
NCERT Solutions Amines is all about the amines, which are an important class of organic compounds. The amines are derived from the ammonia molecule by replacing one or more hydrogen by alkyl/aryl group(s). The two biologically active compounds, ephedrine and adrenaline, contain the secondary amino group. In nature, the amines are present in vitamins, proteins, hormones, and alkaloids. The synthetic examples of amines include dye stuffs, polymers, and drugs.
NCERT Amines Solutions offer well-structured solutions to all questions of this chapter from the NCERT textbooks. The students get reliable study material here for their exam preparation. It will not only help them in scoring good marks in the CBSE Board exam but also in other entrance tests they will participate in later on. It will actually help them understand the concepts well, as the solutions are given in a step-by-step format. After getting a good grasp on the concept, the students learn to solve the related questions.
For getting the complete NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Notes for exam preparation, check here. You will get the solved questions with free PDFs.
- Glance at NCERT Amines Solutions
- NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Amines: Key Topics, Weightage and Important Reactions
- Free PDF: Class 12 NCERT Chemistry Solutions for Chapter 9 Amines
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines
- Benefit of using NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9
Glance at NCERT Amines Solutions
Here is a quick summary of the NCERT Amines solutions:
- Amines are the derivatives of ammonia. They are obtained from the replacement of hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups.
- The amines can be classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary amines.
- If the alkyl or aryl groups are the same, the secondary and tertiary amines are known as simple amines, and if the groups are different, it is called mixed amines.
- Amines are normally composed of halides, nitro compounds, imides, amides, etc.
- Other concepts covered in this chapter include alkylamines, aromatic amines, aniline, acylation, aryldiazonium salts, and trimethylamine.
To get the NCERT Class 12 notes of all three subjects, including Physics, Chemistry, and Maths, check here. It offers in-depth conceptual knowledge in an easy and simple language.
NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Amines: Key Topics, Weightage and Important Reactions
In NCERT Solutions Amines, students must focus on the classification, nomenclature, preparation, structure, chemical and physical properties of amines. It is important to understand the basic character of amines and their reactions. The key topics to focus on are the primary, secondary, and tertiary amines and diazonium salts. Here are the topics covered in this chapter:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 9.1 | Structure of Amines |
| 9.2 | Classification |
| 9.3 | Nomenclature |
| 9.4 | Preparation of Amines |
| 9.5 | Physical Properties |
| 9.6 | Chemical Reactions |
| 9.7 | Method of Preparation of Diazoniun Salts |
| 9.8 | Physical Properties |
| 9.9 | Chemical Reactions |
| 9.10 | Importance of Diazonium Salts in Synthesis of Aromatic Compounds |
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines Weightage in NEET, JEE Mains
| Exam | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| NEET | - | 3.80% |
| JEE Mains | 9-10 questions | 3.8% |
Key Topics covered in Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines
- Structure of Amines
- Classification
- Nomenclature
- Preparation of Amines
- Physical Properties
- Chemical Reactions
- Methods of preparation of Diazonium Salts
- Physical Properties
- Chemical reactions
- Importance of Diazonium salts in Synthesis of aromatic Compounds
Important Reactions of NCERT Class 12 Chemistry: Amines for CBSE and other Competitive Exams
1. Preparation of Amines
- Reduction of Nitro Compounds
RNO₂ + H₂ → RNH₂ (Sn/HCl or Fe/HCl) - Ammonolysis of Alkyl Halides
RX + NH₃ → RNH₂ + HX - Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis (For Primary Amines Only)
C₆H₄(CO)₂N⁻K⁺ + RX → C₆H₄(CO)₂NR
C₆H₄(CO)₂NR + H₂O → RNH₂ - Hoffmann Bromamide Reaction
RCONH₂ + Br₂ + NaOH → RNH₂ + Na₂CO₃ + NaBr + H₂O
2. Chemical Reactions of Amines
- Basic Nature of Amines
RNH₂ + H₂O → RNH₃⁺ + OH⁻ - Reaction with Acids (Salt Formation)
RNH₂ + HCl → RNH₃⁺Cl⁻ - Alkylation (Formation of Higher Amines)
RNH₂ + R'X → RNHR' - Acylation (Reaction with Acid Chlorides & Anhydrides)
RNH₂ + R'COCl → RNHCOR' - Reaction with Nitrous Acid (Different Products Based on Amine Type)
Primary Amine: RNH₂ + HNO₂ → ROH + N₂ + H₂O
Secondary Amine: R₂NH + HNO₂ → R₂NN=O (Nitrosoamine) - Hinsberg Test (Distinguishing Primary, Secondary & Tertiary Amines)
Primary Amines → Forms soluble sulfonamide
Secondary Amines → Forms insoluble sulfonamide - Carbylamine Reaction (For Primary Amines Only, Test for Primary Amines)
RNH₂ + CHCl₃ + KOH → RNC (Foulsmelling isocyanide) - Electrophilic Substitution in Aromatic Amines
- Bromination: C₆H₅NH₂ + Br₂ → 2,4,6Tribromoaniline
- Nitration: C₆H₅NH₂ + HNO₃ → mNitroaniline
- Sulphonation: C₆H₅NH₂ + H₂SO₄ → pAminobenzenesulphonic Acid
- Diazotization Reaction (Formation of Diazonium Salts from Primary Aromatic Amines)
C₆H₅NH₂ + HNO₂ → C₆H₅N₂⁺Cl⁻ + H₂O - Coupling Reactions (Reaction of Diazonium Salts with Phenols & Amines)
C₆H₅N₂⁺Cl⁻ + C₆H₅OH → pHydroxyazobenzene
C₆H₅N₂⁺Cl⁻ + C₆H₅NH₂ → pAminoazobenzene
Free PDF: Class 12 NCERT Chemistry Solutions for Chapter 9 Amines
The Class 12 Science students must download the free NCERT Amines PDF from the link given below. The solutions are created by the subject matter experts. It will help the students to improve their exam preparation.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines NCERT Solutions PDF Download: Download Free PDF
More Links
| NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 | Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions | NCERT Solutions Class 11 and 12 for Maths, Physics, Chemistry |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines
| Q 13.1 Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary.
|
|
(ii) Tertiary, because the Nitrogen atom is attached to the 3 carbon atoms. |
| Q 13.2 (i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N. (ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers. (iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines? |
| Ans (i) & (ii) There are total 8 geometrical isomers of the given compound. (iii) a) Pairs 1,2,6,7 Exhibit Position isomerism; means the change in position of the substituent. b) Pairs 1,3 and 1,4 and 2,3 and 2,4 exhibit chain isomerism i.e. in this type of isomerism the different structures can be produced by changing the chain of the c) Pairs 5,6 and 5,7 exhibit metamerism; e. different group on either side of the central atom. d) All Primary amines exhibit functional isomers. All secondary amines share functional isomerism and same for The functional isomerism means same functional group. |
| Q 13.3 How will you convert (i) Benzene into aniline (ii) Benzene into N, N-dimethylaniline (iii) Cl–(CH2)4–Cl into hexan-1,6-diamine? |
| Ans Benzene into aniline When Benzene is treated with HNO3/H2SO4 it forms nitrobenzene. When Nitrobenzene reduced with Sn/HCL it forms Aniline because Sn/HCl is a reducing Mixture. When Benzene is reacted with nitrating mixture it forms nitrobenzene. When it Reduced H2/Pd in ethanol or Sn/HCl, it forms Aniline. When Aniline reacts 2 times with CH3Cl It forms N, N- dimethylaniline. When 1,4-dichlorobutane reacts with NaCN it forms Di cyanide compound, After Hydrogenation it forms the Hexane 1,6-Diamine. |
| Q 13.4 Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength: (i) C2H5NH2, C6H5NH2, NH3, C6H5CH2NH2 and (C2H5)2NH (ii) C2H5NH2, (C2H5 )2NH, (C2H5 )3N, C6H5NH2 (iii) CH3NH2, (CH3 )2NH, (CH3)3N, C6H5NH2, C6H5CH2 NH2 . |
| Ans 1- Alkyl group contribute inductive effect which increases the basic strength of NH3
Then C6H5NH2 is having –I effect that reduces strength. And C6H5CH2NH2 increases the basic strength but not as much as C2H5 group. Hence final order will be C6H5NH2<
2- By taking into consideration –R effect and steric hindrance of groups we can arrange them in the order C6H5NH2< C2H5NH2<(C2H5)3N<(C2H5)2NH. Because (C2H5)3N has a lot of steric hindrances that reduces the basic strength. 3- In C6H5NH2 , N is directly attached to the ring that causes delocalization of electrons of the benzene ring. Whereas in case of C6H5CH2NH2 it is not directly connected to benzene ring Hence it has more basic strength. Due to –I effect of (CH3)3 – a group it has more basic strength than C6H5CH2NH2. Hence final order will be C6H5NH2< C6H5CH2NH2<(CH3)3N< CH3NH2< (CH3)2NH |
Commonly asked questions
13.13 Arrange the following:
(i) In decreasing order of the pKb values: C2H5NH2 , C6H5NHCH3 , (C2H5 ) 2NH and C6H5NH2
(ii) In increasing order of basic strength: C6H5NH2 , C6H5N(CH3)2 , (C2H5)2NH and CH3NH2
(iii) In increasing order of basic strength: (a) Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine (b) C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3 , C6H5CH2NH2
(iv) In decreasing order of basic strength in gas phase: C2H5NH2 , (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N and NH3
(v) In increasing order of boiling point: C2H5OH, (CH3 )2NH, C2H5NH2
(vi) In increasing order of solubility in water: C6H5NH2 , (C2H5 ) 2NH, C2H5NH2 .
Pkb value is the negative logarithm of the basicity constant (Kb) .i.e., pKb = -logKb
Evidently, smaller the value of pKb , stronger is the base (strong tendency to donate electrons). Aliphatic amines(R-NH2) are more basic(tendency to donate electrons) than aromatic amines(C6H5NH2) because of the following reasons:
=>In aliphatic amines, alkyl groups are present. Alkyl groups are electron releasing groups, hence they increase the elecron density of N-atom and thus is easily available to donate electrons. This poperty makes aliphatic amines more basic.
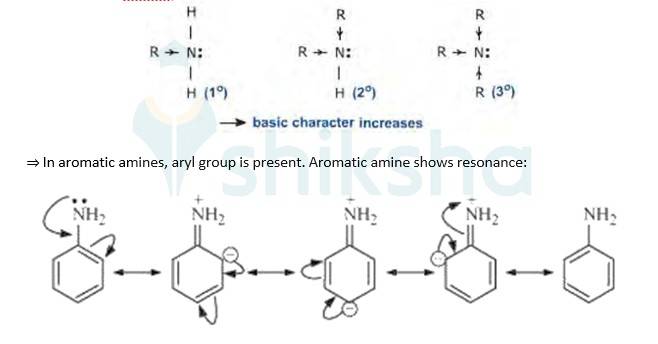
As a result of resonance, the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom gets delocalized over benzene ring. As a result, electron density on the nitrogen decreases and thus is less easily available to donate electrons making it less basic. Hence aliphatic amines(R-NH2) are more basic than aromatic amines (C6H5NH2).
Now, in C2H5NH2, one ethyl group (alkyl) is present and in (C2H5)2NH2 two ethyl groups are present. As we know that more alkyl groups are present, more basic will be the amine.
Hence, (C2H5)2NH2 is more basic than the C2H5NH2
Now in C6H5NH2, due to delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of the N-atom over the benzene ring, makes it less basic than (C2H5)2NH2 and C2H5NH2
Now, in C6H5NHCH3, due to presence of CH3 group, makes it more basic than C6H5NH2 but less basic than (C2H5)2NH2 and C2H5NH2 due to the presence of aromatic ring which is responsible for the delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of N-atom over the benzene ring.
Combining all these facts, the relative basic strength of these four amines decrease in the order:
(C2H5)2NH2 > C2H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C6H5NH2
Since, a stronger base has a lower pkb value, therefore, pKb values decrease in the reverse order:
C6H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2NH2
In (C2H5)2NH2, two ethyl groups are present and in CH3NH2 one methyl group is present. As we know that more alkyl groups are present, more basic will be the amine. Hence, (C2H5)2NH2 is more basic than the CH3NH2
Now in C6H5NH2, due to delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of the N-atom over the benzene ring (decreases the electron density of N-atom) makes it less basic than (C2H5)2NH2 and CH3NH2
Now, in C6H5N(CH3)2 due to presence of two CH3 groups (increases the electron density of N- atom) makes it more basic than C6H5NH2 but less basic than (C2H5)2NH2 and CH3NH2 due to the presence of aromatic ring which is responsible for the delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of N-atom over the benzene ring (decreases the electron density of N-atom)
Combining all these facts, the relative basic strength of these four amines increases in the order:
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < CH3NH2 < (C2H5)2NH
(a) Electron-donating groups such as –CH3, -OCH3, -NH2, etc. increase the basicity and electron- withdrawing groups such as –NO2, -CN, -SO3H, -COOH, -X(halogen), etc. decrease the basicity of
Explanation: Electron-donating groups releases electrons, stabilizes the conjugate acid (cation) and thus increases the basic strength. Electron-withdrawing groups withdraws electrons, destabilizes the conjugate acid (cation) and thus decreases the basic strength.
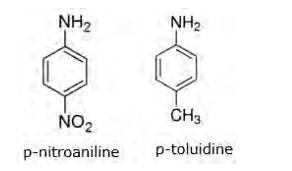
In p-nitroaniline, NO2 group is present. As we know that NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group which decreases the basic strength of amine. In p-toluidine, CH3 group is present and as we know that CH3 group is an electron donating (releasing) group which increases the basic strength of amine. Hence, p-toluidine is more basic than p-nitroaniline
Now in C6H5NH2 (aniline), due to delocalisation of lone pair of electrons of the N-atom over the benzene ring (decreases the electron density of N-atom) makes it less basic than p-toluidine but more basic than p-nitroaniline (NO2 group is present which decreases the density of aniline)
Combining all these facts, the relative basic strength of these three amines increases in the order:
p-nitroaniline< aniline < p-toluidine
(b) C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5CH2NH2
In C6H5NH2 and C6H5NHCH3, the N-atom is directly attached to the aromatic ring. Hence, they both show resonance in which delocalization of lone pair of electrons N-atom takes place. As a result the electron density of N-atom decreases. Hence both are weaker bases. However in C6H5NHCH3, CH3 group (electron withdrawing) is present which increases the overall density of electrons. Hence, C6H5NHCH3 is more basic than C6H5NH2
In C6H5CH2NH2, the N-atom is not directly attached to the aromatic ring. As a result, it does not show resonance. There is no effect on the electron density of lone pair of electrons of N-atom. Hence, it is more basic than C6H5NH2 and C6H5NHCH3
Combining all these facts, the relative basic strength of these three amines increases in the order:
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5CH2NH2
Amines in gas phase or in non-aqueous solvents, there is no solvation effect (getting influenc
13.5 Complete the following acid-base reactions and name the products: (i) CH3CH2CH2NH2 +HCl → (ii) (C2H5 ) 3N + HCl → (Beginners)
(i) CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl → CH3CH2CH2N+H3Cl-
The final product is (N-propyl ammonium chloride.)
(ii) (C2H5)3N + HCl → (C2H5)3N+HCl-
The final product is (Tri ethyl ammonium chloride)
13.4 Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength:
(i) C2H5NH2, C6H5NH2, NH3, C6H5CH2NH2 and (C2H5)2NH
(ii) C2H5NH2, (C2H5 )2NH, (C2H5 )3N, C6H5NH2
(iii) CH3NH2, (CH3 )2NH, (CH3)3N, C6H5NH2, C6H5CH2 NH2 .
1- Alkyl group contribute inductive effect which increases the basic strength of
NH3
Then C6H5NH2 is having –I effect that reduces strength. And C6H5CH2NH2 increases the basic strength but not as much as C2H5 group.
Hence final order will be C6H5NH2<
2- By taking into consideration –R effect and steric hindrance of groups we can arrange them in the order
C6H5NH2< C2H5NH2< (C2H5)3N< (C2H5)2NH.
Because (C2H5)3N has a lot of steric hindrances that reduces the basic strength.
3- In C6H5NH2, N is directly attached to the ring that causes delocalization of electrons of the benzene ring. Whereas in case of C6H5CH2NH2 it is not directly connected to benzene ring Hence it has more basic strength.
Due to –I effect of (CH3)3 – a group it has more basic strength than C6H5CH2NH2. Hence final order will be
C6H5NH2< C6H5CH2NH2< (CH3)3N< CH3NH2< (CH3)2NH
13.6 Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Primary amine: A primary (1°) amine is an amine that has the following general structural formula. R= alkyl or aryl group Secondary amine: A secondary (2°) amine is an amine that has the following general structural formula. R1 and R2= alkyl or aryl group Tertiary amine: A tertiary amine is an amine that has the following structure R1, R2 and R3 are alkyl or aryl groups Identification of Primary, Secondary and Tertiary amines Primary, secondary and tertiary amines can be identified by the following test: Hinsberg's test: This is an excellent test for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. In this test, the amine is shaken with benzenesulphonyl chloride ( Hinsberg's reagent) in the presence of an excess of aqueous KOH solution when (i) A primary amine gives a clear solution which on acidification gives an N-alkylbenzene sulphonamide which is soluble in Due to the presence of strong electron withdrawing sulphonyl group in the sulphonamide, the H-atom attached to nitrogen can be easily released as a proton. So it is acidic and dissolves in alkali. (ii) A secondary amine reacts with Hinsberg's reagent to give a sulphonamide which is soluble in There is no H-atom attached to the N-atom in the sulphonamide Therefore it is not acidic and soluble in alkali. (iii) A Tertiary amine does not react with Hinsberg's reagent at all |
13.21 Why cannot aromatic primary amines be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is used for the preparation of aliphatic primary amines. It involves nucleophilic substitution (SN2) of alkyl halides by the anion formed by the phthalimide.But aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by the phthalimide.
Therefore aromatic primary amines cannot be formed by gabriel phthalimide process.
13.20 Complete the following reactions:
(i) C6H5NH2 + CH3Cl + KOH →
(ii) C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O →
(iii) C6H5NH2 + H2SO4 (conc) →
(iv) C6H5N2Cl + C2H5OH à
(v) C6H5NH2 + Br2 (aq) à
(vi) C6H5NH2 + (CH3CO)2O à
(vii) C6H5N2Cl
1- C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + KOH
It is a carbylamine reaction in which a isocyanide compound is formed along with side products of potassium chloride.Basically the name of reaction is given is due to formation of a foul smelling compound called as isocyanide.
2- C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O
Benzenediazonium chloride is a very reactive compound which oxidises hypophosphorous acid to hypophosphoric acid and the reactant is reduced to benzene.
3- C6H5NH2 + H2SO4 (conc.)
Aniline undergoes sulphonation to anillium hydrogensulphate.
4- C6H5N2Cl + C2H5OH
Aniline is very activating group which undergoes reaction to give ortho and para product. But in acidic medium aniline accquires positive charge on N atom which is metadirecting group and hence the product.
5- C6H5NH2 + Br2 (aq)
It is clubbing reaction of a very reactive compound undergoing addition to give benzene.
6- C6H5NH2 + (CH3CO)2O
As mentioned aniline is avery activating group, so to reduce its activity it is reacted with anhydride to give n-phenylethanamine.
7- C6H5N2Cl
Hydrofluroburic acid reacts qith benzenediazonium chloride along with sodium nitrite to give a reduced product as Nitrobenzene.
13.1 Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary.
(ii) Tertiary, because the Nitrogen atom is attached to the 3 carbon atoms.
(iii) Primary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon atom.
(iv) Secondary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon.
13.16 Write short notes on the following:
(i) Carbylamine reaction
(ii) Diazotisation
(iii) Hofmann’s bromamide reaction
(iv) Coupling reaction
(v) Ammonolysis
(vi) Acetylation
(vii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
(i) Carbylamine reaction
Carbylamine reaction is used as a test for the identification of primary amines. When aliphatic and aromatic primary amines are heated with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, carbylamines (or isocyanides) are formed. These carbylamines have very unpleasant odours. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to this test.
For example,
(ii) Diazotisation
Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2 and a mineral acid such as HCl) at low temperatures (273-278 K) to form diazonium salts. This conversion of aromatic primary amines into diazonium salts is known as diazotization.
For example, on treatment with NaNO2 and HCl at 273?278 K, aniline produces
benzenediazonium chloride, with NaCl and H2O as by-products.
(iii) Hoffmann bromamide reaction
When an amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide, a primary amine with one carbon atom less than the original amide is produced. This degradation reaction is known as Hoffmann bromamide reaction. This reaction involves the migration of an alkyl or aryl group from the carbonyl carbon atom of the amide to the nitrogen atom.
For example,
(iv) Coupling reaction
The reaction of joining two aromatic rings through the? N=N? bond is known as coupling reaction. Arenediazonium salts such as benzene diazonium salts react with phenol or aromatic amines to form coloured azo compounds.
It can be observed that, the para-positions of phenol and aniline are coupled with the diazonium salt. This reaction proceeds through electrophilic substitution.
(v) Ammonolysis
When an alkyl or benzyl halide is allowed to react with an ethanolic solution of ammonia, it undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the halogen atom is replaced by an amino (? NH2) group. This process of cleavage of the carbon-halogen bond is known as ammonolysis.
When this substituted ammonium salt is treated with a strong base such as sodium hydroxide, amine is obtained.
Though primary amine is produced as the major product, this process produces a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines, and also a quaternary ammonium salt as shown.
(vi) Acetylation
Acetylation (or ethanoylation) is the process of introducing an acetyl group into a molecule. Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines undergo acetylation reaction by nucleophilic substitution when treated with acid chlorides, anhydrides or esters. This reaction involves the replacement of the hydrogen atom of? NH2 or > NH group by the acetyl group, which in turn leads to the production of amides. To shift the equilibrium to the right hand side, the HCl formed during the reaction is removed as soon as it is formed. This reaction is carried out in the presence of a base (such as pyridine) which is stronger than the amine.
When amines react with benzoyl chloride, the reaction is also known as benzoylation. For example,
(vii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is a very useful method for the preparation of aliphatic primary amines. It involves the treatment of phthalimide with ethanolic potassium hydroxide to form
potassium salt of phthalimide. This salt is further heated with alkyl halide, followed by alkaline hydrolysis to yield the corresponding primary amine.
13.23 Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
(i) Why are amines less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses?
(ii) Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
(iii) Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than aromatic amines?
(i) Aromatic amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2and a mineral acid such as HCl) at 273 - 278 K to form stable aromatic diazonium salts e., NaCl and water.
(ii) Aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2and a mineral acid such as HCl) to form unstable aliphatic diazonium salts, which further producealcohola and acid called as hydrochloric acid and evolution of nitrogen
(iii) Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines due to following reasons:
(a) The lone pair of electrons of the nitrogen atom of aromatic amines is involved in
conjugation with the π−bond pairs of the ring as follows
(b) Anilinium ion obtained by accepting a proton is less stabilized by resonance. Due to the −R effect of the benzene ring, the electrons on the N- atom are less available in the case of aromatic amines. Therefore, the electrons on the N-atom in aromatic amines cannot be donated
So, aniline is a weaker base than alkyl amines, in which +1 effect increases the electron density on the nitrogen atom.
13.18 Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions:
(i) Ethyl iodide reacts with NaCN gives a substitution reactions to give propanitrile upon partial hydrolysis gives B, upon reaction with sodium hydroxide gives C.
(ii) Benzenediazoniumchloride gives nucleophilic substitution reactions gives A, upon hydrolysis the CN ion is replaced by OH ion which is less better leaving group gives B upon heating with ammonia gives C.
(iii) Ethylbromide gives nucleophilic substitution reactions gives B, upon reduction gives B followed by reacting with nitrous acid, i.e oxidation gives propanol.
(iv) Nitrobenzene upon reduction with iron/acid gives A, reacting with sodium nitrite gives benzenediazonium chloride, followed by complete Hydrolysis gives phenol.
(v) Acetic acid upon heating with ammmonia gives A, which is an amide. This amide reacts with NaOBr which extracts the carbonyl carbon giving B, followed by reacting with sodium nitrite gives methanol.
(vi) Nitrobenzene upon reduction with iron/acid mixture gives A, followed by oxidation with nitrous acid gives B and reacting with phenol undergoes addition reaction to give C.
13.3 How will you convert
(i) Benzene into aniline
(ii) Benzene into N, N-dimethylaniline
(iii) Cl–(CH2)4–Cl into hexan-1,6-diamine?
Benzene into aniline
When Benzene is treated with HNO3/H2SO4 it forms nitrobenzene. When Nitrobenzene reduced with Sn/HCL it forms Aniline because Sn/HCl is a reducing Mixture.
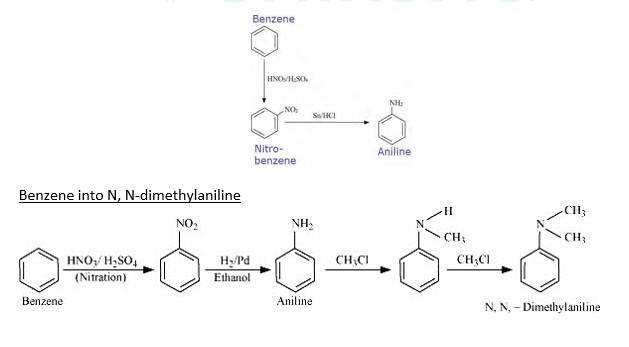
When Benzene is reacted with nitrating mixture it forms nitrobenzene. When it Reduced H2/Pd in ethanol or Sn/HCl, it forms Aniline. When Aniline reacts 2 times with CH3Cl It forms N, N- dimethylaniline.
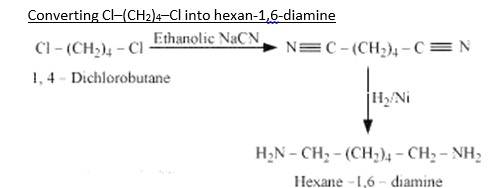
When 1,4-dichlorobutane reacts with NaCN it forms Di cyanide compound, After Hydrogenation it forms the Hexane 1,6-Diamine.
13.2 (i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N.
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
(i) & (ii) There are total 8 geometrical isomers of the given compound.
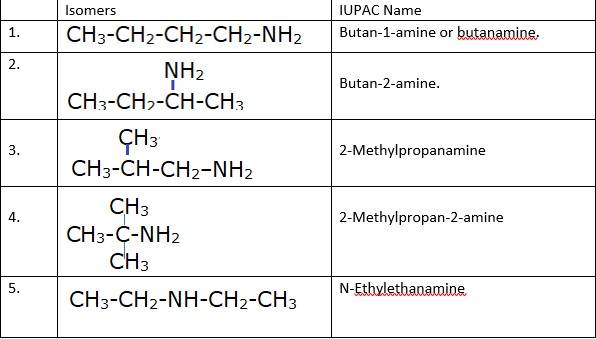
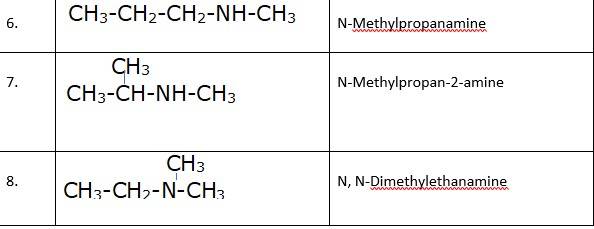
(iii) a) Pairs 1,2,6,7 Exhibit Position isomerism; means the change in position of the substituent.
b) Pairs 1,3 and 1,4 and 2,3 and 2,4 exhibit chain isomerism i.e. in this type of isomerism the different structures can be produced by changing the chain of the
c) Pairs 5,6 and 5,7 exhibit metamerism; e. different group on either side of the central atom.
d) All Primary amines exhibit functional isomers. All secondary amines share functional isomerism and same for The functional isomerism means same functional group.
13.22 Write the reactions of
(i) Aromatic
(ii) Aliphatic primary amines with nitrous acid.
(i) Aromatic amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ fromNaNO2 and a mineral acid such as HCl) at 273 - 278 K to form stable aromatic diazonium salts i.e., NaCl and water. This reaction is widely used for preparation of variety of compounds.
(ii) Aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2 and a mineral acid such as HCl) to form unstable aliphatic diazonium salts, which is very reactive, which further produce alcohol and HCl with the evolution of nitrogen gas.
13.19 An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.
It is given that compound 'C' having the molecular formula, C6H7N is formed by heating compound 'B' with Br2and KOH. This is a Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction (in which isocyanide compound is formed). Therefore, compound 'B' is an amide and compound 'C' is an amine. The only amine having the molecular formula, C6H7N is aniline. Therefore, compound 'B' (from which 'C' is formed) must be benzamide.
Further, benzamide is formed by heating compound 'A' with aqueous ammonia. Therefore, compound 'A' must be benzoic acid. The given reactions can be explained with the help of the following equations:
Benefit of using NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9
Students who are in class 12 can benefit from NCERT solutions for class 12 chapter 9 in the following ways.
- Conceptual Knowledge: Students' basic concepts become clear by attempting various questions that help solve the problem easily.
- Improve problem-solving skills: The complex solutions provided are explained in a simple way, which helps students easily solve the questions.
- Revision and Practice: Students while preparing for the examination, can use the Amines ncert solutions for self-assessment. Knowing the weaker topics, students can focus on it.
Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th Exam
