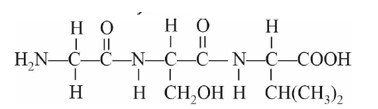- Hydrocarbons Questions and Answers
- qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq
Hydrocarbons Questions and Answers
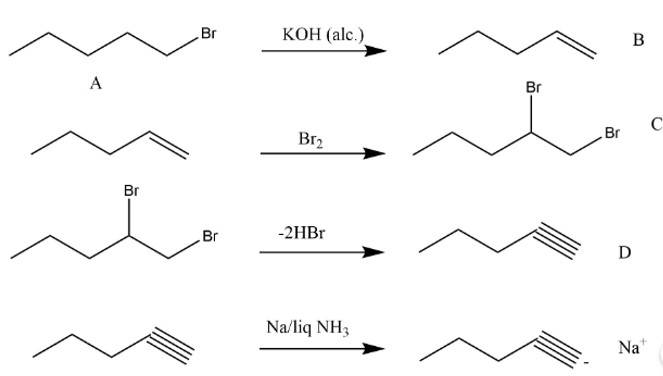
| 1. An alkyl halide C5H11Br (A) reacts with ethanolic KOH to give an alkene ‘B’, which reacts with Br2 to give a compound ‘C’, which on dehydrobromination gives an alkyne ‘D’. On treatment with sodium metal in liquid ammonia one mole of ‘D’ gives one mole of the sodium salt of ‘D’ and half a mole of hydrogen gas. Complete hydrogenation of ‘D’ yields a straight chain alkane. Identify A,B, C and D. Give the reactions invovled. |
| Ans: |
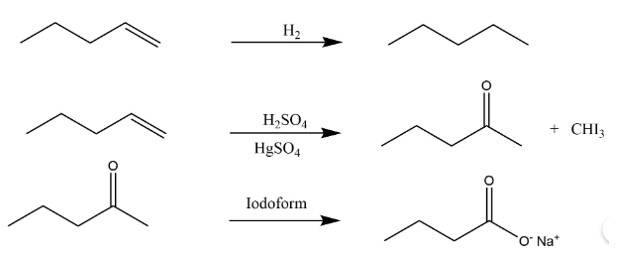
| 2. 896 mL vapour of a hydrocarbon ‘A’ having carbon 87.80% and hydrogen 12.19% weighs 3.28g at STP. Hydrogenation of ‘A’ gives 2-methylpentane. Also ‘A’ on hydration in the presence of H2SO4 and HgSO4 gives a ketone ‘B’ having molecular formula C6H12O. The ketone ‘B’ gives a positive iodoform test. Find the structure of ‘A’ and give the reactions involved. | |||||||||||||||
| Ans: The molar mass of the compound = 3.38 x 22400/896 =831gmol-1
Thus the empirical formula of the compound is C3H5 Molecular formula =n x empirical formula = 831/41 x C3H5 = C6H10 |
| 4. In the presence of peroxide addition of HBr to propene takes place according to anti Markovnikov’s rule but peroxide effect is not seen in the case of HCl and HI. Explain. |
Commonly asked questions
The relative reactivity of 1°, 2°, 3° hydrogen’s towards chlorination is 1 : 3.8 : 5. Calculate the percentages of all monochlorinated products obtained from 2-methylbutane.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The structure of 2-methylbutane is
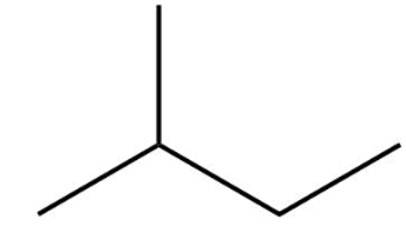
2-methylbutane
Total number | Total amount of monochlorinated Product | % of monochlorinated product | |
1° | 9 | 9 | 41.7 |
2° | 2 | 7.6 | 35.2 |
3° | 1 | 5 | 23.1 |
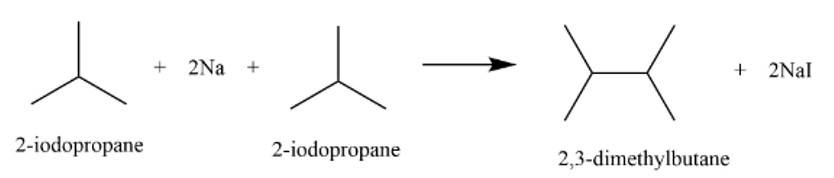
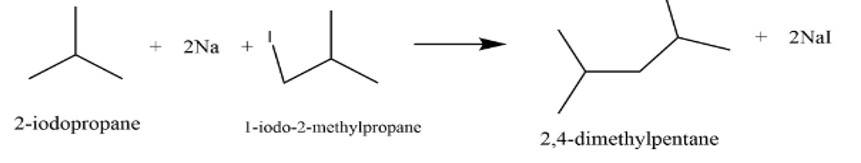
Write the structures and names of products obtained in the reactions of sodium with a mixture of 1-iodo-2-methylpropane and 2-iodopropane.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
It is a Wurtz reaction where alkane is formed.
Which of the following will not show geometrical isomerism?
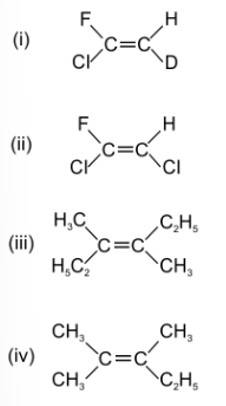
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) The two substituents attached to the same C atom of the C=C bond should be different to exhibit geometrical isomerisms.
Nucleophiles and electrophiles are reaction intermediates having electron rich and electron deficient centres respectively. Hence, they tend to attack electron deficient and electron rich centres respectively. Classify the following species as electrophiles and nucleophiles.
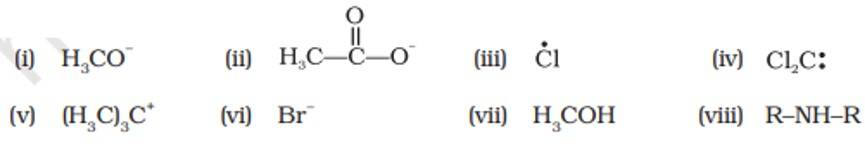
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Electrophiles | Nucleophiles |
(iii), (iv), (v) | (i), (ii), (vi), (vii), (viii) |
Write hydrocarbon radicals that can be formed as intermediates during monochlorination of 2-methylpropane? Which of them is more stable? Give reasons
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The 2-methylpropane would lead to two types of radicals.
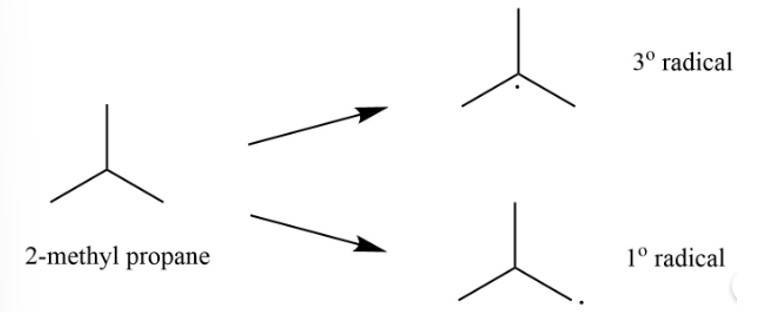
Among the two 3o radical is most stable as it contains 9 ∝ -hydrogen whereas 1o radical contains only 1 ∝ -hydrogen.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points.
(A) n–butane
(B) 2–methylbutane
(C) n-pentane
(D) 2,2–dimethylpropane
(i) A > B > C > D
(ii) B > C > D > A
(iii) D > C > B > A
(iv) C > B > D > A
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) C > B > D > A
The boiling point increases with the increase in the length of the side chain. However, with the branching, the boiling point decreases due to the decrease in the surface area.
Arrange the following hydrogen halides in order of their decreasing reactivity with propene.
(i) HCl>HBr> HI
(ii) HBr> HI >HCl
(iii) HI >HBr>HCl
(iv) HCl> HI >HBr
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) The addition of alkyl halides to propene depends upon the H-X bond strength i.e. lesser the bond strength higher will be the reactivity of the alkyl halide. As down the group size of the halogens increases thus the bond strength decreases.
An alkyl halide C5H11Br (A) reacts with ethanolic KOH to give an alkene ‘B’, which reacts with Br2 to give a compound ‘C’, which on dehydrobromination gives an alkyne ‘D’. On treatment with sodium metal in liquid ammonia one mole of ‘D’ gives one mole of the sodium salt of ‘D’ and half a mole of hydrogen gas. Complete hydrogenation of ‘D’ yields a straight chain alkane. Identify A,B, C and D. Give the reactions invovled.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
896 mL vapour of a hydrocarbon ‘A’ having carbon 87.80% and hydrogen 12.19% weighs 3.28g at STP. Hydrogenation of ‘A’ gives 2-methylpentane. Also ‘A’ on hydration in the presence of H2SO4 and HgSO4 gives a ketone ‘B’ having molecular formula C6H12O. The ketone ‘B’ gives a positive iodoform test. Find the structure of ‘A’ and give the reactions involved.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The molar mass of the compound = 3.38 x 22400/896 =831gmol-1
Element | Percentage | At.mass | Relative ratio | the simplest ratio |
C | 87.8% | 12 | 7.31 | 3 |
H | 12.19% | 1 | 12.19 | 5 |
Thus the empirical formula of the compound is C3H5
Molecular formula =n x empirical formula = 831/41 x C3H5 = C6H10
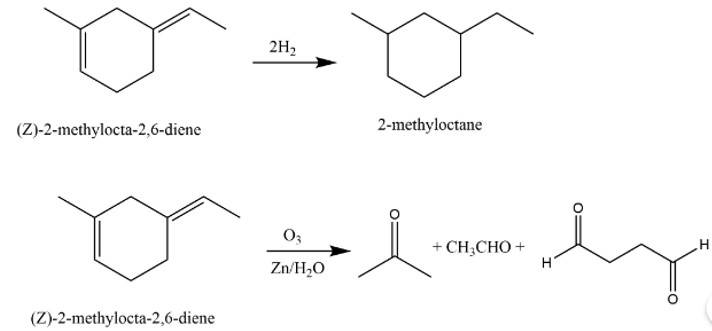
An unsaturated hydrocarbon ‘A’ adds two molecules of H2 and on reductive ozonolysis gives butane-1,4-dial, ethanal and propanone. Give the structure of ‘A’, write its IUPAC name and explain the reactions involved.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The structure of A is
The reaction involved are as follows:
In the presence of peroxide addition of HBr to propene takes place according to anti Markovnikov’s rule but peroxide effect is not seen in the case of HCl and HI. Explain.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The bond energy of HCl is higher than that of HBr thus it is not cleaved by free radical mechanism to exhibit peroxide effect. However in case of HI the bond energy is so low that the iodine radical forms readily and after formation it combines to form an iodine molecule.
Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If arenes would undergo electrophilic addition reaction then they would lose their aromaticity which would lead to comparatively less stability. However, alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reaction via carbocation intermediate.
Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia form trans alkenes. Will the butene thus formed on reduction of 2-butyne show the geometrical isomerism?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes, it will execute geometrical isomerism as the product formed can be either cis-2-butene or trans-2-butene.
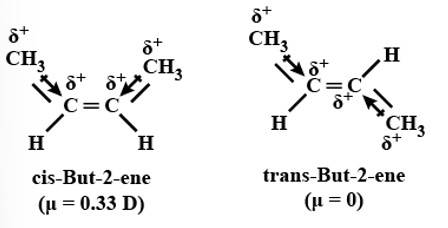
Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The rotation around C-C single bond is possible but it is not completely free due to the torsional strain which is about 1-20 KJ mol-1.
The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI, HBr and HCl with propene is the same and the bond energy of HCl, HBr and HI is 430.5 kJ mol–1, 363.7 kJ mol–1 and 296.8 kJ mol–1 respectively. What will be the order of reactivity of these halogen acids?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The rate-determining step involved in the reaction is
CH3-CH=CH2 + HX → CH3-CH+-CH3 + X-
So the rate-determining step depends on the bond energy of HX i.e. higher the bond energy lesser would be reactivity.
Thus the order of reactivity of these halogen acids is
HI>HBr>HCl
What will be the product obtained as a result of the following reaction and why?
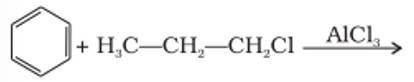
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The benzene here would undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction where carbocation is formed as an intermediate, thus secondary carbocation is formed as an intermediate due to its greater stability than that of the primary carbocation.
The final product obtained is
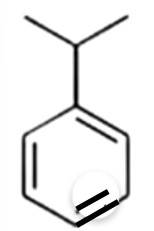
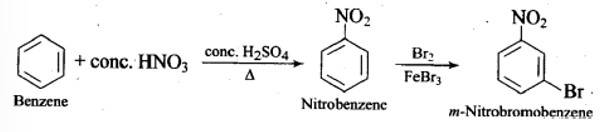
How will you convert benzene into
(i) p – nitrobromobenzene
(ii) m – nitrobromobenzene
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
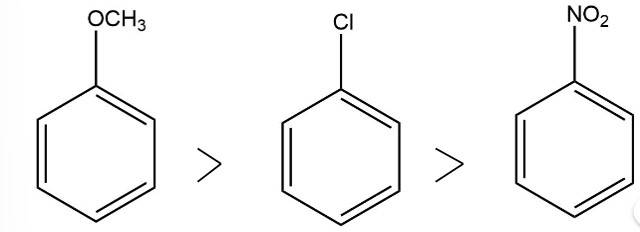
Arrange the following set of compounds in the order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile.Give reason
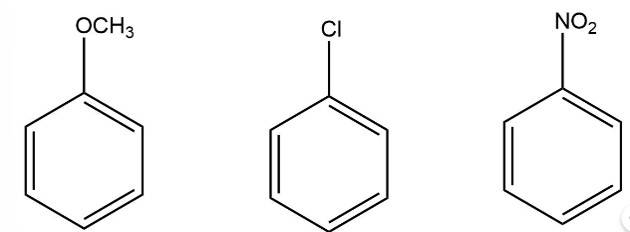
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electron donating group increases the reactivity in electrophilic substitution reaction whereas the electron withdrawing group decreases the reactivity in electrophilic substitution.
Thus, the order of reactivity
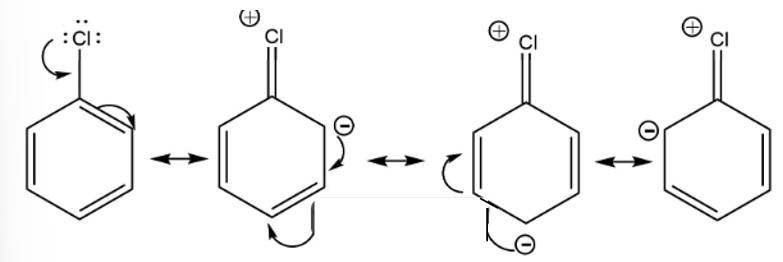
Despite their - I effect, halogens are o- and p-directing in haloarenes. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to the +R effect halogens are ortho and para directing groups.
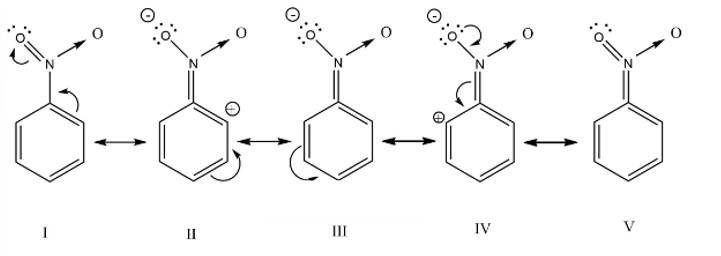
Why does presence of a nitro group make the benzene ring less reactive in comparison to the unsubstituted benzene ring. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The nitro group strongly deactivate the benzene towards the electrophilic substitution reaction due to the -R and -I effect
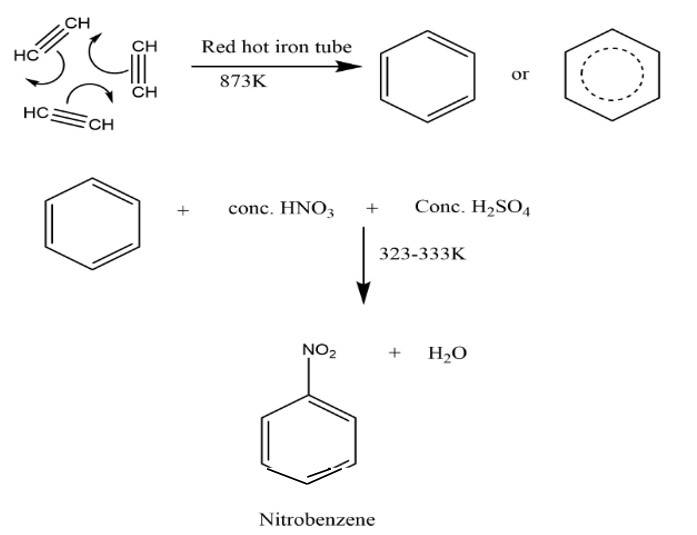
Suggest a route for the preparation of nitrobenzene starting from acetylene?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Predict the major product (s) of the following reactions and explain their formation.
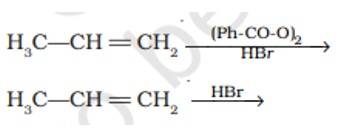
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In presence of (Ph-CO-O)2it lead to CH3-CH2-CH2Br as the reaction undergo by free radical mechanism
However in absence of (Ph-CO-O)2 the reaction undergo by carbocation intermediate thus lead to give CH3-CHBr-CH3
An alkane C8H18 is obtained as the only product on subjecting a primary alkyl halide to Wurtz reaction. On monobromination this alkane yields a single isomer of a tertiary bromide. Write the structure of alkane and the tertiary bromide.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction is
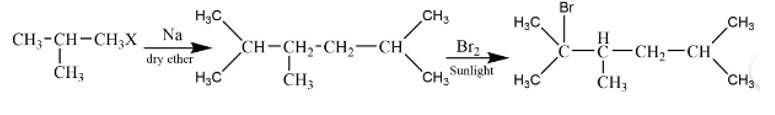
The alkane is
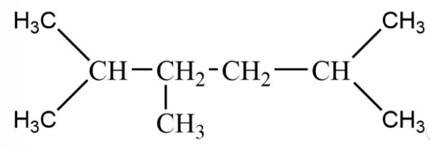
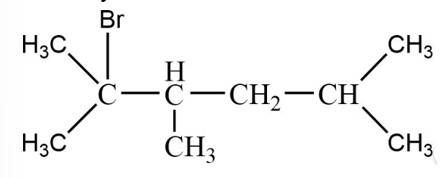
The tertiary bromide is
Arrange the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
(i) I2< Br2< Cl2< F2
(ii) Br2< Cl2< F2< I2
(iii) F2< Cl2< Br2< I2
(iv) Br2< I2 < Cl2< F2
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) I2< Br2< Cl2< F2
The reactivity of halogens with alkanes depends on the electronegativity i.e. higher the electronegativity higher would be the reaction. As down the group reactivity decrease so thus its reactivity.
The increasing order of reduction of alkyl halides with zinc and dilute HCl is
(i) R–Cl< R–I < R–Br
(ii) R–Cl< R–Br < R–I
(iii) R–I < R–Br < R–Cl
(iv) R–Br< R–I < R–Cl
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(ii) R–Cl< R–Br < R–I
The reduction of alkyl halides depends upon the C-X bond strength i.e. lesser the bond strength higher will be the reactivity of alkyl halide. As down the group size of the halogens increases thus the bond strength decreases.
The correct IUPAC name of the following alkane is
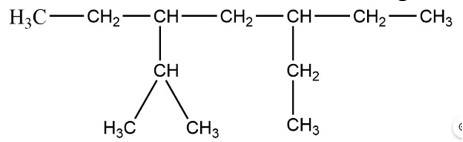
(i) 3, 6 – Diethyl – 2 – methyl octane
(ii) 5 – Isopropyl – 3 – ethyl octane
(iii) 3 – Ethyl – 5 – isopropyl octane
(iv) 3 – Isopropyl – 6 – ethyl octane
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) 3, 6 – Diethyl – 2 – methyl octane
Octane is the longest chain here and the side chain follows the lowest sum rule.
The addition of HBr to 1-butene gives a mixture of products A, B and C
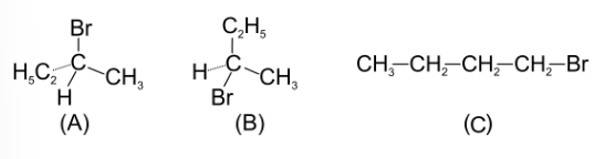
The mixture consists of
(i) A and B as major and C as minor products
(ii) B as major, A and C as minor products
(iii) B as minor, A and C as major products
(iv) A and B as minor and C as major products
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) The reaction follows Markovnikov's rule leading to giving 2o carbocation as an intermediate.
Arrange the following carbanions in order of their decreasing stability.
(A) H3C - C ≡ C -(B) H - C ≡ C - (C) H3C - CH2
(i) A > B > C
(ii) B > A > C
(iii) C > B > A
(iv) C > A > B
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(ii) The electronegativity of sp hybridization is higher than that of sp3 hybridization.
The +I effect destabilizes the carbanion.
Arrange the following alkyl halides in decreasing order of the rate of β– elimination reaction with alcoholic KOH.
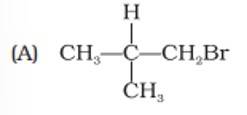
(B) CH3—CH2—Br
(C) CH3—CH2—CH2—Br
(i) A > B > C
(ii) C > B > A
(iii) B > C > A
(iv) A> C > B
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) The order of reactivity of β– elimination reaction is 3o>2o>1o
Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion:
(i) 2CH4 + O2 ![]() 2CH3OH
2CH3OH
(ii) CH4 + O2![]() HCHO + H2O
HCHO + H2O
(iii) CH4 + O2 → C (s) + 2H2O (l)
(iv) CH4 + O2 → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) As the unburn carbon left out in this reaction thus it is an incomplete reaction
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
(i) CH4 + O2 → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
(ii) CH4 + O2 → C (s) + 2H2O (l)
(iii) CH4 + O2 ![]() HCHO + H2O
HCHO + H2O
(iv) 2CH4 + O2![]() 2CH3OH
2CH3OH
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) & (iv) Methane is a controlled oxidation reaction that leads to giving formaldehyde and methanol.
Which of the following alkenes on ozonolysis give a mixture of ketones only?
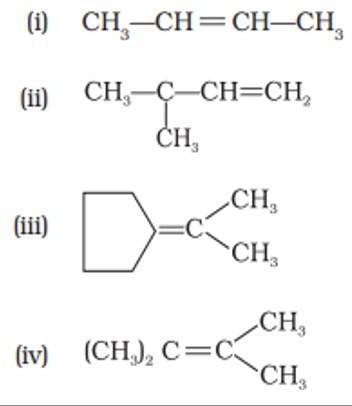
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) & (iv) When only the alkyl group is attached to the C atom of the C=C bond then only it would lead to giving only ketone on ozonolysis.
Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?
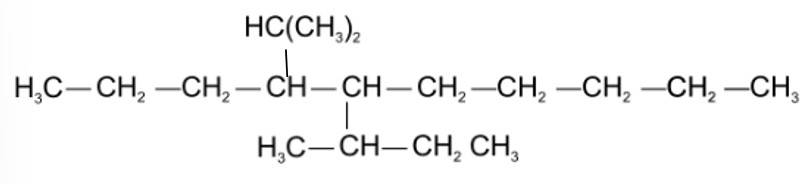
(i) 5– Butyl – 4– isopropyldecane
(ii) 5– Ethyl – 4– propyldecane
(iii) 5– sec-Butyl – 4– iso-propyldecane
(iv) 4–(1-methylethyl)– 5 – (1-methylpropyl)-decane
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) & (iv) The longest carbon chain is of 10 carbon atom
Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?
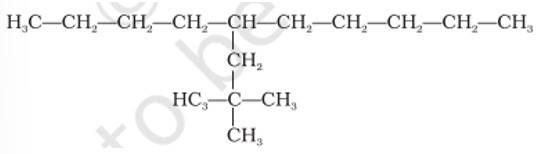
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) & (iv) The longest carbon chain is of 10 carbon atom
For an electrophilic substitution reaction, the presence of a halogen atom in the benzene ring _______.
(i) Deactivates the ring by inductive effect
(ii) Deactivates the ring by resonance
(iii) Increases the charge density at ortho and para position relative to meta position by resonance
(iv) Directs the incoming electrophile to meta position by increasing the charge density relative to ortho and para position.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) & (iii)
The halogens atom weakly deactivate the ring due to the -I effect and directs the incoming group to the ortho and para position due to the +R effect.
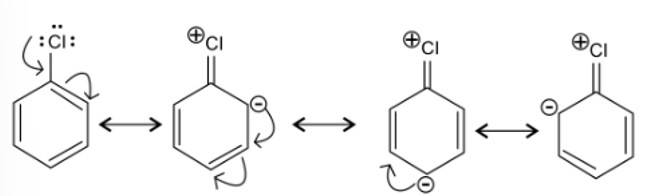
In an electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrobenzene, the presence of nitro group ________.
(i) Deactivates the ring by inductive effect.
(ii) Activates the ring by inductive effect.
(iii) Decreases the charge density at ortho and para position of the ring relative to meta position by resonance.
(iv) Increases the charge density at meta position relative to the ortho and para positions of the ring by resonance
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) & (iii) The nitro group strongly deactivate the ring due to the -R effect and -I effect
(i) CH3—O—CH2⊕ is more stable than CH3—CH2⊕
(ii) (CH3)2CH⊕ is less stable than CH3—CH2—CH2⊕
(iii) CH2=CH—CH2⊕ is more stable than CH3—CH2—CH2⊕
(iv) CH2=CH⊕is more stable than CH3—CH2⊕
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) & (iii)
The +I effect of the -OCH3 group stabilizes the carbocation.
The two resonating structure of CH2=CH-CH2⊕↔⊕CH2-CH=CH2 makes it more stable
Four structures are given in options (i) to (iv). Examine them and select the aromatic structures.
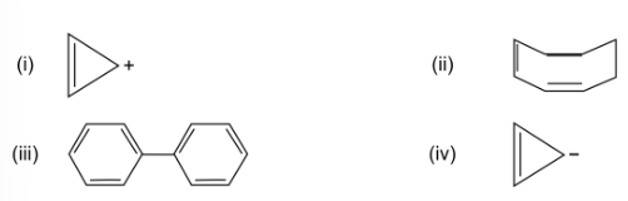
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) & (iii)
The structures that follow the (4n+2) Huckle rule of aromaticity is considered to be aromatic
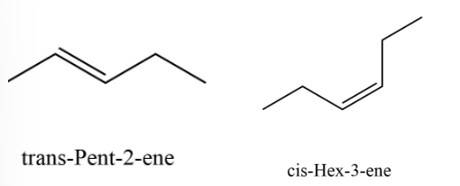
The molecules having dipole moment are __________.
(i) 2,2-Dimethylpropane
(ii) Trans-Pent-2-ene
(iii) Cis-Hex-3-ene
(iv) 2, 2, 3, 3 - Tetramethylbutane.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(ii) & (iii)
Match the reagent from Column I which on reaction with
CH3 – CH=CH2 gives some product given in Column II as per the codes given below:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) O3/Zn + H2O |
(a) Acetic acid and CO2 |
|
(ii) KMnO4/H+ |
(b) Propan-1-ol |
|
(iii) KMnO4/OH- |
(c) Propan-2-ol |
|
(iv) H2O/H+ |
(d) Acetaldehyde and formaldehyde |
|
(v) B2H6/NaOH and H2O2 |
(e) Propan-1,2-diol |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (d); (ii) → (a); (iii) → (e) : (iv) → (c) : (v) → (b)
Match the hydrocarbons in Column I with the boiling points given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) n-pentane |
(a) 282.5 K |
|
(ii) iso-pentane |
(b) 309 K |
|
(iii) neo-pentane |
(c) 301 K |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (b); (ii) → (c); (iii) → (a)
Match the following reactants in Column I with the corresponding reaction products in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Benzene + Cl2 |
(a) Benzoic acid |
|
(ii)Benzene + CH3Cl |
(b) Methyl phenyl ketone |
|
(iii)Benzene + CH3COCl |
(c) Toluene |
|
(iv)Toluene |
(d) Chlorobenzene |
|
(e) Benzene hexachloride |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (d); (ii) → (c); (iii) → (b) : (iv) → (a)
Match the reactions given in Column I with the reaction types in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) CH2=CH2 + H2O |
(a) Hydrogenation |
|
(ii) CH2 ≡ CH2 + H2 |
(b) Halogenation |
|
(iii) CH2 ≡ CH2 + Cl2 → ClCH2CH2Cl |
(c) Polymerisation |
|
(iv) 3CH ≡ CH |
(d) Hydration |
|
(e) Condensation |
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) → (d); (ii) → (a); (iii) → (b) : (iv) → (c)
It is cyclic and has conjugated 8π-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
Reason (R) : (4n + 2) π electrons rule does not hold good and ring is not planar.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Because cyclooctatetraene is tubbed shaped.
Assertion (A): Toluene on Friedal Crafts methylation gives o– and p–xylene.
Reason (R): CH3-group bonded to benzene ring increases electron density at o– and p– position.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) The -CH3 group is an activating group and it directs the upcoming substituent to the ortho and para position.
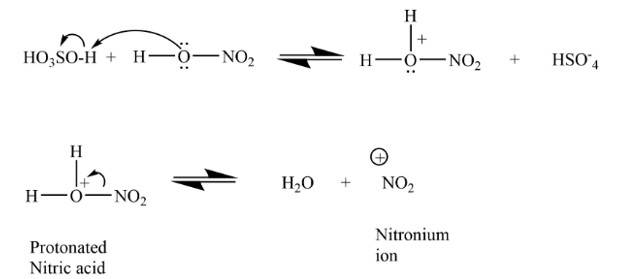
Assertion (A): Nitration of benzene with nitric acid requires the use of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Reason (R): The mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid produces the electrophile, NO2 +.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) The sulphuric acid helps in furnishing NO2+ (electrophile).
Assertion (A): Among isomeric pentanes, 2, 2-dimethylpentane has highest boiling point.
Reason (R): Branching does not affect the boiling point.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) With the branching the boiling decreases due to the decrease in surface area which leads to decrease its van there Waals force.
1.34% solution of KNO? is isotonic with 4.77% solution of glucose. Find the percent of dissociation of KNO?. (Given : Atomic mass K = 39.1 amu, N = 14 amu and O = 16 amu)
Hence, extent of dissociation is
A weakly alkaline solution of permanganate is electrolysed for 50 minutes using 2A current. The amount of oxide of manganese obtained. (Given : Atomic mass Mn = 55 amu and O = 16 amu)
Charge (q)
Mass of deposited
The number of ketonic >C=O groups present in a tripeptide gly-ser-val are ____.
The number of >C = 0 groups in tripeptide is 0 .
The density of a solution prepared by dissolving 1 gram molecule of sucrose in 1000 gram of water is 1.15 gm/ml. The molarity of the solution is ____.
Molarity
The volume (in mL) of 0.01M NaOH required to neutralise 20ml of 0.01M ortho-phosphoric acid is ____.
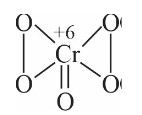
How many peroxide linkages are present in a compound of chromium with oxygen which is blue in colour and soluble in amyl alcohol, produced by treating K?CrO? with acidified H?O??
How many of these compounds will undergo disproportionation on hydrolysis? CO?, NO?, Cl?, F?, ClO?, Cl?O?, N?O?, SO?, P?O??
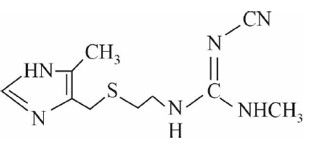
Number of degree of unsaturation present in cimetidine ____.
Kindly consider the following Image
Identify the numbers of amphiprotic species in the following list?
H?O?, HPO?²?, HCO??, H?O, HPO?²?, H?PO?, H?PO??, H?PO?, PO?³?, NH??
Amphiprotic species are those which behave like acid and base both. They can donate and accept a proton.
Number of geometrical isomers of a complex ion [Pt(PPh?)?(Py)?Cl?]²? are x, if 1 mole of ethylenediamine replaces two weakest ligands then new complex formed has ‘y’ number of geometrical isomers. Find the values of x/y.
Geometrical Isomers
qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq
qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq
Commonly asked questions
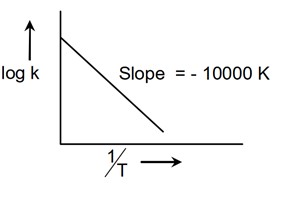
For the reaction aA + bB->cC + dD, the plot of log K vs is given below:
This temperature at which the rate constant of the reaction is 10-4 s-1 is----------K.
(Rounded – off to the nearest integer)
[Given : The rate constant of the reaction is 10-5 s-1 at 500 K]
(at 500 K temperature)
In basic medium oxidises to form and itself changes into Cr(OH)4-. The volume of 0.154M required to react with 40mL of 0.25 M -------------- mL.
(Rounded – off to the nearest integer)
O.N.C = 4
n factor of S2O3-- = 8
n factor of CrO4-- = 3
= 173.16 ml 173 ml
0.4g mixture of NaOH, Na2CO3 and some inert impurities was first titrated with using phenolphthalein as an indicator, 17.5mL of HCl was required at the end point . After this methyl orange was added and titrated. 1.5mL of same HCl was required for the next end point. The weight percentage of Na2CO3 in the mixture is----------. (Rounded – off to the nearest integer)
NaOH + Na2CO3
(1) When Hph is added
m.e NaOH + (m.e = milli equivalents)
(2) When MeOH is added after Hph
The reaction of cyanamide, NH2CN(s) with oxygen was run in a bomb calorimeter and was found to be -742.24 kJ mol-1. The magnitude of for the reaction
------------- kJ. (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[Assume ideal gases and R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1]
NH2CN (s) + O2 (g) ® N2 (g) + O2 (g) + H2O (l)
=
So, magnitude of
1 molal aqueous solution of an electrolyte A2B3 is 60% ionized. The boiling point of the solution at 1 atm is----------- K. (Rounded – off to the nearest integer)
[Given Kb for (H2O) = 0.52 K kg mol-1]
1-α 2α 3α
A car tyre is filled with nitrogen gas at 35 psi at 27°C. It will burst if pressure exceeds 40 psi. The temperature in °C at which the car tyre will burst is--------------. (Rounded – off to the nearest integer)
The ionization enthalpy of Na+ formation from Na(g) is 495.8 kJ mol-1, while the electron gain enthalpy of Br is - 325.0 kJ mol-1. Given the lattice enthalpy of NaBr is - 728.4 kJ mol-1. The energy for the formation of NaBr ionic solid is (-) -------------- × 10-1kJ mol-1.
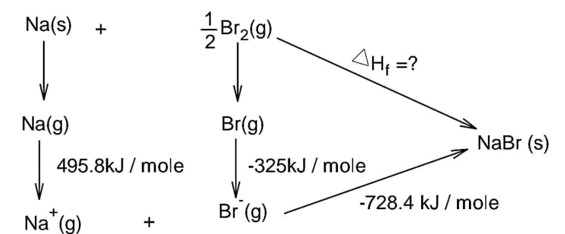
Bond dissociation energy of Br2 = 228 kJ/mole
Note : In question is neglect
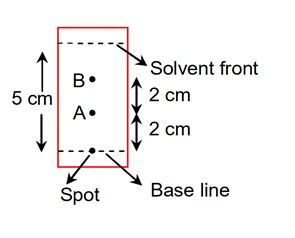
Using the provided information in the following paper chromatogram: Fig : Paper chromatography for compounds A and B. The calculated Rf value of A------------× 10-1
Consider the following chemical reaction.
The number of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms (s) present in the product is--------------.
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Thirteen Exam

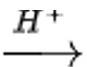 CH3CH2OH
CH3CH2OH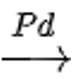 CH3CH3
CH3CH3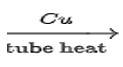 C6H6
C6H6