- The S Block Elements Questions and Answers
- JEE MAINS 26th February 2021 first shift
The S Block Elements Questions and Answers
| 1. The s-block elements are characterised by their larger atomic sizes, lower ionisation enthalpies, invariable +1 oxidation state and solubilities of their oxosalts.In the light of these features describe the nature of their oxides, halides and oxosalts. |
| Ans: Alkali metals are ionic in nature due to their larger size. They have +1 oxidation states. Alkali metals forms three types of oxides such as peroxides, superoxides and normal oxides. The basic character of normal oxides increases from lithium oxide to caesium oxide. The halides of alkali metals are also ionic except lithium halide. Lithium halide is covalent in nature because of small size and high polarizing power. Oxosalts of alkali metal are solid water-soluble ionic compounds. Oxosalts of lithium show different properties due to small size of lithium. |
| 2. Present a comparative account of the alkali and alkaline earth metals with respect to the following characteristics: (i) Tendency to form ionic / covalent compounds |
| (i) Alkaline earth metal compounds are less ionic than alkali metals because of small size and more effective nuclear charge. |
| (ii) Nature of oxides and their solubility in water |
| (ii) Oxides of alkali metals are more basic than alkaline earth metals. This are water soluble and highly exothermic. The hydroxides of alkaline earth metals are less basic than alkali metals. |
| (iii) Formation of oxosalts |
| (iii) Alkaline earth metals give oxosalts. The reactivity of alkali metals is faster than the reactivity of alkaline earth metal. The reactivity of alkaline earth metal is less due to small size and more effective nuclear charge. |
| (iv) Solubility of oxosalts |
| (iv) The oxo salts of alkali metals are less soluble than the oxo salts of alkaline earth metal because of small size of cation and high hydration enthalpy. |
| (v) Thermal stability of oxosalts |
| (v) The thermal stability of the oxo salts of alkali metals are more than the alkaline earth metals. The sodium carbonate is stable towards heat. |
| 3. When a metal of group 1 was dissolved in liquid ammonia, the following observations were obtained: (i) Blue solution was obtained initially. (ii) On concentrating the solution, blue colour changed to bronze colour. How do you account for the blue colour of the solution? Give the name of the product formed on keeping the solution for some time. |
| Ans: (i) The alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia and give a blue solution, which is conductive in nature. A solution of sodium in liquid ammonia at -30C conducts electricity. The ammoniated electrons are responsible for the blue color of the solution as they absorb energy in the visible region of light and impart blue color to the solution. Both the ammoniated cations and ammoniated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution. Na + (x+y)NH3→[Na(NH3)x]+ + [e(NH3)y]− (ii) The blue color changes to bronze color in concentrated solution due to the formation of a cluster of metal ions. The standing blue solution liberates hydrogen gas with the formation of amide. M+ + e− + NH3→MNH2 + 12H2 |
| 4. The stability of peroxide and superoxide of alkali metals increase as we go down the group. Explain giving reason. |
| Ans: As the size of metal ions increases, the stability of peroxides and superoxides increases. Peroxide and superoxide ions combine with a large size of alkali metals. Lithium forms monoxide, sodium forms peroxide and potassium, rubidium and caesium forms superoxide. Li+O2→Li2O Na+O2→Na2O2 K+O2→KO2 |
Commonly asked questions
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): The carbonate of lithium decomposes easily on heating to form lithium oxide and CO2⋅
Reason (R): Lithium being very small in size polarises large carbonate ion leading to the formation of more stable Li2O and CO2.
(A) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) Both A and R are not correct.
(D) A is not correct but R is correct.
This is a assertion and reason type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(A) Lithium beimg small in size, polarises large carbonate ion. Polarisation is the distortion of electron cloud of the anion by the cation. Thus, the carbonate of lithium decomposes easily on heating to form lithium oxide and CO2. The reaction is shown below.
Li2CO3 → Li2O+CO2
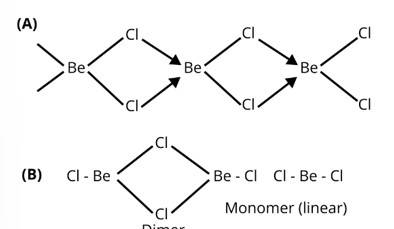
What is the structure of BeCl2 molecule in gaseous and solid state?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the solid state BeCl2 has a polymeric chain like structure. Be atom is surrounded by four Cl atoms among which two of them are bonded through covalent bond and other two are through co-ordinate bond. Structure of BeCl2 is given by structure A.
In gaseous state beryllium chloride exists as dimer (Be2Cl4) which dissociates to the monomer at about 1200 K temperature which is linear in structure.
Structure of BeCl2 in gaseous state is given by the structure B.
Present a comparative account of the alkali and alkaline earth metals with respect to the following characteristics:::
(i) Tendency to form ionic / covalent compounds
(ii) Nature of oxides and their solubility in water
(iii) Formation of oxosalts
(iv) Solubility of oxosalts
(v) Thermal stability of oxosalts
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Alkaline earth metal compounds are less ionic than alkali metals because of small size and more effective nuclear charge.
(ii) Oxides of alkali metals are more basic than alkaline earth metals. This are water soluble and highly exothermic. The hydroxides of alkaline earth metals are less basic than alkali metals.
(iii) Alkaline earth metals give oxosalts. The reactivity of alkali metals is faster than the reactivity of alkaline earth metal. The reactivity of alkaline earth metal is less due to small size and more effective nuclear charge.
(iv) The oxo salts of alkali metals are less soluble than the oxo salts of alkaline earth metal because of small size of cation and high hydration enthalpy.
(v) The thermal stability of the oxo salts of alkali metals are more than the alkaline earth metals. The sodium carbonate is stable towards heat.
Write Lewis strucure of O2 – ion and find out oxidation state of each oxygen atom? What is the average oxidation state of oxygen in this ion?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The lewis structure of O2– ion is,
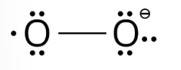
Oxygen atom having no charge has 6 electrons, so its oxidation number is zero. Oxygen atoms containing −1 charge have 7 electrons, so its oxidation number is −1. The average oxidation state of oxygen in this ion is, =1/2
Match the elements given in Column I with the colour they impart to the flame given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Cs |
(a) Apple green |
|
(ii) Na |
(b) Violet |
|
(iii) K |
(c) Brick red |
|
(iv) Ca |
(d) Yellow |
|
(v) Sr |
(e) Crimson red |
|
(vi) Ba |
(f) Blue |
This is a matching type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (f); (ii) → (d); (iii) → (b) : (iv) → (c) ; (v) → (e); (vi) → (a)
All alkali metal and alkaline earth metals except beryllium and magnesium gives characteristic color when introduced into flame. Due to released energy being absorbed in the visible region, alkali metals and alkaline earth metals gives characteristic color.
(i) Caesium imparts blue color when introduced into flame.
(ii) Sodium imparts yellow color when introduced into flame.
(iii) Potassium imparts violet color when introduced into flame.
(iv) Calcium imparts brick red color when introduced into flame.
(v) Strontium imparts crimson red color when introduced into flame.
(vi) Barium imparts apple green color when introduced into flame.
(iv) Calcium imparts brick red color when introduced into flame.
(v) Strontium imparts crimson red color when introduced into flame.
(vi) Barium imparts apple green color when introduced into flame.
Assertion (A): Beryllium carbonate is kept in the atmosphere of carbon dioxide. Reason (R): Beryllium carbonate is unstable and decomposes to give beryllium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(A) Both A and R are correct and A is the correct explanation of R.
(B) Both A and R are correct but A is not the correct explanation of R.
(C) Both A and R are not correct.
(D) A is not correct but R is correct.
This is a assertion and reason type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(A) Explanation:
Alkaline earth metals are stable at room temperature except beryllium carbonate. It decomposes to give beryllium oxide and carbon dioxide. It is kept in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide so that equilibrium shifts to the right. The reaction is shown below. BeCO3 → BeO+CO2
Based on the passage, which of the following best captures the meaning of HIF, or hypoxia-inducible factor?
A. It is a protein that increases inside the cell when the oxygen levels fall, helping the cell survive.
B. It inhibits oxygen carrying process in the body as the oxygen level increases inside the cell.
C. It enables cells to adapt quickly to the changing environment and helps in its survival.
D. It regulates the amount of oxygen available to the cell and the body during exercise.
Answer-A
Only first option clearly defines the meaning of HIF, by using the term 'protein'. Option C can be a characteristic but not a complete meaning. The meaning can be derived with the help of the following lines “When oxygen levels decrease, the HIF protein inhibits oxygen-consuming processes of the cells by altering the activity of numerous genes”.
The s-block elements are characterised by their larger atomic sizes, lower ionisation enthalpies, invariable +1 oxidation state and solubilities of their oxosalts.In the light of these features describe the nature of their oxides, halides and oxosalts.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Alkali metals are ionic in nature due to their larger size. They have +1 oxidation states. Alkali metals forms three types of oxides such as peroxides, superoxides and normal oxides. The basic character of normal oxides increases from lithium oxide to caesium oxide.
The halides of alkali metals are also ionic except lithium halide. Lithium halide is covalent in nature because of small size and high polarizing power.
Oxosalts of alkali metal are solid water-soluble ionic compounds. Oxosalts of lithium show different properties due to small size of lithium.
When a metal of group 1 was dissolved in liquid ammonia, the following observations were obtained:
(i) Blue solution was obtained initially.
(ii) On concentrating the solution, blue colour changed to bronze colour. How do you account for the blue colour of the solution?......
Give the name of the product formed on keeping the solution for some time.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) The alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia and give a blue solution, which is conductive in nature. A solution of sodium in liquid ammonia at -30C conducts electricity. The ammoniated electrons are responsible for the blue color of the solution as they absorb energy in the visible region of light and impart blue color to the solution. Both the ammoniated cations and ammoniated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution.
Na + (x+y)NH3→ [Na (NH3)x]+ + [e (NH3)y]−
(ii) The blue color changes to bronze color in concentrated solution due to the formation of a cluster of metal ions. The standing blue solution liberates hydrogen gas with the formation of amide.
M+ + e? + NH3? MNH2 + 12H2
The stability of peroxide and superoxide of alkali metals increase as we go down the group. Explain giving reason.????
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the size of metal ions increases, the stability of peroxides and superoxides increases. Peroxide and superoxide ions combine with a large size of alkali metals. Lithium forms monoxide, sodium forms peroxide and potassium, rubidium and caesium forms superoxide.
Li+O2→Li2O
Na+O2→Na2O2
K+O2→KO2
When water is added to compound (A) of calcium, solution of compound (B) is formed. When carbon dioxide is passed into the solution, it turns milky due to the formation of compound (C). If excess of carbon dioxide is passed into the solution milkiness disappears due to the formation of compound (D). Identify the compounds A, B, C and D. Explain why the milkiness disappears in the last step .??????
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Compound A reacts with water to form compound B. So, the compound A is calcium oxide. When water is added to calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide is formed. It is lime water. The compound gives a milky appearance which is compound C. The compound C is calcium carbonate. On passing, excess carbon dioxide milkiness disappears due to the formation of compound D. The compound is calcium hydrogen carbonate. The reactions are as follows:
CaO+H2O→Ca (OH)2
Ca (OH)2+CO2→CaCO3
Ca (OH)2+CO2+H2O→Ca (HCO3)2
Lithium hydride can be used to prepare other useful hydrides. Beryllium hydride is one of them. Suggest a route for the preparation of beryllium hydride starting from lithium hydride. Write chemical equations involved in the process.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Beryllium being least reactive does not form hydride by direct heating with dihydrogen. It is prepared by reacting it with lithium aluminum hydride. The reactions are shown below.
8LiH + Al2Cl6→2LiAlH4+6LiCl
2BeCl2+LiAlH4→2BeH2+LiCl+AlCl3
An element of group 2 forms covalent oxide which is amphoteric in nature and dissolves in water to give an amphoteric hydroxide. Identify the element and write chemical reactions of the hydroxide of the element with an alkali and an acid.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In group 2, only beryllium is amphoteric in nature which means it reacts with both acids and bases. Also, beryllium only forms covalent oxide due to the covalent nature. So, the element is beryllium.
It reacts with acid to form beryllium chloride and it reacts with base to form beryllate ion which is soluble in sodium hydroxide. The reaction is shown below.
Be (OH)2+2OH− → [Be (OH)4]2−
Be (OH)2+2HCl →BeCl2+2H2O
Ions of an element of group 1 participate in the transmission of nerve signals and transport of sugars and amino acids into cells. This element imparts yellow colouctor the flame in flame test and forms an oxide and a peroxide with oxygen. Identify the element and write a chemical reaction to show the formation of its peroxide. Why does the element impart colour to the flame?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The element imparts yellow colour to the flame in flame test which means the element of group 1 is sodium. Sodium is used in the transmission of nerve signals and transport of sugars and amino acids into cells. Reactions are shown below.
2Na+O2→Na2O2
4Na+O2→2Na2O
2Na2O+O2→2Na2O2
How do you account for the strong reducing power of lithium in aqueous solution?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Lithium has the highest negative reduction potential value. Due to the small size of lithium it has the highest ionization enthalpy. Due to this, the reducing power of lithium is the highest in an aqueous solution.
When heated in air, the alkali metals form various oxides. Mention the oxides formed by Li, Na and K
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Alkali metals forms oxide when reacted with air. Lithium forms monoxide, sodium forms peroxide and potassium forms superoxide.
4Li+O2→2Li2O
Na+O2→Na2O2
K+O2→KO2
Complete the following reactions
(i) O2 2– + H2O →
(ii) O2– + H2O →
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) O22−+ 2H2O → H2O2+2OH−
(ii) 2O2−+2H2O→2OH−+H2O2+O2
Lithium resembles magnesium in some of its properties. Mention two such properties and give reasons for this resemblance.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
These two elements have similar properties because of their similar atomic and ionic radii.
(i) Both are lighter element and harder than the other metals in their respective groups.
(ii) The halides of both elements, LiCl and MgCl2 are soluble in ethanol.
Name an element from Group 2 which forms an amphoteric oxide and a water soluble sulphate
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The element from group 2 is beryllium. Be (OH)2 is amphoteric. It reacts with both acids and bases. It reacts with acid to form beryllium chloride and it reacts with base to form beryllate ion which is soluble in sodium hydroxide. The reaction is shown below.
Be (OH)2+2OH−→ [Be (OH)4]2−
Be (OH)2+2HCl→BeCl2+2H2O
Beryllium sulfate are readily soluble in water.
Discuss the trend of the following:
(i) Thermal stability of carbonates of Group 2 elements.
(ii) The solubility and the nature of oxides of Group 2 elements.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) As the size of the cation increases, the thermal stability of carbonate increases. The more stable will be the oxide of an alkaline earth metal, the less stable will be the carbonate. Hence, beryllium carbonate will be highly unstable because its oxide will be stable.
(ii) Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals form oxides with oxygen and give metal oxides. The oxides are basic in nature. BeO is an exception because BeO is amphoteric.
They also react with water to form sparingly soluble hydroxides. On increasing the size of the cations beryllium oxide and magnesium oxide have the highest lattice energy and they are insoluble in water.
Why are BeSO4 and MgSO4 readily soluble in water while CaSO4, SrSO4 and BaSO4 are insoluble?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
BeSO4 and MgSO4 readily soluble in water while CaSO4, SrSO4 and BaSO4 are insoluble The greater hydration enthalpy of Be2+ and Mg2+ ions overcome the lattice enthalpy factor and therefore, their sulfates are soluble.
All compounds of alkali metals are easily soluble in water but lithium compounds are more soluble in organic solvents. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ionic compounds are formed from the alkali metals due to their large ionic size and low ionization enthalpy. Thus, they are soluble in water. But, due to the small ionic size, high ionization enthalpy, and high electronegativity of lithium, it forms compounds of covalent nature and thus, are soluble in organic solvents.
In the Solvay process, can we obtain sodium carbonate directly by treating the solution containing (NH4) 2CO3 with sodium chloride? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the Solvay process, carbon dioxide is transferred through a concentrated solution of ammoniacontaining sodium chloride, which forms ammonium carbonate followed by ammonium hydrogen carbonate. The chemicals in ammonium hydrogen carbonate are different and are heated to form sodium carbonate. NH3 is found in a solution containing NH4Cl that is heated and treated with Ca (OH)2? The reaction of (NH4)2CO3 with NaCl provides two products, Na2CO3 and NH4Cl both soluble in water which do not shift to the right balance.
Why do beryllium and magnesium not impart colour to the flame in the flame test?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The flame is due to the excitation of the electron from its higher energy state to the lower energy states. Due to the small atomic and ionic size of beryllium and magnesium, electrons are tightly bound to the atom. The electrons of Be and Mg does not gain excitation from the energy provided by the flame. Hence they do not show any flame in the flame test.
The alkali metals are low melting. Which of the following alkali metal is expected to melt if the room temperature rises to 30°C?
(i) Na
(ii) K
(iii) Rb
(iv) Cs
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option (iv)
In alkali metals, on going down the group, as the metallic strength decreases, melting point decreases. Thus, Cs has the lowest melting point and melts at 30°C.
Alkali metals react with water vigorously to form hydroxides and dihydrogen. Which of the following alkali metals reacts with water least vigorously?
(i) Li
(ii) Na
(iii) K
(iv) Cs
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option (i)
The reactivity of alkali metals increases on moving down the group. So, Li is least reactive. It will react with water least vigorously.
The reducing power of a metal depends on various factors. Suggest the factor which makes Li, the strongest reducing agent in aqueous solution.
(i) Sublimation enthalpy
(ii) Ionisation enthalpy
(iii) Hydration enthalpy
(iv) Electron-gain enthalpy
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option (iii)
Li due to its small size it has a high value of hydration enthalpy. Due to the high hydration enthalpy of Li atom, it is the strongest reducing agent in the aqueous medium.
Metal carbonates decompose on heating to give metal oxide and carbon dioxide. Which of the metal carbonates is most stable thermally?
(i) MgCO3
(ii) CaCO3
(iii) SrCO3
(iv) BaCO3
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (iv)
BaCO3 will be the most thermal stable. The size of Ba2+ is very large due to which it has low Polarising power and cannot polarise the oxygen atom. As the positive ions gets larger on moving down the group, the effect on the carbonate ion near them decreases. Thus, the carbonate ions of large cations are stable.
Which of the carbonates given below is unstable in air and is kept in CO2 atmosphere to avoid decomposition.
(i) BeCO3
(ii) MgCO3
(iii) CaCO3
(iv) BaCO3
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
Due to the smaller size of the cation Be2+, and larger size of the anion CO32? , BeCO3 is unstable in air. Therefore, it is kept in CO2 atmosphere to avoid decomposition.
Metals form basic hydroxides. Which of the following metal hydroxide is the least basic?
(i) Mg(OH)2
(ii) Ca(OH)2
(iii) Sr(OH)2
(iv) Ba(OH)2
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
As the size of the metal increases, the basic character of the hydroxide increases down the group. The solubility of hydroxide increases, and hydroxide of Be and Mg is almost insoluble.
Some of the Group 2 metal halides are covalent and soluble in organic solvents. Among the following metal halides, the one which is soluble in ethanol is
(i) BeCl2
(ii) MgCl2
(iii) CaCl2
(iv) SrCl2
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
BeCl2 is covalent in nature due to the high polarising power of beryllium (+2) ion. On moving down the group, as the size increases, covalent nature decreases. Therefore, beryllium chloride being most covalent is soluble in ethanol.
The order of decreasing ionisation enthalpy in alkali metals is
(i) Na > Li > K > Rb
(ii) Rb < Na < K < Li
(iii) Li > Na > K > Rb
(iv) K < Li < Na < Rb
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option (iii)On moving down the group as the size increases, the nuclear charge attraction decreases. The effect of increasing size outweighs the increasing nuclear charge. Thus, ionization enthalpy decreases. The order of decreasing ionization enthalpy is,
Li>Na>K>Rb
The solubility of metal halides depends on their nature, lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy of the individual ions. Amongst fluorides of alkali metals, the lowest solubility of LiF in water is due to
(i) Ionic nature of lithium fluoride
(ii) High lattice enthalpy
(iii) High hydration enthalpy for lithium ion.
(iv) Low ionisation enthalpy of lithium atom
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (ii)
The solubility of salt depends on the lattice and hydration energy both. By increasing lattice energy and decreasing hydration energy solubility decreases. In case of biE, both the ions are small, thus the compound has high lattice energy and is insoluble in water. If both the cations and anions are comparable in size, then stability is maximum and solubility is minimum
Amphoteric hydroxides react with both alkalies and acids. Which of the following Group 2 metal hydroxides is soluble in sodium hydroxide?
(i) Be(OH)2
(ii) Mg(OH)2
(iii) Ca(OH)2
(iv) Ba(OH)2
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
Be (OH)2 is amphoteric. It reacts with both acids and bases. It reacts with acid to form beryllium chloride and it reacts with base to form beryllate ion which is soluble in sodium hydroxide. The reaction is shown below.
Be (OH)2+2OH−→ [Be (OH)4]2−
Be (OH)2+2HCl→BeCl2+2H2O
In the synthesis of sodium carbonate, the recovery of ammonia is done by treating NH4Cl with Ca(OH)2. The by-product obtained in this process is
(i) CaCl2
(ii) NaCl
(iii) NaOH
(iv) NaHCO3
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
Sodium carbonate is prepared by Solvay's process. In this process, ammonia is recovered when ammonium chloride reacts with calcium hydroxide. On reacting NH4Cl with Ca (OH)2 calcium chloride is obtained as a by-product. The reaction is given below.
2NH4Cl+Ca (OH)2→2NH3+CaCl2+H2O
When sodium is dissolved in liquid ammonia, a solution of deep blue colour is obtained. The colour of the solution is due to
(i) Ammoniated electron
(ii) Sodium ion
(iii) Sodium amide
(iv) Ammoniated sodium ion
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
The alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia and give a blue solution, which is conductive in nature. A solution of sodium in liquid ammonia at −30? C conducts electricity. The ammoniated electrons are responsible for the blue color of the solution as they absorb energy in the visible region of light and impart blue color to the solution.
By adding gypsum to cement
(i) Setting time of cement becomes less.
(ii) Setting time of cement increases.
(iii) Solour of cement becomes light.
(iv) Shining surface is obtained.
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (ii)
On adding water to cement it gets harder over a period of time. This is known as setting of cement. Gypsum is added to the cement to slow the setting time of cement which occurs in the presence of water.
Dead burnt plaster is
(i) CaSO4
(ii) CaSO4⋅ H2O
(iii) CaSO4⋅H2O
(iv) CaSO4⋅2H2O
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
An anhydrous calcium sulfate is dead burnt paris. It is known as dead burnt because it does not set like plaster when moistened with water. When gypsum is heated the water of crystallization is lost and an anhydrous calcium sulphate is obtained.
Suspension of slaked lime in water is known as
(i) Lime water
(ii) Quick lime
(iii) Milk of lime
(iv) Aqueous solution of slaked lime
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option (iii)
Ca (OH)2 saked lime is only sparingly soluble in water. When CaO is soaked in water, it produces a white suspension, and the reaction is highly exothermic. White suspension is called milk of lime and it is used for white washing.
Which of the following elements does not form hydride by direct heating with dihydrogen?
(i) Be
(ii) Mg
(iii) Sr
(iv) Ba
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
Beryllium being least reactive does not form hydride by direct heating with dihydrogen. Also due to its small size and high ionization enthalpy it cannot form hydrides by direct heating.
The formula of soda ash is
(i) Na2CO3⋅10H2O
(ii) Na2CO3⋅2H2O
(iii) Na2CO3⋅H2O
(iv) Na2CO3
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (iv)
Anhydrous sodium carbonate is known as soda ash. The formula of soda ash is Na2CO3? It is also known as washing soda.
A substance which gives brick red flame and breaks down on heating to give oxygen and a brown gas is
(i) Magnesium nitrate
(ii) Calcium nitrate
(iii) Barium nitrate
(iv) Strontium nitrate
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (ii)
Alkali and alkaline metals impart characteristic color. Calcium gives brick red color, Strontium gives crimson red color, Barium gives apple green color, and radium gives crimson color. So, the compound is calcium nitrate. On heating calcium nitrate, it gives calcium oxide, nitrogen and nitrogen dioxide gas which is brown in color.
Ca (NO3)2→CaO+O2+NO2↑
Which of the following statements is true about Ca(OH)2?
(i) It is used in the preparation of bleaching powder
(ii) It is a light blue solid
(iii) It does not possess disinfectant property.
(iv) It is used in the manufacture of cement
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i)
Calcium hydroxide is used in the preparation of bleaching powder. It reacts with chlorine to form hypochlorite, a constituent of bleaching powder.
Ca (OH)2+Cl2→CaCl2+H2O+Ca (OCl)2
It is a white amorphous powder and is sparingly soluble in water.
A chemical A is used for the preparation of washing soda to recover ammonia. When CO2 is bubbled through an aqueous solution of A, the solution turns milky. It is used in white washing due to disinfectant nature. What is the chemical formula of A ?
(i) Ca(HCO3)2
(ii) CaO
(iii) Ca(OH)2
(iv) CaCO3
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct Option (iii)
The chemical formula of A is Ca (OH)2 Sodium carbonate is prepared by Solvay's process. In this process, ammonia is recovered when ammonium chloride reacts with calcium hydroxide. On reacting NH4Cl with Ca (OH)2, calcium chloride is obtained as a by-product. The reaction is given below.
2NH4Cl+Ca (OH)2→2NH3+CaCl2+H2O
When CO2 is bubbled through an aqueous solution of Ca (OH)2 the solution turns milky. It is used in whitewashing due to its disinfectant nature.
Dehydration of hydrates of halides of calcium, barium and strontium i.e., CaCl26H2O, BaCl2.2H2O, SrCl2.2H2O, can be achieved by heating. These become wet on keeping in air. Which of the following statements is correct about these halides?
(i) Act as dehydrating agent
(ii) Can absorb moisture from air
(iii) Tendency to form hydrate decreases from calcium to barium
(iv) All of the above
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (iv)
Chlorides of alkaline earth metals are hydrated salts. They can be used as dehydrating agents due to their hygroscopic nature to absorb moisture from air. Extent of hydration decreases from Mg to Ba.
Therefore, dehydration of hydrates of halides of calcium, barium and strontium i.e., CaCl2.6H2O, BaCl2.2H2O, SrCl2.2H2O can be achieved by heating.
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
22. Metallic elements are described by their standard electrode potential, fusion enthalpy, atomic size, etc. The alkali metals are characterised by which of the following properties?
(i) High boiling point
(ii) High negative standard electrode potential
(iii) High density
(iv) Large atomic size
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (ii) and (iv)
Alkali metals have larger atomic size and low density. These metals lose electrons due to less effective nuclear charge. They have a high value of electrode potential.
Lithium has the highest negative reduction potential value. Due to the small size of lithium it has a small atomic size and the highest ionization enthalpy.
Several sodium compounds find use in industries. Which of the following compounds are used for textile industry?
(i) Na2CO3
(ii) NaHCO3
(iii) NaOH
(iv) NaCl
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i) and (iii)
Na2CO3 is used in paper paints and textile industry. It is used to manufacture soap powders.
NaOH is used in textile industry for mercerising cotton fabrics.
Which of the following compounds are readily soluble in water?
(i) BeSO4
(ii) MgSO4
(iii) BaSO4
(iv) SrSO4
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i) and (ii)
On moving down the group, as the size increases the hydration enthalpy decreases. The hydration enthalpy of beryllium and magnesium ions are high due to the small size. Thus, sulfates are readily soluble in water.
When Zeolite, which is hydrated sodium aluminium silicate is treated with hard water, the sodium ions are exchanged with which of the following ion(s)?
(i) H+ ions
(ii) Mg2+ ions
(iii) Ca2+ ions
(iv) SO42– ions
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (ii) and (iii)
Zeolite is sodium aluminum silicate. It is used to reduce the hardness of water. It has a property to exchange Mg2+ ions and Ca2+ ions from hard water by the Na+ions of zeolite.
Identify the correct formula of halides of alkaline earth metals from the following.
(i) BaCl2.2H2O
(ii) BaCl2 .4H2O
(iii) CaCl2 .6H2O
(iv) SrCl2.4H2O
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i) and (iii)
The chlorides of alklaje earth metals are hydrated. On moving down the group, the extent of hydration decreases. Therefore, the correct formula of halides are: CaCl2?6H2O and BaCl2?2H2O.
Choose the correct statements from the following.
(i) Beryllium is not readily attacked by acids because of the presence of an oxide film on the surface of the metal.
(ii) Beryllium sulphate is readily soluble in water as the greater hydration enthalpy of Be2+ overcomes the lattice enthalpy factor.
(iii) Beryllium exhibits coordination number more than four.
(iv) Beryllium oxide is purely acidic in nature.
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i) and (ii)
Beryllium resembles aluminum through the diagonal relation. Beryllium forms a protective film of oxide on the surface, and thus, is prevented by the attack of acids.
Thus, statement (1) is correct.
On moving down the group, as the size increases the hydration enthalpy decreases. The hydration enthalpy of beryllium ions are high due to the small size. Thus, sulfates are readily soluble in water. Thus, statement (2) is correct.
Beryllium does not exhibit coordination numbers more than four. As it has no d orbitals.
Thus, statement (3) is not correct.
Beryllium oxide is amphoteric in nature. It reacts with both acids and bases. It reacts with acid to form beryllium chloride and it reacts with base to form becyllate ion which is soluble in sodium hydroxide. The reaction is shown below.
Be (OH)2+2OH−→ [Be (OH)4]2−
Be (OH)2+2HCl→BeCl2+2H2O
Thus, statement (4) is not correct.
Which of the following are the correct reasons for anomalous behaviour of lithium?
(i) Exceptionally small size of its atom
(ii) Its high polarising power
(iii) It has high degree of hydration
(iv) Exceptionally low ionisation enthalpy
This is a multiple choice type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option (i) and (ii)
Among the alkali metals, lithium has an exceptionally small size. Due to the small size of lithium and high nuclear charge it has high palajising power.
In the following questions more than one option of column I and II may be correlated.
1. Match the elements given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Li |
(a) Insoluble sulphate |
|
(ii) Na |
(b) Strongest monoclinic base |
|
(iii) Ca |
(c) Most negative Eo value among alkali metals |
|
(iv) Ba |
(d) Insoluble oxalate |
|
(e) 6s2 outer electronic configuration |
This is a matching type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (c); (ii) → (b); (iii) → (d) : (iv) → (a); (e)
(i) Lithium has the highest negative reduction potential value. Due to the small size of lithium it has a small atomic size, the highest ionization enthalpy Due to this, the reducing power of lithium is the highest.
(ii) Sodium is a stronger monoacidic base due to lower first ionization enthalpy of sodium. Also sodium forms sodium hydroxide Therefore 1 mole of it replaces one mole of hydrogen ions from acids.
(iii) Calcium oxalate is an ionic compound because its hydration enthalpy is low. It is highly insoluble and dissolves poorly in water.
(iv) Barium sulfate is insoluble due to the high hydration energy. The electronic configuration of barium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2
Thus, option (iv) from column I is matched with (a) and (e) from column II.
Match the compounds given in Column I with their uses mentioned in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) CaCO3 |
(a) Density, ornamental work |
|
(ii) Ca(OH)2 |
(b) Manufacture of sodium carbonate from caustic soda |
|
(iii) CaO |
(c) Manufacture of high quality paper |
|
(iv) CaSO4 |
(d) Used in white washing |
This is a matching type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (c); (ii) → (d); (iii) → (b) : (iv) → (a)
(i) CaCO3 is used in manufacturing of high quality paper.
(ii) Due to the disinfectant nature of Ca (OH)2 is used in white wash.
(iii) CaO is used in the manufacture of sodium carbonate from caustic soda.
(iv)CaSO4 is used in dentistry, ornamental work and for making statues.
JEE MAINS 26th February 2021 first shift
JEE MAINS 26th February 2021 first shift
Commonly asked questions
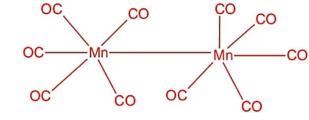
Number of bridging CO ligands in is----------.
[Mn2 (CO)10]
A certain gas obeys The value of The value of x is------------.
(Integer answer) (Z : compressibility factor)
So, comparing with
x = 1
Consider the following reaction
The quantity of electricity required is Faraday to reduce five moles of is--------.
(Integer answer)
Quantity of electricity required to reduce 1 mole of is 5F
So, for 5 mole 25F electricity is required.
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change during the reaction is -20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is-----------. (Integer answer)
X → Y
An homogeneous ideal gaseous reaction is carried out in a 25 litre flask at 27°C. The initial amount of AB2 was 1 mole and the equilibrium pressure was 1.9atm. The value of Kp is x × 10-2. The value of x is-----------. (Integer answer).
[R = 0.08206 dm3 atm K-1 mol-1]
Initial1 mole -
At equilirbium 1-x mole x mole2x mole
V = 25 L and
T = 300 K.
At equilibrium, P = 1.9 atm
Total moles at equilibrium, n = 1 + 2x
V = 25 L
T = 300 K
Using, PV = nRT
1.9 × 25 = (1 + 2x) × 0.08206 × 300
x = 0.465
Now;Partial pressure of AB2 at equilibrium =
Using ;
= 0.728
KP = 0.73
Kp = 73 × 10-2
So; x = 73
Dichromate ion is treated with base, the oxidation number of Cr in the product formed is-----------.
Dichromate ion converted to chromate ion in basic medium and oxidation number of Cr in is +6.
3.12g of oxygen is adsorbed on 1.2g of platinum metal. The volume oxygen adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent at 1 atm and 300 K in L is-----------.
[R = 0.0821 L atm K-1 mole-1]
PV = nRT
1 × V =
V = 2.4 litre
Vol of O2 adsorbed per gm = 2.4 / 1.2 = 2 litre
224mL of SO2(g) at 298K and 1 atm passes through 100mL of 0.1M NaOH solution. The non-volatile solute produced is dissolved is 36g of water. The lowering of vapour pressure of solution (assuming the solution is dilute) of Hg, the value of x is-----------. (Integer answer)
Moles of SO2 =
=0.01 mole
Moles of NaOH = 0.1 × 0.1
= 0.01 mole
SO2+NaOHNaHSO3
0.01 mole0.01 mole-
-0.01 mole
Non-volatile solute is NaHSO3
Moles of water =
Using ; relative lowering in V.P
Where; is lowering in V.P
i for NaHSO3 = 2
here; since solution is dilute
So; x = 24
The number of significant figures in 50000.020 × 10-3 is………………
50000.020 * 10-3
The significant figure in the given number is 8.
For a chemical reaction A + B C + D
the entropy change depends on the temperature T (in K) as
Minimum temperature at which it will become spontaneous is-------------K. (Integer)
For a reaction to be spontaneous;
So, minimum T at which reaction will be spontaneous is 200 K.
Consider the following reactions:
(A)
Side products
(B) dilute)
(C) + Side products
The sum of the total number of atoms in one molecule each of and is
The standard heat of formation of ethane (in ), if the heat of combustion of ethane, hydrogen and graphite are and respectively is
192.5
The flocculation value of for arsenic sulphide sol is . If is used for the flocculation of arsenic sulphide, the amount, in grams of in required for the above purpose is (Molecular mass of )
of
Then in will be
will be
The number of -hybridized carbons present in "Aspartame" is
The dotted ones are carbons
of acetic acid is added to of and the solution made up to . To of this solution of is added. The of the solution is
[Given: of acetic acid , molar mass of acetic acid ] Neglect any changes in volume.
has
has
and has
so has
added in is
So, (left)
1.5
2
1.5
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Ten Exam