Initially the particle was at rest at . Other then the initial position the kinetic energy of the particle becomes zero when the distance of the particle from the origin is:
Sol.
The value of current flowing from to in the circuit diagram is:
Sol.
Two identical cylindrical vessels are kept on the ground and each contain the same liquid of density . The area of the base of both vessels is but the height of liquid in one vessel is and in the other, . When both cylinders are connected through a pipe of negligible volume very close to the bottom, the liquid flows from one vessel to the other until it comes to equilibrium at a new height. The change in energy of the system in the process is :
Sol.
A series circuit is connected to a battery of emf . If the circuit is switched on at 0 , then the time at which the energy stored in the inductor reaches times of its maximum value, is :
Sol. Mono atomic
Di- atomic
(Rigid)
Di-atomic
(Non-Rigid)
Tri-atomic
(Rigid)
The electric field of a plane electromagnetic wave is given by Its magnetic field will be given by:
Kindly go through the solution
A person pushes a box on a rough horizontal platform surface. He applies a force of 200 over a distance of . Thereafter, he gets progressively tired and his applied force reduces linearly with distance to . The total distance through which the box has been moved is . What is the work done by the person during the total movement of the box?
Sol. (n)
: Integers
are integers.
So,
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of when it is placed in an external magnetic field of at a temperature of . When the sample is placed in an external magnetic field of at a temperature of , then the magnetisation will be :
Sol.
A body is moving in a low circular orbit about a planet of mass and radius . The radius of the orbit can be taken to be itself. Then the ratio of the speed of this body in the orbit to the escape velocity from the planet is :
Sol.
A small ball of mass is thrown upward with velocity from the ground. The ball experiences a resistive force where is it speed. The maximum height attained by the ball is:
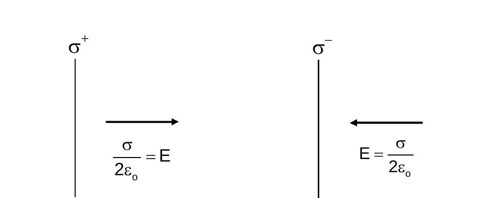
Sol. Sol. ![]() Electric field due to infinite sheet is uniform
Electric field due to infinite sheet is uniform
Match the thermodynamics processes taking place in a system with the correct conditions. In the table: is the heat supplied, is the work done and is change in internal energy of the system. Match the following:
Sol.
loss
loss
A cube of metal is subjected to a hydrostatic pressure 4GPa. The percentage change in the length of the side of the cube is close to: (Given bulk modulus of metal,
Sol.
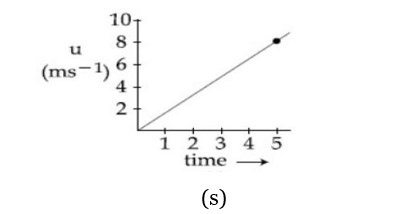
The speed verses time graph for a particle is shown in the figure. The distance travelled (in ) by the particle during the time interval to will be .
Sol.
The distance between an object and a screen is . A lens can produce real image of the object on the screen for two different positions between the screen and the object.
The distance between these two positions is . If the power of the lens is close to where is an integer, the value of is
Sol.
The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were and 2 atm. respectively. If then value of in (K/atm) is ....
Sol.
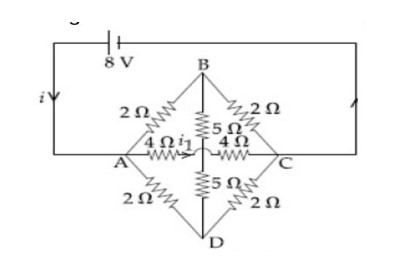
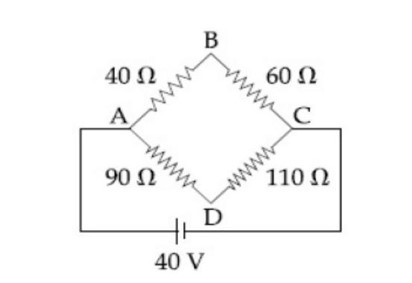
Four resistance , and make the arms of a quadrilateral ABCD. Across is a battery of emf and internal resistance negligible. The potential difference across in is
10553.33
Sol.
For Paschan
Orange light of wavelength illuminates a single slit of width . the maximum possible number of diffraction minima produced on both sides of the central maximum is
20
Sol. Angular momentum conservation:
JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, physics, First shift
Commonly asked questions
On the -axis and at a distance from the origin, the gravitational field due to a mass distribution is given by in the -direction. The magnitude of gravitational potential on the -axis at a distance , taking its value to be zero at infinity is:
Let,
Given figure shows few data points in a photo electric effect experiment for a certain metal. The minimum energy for ejection of electron from its surface is: (Plancks constant )
Dimensional formula for thermal conductivity is (here denotes the temperature):
Particle of mass moving along the -axis with velocity collides elastically with another particle at rest having mass . If both particles move along the axis after the collision, the change in de-Broglie wavelength of particle , in terms of its de-Broglie wavelength before collision is:
A wire , bent in the shape of an arc of a circle, carrying a current of and having radius and another wire , also bent in the shape of arc of a circle, carrying a current of and having radius of , are placed as shown in the figure. The ratio of the magnetic fields due to the wires and at the common centre is:
.
The specific heat of water and the latent heat of ice . 100 grams of ice at is placed in of water at . The amount of ice that will melt as the temperature of water reaches is close to (in grams):
A beam of plane polarized light of large cross-sectional area and uniform intensity of falls normally on a polarizer (cross sectional area ) which rotates about its axis with an angular speed of . The energy of light passing through the polariser per revolution, is close to:
Choose the correct option relating wavelengths of different parts of electromagnetic wave spectrum:
Kindly go through the solution
For a transverse wave traveling along a straight line, the distance between two peaks (crests) is 5
, while the distance between one crest and one trough is 1.5 m. The possible wavelengths (in ) of the waves are:
(n)
: Integers
are integers.
So,
A air bubble of radius 1 cm in water has an upward acceleration 9.8 cm-2 . The density of water is 1 gmcm-3 and water offers negligible drag force on the bubble. The mass of the bubble is: (g=980 cm/s2)
A small bar magnet placed with its axis at with an external field of experiences a torque of . The minimum work required to rotate it from its stable to unstable equilibrium position is:
Starting from the origin at time , with initial velocity , a particle moves in the plane with a constant acceleration of . At time , its coordinates are . The values of and are, respectively:
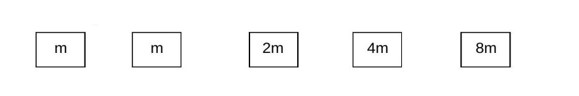
Blocks of masses and are arranged in a line on a frictionless floor. Another block of mass , moving with speed along the same line (see figure) collides with mass in perfectly inelastic manner. All the subsequent collisions are also perfectly inelastic. By the time the last block of mass starts moving the total energy loss is of the original energy. Value of ' ' is close to:
loss
loss
A battery of is connected to a resistor dissipating of power. If the terminal voltage of the battery is , the power dissipated within the internal resistance is:
A closed vessel contains 0.1 mole of a monatomic ideal gas at . If 0.05 mole of the same gas at is added to it, the final equilibrium temperature (in ) of the gas in the vessel will be close to
In a compound microscope, the magnified virtual image is formed at a distance of from the eye-piece. The focal length of its objective lens is . If the magnification is 100 and the tube length of the microscope is , then the focal length of the eyepiece lens (in ) is
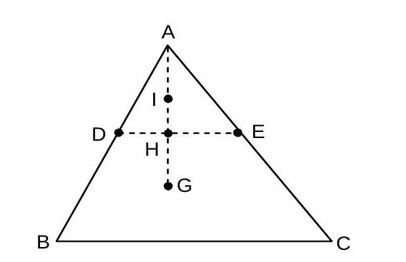
is a plane lamina of the shape of an equilateral triangle. are mid points of and is the centroid of the lamina. Moment of inertia of the lamina about an axis passing through and (Rotational)
Perpendicular to the plane is . If part is removed, the moment of inertia of the remaining part about the same axis is where is an integer. Value of is
For Paschan
A Tennis ball is released from a height and after freely falling on a wooden floor it rebounds and reaches height . The velocity versus height of the ball during its motion may be represented graphically by:
(graphs are drawn schematically and on not to scale)
Take the breakdown voltage of the zener diode used in the given circuit as . For the input voltage shown in figure below, the time variation of the output voltage is: (Graphs drawn are schematic and not to scale)
Kindly go through the solution
A two point charges and are fixed on the -axis at and , respectively. If a third point charge ' ' is taken from the origin to along the semicircle as shown in the figure, the energy of the charge will:
Match the ratio for ideal gases with different type of molecules:
Match the correct option?
Mono atomic
Di- atomic
(Rigid)
Di-atomic
(Non-Rigid)
Tri-atomic
A small bar magnet is moved through a coil at constant speed from one end to the other. Which of the following series of observations will be seen on the galvanometer G attached across the coil?
Three positions shown describe:
(a) The magnet's entry
(b) Magnet is completely inside and
(c) Magnet's exit
Kindly go through the solution
Two charged thin infinite plane sheets of uniform surface charge density and , where , intersect at right angle. Which of the following best represents the electric field lines for this system.
Electric field due to infinite sheet is uniform.
25th June 2022 first shift
Commonly asked questions
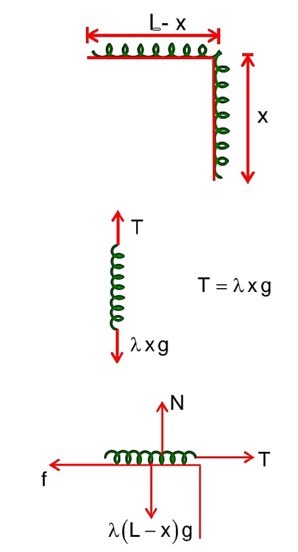
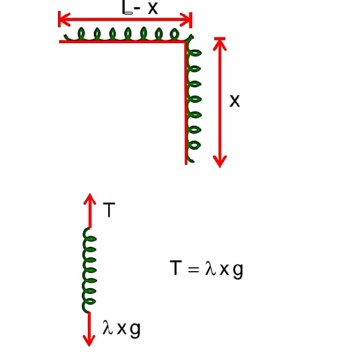
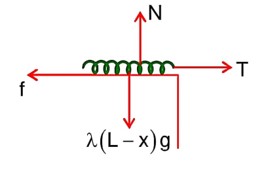
A uniform chain of 6m length is placed on a table such that a part of its length is hanging over the edge of the table. The system is at rest. The co-efficient of static friction between the chain and the surface of the table is 0.5, the maximum length of the chain hanging from the table is………….m.
F.B.D. of hanging length
F.B.D. of chain lying on the table
f = T =
x = 2m
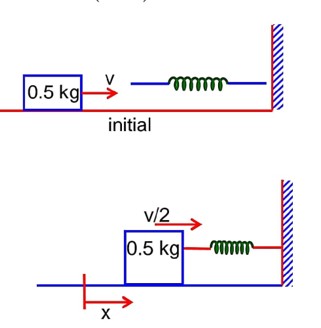
A 0.5kg block moving at a speed of 12ms-1 compresses a spring through a distance 30cm when its speed is halved. The spring constant of the spring will be…………Nm-1.
The velocity of upper layer of water in a river is 36kmh-1. Shearing stress between horizontal layers of water is 10-3 Nm-2. Depth of the river is……..m. (Co-efficient of viscosity of water is 10-2 Pa.s)
Given
(shear stress)
h =?
v = 36 km/hr = 10 m/sec
h = 100 m
A steam engine intakes 50g of steam at per minute and cools it down to If latent heat of vaporization of steam is 540 cal g-1, then the heat rejected by the steam engine per minute is………….× 103 cal.
(Given : specific heat capacity of water : 1 cal g-1 0C-1)
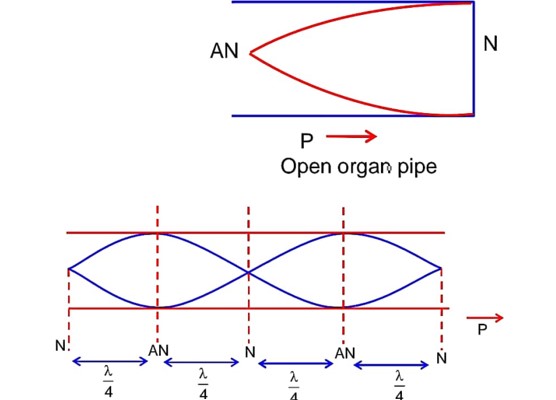
The first overtone frequency of an open organ pipe is equal to the fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe. If the length of the closed organ pipe is 20cm. The length of the open organ pipe is……….cm.
Now first overtone for open organ pipe
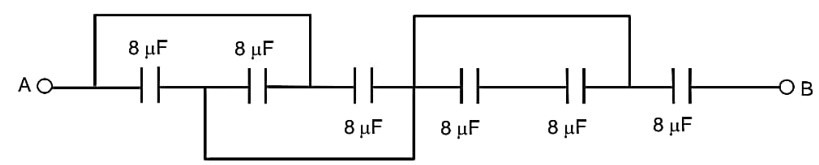
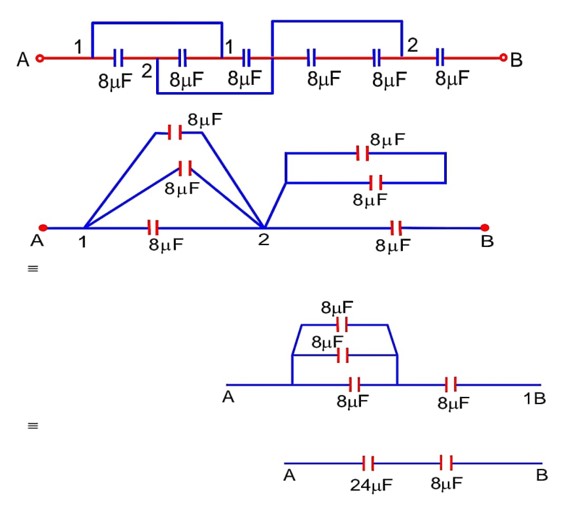
The equivalent capacitance between points A and B in below shown figure will be………….
A resistor develops 300 J of thermal energy in 15s, when a current of 2 A is passed through it. If the current increases to 3 A, the energy developed in 10s is……………..J.
Now for 3A, time = 10 sec
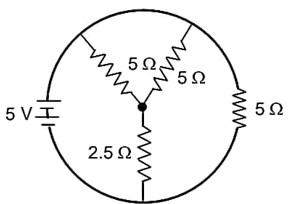
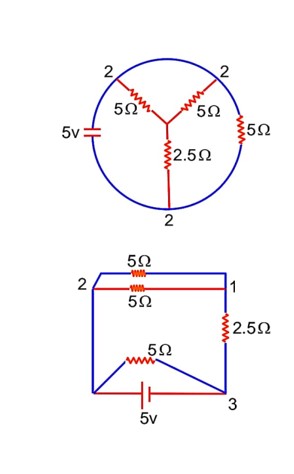
The total current supplied to the circuit is shown in figure by the 5 V battery is……………..A.
The current in a coil of self inductance 2.0 H is increasing according to I = 2sin(t2)A. The amount of energy spent during the period when current changes from 0 to 2 A is…………J.
Given, L = 2H
l = 2 sin (t2)
A force on an object of mass 100g is The position of that object at t = 2s is after starting from rest. The value of will be
Sx = 200 m
A uniform chain of 6m length is placed on a table such that a part of its length is hanging over the edge of the table. The system is at rest. The co-efficient of static friction between the chain and the surface of the table is 0.5, the maximum length of the chain hanging from the table is………….m.
F.B.D. of hanging length
F.B.D. of chain lying on the table
f = T =
x = 2m
A 0.5kg block moving at a speed of 12ms1 compresses a spring through a distance 30cm when its speed is halved. The spring constant of the spring will be…………Nm1.
by conservation of mechanical energy
K.Ei + P.Ei = K.Ef + P.Ef
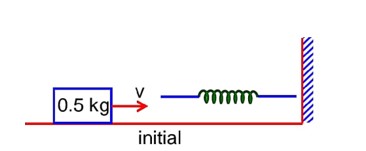
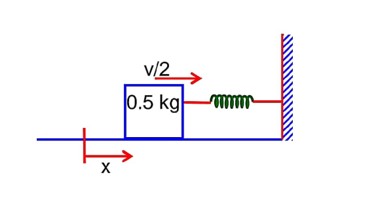
k = 600 N/m1
The velocity of upper layer of water in a river is 36kmh1. Shearing stress between horizontal layers of water is 103 Nm2. Depth of the river is……..m. (Co-efficient of viscosity of water is 102 Pa.s)
Given
(shear stress)
h =?
v = 36 km/hr = 10 m/sec
h = 100 m
A steam engine intakes 50g of steam at per minute and cools it down to If latent heat of vaporization of steam is 540 cal g1, then the heat rejected by the steam engine per minute is………….× 103 cal.
(Given : specific heat capacity of water : 1 cal g1 0C1)
The first overtone frequency of an open organ pipe is equal to the fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe. If the length of the closed organ pipe is 20cm. The length of the open organ pipe is……….cm.
Now first overtone for open organ pipe
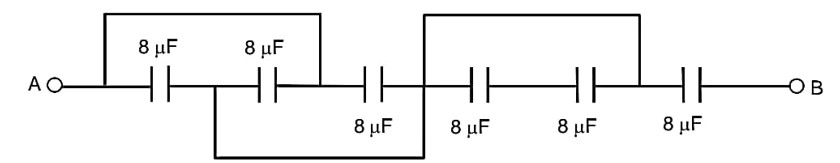
The equivalent capacitance between points A and B in below shown figure will be………….
ceq =
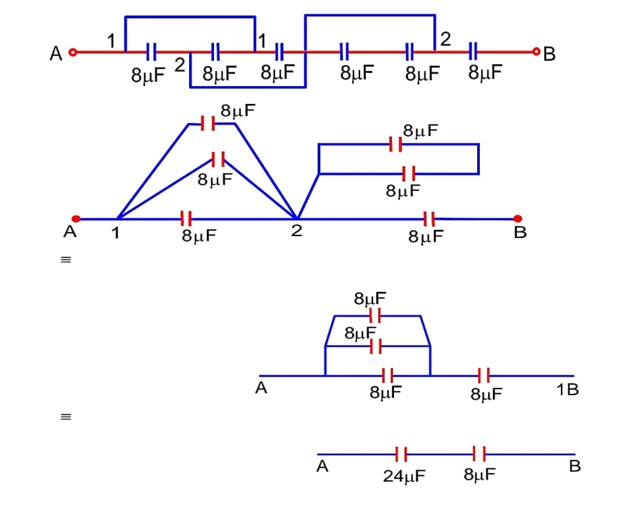
A resistor develops 300 J of thermal energy in 15s, when a current of 2 A is passed through it. If the current increases to 3 A, the energy developed in 10s is……………..J.
Now for 3A, time = 10 sec
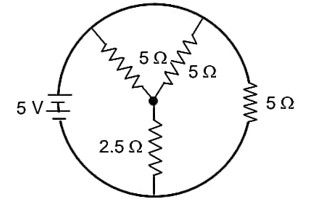
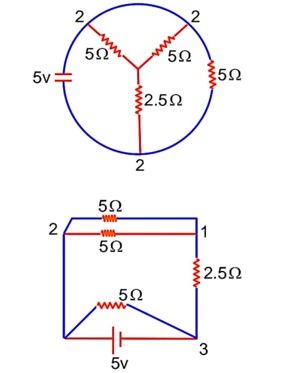
The total current supplied to the circuit is shown in figure by the 5 V battery is……………..A.
The current in a coil of self inductance 2.0 H is increasing according to I = 2sin(t2)A. The amount of energy spent during the period when current changes from 0 to 2 A is…………J.
Given, L = 2H
l = 2 sin (t2)
A force on an object of mass 100g is The position of that object at t = 2s is after starting from rest. The value of will be………
Sx = 200 m
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Twelve Exam