
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Short Answer Type Questions
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Long Answer Type Questions
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Other Questions
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Objective Type Questions
- JEE MAINS 2 April 2025
- qqqqqqqqqqq
- pppppppppppppppppp
- JEE Mains 2021
- JEE Mains 2020
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Short Answer Type Questions
| 1. For a positive integer , find the value of . |
| Sol. |
| 2. Evaluate , where . |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
For a positive integer , find the value of .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Evaluate , where .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then find .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then find the value of .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then find .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , find the value of .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then show that .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then show that , where , represents a circle.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the real part of is 4, then show that the locus of the point representing in the complex plane is a circle.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Show that the complex number , satisfying the condition , lies on a circle.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Solve the equation .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Long Answer Type Questions
| 1. If , then find . |
| Sol. |
| 2. If , then find , where . |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
If , then find , where .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then find .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Show that represents a circle. Find its centre and radius.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If is a purely imaginary number ( ), then find the value of .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
and are two complex numbers such that and , then show that .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If ( ) and , then show that the real part of is zero.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If and are two pairs of conjugate complex numbers, then find .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then show that .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If for complex numbers and , , then show that
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Solve the system of equations .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the complex number satisfying the equation .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Write the complex number in polar form.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If and are two complex numbers such that and , then show that .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Other Questions
| 1. What is the conjugate of z |
| Sol. |
| 2. If , is it necessary that ? |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
What is the conjugate of z
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , is it necessary that ?
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , is it necessary that ?
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find if and .
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the principal argument of .
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Where does lie, if
This is Other Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Objective Type Questions
| 1. and are conjugate to each other for: (a) (b) (c) (d) no value of |
| Sol. |
| 2. The real value of for which the expression is purely real is: (a) (b) (c) (d) None of these, where |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
If is a complex number, then
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
and are conjugate to each other for:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) no value of
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The real value of for which the expression is purely real is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these, where
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If lies in the third quadrant, then also lies in the third quadrant if:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The value of is equivalent to:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If then
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) , where
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A real value of satisfies the equation if
(a) 1
(b) -1
(c) 2
(d) -2
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Which of the following is correct for any two complex numbers and ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The point represented by the complex number is rotated about the origin through an angle in the clockwise direction, the new position of the point is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let , then is a non-real complex number if:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The complex number which satisfies the condition lies on Circle
(a) Circle
(b) The x-axis
(c) The y-axis
(d) The line .
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
is possible if:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The real value of for which the expression is a real number is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The value of when is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , where , then is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
JEE MAINS 2 April 2025
JEE MAINS 2 April 2025
qqqqqqqqqqq
qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq
Commonly asked questions
Let be an integer. IF the shortest distance between the lines and , then the value of
For integers n and r, let 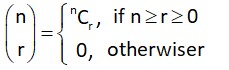
The maximum value of k for which the sum
= Equating the coefficient of ..............(i)
= Equating the coefficient of
From (i) and (ii)
Hence
But maximum value of k is not defined bonus
Let If and n = be the greatest integral part of Then is equal to………………..
=
=
55 + 135 + 120 = 310
The number of the real roots of the equation (x + 1)2 +
Case l x < 5
Case II x 5
because x > 5
Let a point P be such that its distance from the point (5,0) is thrice the distance of P from the point (-5,0). If the locus of the point P is a circle of radius r, then 4r2 is equal to………………….
Let P (h, k)
The sum of first four terms of a geometric progression (G. P) is and the sum of their respective reciprocals is If the product of first three terms of the G.P is 1,and the third term is a, then 2a is………………
Let a, ar, ar2, ar3 are in G.P.
a + ar + ar2 + ar3 =
The students S1, S2,…………….S10 are to be divided into 3 groups A, B and C such that each group has at least one student and the group C has at most 3 students. Then the total number of possibilities of forming such groups is……………..
A B C
- - 1
- - 2
- - 3
Number of groups
Number of groups
Number of groups =
Total number of groups = 31650
If a + a = 1, b + b = 2 and af(x) + then the value of the equation is………………..
Replace x by
IF the variance of 10 natural numbers 1, 1, 1……… 1, k less than 10, then the maximum possible value of k is…………………
maximum value of k is 11
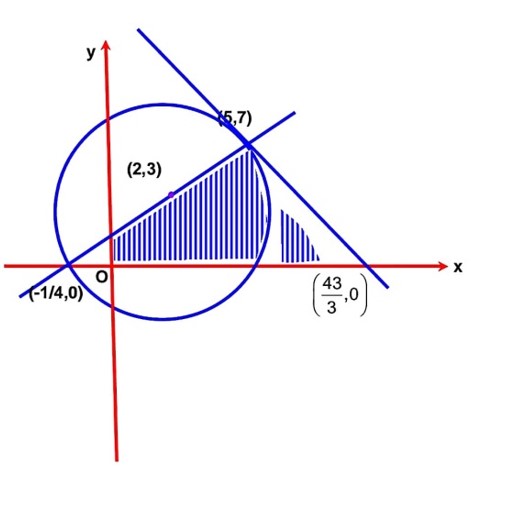
If the area of the triangle formed by the positive x-axis, the normal and the tangent to the circle (x - 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 25 at the point (5, 7) is A, then 24A is equal to………………
Equation of normal is 4x – 3y + 1 = 0
Equation of tangent is 3x + 4y – 43 = 0
Area of triangle =
pppppppppppppppppp
pppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppp
Commonly asked questions
is equal to___________.
For n value =
If the least and the largest real values of a, for which the equation z + a has a solution, are p and q respectively, then is equal to
Let z = x + iy
for
= 0
Let M be any 3 × 3 matrix with entires from the set {0, 1, 2}. The maximum number of such matrices, for which the sum of diagonal elements MTM is seven is____________.
all i = 1, 2, 3
Case 1 7 one’s and two zeroes which can occur in 
Case 2 One 2 three 1’s five zeroes =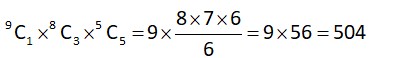
total such matrices = 504 + 36 = 540
The minimum values of a for which the equation has at least one solution in
Let sin x = t, t (0, 1)
Minimum value of a for which solution exist = 9
is equal to___________.
For n value =
If the least and the largest real values of a, for which the equation z + a has a solution, are p and q respectively, then is equal to
Let z = x + iy
for
= 0
Let M be any 3 × 3 matrix with entires from the set {0, 1, 2}. The maximum number of such matrices, for which the sum of diagonal elements MTM is seven is____________.
all i = 1, 2, 3
Case 1 7 one’s and two zeroes which can occur in 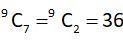
Case 2 One 2 three 1’s five zeroes =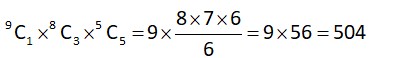
total such matrices = 504 + 36 = 540
The minimum values of a for which the equation has at least one solution in
Let sin x = t, t
Minimum value of a for which solution exist = 9
Let A =
B =
And C = for some
If the sum of all the elements of the set is 274 × 400, then is equal to___________.
Sum of elements
In set B numbers of the form 9k + 2 are {101, 109, ....992}
Another possible number is 9k + 5 forms are {104, ..........995}
possible value of = 5
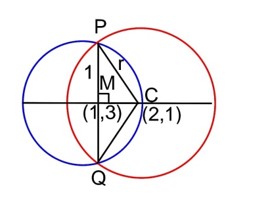
If one of the diameters of the circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y + 6 = 0 is a chord of another circle ‘C’, whose centre is at (2, 1), then its radius is_________
Let Bi (i = 1, 2, 3) be three independent events in a sample space. The probability that only B1 occurs is a, only B2 occurs is b and B3 occurs is Let p be the probability that none of the events B1 occurs and these 4 probabilities satisfy the equations (a - 2b) = ab and (b - 3 p = (All the probabilities are assumed to lie in the integral (0, 1)). The is equal to_________.
Let P (B1) = a P (B2) = b P (B3) = c
Given a (1 – b) (1 – c) = a . (i)
b (1 – a) (1 – c) = b . (ii)
c (1 – b) (1 – a) =
(1 – a) (1 – b) (1 – c) = p . (iv)
->a – ab – 2b + 2ab = ab Þ a = 2b . (v)
Again
->b – bc – 3c + 3bc = 2bc Þ b = 3c . (vi)
Let three vectors be such that is coplanar with is perpendicular to then the value of 2 is____________.
From
Solving
Let P = Suppose Q = [qij] is a matrix satisfying PQ = kI3 for some non-zero k R. If is equal to_________.
If denotes the greatest integer then is equal to__________.
JEE Mains 2021
JEE Mains 2021
Commonly asked questions
Let L be a common tangent line to the curves Then the square of the slope of the line L is………….
Given curves
&
Equation of any tangent to (i) be y = mx +
For common tangent (iii) also should be tangent to (ii) so by condition of common tangency
OR 36m2 + 16 = 31 + 31m2
=>m2 = 3
If the arithmetic mean and geometric mean of the pth and qth terms of the sequence -16,8,-4,2,…. satisfy the equation 4x2 – 9x + 5 = 0, then p + q is equation to……….
Given sequence is -16, 8, -4, 2, .....
are in G.P. with first term a = -16 & common ratio r =
Now
So A.M. = -8
Given equation is 4x2 – 9x + 5 = 0 gives
From roots we get possible value of b = 1 so
The total number of 4-digit numbers whose greatest common divisor with 18 is 3, is…….
18 = 32 * 2
For G.C.D to be 3. no. of four digits should be only multiple of 3, but not multiple of 9 & also should not be even.
As we know no. of the form 9 k -> 1000
9 k + 1 -> 1000
9 k + 2 -> 1000
9 k + 3 -> 1000 -> Total no. = 2000
9 k + 4 -> 1000
9 k + 5 -> 1000
9 k + 6 ->1000
9 k + 7 -> 1000
9 k + 8 -> 1000
In which half will be even & half be odd so Required no. = 1000
Let a and b be two real numbers such that α + β = 1 and αβ = -1. Let Pn-1 = 11 and Pn+1 = 29 for some integer Then, the value of is……
Given
Now quadratic equation having roots α & β will be x2 – (α + β)x + αβ = 0
i.e. x2 – x – 1 = 0, put x = α and put x = β
So α2 = α + 1 & β2 = β + 1
(i)
= >
Let z be those complex numbers which satisfy
If the maximum value of then the value of (α + β) is…….
->Represent a circle
->Represent a line X – y
So max |z + 1|2 = AQ2
Hence α + β) = 48
Let ta be an integer such that all the real roots of the polynomial 2x5 + 5x4 + 10x3 + 10x2 + 10x + 10 lie in the interval (a, a +1). Then is equal to……….
Given
So at least one root will lie in (2, 1)
now
So, f (x) be purely increasing function so exactly one root of f (x) that will lie in (-2, 1). Hence |a| = 2
Let X1, X2,…..X18 be eighteen observations such that where a and b are distinct real numbers. If the standard deviation of these observations is 1, then the value of
Given
&
(i) & (ii)
Now variance = 1 given
=> (α - β) (α - β + 4) = 0
Since
If Im,n = then a equals…....
Given
put 1 - x =
dx = -dt
From (i)
(i)
Similarly by (ii)
Adding (iii) & (iv)
Putting
Hence dx = α lm, n
=> α = 1
Let the normal at all the points on a given curve pass through a fixed point (a, b). If the curve passes through (3, -3) and and given that then is equal to…………
Let the equation of normal is Y – y = -
where m is slope of tangent to the given curve then
It passes through (a, b) so b – y =
=> (a – x) dx = (y – b) dy
On integration
(ii) passes through (3, -3) & then
3a – 3b – c = 9 .........(ii)
& 4a - - c = 12 .........(iii)
also given
Solve (ii), (iii) & (iv) b = 0, a = 3
Hence a2 + b2 + ab = 9
If the matrix A = satisfies the equation A20 = αA19 + βA = for some real numbers α and β, then β - α is equal to…………
Similarly we get A19 =
=
So, β = 2
Hence β - α = 4
Let f : R -> R be defined as
If f(x) is continuous on R, then a + b equals:
Given
If f (x) is continuous for all
At x = -1, L.H.L = R.H.L. Þ 2 = |a + b - 1|
=>a + b – 3 = 0 OR a + b + 1 = 0 . (i)
=>a + b + 1 = 0 . (ii)
(i) & (ii), a + b =-1
JEE Mains 2020
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Five Exam
