
NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Polymers Solutions is available on this page. NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Solutions are curated by the subject experts to help students to score well in the exam.
Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating subunits called monomers. They are macromolecules formed through a process called polymerization, in which monomers chemically bond together to create a long chain-like structure. The word "polymer" comes from the Greek words "poly," meaning "many," and "meros," meaning "parts" or "units."
There are several types of polymers, including synthetic polymers, which are human-made, and natural polymers, which occur in nature. Synthetic polymers are widely used in various industries due to their versatility, durability, and ability to be tailored for specific applications.
- Topics Covered in NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Polymers Chapter
- NCERT Chemistry Class 12th Solution PDF - Polymers Chapter Download
- Polymers Solutions
Topics Covered in NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Polymers Chapter
Here are some key aspects of polymers:
Structure: Polymers have a repetitive structure, with the monomer units repeating in a specific sequence or pattern. The arrangement of monomers affects the physical and chemical properties of the polymer. Polymers can be linear, branched, or cross-linked, depending on the type of bonding between the monomer units.
Classification: Polymers can be classified based on their origin, chemical structure, and behavior. They can be further categorized into thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers. Thermoplastics can be melted and reprocessed multiple times without significant degradation, while thermosetting polymers undergo irreversible chemical reactions upon curing and cannot be melted and reprocessed.
Properties: Polymers possess a wide range of properties, including mechanical strength, flexibility, electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. The properties of a polymer depend on factors such as the nature of monomers, polymer chain length, branching, cross-linking, and intermolecular forces.
Applications: Polymers have numerous applications across various industries. They are used in the production of plastics, fibers, elastomers, coatings, adhesives, and films. Polymers are found in everyday items such as bottles, packaging materials, clothing, automotive parts, medical devices, and electronic components.
Polymer Processing: Polymers can be processed into various forms, including extrusion, injection molding, blow molding, and casting. These processes allow the shaping and forming of polymers into desired products with different geometries and sizes.
Polymer Characterization: Scientists and engineers use various techniques to characterize polymers, such as gel permeation chromatography (GPC), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and mechanical testing. These methods provide information about molecular weight, chemical composition, thermal behavior, and mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact: Due to the widespread use of polymers and their resistance to degradation, the disposal of plastic waste has become a significant environmental concern. Efforts are being made to develop biodegradable and sustainable polymers, as well as improve recycling processes to reduce the environmental impact of polymer waste.
Overall, polymers are versatile materials with a wide range of applications and properties. They have revolutionized various industries and continue to play a vital role in technological advancements and everyday life.
NCERT Chemistry Class 12th Solution PDF - Polymers Chapter Download
Candidates can check and download here NCERT Chemistry class 12 solution for Polymers PDF. The chapter's solution is prepared by the subject experts and are easy to understand. Polymers is an important chapter and many questions are asked from this chapter in class 12 board exams as well as JEE Mains.
Download Here: NCERT Solution for Class XII Chemistry Polymers PDF
Polymers Solutions
| Intext Q 15.1 What are polymers? |
| A 15.1 Polymer=Poly + Mer Poly means “many” and “Mer” means unit or part. A polymer is a large molecule which is formed by linking repeating structural units. The structural units are generally simple molecules and they are linked by a covalent bond to form a polymer. |
| Intext Q 15.2 Write the names of monomers of the following polymers: |
| A 15.2 Polymers are classified based on structure, into 3 types:
|
| Intext Q 15.3 Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers: Terylene, Bakelite, Polythene, Teflon. |
|
| Intext Q 15.4 Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S. | ||||||||
| A 15.4
|
Commonly asked questions
15.5 Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces. Nylon 6,6, Buna-S, Polythene.
15.5
Different types of polymers have different intermolecular forces of attraction. Elastomers or rubbers have the weakest while fibres have the strongest intermolecular forces of attraction. Plastics have intermediate intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, the increasing order of the intermolecular forces of the given polymers is as follows:
Buna? S < polythene < Nylon 6, 6
Neoprene < polyvinyl chloride < Nylon 6
15.6 Explain the terms polymer and monomer.
15.1
The word polymer comes from poly- (many) and -mer (part). Polymers are generally high molecular mass substances that have repeating units of smaller molecules. They may be a natural or synthetic macromolecule. The single molecular units of which a large chains are made is known as 'monomer'. These monomers generally have high molecular mass (103- 107u). Some examples of polymers are polythene, Bakelite, rubber, Buna-N and many more.
15.1 What are polymers?
15.1
Polymer=Poly + Mer
Poly means “many” and “Mer” means unit or part. A polymer is a large molecule which is formed by linking repeating structural units. The structural units are generally simple molecules and they are linked by a covalent bond to form a polymer.
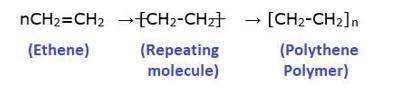
15.2 Write the names of monomers of the following polymers:
15.2
Polymers are classified based on structure, into 3 types:
Linear Polymer: They have a long and straight chain of Ex: high-density Polythene, Polyvinyl chloride

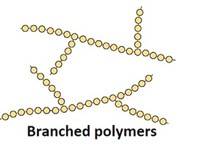
Branched-chain Polymers: They have linear molecular chains along with some Ex: less density polythene.
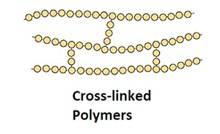
Cross-linked or network Polymers: In these polymers, strong covalent bonds are between the linear chains. Generally, they contain 2 or 3 types of functional groups. Ex: Bakelite, melamine.
15.3 Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers: Terylene, Bakelite, Polythene, Teflon.
15.3
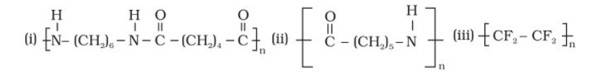
The monomer is OC- (CH2)5-NH known as Caprolactam. The cyclic structure of the monomer changes to linear to form the polymer, as shown below:
The monomer is Tetrafluroethene (CF2= CF2), the double bond breaks to form the polymeric
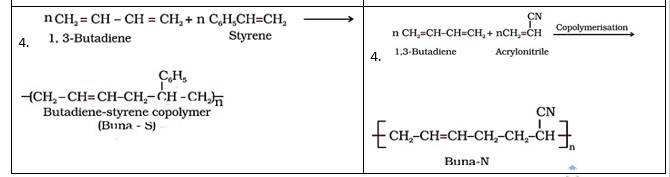
15.4 Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S.
15.4
Buna-S | Buna-N |
1. It is formed from 1,3- butadiene and styrene in presence of sodium. | It is formed from 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile in presence of sodium. |
2. Bu refers Butadiene, Na refers Sodium and S refers Styrene | Bu refers Butadiene, na refers Sodium and N refers acrylonitrile |
3. It is used for making automobile tyres, rubber belts, etc. | It is used for manufacturing of tank linings, protective gloves etc. |
15.7 What are natural and synthetic polymers? Give two examples of each type.
15.7 Based on source, polymers can be classified as below:
Natural polymers: Those polymers obtained from plants and animals such as proteins, cellulose, starch and other resins.
Semi Natural polymers: Those polymers that are derivatives of natural polymers fall under this category. Cellulose Nitrate used as a propellant and in guncotton and Cellulose Acetate used in photography are prepared from Cellulose.
Synthetic polymers: Those polymers which are prepared in the laboratory are called synthetic Bakelite, Polythene, synthetic fibers and rubbers are some of its examples.
15.8 Distinguish between the terms homopolymer and copolymer and give an example of each.
15.8 Copolymers are those polymers that consist of more than one monomeric repeating unit. Some of the copolymers are Saran, Butadiene, Nitrile Rubber, Butyl Rubber, Viton and many more.
Homopolymers are those in which there is only one monomeric unit. Some of the examples of homopolymers are polypropylene, Polythene and many more.
15.9 How do you explain the functionality of a monomer?
15.9
The functionality of a monomer is defined as the number of bonds that a monomer's repeating unit forms in a polymer with other monomers. A linear polymer is formed by polymerizing if the functionality of monomer is two and is bifunctional (a thermoplastic).
15.10 Define the term polymerisation.
15.10
In chemical reactions when monomer units form chains or three–dimensional networks, it is known as polymerization. Various methods of polymerization are Step-growth polymerization, Chain-growth polymerization and Condensation polymerization.
15.11 Is ( NH-CHR-CO )n , a homopolymer or copolymer?
15.11
It is polyvinylchloride. It is a homopolymer as it is made up of the same type of repeating monomeric units.
15.12 How can you differentiate between addition and condensation polymerisation?
15.12
In Addition polymerisation, monomers generally join together to form saturated There are three steps to chain reaction to form addition polymer, they are initiation, propagation and termination. In condensation polymerisation, functional groups of two monomers react together to release a small molecule to form a polymer. Generally, small molecules like water or HCl are released as by-products.
15.13 Explain the term copolymerisation and give two examples.
15.13
Copolymers are those polymers that consist of more than one monomeric repeating unit. Copolymerisation is a process of reacting a mixture of more than one monomeric species and form a copolymer. The copolymer can be made not only by chain growth polymerisation but by step growth polymerisation also. For example, a mixture of 1, 3 – butadiene and styrene forms Buna-S and 1-3 – butadiene and acrylonitrile form Buna-N.
15.14 Write the free radical mechanism for the polymerisation of ethene.
15.14
The chain is initiated by free radicals, Ra•, produced by the reaction between some of the ethene and the oxygen initiator.
Chain propagation
Each time a free radical hits an ethene molecule a new longer free radical is formed.
Ra• + CH2 = CH2→ RaCH2CH2•
RaCH2CH2• + CH2 = CH2→ RaCH2CH2CH2CH2 •
Chain termination
Eventually two free radicals hit each other producing a final molecule. The process stops here because no new free radicals are formed.
Ra(CH2)m• + •(CH2)n Ra → Ra(CH2)m(CH2)nRa
Because chain termination is a random process, polyethene will be made up of chains of all sorts of different lengths.
15.15 Define thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers with two examples of each.
15.15
Thermoplastic Polymers: They are linear or slightly branched long chain molecules capable of repeatedly softening on heating and hardening on cooling. They possess intermolecular forces of attraction intermediate between elastomers and Some common thermoplastics are polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyl, etc.
Thermosetting Polymers: They are cross-linked or heavily branched molecules, which on heating undergo extensive cross-linking in moulds and again become infusible. Some common examples are Bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resins, etc.
15.16 Write the monomers used for getting the following polymers. (i) Polyvinyl chloride (ii) Teflon (iii) Bakelite
15.16
(i) Ethylene dichloride
(ii) Tetrafluoroethene
(iii) Phenol and formaldehyde
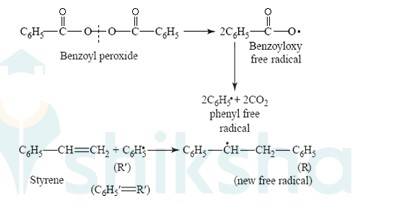
15.17 Write the name and structure of one of the common initiators used in free radical addition polymerisation.
15.17 One of the common initiators used in free radical addition polymerization is Benzoyl peroxide. Its structure is
15.18 How does the presence of double bonds in rubber molecules influence their structure and reactivity?
15.18
Natural rubber is a linear cis-1, 4-polyisoprene in which double bonds are present between C2& C3. It increases the elasticity of the rubber, as the chains are held together by weak van there waals forces and have coiled structure. Therefore, the natural rubber has coiled structure & shows elasticity & is non-crystalline.
15.19 Discuss the main purpose of vulcanisation of rubber.
15.19
Vulcanization of natural rubber is done to improve upon all these properties. In this process, a mixture of raw rubber with sulphur and appropriate additive is heated at a temperature range between 373 K and 415 K.
This is a slow process; therefore, some additives like zinc oxide etc. are used to accelerate the process. During this process, sulphur cross links are formed which makes rubber hard, tough with greater tensile strength .The vulcanized rubber has excellent elasticity, low water absorption, resistance to oxidation & organic solvents.
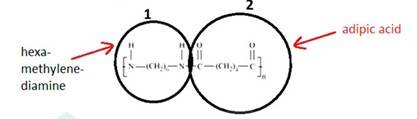
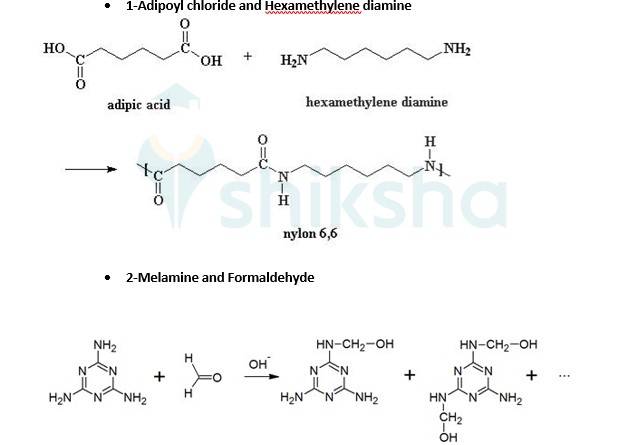
15.20 What are the monomeric repeating units of Nylon-6 and Nylon-6,6?
15.20
Monomeric units of nylon-6 is Caprolactam and for Nylon-6,6 is adipoyl chloride and hexamethylene diamine.
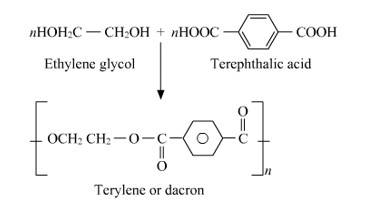
15.23 How is dacron obtained from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid?
15.23
Dacron is a polyester batting that should be added to any foam surface so that it will not be exposed directly to the fabric. Dacron has many indispensable qualities like batting reduces the friction foam has, and thus reduces wear to fabric and because polyester batting remains springy, it is ever ready to put some light pressure against fabric. This means that even as the fabric stretches with age (and always happens) batting will push against the fabric and keep wear-worn waves from developing.
15.24 What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
15.24
Biodegradable polymers are designed to degrade into simpler components like water, CO2, Nitrogen etc. upon disposal by the action of living organisms. Extraordinary progress has been made in the development of practical processes and products from polymers such as starch, cellulose, and lactic acid. The need to create alternative biodegradable water- soluble polymers for down-the-drain products such as detergents and cosmetics has taken on increasing importance. Aliphatic polyesters are one of the important classes of biodegradable polymer. Example. Poly β-hydroxybutyrate – co-β-hydroxy valerate (PHBV)
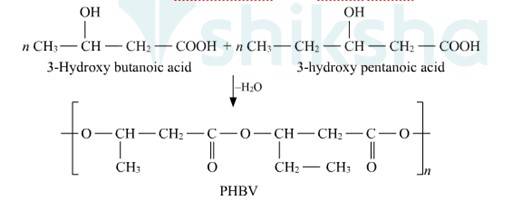
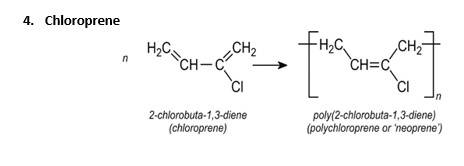
15.21 Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: (i) Buna-S (ii) Buna-N (iii) Dacron (iv) Neoprene
15.17 Kindly consider the following

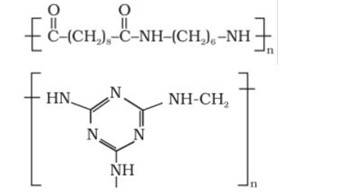
15.22 Identify the monomer in the following polymeric structures.
Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th Exam
Student Forum
Other Similar chapters for you
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Polymers
- Surface Chemistry
- General Principles & Processes of Isolating Elemen
- P Block Elements
- Alcohol Phenol And Ethers
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Amines
- NCERT Chemistry 12th
- Biomolecules
- Coordination Compounds
- Block D and F Elements
- Chemical Kinetics
- Electrochemistry
