
- Differential Equations Questions and Answers
- JEE Mains Solution 2022
Differential Equations Questions and Answers
| Q1.Solve: . |
| Sol:
|
| Q2.Find the general solution of . |
| Sol:
|
| Q3.Solve: . [Hint: Substitute ] |
| Sol:
|
| Q4.Find the general solution of . |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Solve: .
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the general solution of .
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve: . [Hint: Substitute ]
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the general solution of
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the equation of a curve passing through if the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point is
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the equation of the curve through the point if the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point is
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the equation of a curve passing through the origin if the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point is equal to the square of the difference of the abscissa and ordinate of the point.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
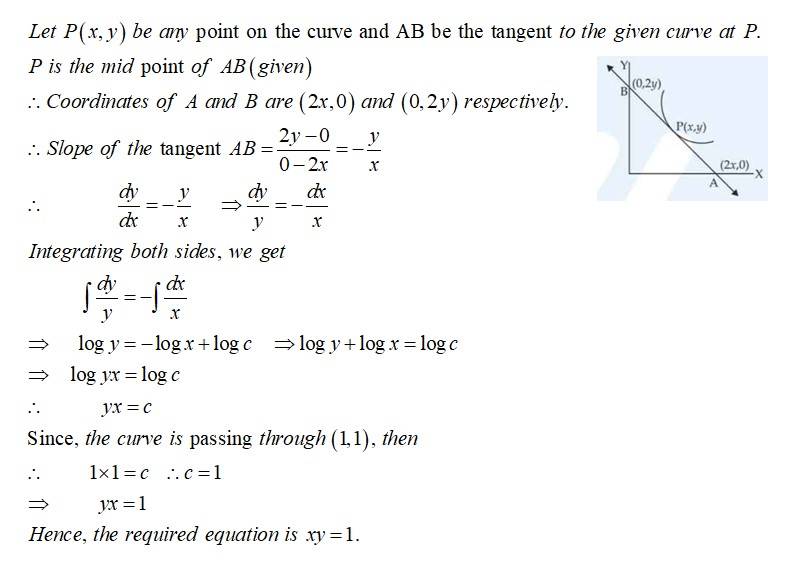
Find the equation of a curve passing through the point . If the tangent drawn at any point on the curve meets the coordinate axes at and such that is the midpoint of .
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve:
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the solution of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the differential equation of all non-vertical lines in a plane.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Given that and when . Find the value of when .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve the differential equation .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve the differential equation .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the general solution of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve the differential equation .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve: .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve the differential equation , when , .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the general solution of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If is a solution of and , then find the value of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If is a solution of and , then show that .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Form the differential equation having , where and are arbitrary constants, as its general solution.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

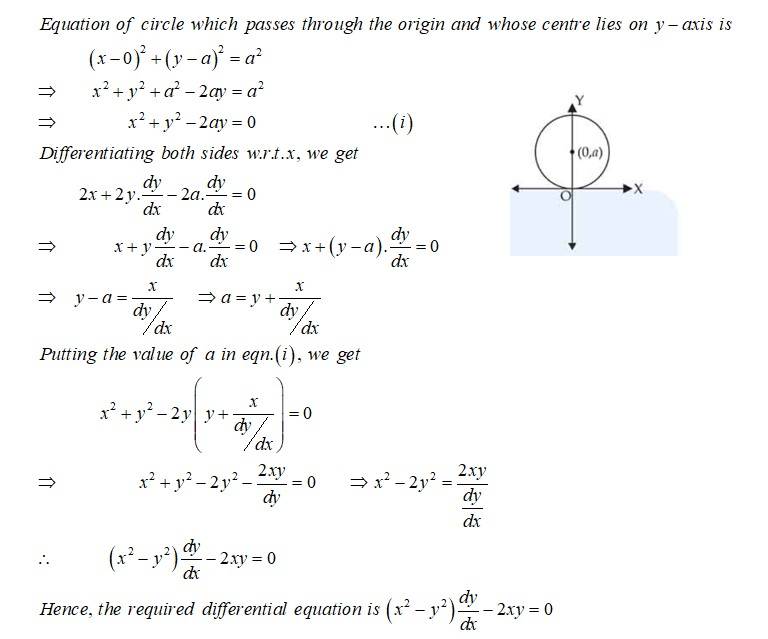
Form the differential equation of all circles which pass through the origin and whose centers lie on the y-axis.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the equation of a curve passing through the origin and satisfying the differential equation
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve:
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the general solution of the differential equation
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the general solution of .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve: .Hint: Substitute after separating and .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve: given that .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve the differential equation given that when .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Form the differential equation by eliminating and in .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solve the differential equation
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the differential equation of the system of concentric circles with center .
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Choose the correct answer from the given four options in each of the Exercises from 1 to 42 (M.C.Q)
Q1.The degree of the differential equation is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) Not defined
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The degree of the differential equation is
(A) 4
(B)
(C) Not defined
(D) 2
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The order and degree of the differential equation respectively, are
(A) 2 and not defined
(B) 2 and 2
(C) 2 and 3
(D) 3 and 3
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , then is a solution of
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The differential equation for , where A and B are arbitrary constants, is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solution of the differential equation represents:
(A) A rectangular hyperbola
(B) A parabola whose vertex is at the origin
(C) A straight line passing through the origin
(D) A circle whose center is at the origin
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Integrating factor of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Family of curves is represented by the differential equation of degree:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Integrating factor of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Solution of is given by
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The number of solutions of when is:
(A) None
(B) One
(C) Two
(D) Infinite
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Which of the following is a second-order differential equation?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Integrating factor of the differential equation
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
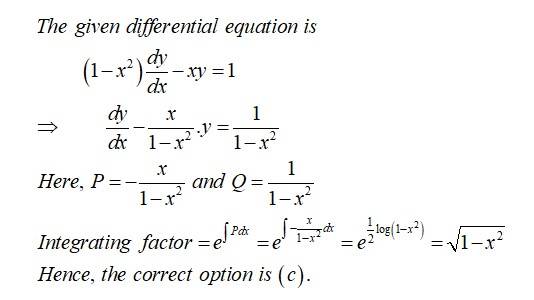
is the general solution of the differential equation:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The differential equation represents:
(A) Family of hyperbolas
(B) Family of parabolas
(C) Family of ellipses
(D) Family of circles
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The general solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The degree of the differential equation is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 5
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The integrating factor of the differential equation is:
(A) Cos
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
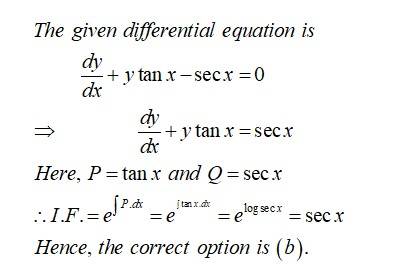
The solution of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The integrating factor of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
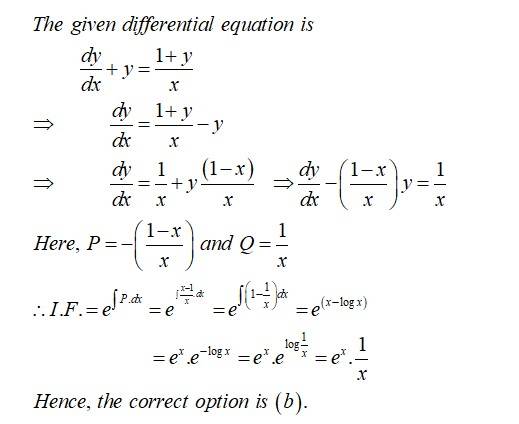
satisfies which of the following differential equations?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The differential equation of the family of curves where a is an arbitrary constant, is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The family of curves corresponds to a differential equation of order:
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 1
(D) Not defined
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The general solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The curve for which the slope of the tangent at any point is equal to the ratio of the abscissa to the ordinate of the point is:
(A) An ellipse
(B) A parabola
(C) A circle
(D) A rectangular hyperbola
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The general solution of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of the equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The differential equation for which is a solution, is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The order and degree of the differential equation are:
(A) 1, 4
(B) 3, 4
(C) 2, 4
(D) 3, 2
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The order and degree of the differential equation are:
(A) 2, 3/2
(B) 2, 3
(C) 2, 1
(D) 3, 4
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The differential equation of the family of curves is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Which of the following is the general solution of ?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The general solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C) tan
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The general solution of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) y
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of the differential equation is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The solution of is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
JEE Mains Solution 2022
JEE Mains Solution 2022
Commonly asked questions
Let R be a relation from the set to itself such that R = where p, q 3 are prime numbers. Then, the number of elements in R is:
R = { (a, b): b = pq, where p, q are prime}
p, q {3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 3, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59} total 16
p, q {3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19}
{3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19}
7 + 3 + 1 = 11
If z = 2 + 3 i, then z5 + is equal to:
Let A and B be two 3 × 3 non-zero real matrices such that AB is a zero matrix. Then
only .
then the maximum value of a is:
LHS =
If where then which of the following is NOT correct?
The integral is equal to:
Let the solution curve y = y(x) of the differential equation pass through the point Then, is equal to:
IF =ex
= tan-1 (t) + c
Let a line L pass through the point of intersection of the lines bx + 10y – 8 = 0 and If the line L also passes through the point (1, 1) and touches the circle 17(x2 + y2) = 16, then the eccentricity of the ellipse is:
y – 1 = m(x – 1)
mx – y + 1 – m = 0
m2 – 3m + 1 = 0
b =
b2 = 2
2 = 5 (1 – e2)
IF the foot of the perpendicular from the point A(1, 4, 3) on the plane P : 2x + my + nz = 4, is then the distance of the point A form the plane P, measured parallel to a line with direction ratios 3, 1, 4, is equal to:
A (1, 4, 3)
2x + my + nz = 4
7m + 3n = 16
m = 1, n = 3
Plane : 2x + y + 3z = 4
AM =
Let Let be vector satisfying If are non-parallel, then the value of is:
= (3 + 2)= 5
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point A due north of it and from a point B at a distance of 9 units due west of A is If the distance of the point B from the tower is 15 units, then cot is equal to:
The statement is equivalent to:
Option (D) is correct
Let the circumcentre of a triangle with vertices A(a, 3), B(b, 5) and C(a, b), ab > 0 be P(1, 1). If the line AP intersects the line BC at the point Q(k1, k2), then k1 + k2 is equal to:
= 3, 1= 5, 3
x + 2y = 3 …… (i)
3x – y = 8…… (ii)
x + 2y = 3
3x – y = 83 × 2
Let be two unit vectors such that the angle between them is If is the angle between the vectors then the value of 164cos2 is equal to:
= 1 + + 2 + 0 + 0
164 cos2 (θ)= 90 +
If f(X) =
The area of the region is equal to:
Let the focal chord of the parabola P : y2 = 4x along the line L : y = mx + c, m > 0 meet the parabola at the points M and N. Let the line L be a tangent to the hyperbola H : x2 – y2 = 4. If O is the vertex of P and F is the focus of H on the positive x-axis, then the area of the quadrilateral OMFN is:
L : y = mx + c, m > 0
y = m (x – 1)
The number of points, where the function f : R R,
is NOT differentiable, is:
x = 1, 4 (doubtful points)
Diff. at x = 1
Not diff. at x = 4
Let S = {1, 2, 3,…., 2022}. Then the probability, that a randomly chosen number n from the set S such that HCF (n, 2022) = 1, is:
S = {1,2, 3, …., n, 2022}
HCF (n, 2022) = 1
2022 = 2 × 1011 ->3 × 337
2022 = 2 × 3 × 337 (prime factorization)
Let n (A) = no members divisible by 2 = 1011
Let n (B) = no members divisible by 3 = 674
Let n (C) = no members divisible by 337 = 6
= 1011 + 674 + 6 – 337 – 2 – 3 + 1
= 1350
Prob.
Let f(x) = Then which of the following statements are true?
P : x = 0 is a point of local minima of f
Q : x = is a point of inflection of f
R : is increasing for x >
From graph : P, Q, R
Let Then, the sum of roots of all the equations
Put cos 2 = t
Equation 2t2– 5t = 0, t (2t – 5) = 0
cos 20 = 0, 0 < 2 < 4
Let the mean and the variance of 20 observations x1, x2,…….x20 be 15 and 9, respectively. For , if the mean of is 178, then the square of the maximum value of is equal to………….
= 2, 28
Let a line with direction ratios a, 4a, 7 be perpendicular to the lines with direction ratios 3, 1, 2b and b, a, 2. If the point of intersection of the line and the plane x – y + z = 0 is is equal to………
(a, 4a, 7). (3, 1, 2b)= 0
3a + 4a – 14b = 0 a – 2b = 0 ……. (i)
(a, 4a, 7) . (b, a, 2) = 0
ab – 4a2 + 14 = 0……… (ii)
(i) & (ii) =>2b2 – 16b2+ 14 = 0
Plane : x – y + z = 0
P (4, 5, 1)
4 + 5 + 1 = 10
Le aa1, a2, a3,…… be an A.P. If then 4a2 is equal to……
= 1
a + d = 4
4 (a + d) = 16
Let the ratio of the fifth term from the beginning to the fifth term from the end in the binomial
The number of matrices of order 3 × 3, whose entries are either 0 or 1 and the sum of all the entries is a prime number, is……….
S = is prime
Prime value = 2,3, 5, 7
Total number of matrices
= 36 + 84 + 126 + 36 = 282
Let p and p + 2 be prime numbers and let
Then the sum, of the maximum values of and , such that p and (p + 2) divide is…………..
= 2(p + 3) – 2 (p + 2) = 2
If then 34 k is equal to………….
34 k = 286
Let S = {4, 6, 9} and T = {9, 10, 11,…., 1000}.
If A = then the sum of all the elements in the set T – A is equal to…………….
T = {9, 10, 11, 12, …., 1000}
S = {4, 6, 9}
A =
Let 4 appear x no. of times
6 appear y no. of times
9 appear z no. of times
10 then set A has n element 4x + 6y + 9z
Concept : Let a and b are co-prime numbers, then members from (a - ) (b – 1) and more can be expressed in the form ax + by where x, y {0, 1, 2, …}
So, all the number of the form
2y + 3z are (2 1). (3 – 1), ….
i.e., 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, ….
form : 2 + t, t = 0, 1, 2, 3, ….
So, 6y + 9z = 3 (2y + 3z) = 3 (2 + t) = 6 + 3t, t = 0, 1, 2, 3, …
sum of element of T – A is 11
Let the mirror image of a circle c1 : x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y + a = 0 in line y = x + 1 be c2 : 5x2 + 5y2 + 10gx + 10fy + 38 = 0. If r is the radius of circle c2, then a + 6r2 is equal to…………..
A’ = 2m – A = (b – 1, a + 1)
r
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine Exam

