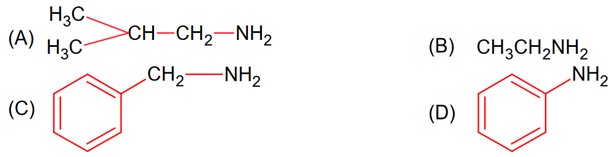- Redox Reactions Long Answer Type Questions
- JEE Mains 2021
- JEE Mains 2025
- JEE Mains 2021
- KJCnAJKCNsJKD
Redox Reactions Long Answer Type Questions
| 1. Explain redox reactions on the basis of electron transfer. Give suitable examples. |
| Ans: The given reaction is a redox change. 2Na(s)+H2(g)→2NaH(s) The half reaction is: 2Na(s)→2Na+(g)+2e- The other half reaction is: H2(g)+2e-→2H-(g) This splitting of the reaction into two half-reactions automatically reveals here that sodium is oxidized, and hydrogen is reduced. Any substance which loses electron is oxidized and gains electron is reduced hence is the case of sodium and hydrogen atoms respectively. Hence, the complete reaction is a redox change. |
| 2. On the basis of standard electrode potential values, suggest which of the following reactions would take place? (Consult the book for E V value). (i) Cu + Zn2+ → Cu2+ + Zn (ii) Mg + Fe2+ → Mg2+ + Fe (iii) Br2 + 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2Br– (iv) Fe + Cd2+ → Cd + Fe2+ |
| Ans: On the basis of standard reduction potential suggested in the reactivity series (ii) reaction can take place as Mg has more negative value of Eᶱcell. Hence, Mg will be oxidized by losing electron and iron will be reduced by gaining electron. |
| 3. Why does fluorine not show disproportionate reaction? |
| Ans: Disproportionate is defined as the reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states So, to occur such type of redox reaction, the element should exist in at least three oxidation states. So that element present in the intermediate state and it can change to both higher and lower oxidation state during disproportionate reaction. Fluorine is the most electronegative element and a strong oxidizing agent and is the smallest in size of all the halogens. It does not show a positive oxidation state (shows only −1 oxidation state) and hence, does not undergo disproportionate reaction. |
| 4. Write redox couples involved in the reactions (i) to (iv) given in question 2. |
| Ans: Redox couple are given as Cu2+/Cu and Zn2+/Zn Mg2+/Mg and Fe2+ /Fe Br2/Br- and Cl2 / Cl- Fe2+ /Fe and Cd2+/Cd |
Commonly asked questions
Explain redox reactions on the basis of electron transfer. Give suitable examples.
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The given reaction is a redox change.
2Na (s)+H2 (g)→2NaH (s)
The half reaction is:
2Na (s)→2Na+ (g)+2e-
The other half reaction is:
H2 (g)+2e-→2H- (g)
This splitting of the reaction into two half-reactions automatically reveals here that sodium is oxidized, and hydrogen is reduced. Any substance which loses electron is oxidized and gains electron is reduced hence is the case of sodium and hydrogen atoms respectively. Hence, the complete reaction is a redox change.
On the basis of standard electrode potential values, suggest which of the following reactions would take place? (Consult the book for E V value).
(i) Cu + Zn2+ → Cu2+ + Zn
(ii) Mg + Fe2+ → Mg2+ + Fe
(iii) Br2 + 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2Br–
(iv) Fe + Cd2+ → Cd + Fe2+
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
On the basis of standard reduction potential suggested in the reactivity series (ii) reaction can take place as Mg has more negative value of E? cell. Hence, Mg will be oxidized by losing electron and iron will be reduced by gaining electron.
Why does fluorine not show disproportionate reaction?
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Disproportionate is defined as the reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states So, to occur such type of redox reaction, the element should exist in at least three oxidation states. So that element present in the intermediate state and it can change to both higher and lower oxidation state during disproportionate reaction. Fluorine is the most electronegative element and a strong oxidizing agent and is the smallest in size of all the halogens. It does not show a positive oxidation state (shows only −1 oxidation state) and hence, does not undergo disproportionate reaction.
Write redox couples involved in the reactions (i) to (iv) given in question 2.
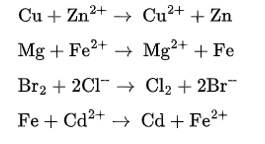
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Redox couple are given as
Cu2+/Cu and Zn2+/Zn
Mg2+/Mg and Fe2+ /Fe
Br2/Br- and Cl2 / Cl-
Fe2+ /Fe and Cd2+/Cd
Find out the oxidation number of chlorine in the following compounds and arrange them in increasing order of oxidation number of chlorine. NaClO4 , NaClO3 , NaClO, KClO2 , Cl2O7 , ClO3 , Cl2O, NaCl, Cl2 , ClO2 . Which oxidation state is not present in any of the above compounds?
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We can calculate the oxidation states by - ]
NaClO4 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +7
Suppose oxidation number of chlorine is x then, 1 + x + 4 × (−2) = 0
∴ x - 7 = 0
x = +7
We can calculate, the oxidation states, as given below-
NaClO3 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +5
? NaClO Oxidation no. of chlorine = +1
? KClO2 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +3
? Cl2O7 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +7
ClO3 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +6
Cl2O Oxidation no. of chlorine = +1
NaCl Oxidation no. of chlorine = −1
Cl2 Oxidation no. of chlorine = 0
ClO2 Oxidation no. of chlorine = +4.
Oxidation state (+2) is not present in any of the above compounds.
Which method can be used to find out strength of reductant/oxidant in a solution? Explain with an example.
This is a Long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We can Measure the electrode potential of the given species by connecting the redox couple of the given species with standard hydrogen electrode. If it is positive, the electrode of the given species acts as reductant and if it is negative, it acts as an oxidant. Find the electrode potentials of the other given species in the same way, compare the values and determine their comparative strength as an reductant or oxidant. Example Measurement of standard electrode potential of electrode E? Zn2+/Zn using SHE as a reference electrode.
Types of Redox Reactions
The different types of Redox Reactions are:
Decomposition Reaction
Combination Reaction
Displacement Reaction
Disproportionation Reactions
The reaction
Cl2 (g) + 2OH– (aq) → ClO– (aq) + Cl– (aq) + H2O (l)
represents the process of bleaching. Identify and name the species that bleaches the substances due to its oxidising action.
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The given reaction is as below-
Cl2 (g) +2OH-- (aq)→ClO-- (aq)+ Cl-- (aq) + H2O (l)
In the given reaction, oxidation number of Cl increases from 0 (in Cl2) to +1 (in ClO-) and decreases to -1 (in Cl-). Therefore, Cl2 is both oxidized to ClO- and reduced to Cl-. Since Cl- ion cannot act as an oxidizing agent (because it cannot decrease its O.N. lower than -1), hence, Cl2 bleaches substances due to oxidizing action of hypochlorite, ClO ion.
MnO42– undergoes disproportionation reaction in acidic medium but MnO4– does not. Give reason.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In MnO42–, Mn is in the highest oxidation state that is +7 hence here manganese cannot undergo oxidation that is why disproportionate is not possible whereas in MnO42- manganese is in +6 oxidation state which can be oxidized as well as reduced.
PbO and PbO2 react with HCl according to following chemical equations :
2PbO + 4HCl → 2PbCl2 + 2H2O
PbO2 + 4HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Why do these compounds differ in their reactivity?
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The given compound can differ in reactivity as-Lead is present in +4 oxidation state, whereas the stable oxidation state of lead in PbO is +2. PbO2 thus, can act as an oxidant (oxidising agent) and, therefore, can oxidise chloride ions of HCl into chlorine.
Nitric acid is an oxidising agent and reacts with PbO but it does not react with PbO2 . Explain why?
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since nitric acid itself is an oxidising agent therefore, it is unlikely that the reaction may occur between PbO2 and nitric acid. However, the acid-base reaction occurs between PbO and nitric acid because PbO is a basic oxide.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
(i) Permanganate ion (MnO4 – ) reacts with sulphur dioxide gas in acidic medium to produce Mn2+ and hydrogensulphate ion. (Balance by ion electron method).
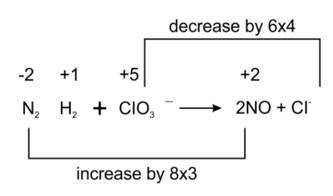
(ii) Reaction of liquid hydrazine (N2H4 ) with chlorate ion (ClO3– ) in basic medium produces nitric oxide gas and chloride ion in gaseous state. (Balance by oxidation number method)
(iii) Dichlorine heptaoxide (Cl2O7 ) in gaseous state combines with an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide in acidic medium to give chlorite ion (ClO2– ) and oxygen gas. (Balance by ion electron method)
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) 2Mn0–4 + 5S02 + 2H20 + H+?5HS0–4 + 2Mn2+
Balancing by ion-electron method:

(ii) We can balance the given reaction by oxidation number method-
Balancing by oxidation number method as to make the electron gain and loss equal as given
3N2H4 + 4ClO3- → 6NO + 4Cl- + 6H2O
The balanced chemical is given as-
(iii) We can balance the given reaction by ion electron method as
Cl2O7(g) + H2O2 (aq) → ClO2- +O2 (acidic medium)
Balancing bu ion electron method
2 × { Cl2O7 + 6H+ + 8e- → 2ClO2- + 3H2O
8 × { H2O2 → O2 + 2H+ + 2e-
The balanced chemical is given as-
2Cl2O7 + 12H+ + 16e- → 4ClO2- + 6H2O
8H2O2 → 8O2 + 16H+ + 16e-
2Cl2O7 + 8H2O2 → 4ClO2- + 6H2O + 8O2 + 4H+
Calculate the oxidation number of phosphorus in the following species.
(a) HPO32–
(b) PO43-
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Let the oxidation number of P in HPO32- be x.
Therefore, +1 + x + (-6) = -2
x = +3
Oxidation number of phosphorus is= +3.
(ii) Let the oxidation number of P in PO43- be x.
Therefore, x + (-8) = -3
x = +5
Oxidation number of phosphorus is= +5.
Calculate the oxidation number of each sulphur atom in the following compounds:
(a) Na2S2O3
(b) Na2S4O6
(c) Na₂SO₃
(d) Na2SO4
(a) let x= oxidation number of sulphur, and +1 is oxidation number of Na, -2 is oxidation number of O, also we can assume total charge on compound = 0 then solving we get.
+2 + 2x - 6 = 0
x = +2.
(b) let x= oxidation number of sulphur, and +1 is oxidation number of Na, -2 is oxidation number of O, also we can assume total charge on compound = 0 then solving we get.
+2 + x - 6 = 0
x = +4
(c) let x= oxidation number of sulphur, and +1 is oxidation number of Na, -2 is oxidation number of O, also we can assume total charge on compound = 0 then solving we get.
+2 + x - 6 = 0
x = +4
(d) let x= oxidation number of sulphur, and +1 is oxidation number of Na, -2 is oxidation number of O, also we can assume total charge on compound = 0 then solving we get.
+2 + x - 8=0
x = +6.
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method
(i) Fe2+ + H+ + Cr22–O7 → Cr3+ + Fe3+ + H2O
(ii) I2 + NO3– → NO2 + IO3 –
(iii) I 2 + S2O32– → I– + S4O62–
(iv) MnO2 + C2 O42– → Mn2+ + CO2
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) We can balance the given equation by oxidation number method-
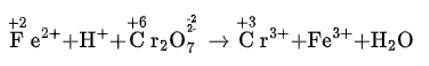
(a)Balance the increase and decrease in O.N.
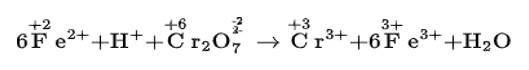
(b) Balancing H and O atoms by adding H+ and H2O molecules
(ii) We can balance the given equation by oxidation number method-
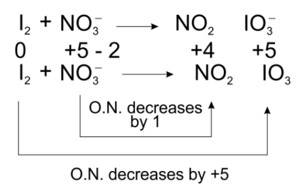
Total decrease in O.N. = 1
To equilize O.N. multiply NO3-, by 10
I2 + 10 NO3-? 10NO2 + IO3-
Balancing atoms other than O and H
I2 + 10 NO3-? 10NO2 + 2 IO3-
Balancing O and H
I2 + 10 NO3- + 8H+? 10NO2 + 2 IO3- + 4H2O
(iii) We can balance the given equation by oxidation number method
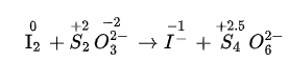
Total increase in O.N. = 0.5 × 4 = 2
Total increase in O.N. = 1 × 2 = 2
to equilize O.N. multiply S2O32– and I- by 2.
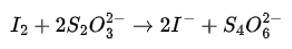
(iv) We can balance the given equation by oxidation number method-
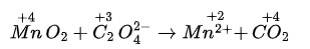
The balanced chemical reaction is given as-
Total increase in O.N. = 5 × 2= 10
To equalize O.N. multiply CO2 by 2.
MnO2 + C2O42- ? Mn2+ + 2CO2
Balance H and O by adding 2H2O on right side, and 4H+ on left side of equation.
MnO2 + C2O42- + 4H+ ? Mn2+ + 2CO2 + 2H2O .
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
(i) 3HCl(aq) + HNO3 (aq) → Cl2 (g) + NOCl (g) + 2H2O (l )
(ii) HgCl2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) → HgI2 (s) + 2KCl (aq)
(iii) Fe2O3 (s) + 3CO (g) → 2Fe (s) + 3CO2 (g)
(iv) PCl3 (l) + 3H2O (l) → 3HCl (aq) + H3 PO3 (aq)
(v) 4NH3 + 3O2 (g) → 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (g)
(i) We can write the given reaction along with their oxidation numbers as-
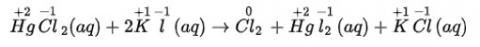
As, chlorine is oxidised in hydrochloric acid (behaving as reducing agent) -as its oxidation number is increases during the reaction from -1 to 0) and nitric acid is reduced (behaving as oxidising agent) as its oxidation number is decreases during the reaction from +5 to +3). Hence, it is the redox reaction.
(ii) We can write the given reaction along with their oxidation numbers as-
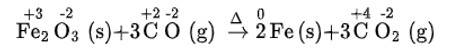
Here, oxidation number of none of the atoms change hence it is not a redox reaction.
(iii) We can write the given reaction along with their oxidation numbers as-
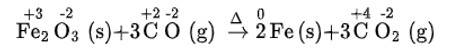
As, carbon is oxidised in carbon monoxide (behaving as reducing agent) -as its oxidation number is increases during the reaction from +2 to +4) and ferric oxide is reduced (behaving as oxidising agent) as its oxidation number is decreases during the reaction from +3to 0). Hence, it is the redox reaction.
(iv) We can write the given reaction along with their oxidation numbers as-
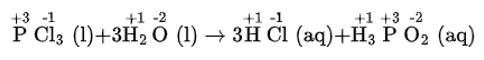
Here, oxidation number of none of the atoms change hence it is not a redox reaction.
(v) We can write the given reaction along with their oxidation numbers as-
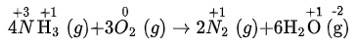
As, nitrogen is oxidised in ammonia (behaving as reducing agent) -as its oxidation number is increases during the reaction from -3 to 0) and oxygen is reduced (behaving as oxidising agent) as its oxidation number is decreases during the reaction from 0 to -2). Hence, it is the redox reaction.
Balance the following ionic equations
(i) Cr2 O72– + H+ + I– → Cr3+ + I2 + H2O
(ii) Cr2 O72– + Fe2+ + H+ → Cr3+ + Fe3+ + H2O
(iii) MnO4– + SO32– + H+ → Mn2+ + SO42– + H2O
(iv) MnO4– + H+ + Br– → Mn2+ + Br2 + H2O
This is a Short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) The balanced chemical is given as –
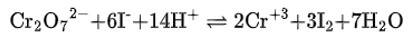
(ii) The balanced chemical is given as –
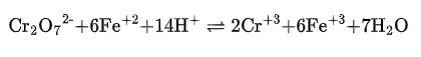
(iii) The balanced chemical is given as –
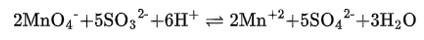
(iv) The balanced chemical is given as –
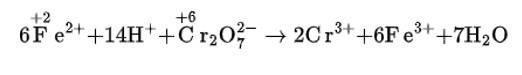
Which of the following is not an example of redox reaction?
(i) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(ii) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(iii) 2K + F2 → 2KF
(iv) BaCl2 + H2 SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
option (iv) is the correct answer.
Redox reaction is defined as the simultaneous oxidation and reduction of reacting species. Thus, change in oxidation state will decide whether a reaction is redox or not. Thus, assigning the oxidation states as:
(i) CuO + H2→ Cu + H2O
Here, oxidation of H and reduction of Cu is taking place.
(ii) Fe2O3 + 3CO→ 2Fe + 3CO2
Here, oxidation of C and reduction of Fe is taking place.
(iii) 2K + F2→2KF
Here, the oxidation of K and reduction of F is taking place.
(iv) BaCl2 + H2SO4→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
This is not a redox reaction, but it is a double displacement reaction.
The more positive the value of EV , the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
EV values: Fe3+/Fe2+ = + 0.77; I2 (s)/I– = + 0.54;
Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34; Ag+/Ag = + 0.80V
(i) Fe3+
(ii) I2 (s)
(iii) Cu2+
(iv) Ag+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv) is the correct answer
The strongest oxidising agent means it has greater tendency to oxidise other species and itself gets easily reduced. So higher the E? values, stronger is the oxidising agent it is. Thus, Ag+ having the highest positive E? value among the given systems, is the strongest oxidising agent.
EᶱV values of some redox couples are given below. On the basis of these values choose the correct option.
EᶱV values : Br2 /Br– = + 1.90; Ag+ /Ag(s) = +0.80
Cu2+/Cu(s) = + 0.34; I2 (s)/I– = + 0.54
(i) Cu will reduce Br–
(ii) Cu will reduce Ag
(iii) Cu will reduce I–
(iv) Cu will reduce Br2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv) is the correct answer
Reduction potential is defined as the tendency of the specie to get reduced. More positive the value of E® , greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced and stronger is the oxidising agent.
On the basis of the given E® values, the order of getting reduced is:
Br2Ag + I2Cu2+
Hence, Cu has the least tendency to get reduced and will itself gets oxidise and reduce other species as: Br2? , Ag+ and I2.
Using the standard electrode potential, find out the pair between which redox reaction is not feasible.
EᶱV values : Fe3+/Fe2+ = + 0.77; I2 /I– = + 0.54
Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34; Ag+ /Ag = + 0.80 V
(i) Fe3+ and I–
(ii) Ag+ and Cu
(iii) Fe3+ and Cu
(iv) Ag and Fe3+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv) is the correct answer.
E? will be negative for the pair Ag and Fe3+. Hence the reaction is not feasible.
Thiosulphate reacts differently with iodine and bromine in the reactions given below:
2S2O32– + I2 → S4O62– + 2I– S2O32–+ 2Br2 + 5H2O → 2SO42– + 2Br– + 10H
Which of the following statements justifies the above dual behaviour of thiosulphate?
(i) Bromine is a stronger oxidant than iodine.
(ii) Bromine is a weaker oxidant than iodine.
(iii) Thiosulphate undergoes oxidation by bromine and reduction by iodine in these reactions.
(iv) Bromine undergoes oxidation and iodine undergoes reduction in these reactions.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) is the correct answer.
Standard reduction potential of bromine is higher than Iodine, hence Bromine is a stronger oxidant than iodine.
The oxidation number of an element in a compound is evaluated on the basis of certain rules. Which of the following rules is not correct in this respect?
(i) The oxidation number of hydrogen is always +1.
(ii) The algebraic sum of all the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero.
(iii) An element in the free or the uncombined state bears oxidation number zero.
(iv) In all its compounds, the oxidation number of fluorine is – 1
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) is the correct answer
In ionic hydrides hydrogen exists in -1 oxidation state because the hydrogen acquires negative charge in the presence of its companion.
In which of the following compounds, an element exhibits two different oxidation states.
(i) NH2OH
(ii) NH4NO3
(iii) N2H4
(iv) N3H
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
The oxidation states are given below-
In NH2OH oxidation of N is -1.
NH4NO3 exists as NH4+.NO3-,
Thus, the oxidation state of N in NH4+ is -3 while in NO3? is +5.
In N2H4 oxidation of N is -2
In N3H oxidation of N is
Which of the following arrangements represent increasing oxidation number of the central atom?
(i) CrO2 – , ClO3 – , CrO4 2– , MnO4 –
(ii) ClO3 – , CrO42– , MnO4 – , CrO2
(iii) CrO2 – , ClO3 – , MnO4 – , CrO4 2–
(iv) CrO4 2– , MnO4 – , CrO2 – , ClO3–
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) is the correct answer
Let the oxidation number of central atom be 'y'.
Oxidation number of O = −2
CrO2−: y + 2 × (−2) = −1
y − 4 = −1 or y = +3
CrO42−? : y + 4 × (−2) = −2
y − 8 = −2 or y = +6
ClO3−: y + 3 × (−2) = −1
y − 6 = −1 or y = +5
MnO4−: y + 4 × (−2) = −1
y − 8 = −1 or y = +7
increasing order of oxidation number of the central atom is:
CrO2 – , ClO3 –, CrO4 2–, MnO4
The largest oxidation number exhibited by an element depends on its outer electronic configuration. With which of the following outer electronic configurations the element will exhibit largest oxidation number?
(i) 3d1 4s2
(ii) 3d3 4s2
(iii) 3d5 4s1
(iv) 3d5 4s2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv) is the correct answer
For 3d1 4s2 can exhibit the highest oxidation state as 2+1 = +3,
For 3d34s2can exhibit the highest oxidation state as 2+3 = +5
For 3d54s1can exhibit the highest oxidation state as 1+5 = +6
For 3d54s2can exhibit the highest oxidation state as 2+5 = +7
Identify disproportionation reaction
(i) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
(ii) CH4 + 4Cl2 → CCl4 + 4HCl
(iii) 2F2 + 2OH– → 2F– + OF2 + H2O
(iv) 2NO2 + 2OH– → NO2 – + NO3 – + H2O
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv) is the correct answer.
Disproportionate reactions are defined as the reactions in which the same substance is oxidized as well as reduced. Here, the below reaction is given as-
2NO2 + 2OH- →NO2 -+ NO3- +H2O
In this reaction, N is both oxidized as well as reduced since O.N. of N increases from +4 in NO3−? to +5 in NO2 ? and decreases from +4 in NO to +3 in NO2−.
Which of the following elements does not show disproportionation tendency?
(i) Cl
(ii) Br
(iii) F
(iv) I
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
As, Cl, Br, I all are having -1 to +7 oxidation state. But Oxidation state of F is fixed (-1) as it is the most electronegative element and do not loose electron. Hence, it does not show disproportionate tendency.
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are not true about the following decomposition reaction.
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
(i) Potassium is undergoing oxidation
(ii) Chlorine is undergoing oxidation
(iii) Oxygen is reduced
(iv) None of the species are undergoing oxidation or reduction
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Options (iii) and (iv) are the correct answers.
As, in the given reaction below-
2KClO3→2KCl+3O2
Potassium remains in same oxidation state and oxygen is being oxidized
Identify the correct statement (s) in relation to the following reaction:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
(i) Zinc is acting as an oxidant
(ii) Chlorine is acting as a reductant
(iii) Hydrogen ion is acting as an oxidant
(iv) Zinc is acting as a reductant
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii) and (iv) is the correct answer.
The given equation is as-
Zn+2HCl→ZnCl2+H2
In this Zn has a negative E? value, which means it will undergo oxidation and will act as a reducing agent (reductant). Zn can produce H2 gas with HCl, as hydrogen has higher standard reduction potential than Zn, hydrogen will undergo reduction and will act as oxidant.
The exhibition of various oxidation states by an element is also related to the outer orbital electronic configuration of its atom. Atom(s) having which of the following outermost electronic configurations will exhibit more than one oxidation state in its compounds.
(i) 3s 1
(ii) 3d 1 4s 2
(iii) 3d2 4s2
(iv) 3s2 3p3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii), (iii) and (iv) are the correct answers.
Elements that are having only s-electrons in the valence shell do not show more than one oxidation state (shows only one oxidation state of +1). Hence, (b), (c) having incompletely filled d-orbital's in the outermost shell show variable oxidation states. Element with outer electronic configuration as 3d1 4S2 shows variable oxidation states of +2 and +3 and the element with outer electronic configuration as 3d24S2 shows variable oxidation states of +2, +3 and +4. P-Block elements also show variable oxidation states due to involvement of d-orbital's and inert pair effect. Hence, element having 3S2 3P3 as the outer electronic configuration shows variable oxidation states of +3 and +5 due to involvement of d-orbital's.
Identify the correct statements with reference to the given reaction.
P4 + 3OH– + 3H2O → PH3 + 3H2PO2
(i) Phosphorus is undergoing reduction only.
(ii) Phosphorus is undergoing oxidation only.
(iii) Phosphorus is undergoing oxidation as well as reduction.
(iv) Hydrogen is undergoing neither oxidation nor reduction.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Hence, option (iii) and (iv) are the correct answers.
The given reaction is as below-
P4+3OH- +3H2O→PH3 + 3H2PO2-
The above reaction is a kind of disproportionate reaction in which phosphorous is being reduced as well as oxidized whereas hydrogen remains same in +1 oxidation state.
Which of the following electrodes will act as anodes, when connected to Standard Hydrogen Electrode?
(i) Al/Al3+ Eᶱ V = –1.66
(ii) Fe/Fe2+ Eᶱ V= – 0.44
(iii) Cu/Cu2+ Eᶱ V= + 0.34
(iv) F2 (g)/2F– (aq) Eᶱ V= + 2.87
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) and (ii) are the correct answers.
The ones which will act as anodes when connected to standard hydrogen electrode as they have more negative standard reduction potential as compared to standard hydrogen electrode. The one which will act as cathodes when connected to standard hydrogen electrode as they have more positive standard reduction potential as compared to standard hydrogen electroDE
Match Column I with Column II for the oxidation states of the central atoms.
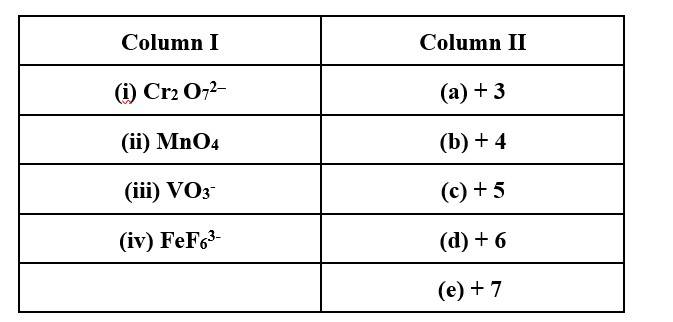
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (d); (ii) → (e); (iii) → (c); (iv) → (a)
Match the items in Column I with relevant items in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Ions having positive charge |
(a) +7 |
|
(ii) The sum of oxidation number of all atoms in a neutral molecule. |
(b) –1 |
|
(iii) Oxidation number of hydrogen ion (H+). |
(c) +1 |
|
(iv) Oxidation number of fluorine in NaF. |
(d) 0 |
|
(v) Oxidation number of fluorine in NaF. |
(e) Cation |
|
(f) Anion |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (e); (ii) → (d); (iii) → (c); (iv) → (b); (v) → (f).
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason (R) : Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) Both A and R are false.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) is the correct answer.
Fluorine is most electronegative element that is why it is best oxidant among halogens
Assertion (A): In the reaction between potassium permanganate and potassium iodide, permanganate ions act as oxidising agent.
Reason (R): Oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7 during the reaction.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii)A is true but R is false.
(iv) Both A and R are false.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii) is the correct answer
As permanganate ion changes to MnO2
Assertion (A) : The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen is an example of disproportionation reaction.
Reason (R) : The oxygen of peroxide is in –1 oxidation state and it is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 and –2 oxidation state in H2O.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) Both A and R are false.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) is the correct answer.
Here the oxygen of peroxide, which is present in -1 state, is converted to zero oxidation state in O2 undergoing oxidation and decreases to -2 oxidation state in H2O undergoing reduction
Assertion (A) : Redox couple is the combination of oxidised and reduced form of a substance involved in an oxidation or reduction half cell.
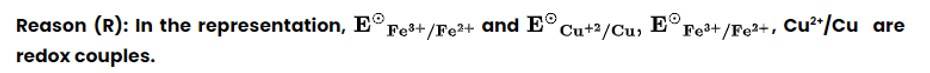
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) Both A and R are false
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
A redox couple is defined as pair of compounds or elements having together the oxidised and reduced forms of it and taking part in an oxidation or reduction half reaction.
JEE Mains 2021
JEE Mains 2021
Commonly asked questions
The total number of amines among the following which can be synthesized by Gabriel synthesis is………………
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is used for 1° Aliphatic /alicyclic amine
1° Amine
CH3 – CH2 – NH2
Sucrose hydrolyses in acid solution into glucose and fructose following first order rate law with a half – life of 3.33 h at 25°C. After 9h, the fraction of sucrose remaining is f. The value of log10 is………………….× 10-2. (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[Assume: In 10 = 2.303, In2 = 0.693]
The solubility product of Pbl2 is 8.0 × 10-9. The solubility of lead iodide in 0.1 molar solution of lead nitrate is x × 10-6 mol/L. The value of x is…………………… (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[Given
Pb (NO3)2 -> Pb2+ +
0.1 M-
-0.1 M 0.1 M
S = 141 × 10-6 M
The formula of a gaseous hydrocarbon which requires 6 times of its own volume of O2 for complete oxidation and produces 4 times its own volume of CO2 is CxHy. The value of y is…………….
V 6V - -
- - 4V
Volume of CO2 = 4 ×
Vx = 4V
x = 4
Volume of O2 = 6 ×
y = 8
1.86g of aniline completely reacts to form acetanilide. 10% of the product is lost during purification. Amount of acetanilide obtained after purification (in g) is…………………..× 10-2.
W = 2.70 g
Mass produced actual = 2.70
The volume occupied by 4.75 of acetylene gas at 50°C and 740 mmHg pressure is………………….L (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[Given R = 0.0826L atm K-1 mol-1]
W = 4.75 g
T = 323 K, R = 0.0826
V =
The magnitude of the change in oxidizing power of the couple is x × 10-4 V, if the H+ concentration is decrease from 1M to 10-4M at 25°C (Assume concentration of and Mn2+ to be same on change in H+ concentration). The value of x is………………… (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[Given : ]
[H+] = 1M
So, difference in E1 & E2 is
= 0.3776 V
= 3776 × 10-4 V
Assuming ideal behaviour, the magnitude of log K for the following reaction at 25°C is x × 10-1. The value of x is ………………… (integer answer)
3HC
[Given : = -2.04 × 105J mol-1 ; R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1]
Equating (i) & (ii)
-2.303 RTlogk = 4.88 × 105
So; magnitude of log K = 855 × 10-1
C6H6 freezes at 5.5°C. The temperature at which a solution of 10g of C4H10 in 200g of C6H6 freeze is……………….. °C (The molal freezing point depression constant of C6H6 is 5.12°C/m)
Among the following allotropic forms of sulphur, the number of allotropic forms, which will show paramagnetism is…………………….
(a) α - sulphur (b) β - sulphur (c) S2 - form
α - sulphur & β - sulphur – Diamagnetic, S2 – form is paramagnetic due to presence of unpaired electron in π* orbital like O2.
Number of amphoteric compounds among the following is___________.
Beo & Be (OH)2 are amphoteric in nature, because they react with both acid and base
The stepwise formation of is given below:
The value of stability constants k1, k2, k3 and k4 are respectively.
The overall equilibrium constants for dissociation of The value of x is________ (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
Stability constant are :
K1 = 104
K2 = 1.58 × 103
K3 = 5 × 102
K4 = 102
Overall stability constant K will be
K = K1 × K2 × K3 × K4
= 7.9 × 1011
Now, overall equilibrium constant for dissociation of [Cu (NH3)4]2+ is
= 1.26 × 10-12
So; x = 1 (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
For the reaction A(g) ® B(g) the value of the equilibrium constant at 300K and 1 atm is equal to 100.0 The value of for the reaction at 300K and 1 atm in J mol-1 is -xR, where x is_________.
(Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[R = 8.31 J mol-1 K-1 and In 10 = 2.3]
A (g) -> B (g) KP = 100
at 300 K and 1 atm
Using
=-R × 300 × 2 × 2.3
So; x = 1380.
At 1990K and 1 atm pressure, there are equal number of Cl2 molecules and Cl atoms in the reaction mixture. The value of KP for the reaction Cl2(g) 2Cl(g) under the above conditions is x × 10-1. The value of x is______ (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
Initially -> 1 mol -
At eq. 1-x mol 2x mol
Here; molecules of Cl2 = atoms of Cl
i.e moles of Cl2 = moles of Cl
So : 1 – x = 2x x = 1/3
Moles of Cl2 at equibrium =
Moles of Cl at equilibrium =
Total moles =
Now:
Here : x = 5
When 9.45g of ClCH2COOH is added to 500ml. of water, its freezing point drops by 0.5°C. The dissociation constant of ClCH2 COOH is x × 10-3. The value of x is__________ (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
Kf = 1.86
Using, density of water = 1g / mL
i = ?
i = 1.344
Now, using
n for ClCH2COOH = 2
a =
Using
So; x = 36
The reaction of sulphur in alkaline medium is given below
The values of ‘a’ is____________. (Integer answer)
The balanced equation is :
Here ; a = 12
4.5g of compound A (MW = 90) was used to make 250 mL of its aqueous solution. The molarity of the solution in M is × 10-1. The value of x is_________ (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
W = 4.5 g
M.W = 90
V = 250 ml
Using M =
M = 2 × 10-1 M
So, x = 2
A proton and a Li3+ nucleus are accelerated by the same potential. If denote the de Brogle wavelength of Li3+ and proton respectively, then the value of The value of x is_________ (Rounded off to the nearest integer) [Mass of Li3+ = 8.3 mass of proton]
Using
= 0.2 = 2 × 10-1
So; x = 2
The coordination number of an atom in a body- centred cubic structure is___________.
[Assume that the lattice is made up of atoms]
Coordination no. of an atom in BCC is 8.
Gaseous cyclobutene isomerizes to butadiene in a first order process which has ‘k’ value of 3.3 × 10-4 s-1 at 153°C. The time in minutes it takes for the isomerization to proceed 40% to completion at this temperature is______ (Rounded off the nearest integer)
K = 3.3 × 10-4 s-1
Time for 40% completion ; t
Using
3.3 × 10-4 =
so; the nearest integer is 26.
The volume (in ) of required to neutralise of phosphinic acid is
Phosphinic acid is hypo phosphorous acid .
For neutrization
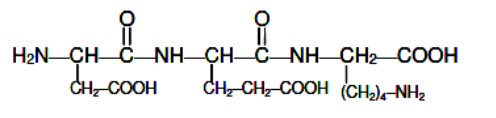
The number of groups present in a tripeptide Asp - Glu - Lys is
Asp - Glu - Lys pripeptide is:
If of an aqueous solution containing of a protein is isotonic with one litre of another aqueous solution containing of a protein , at , the ratio of the molecular masses of and is (to the nearest integer).
For isotonic solution
ffor protein
An acidic solution of dichromate is electrolyzed for 8 minutes using current. As per the following equation . The amount of obtained was . The efficiency of the process (in %) is (Take: , At. Mass of chromium )
According to Faraday law
Where efficiency
or
Putting values
So percentage efficiency
molecules are present in of a substance ' '. The molarity of a solution containing of substance ' ' in solution is .
Number of mole of
So molar mass of
Molarity
Ans.
So
JEE Mains 2025
JEE Mains 2025
Commonly asked questions
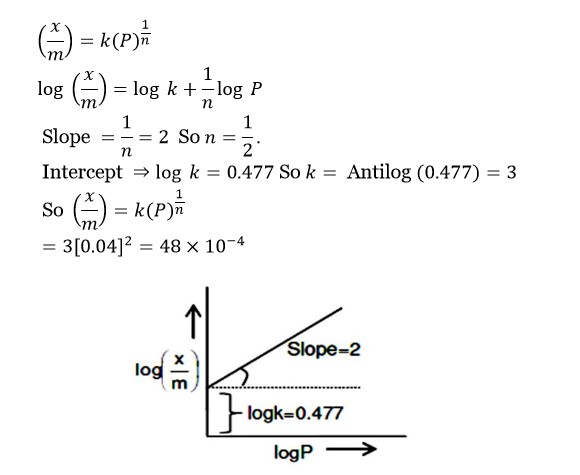
If the solubility product of AB₂ is 3.20 × 10⁻¹¹ M³, then the solubility of AB₂ in pure water is _____ × 10⁻⁴ mol L⁻¹. [Assuming that neither kind of ion reacts with water]
(x/m) = k (P)¹/?
log (x/m) = log k + (1/n) log P
Slope = 1/n = 2 So n = ½
Intercept ⇒ log k = 0.477 So k = Antilog (0.477) = 3
So (x/m) = k (P)¹/? = 3 [0.04]² = 48 × 10?
For Freudlich adsorption isotherm, a plot of log(x/m) ( y-axis) and log p (x-axis) gives a straight line. The intercept and slope for the line is 0.4771 and 2, respectively. The mass of gas adsorbed per gram of adsorbent if the initial pressure is 0.04 atm, is _____ × 10?? g. (log 3 = 0.4771)
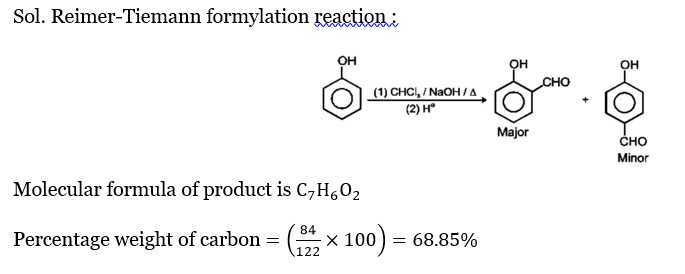
A solution of phenol in chloroform when treated with aqueous NaOH gives compound P as a major product. The mass percentage of carbon in P is (to the nearest integer) _____. (Atomic mass: C = 12; H = 1; O = 16 )
The atomic number of Unnilunium is _____.
According to IUPAC convention for naming of elements with atomic number more than 100, different digits are written in order and at the end ium is added. For digits following naming is used.
0 -nil
1-un
2-bi
3-tri
and so on.
The rate of a reaction decreased by 3.555 times when the temperature was changed from 40°C to 30°C. The activation energy (in kJmol⁻¹ ) of the reaction is _____.
log (k? /k? ) = (Ea / 2.303R) [1/T? - 1/T? ]
log (3.555) = (Ea / (2.303R) [1/303 - 1/313]
1.268 × 8.314 × 303 × 313 = 10Ea
So, Ea = 100 kJ
JEE Mains 2021
JEE Mains 2021
KJCnAJKCNsJKD
cSDVSDVSDV
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Eight Exam