BHU scientists find way for speedy cure of chronic wounds
The findings of the study have been published in the National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Institutes of Health, United States.
A team of scientists from Banaras Hindu University (BHU) has conducted an important study that will benefit those who are suffering from chronic wounds, particularly with diabetic foot ulcers. The team led by Prof Gopal Nath of the department of Microbiology, Institute of Medical Sciences, found out that wounds that took months to years to heal could be cured in days or months. The findings of the study have been published in the National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Institutes of Health, United States.
The other members of the team involved in the clinical studies include Prof SK Bhartiya, Prof VK Shukla, Dr Pooja Gupta, Dr Harishankar Singh, Dr Dev Raj Patel, Rajesh Kumar, Dr Rina Prasad, Subhas Lalkarn. Prof Nath said that a wound is defined as a breach in the skin or body tissues due to injury. An acute wound is defined as a recent break that is yet to progress through sequential stages of healing. The wounds where the normal healing process is stalled due to underlying pathology (vascular and diabetes etc.) or infection beyond three months is defined as chronic wound. While chronic wounds always get infected, the contaminated wounds are reasonably susceptible to infection. Infection with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and biofilm formation halt healing progress. These wounds cause significant psychological and physical morbidity.
The traditional treatment strategies often succeed in healing wounds, he said adding still many wounds have been observed recalcitrant to them, leading to persistence and recurrent infections. Search for alternatives to antibiotics has now become a compulsion. Fortunately, bacteriophage therapy is a re-emerging solution to antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Prof Nath’s team carried out phage therapy of acute and chronic infected wounds in animals and clinical studies. It showed efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a mice wound model. Furthermore, they evaluated the efficacy of phage cocktails in animal models’ acute and chronic osteomyelitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Moreover, they also observed biofilm eradication from K wire in rabbits’ wound infection model.
Read More:

- SWAYAM-NPTEL launches 590+ online certification courses for January 2022 semester
-
One in Four MU-affiliated colleges functioning without principal: RTI report
-
Lucknow University partners UK's varsity to provide fine arts opportunities
- 75 start-ups to get grants assistance, mentorship, and incubation linkage support: Govt
Follow Shiksha.com for latest education news in detail on Exam Results, Dates, Admit Cards, & Schedules, Colleges & Universities news related to Admissions & Courses, Board exams, Scholarships, Careers, Education Events, New education policies & Regulations.
To get in touch with Shiksha news team, please write to us at news@shiksha.com

 Call 8585951111
Call 8585951111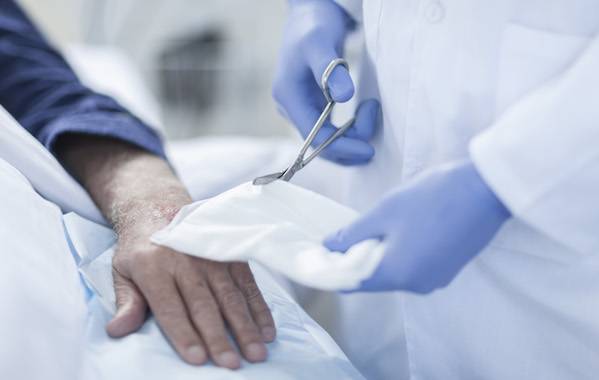
She has over 10 years of experience in the education and publishing sectors. She specialises in exam coverage and content creation. At Shiksha, she writes, analyses, and presents information for students preparing f
Read Full Bio