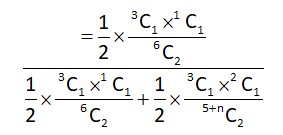- Relations and Function Question and Answers
- JEE Mains 2022
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022,24th june , Maths, first shift
Relations and Function Question and Answers
| Q.1. If , define relations on which have properties of being: (a) Reflexive, transitive but not symmetric (b) Symmetric but neither reflexive nor transitive (c) Reflexive, symmetric and transitive. |
| Sol:
|
| Q.2. Let be a relation defined on the set of natural numbers N as follows: . Find the domain and range of the relation . Also, verify whether is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive. |
| Sol:
|
| Q.3. Given , construct an example of each of the following: (a) An injective mapping from to (b) A mapping from to which is not injective (c) A mapping from to . |
| Sol:
|
| Q.4. Give an example of a map: (i) Which is one-one but not onto (ii) Which is not one-one but onto (iii) Which is neither one-one nor onto. |
| Sol: |
Commonly asked questions
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective.
.
.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , define relations on which have properties of being:
(a) reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
(b) symmetric but neither reflexive nor transitive
(c) reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be a relation defined on the set of natural numbers N as follows:
. Find the domain and range of the relation . Also, verify whether is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Given , construct an example of each of the following:
(a) An injective mapping from to
(b) A mapping from to which is not injective
(c) A mapping from to .
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Give an example of a map:
(i) which is one-one but not onto
(ii) which is not one-one but onto
(iii) which is neither one-one nor onto.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
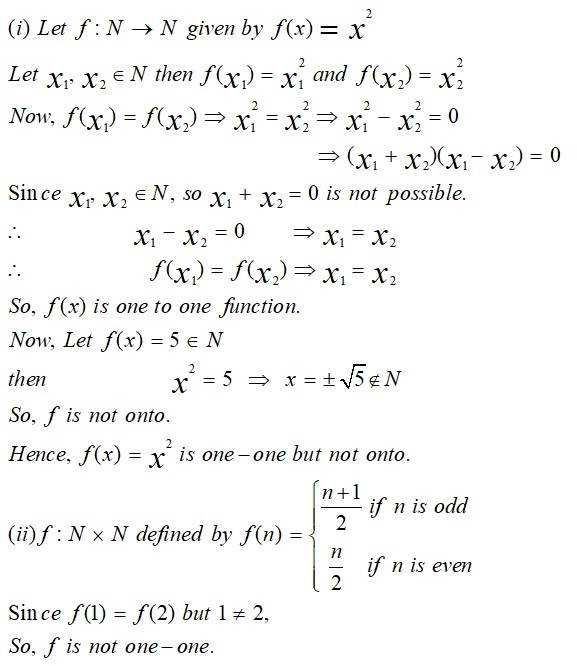
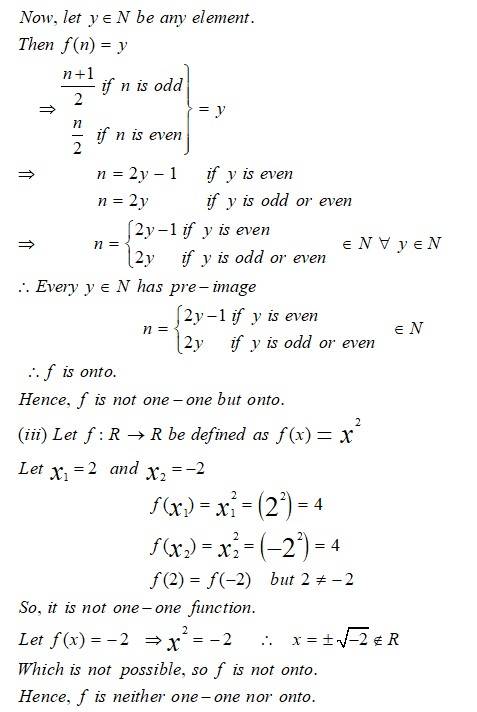
Let . Let be defined by . Then Show that is bijective.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let , Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on are one-one, onto, or bijective:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv) .
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Each of the following defines a relation on :
(i) is greater than
(ii)
(iii)
(iv) .
Determine which of the above relations are reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
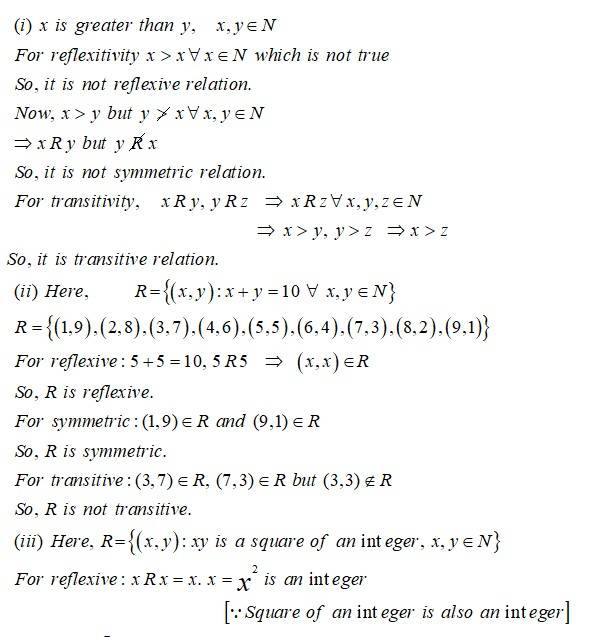

Let and be the relation in defined by if for . Prove that is an equivalence relation and also obtain the equivalent class .
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Using the definition, prove that the function is invertible if and only if is both one-one and onto.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Functions are defined, respectively, by , , find
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the binary operation defined on . Find which of the following binary operations are commutative:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv) .
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be binary operation defined on by . Then the operation is:
(i) Commutative but not associative
(ii) Associative but not commutative
(iii) Neither commutative nor associative
(iv) Both commutative and associative.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let and the relation be defined on as follows:
.
Then, write minimum number of ordered pairs to be added in to make reflexive and transitive.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol: R = { (a, a), (b, c), (a, b)}.
To make R as reflexive we must add (b, b) and (c, c) to R. Also, to make R as transitive we must add
(a, c) to R.
So, minimum number of ordered pair is to be added are (b, b), (c, c), (a, c).
Kindly consider the following

This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
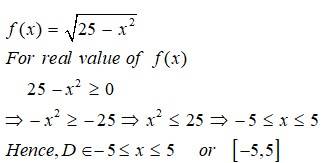
Let be defined by and , .
Respectively then, Find .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the function defined by Write .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If and the function , write
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If is defined by , write .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Is a function? If is described by , then what value should be assigned to and .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Given that, g = { (1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)}.
Here, each element of domain has unique image. So, g is a function.
Now given that, g (x ) = x +
For (1,1) g (1) = +
+ = 1… (i)
For (2,3) g (2) = 2 +
2 + = 3 … (ii)
From Equations. (i) and (ii),
2 (1 - ) + = 3
2 - 2 + = 3
2 - = 3
= - 1
If = - 1, then = 2
= 2, = - 1
If the mappings and are given by
and , write .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the set of complex numbers. Prove that the mapping given by , is neither one-one nor onto.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let the function be defined by Show that is neither one-one nor onto.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let and . Find whether the following subsets of are functions from to or not:
.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If functions and satisfy , then show that is one-one and is onto.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the function defined by . Then, find the range of .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
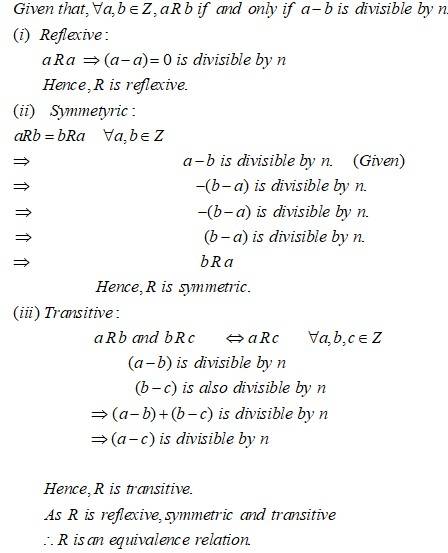
Let be a fixed positive integer. Define a relation in as follows: if and only if is divisible by . Show that is an equivalence relation.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the set of all triangles in the Euclidean plane, and let a relation on be defined as if is congruent to . Then is:
(A) Reflexive but not transitive
(B) Transitive but not symmetric
(C) Equivalence
(D) None of these.
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Consider the non-empty set consisting of children in a family and a relation defined as if is the brother of . Then is:
(A) Symmetric but not transitive
(B) Transitive but not symmetric
(C) Neither symmetric nor transitive
(D) Both symmetric and transitive.
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The maximum number of equivalence relations on the set are
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 5
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If a relation on the set be defined by , then is
(A) Reflexive
(B) Transitive
(C) Symmetric
(D) None of these.
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let us define a relation in as if . Then is:
(A) An equivalence relation
(B) Reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
(C) Symmetric, transitive but not reflexive
(D) Neither transitive nor reflexive but symmetric
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let and consider the relation
.
Then is
(A) Reflexive but not symmetric
(B) Reflexive but not transitive
(C) Symmetric and transitive
(D) Neither symmetric, nor transitive
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The identity element for the binary operation defined on as is
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) 2
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If the set contains 5 elements and the set contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from to is
(A) 720
(B) 120
(C) 0
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let and . Then the number of surjections from into is
(A) np2
(B)
(C)
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

Let be defined by . Then is
(A) One-one
(B) Onto
(C) Bijective
(D) is not defined
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be defined by and by . Then is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Which of the following functions from into are bijections?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the functions defined by . Then is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
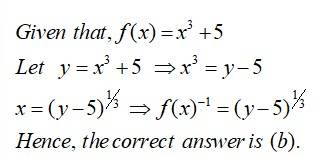
Let and be the bijective functions. Then is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
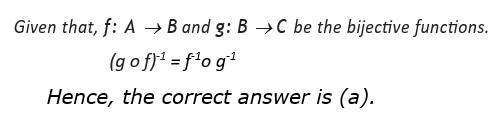
Let be defined by . Then
(A)
(B)
(C) ( )x=-x
(D)
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be defined by
Then
(A) Constant
(B)
(C)
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be the function defined by . Then the range of is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
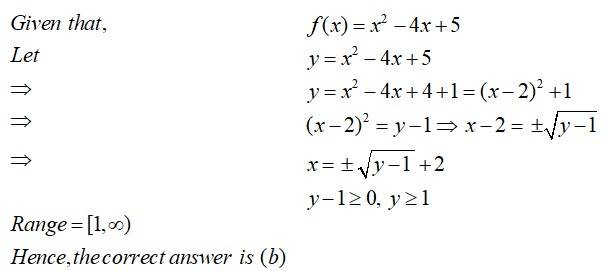
Let be the function defined by and be another function defined by . Then
is
(A) 1
(B) 1
(C)
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be defined by:
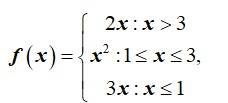
Then is
(A) 9
(B) 14
(C) 5
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let be given by . Then is
(A)
(B)
(C) Does not exist
(D) None of these
This is a Objective Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let the relation be defined in by if . Then
This is a Fill in the Blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
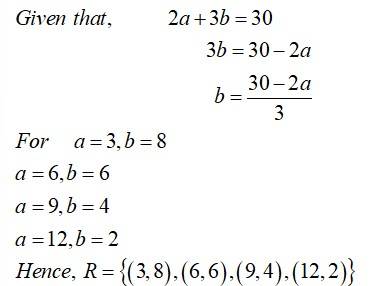
Let the relation be defined on the set by . Then is given by ________
This is a Fill in the Blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

Let and . Then and
This is a Fill in the Blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
![]()
This is a Fill in the Blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
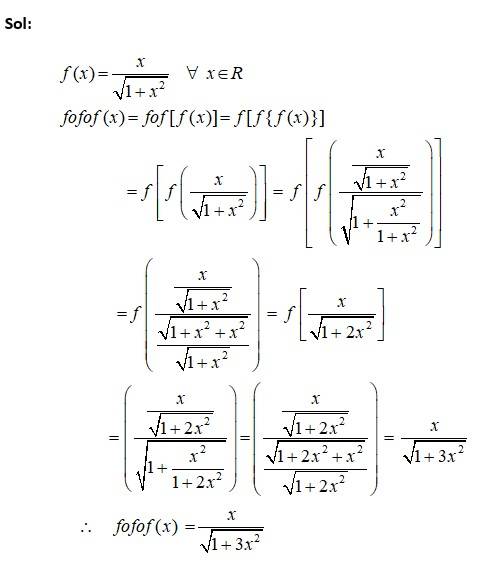
If , then
This is a Fill in the Blanks Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
State True or False for the statements in each of the Exercises 6 to 14:
Let be a relation defined on the set . Then is symmetric, transitive but not reflexive.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

Let be the function defined by . Then is invertible.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Every relation which is symmetric and transitive is also reflexive.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

An integer is said to be related to another integer if is a integral multiple of . This relation in is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let and be the set of natural numbers. Then the mapping defined by , is onto.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
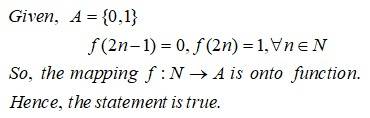
The relation on the set defined as is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
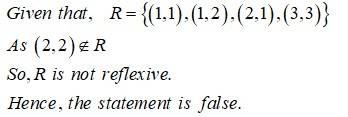
The composition of functions is commutative.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
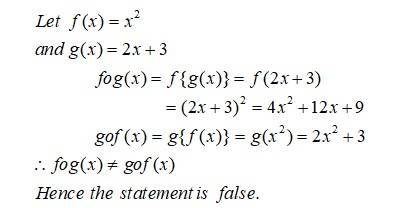
The composition of functions is associative.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Every function is invertible.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
A binary operation on a set has always the identity element.
This is a True or False Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
The number of distinct real roots of the equation x5 + is …………..
are roots of above equation and x5 + 3x – 1 is a monotonic term hence vanishes at exactly one value of x other then 1 or 1.
3 real roots.
Let f : R -> R be a continuous function such that f(3x) – f(x) =. If f(8) = 7, then f(14) is equal to:
f (3x)- f (x) = x
Replace
Again replace
Also putting x = in f (3x) – 3 = F (14) – 3 = 7 f (14) = 10
Let O be the origin and A be the point z1 = 1 + 2i. If B is the point z2, Re(z2) < 0, such that OAB is a right angled isosceles triangle with OB as hypotenuses, then which of the following is NOT true?
If the system of linear equations.
8x + y + 4z = -=2
x + y + z = 0
3y =
has infinitely many solutions, then the distance of the point from the plane 8x + y + 4z + 2 = 0 is
So for = 4, it is having infinitely many solutions. = 6
For distance of from 8x + y + 4z + 2= 0 units
Let A be a 2 × 2 matrix with det(A) = 1 and det Then the sum of the diagonal elements of A can be:
| (A + I) (adj A + I)| = 4 |A adj A + A + Adj A + I| = 4 | (A)I + A + adj A + I|= 4|A| = 1
|A + adj A| = 4
The odd natural number a, such that the area of the region bounded by y = 1, y = 3, x = 0, x = ya is is equal to:
Since a is a odd natural number then
a = 5
Consider two G.P.’s. 2, 22, 23, …… and 4, 42, 43, …… of 60 and n terms respectively. If the geometric mean of all the 60 + n terms is , then is equal to:
Given G.P’s 2, 22, 23, …60 term and 4, 42, 43, … of 60
Now G.M. =
If the function f(x) = is continuous at x = 0, then k is equal to:
for continuity at x = 0
If f(x) = are continuous on R, then (gof)(2) + (fog)(2) is equal to:
f (x) and g (x) are continuous on R a = 4 and b = 1 – 16 = 15
then (gof) (2) + (fog) (2) = g (2) + f (-1) = -11 + 3 = -8
Let f(x) = Then the set of all values of b, for which f(x) has maximum value at x = 1, is:
If f (x) has maximum value at x = 1 then
……. (i)
……. (ii)
From (i) and (ii) we get
If a = and f(x) = , x (0, 1), then:
+ 2y tan x = sin x, 0 < x < and y = 0, then the maximum value of y(x) is:
= cos x – 2 cos2 x=
A point P moves so that the sum of squares of its distances from the points (1, 2) and (2, 1) is 14. Let f(x, y) = 0 be the locus of P, which intersects the x-axis at the points A , B and the y-axis at the points C, D. Then the area of the quadrilateral ACBD is equal to:
Let point P : (h, k)
Therefore according to question,
locus of P (h, k) is
Now intersection with x – axis are
Now intersection with y – axis are
Therefore are of the quadrilateral ABCD is =
Let the tangent drawn to the parabola y2= 24x at the point (α, β) is perpendicular to the line 2x + 2y = 5. Then the normal to the hyperbola at the point ( α+ 4, β+ 4) does NOT pass through the point:
Any tangent to y2 = 24x at (α, β) is βy = 12 (x + α) therefore Slope =
and perpendicular to 2x + 2y = 5 =>12 =β and α= 6 Hence hyperbola is = 1 and normal is drawn at (10, 16)
therefore equation of normal This does not pass through (15, 13) out of given option.
The length of the perpendicular from the point (1, 2, 5) on the line passing through (1, 2, 4) and parallel to the line x + y – z = 0 = x – 2y + 3z – 5 is:
he line x + y – z = 0 = x – 2y + 3z – 5 is parallel to the vector
Equation of line through P(1, 2, 4) and parallel to
Let
is perpendicular to
Hence
Let If the projection of on the vector is 30, then equal to:
Given :
Projection of on
On solving (Rejected as > 0) and = 7
The mean and variance of a binomial distribution are and respectively. If P(X = 1) = then P(X = 4 or 5) is equal to:
Given, mean = np = . and variance = npq =
Let E1, E2, E3 be three mutually exclusive events such that P(E1) = , P(E3) = and P(E3) = If the maximum and minimum values of p are p1 and p2, then (p1 + p2) is equal to:
Taking intersection to all
Let S = Then is equal to:
Now apply AM for
is equal to:
The statement
(D)
q is equivalent to p
If for some q, q, r R, not at all have same sign, one of the roots of the equation is also a root of the equation x2 + 2x – 8 = 0, then is equal to………….
Let and are the roots of
Also, it has a common root with x2 + 2x – 8 = 0
The common root between above two equations is 4.
The number of 5-digit natural numbers, such that the product of their digits is 36, is………
Factors of 36 = 22.32.1
Five-digit combinations can be
(1, 2, 3, 3), (1, 4, 3, 1), (1, 9, 2, 1), (1, 4, 9, 11), (1, 2, 3, 6, 1), (1, 6, 1, 1)
i.e., total numbers
The series of positive multiples of 3 is divided into sets : Then the sum of the elements in the 11th set is equal to…………..
Given series
11th set will have 1 + (10)2 = 21 terms
Also up to 10th set total 3 × k type terms will be 1 + 3 + 5 + ……… +19 = 100 terms
Sum of elements = 3 × (101 + 102 + ….+121)
If the coefficients of x and x2 in the expansion of (1 + x)p (1 – x)q, p, q 15, are -3 and -5 respectively, then the coefficient of x3 is equal to…………………
Coefficient of x in
Coefficient of x2 in
Coefficient of x3 in
If dx, then n N is equal to………….
using by parts we get,
Let a cure y = y(x) pass through the point (3, 3) and the area of the origin under this curve, above the x-axis and between the abscissae 3 and x (>3) be . If the curve also passes through the point in the first quadrant, then is equal to………….
differentiating w.r.to x
After solving we get also curve passes through (3, 3) c = -2
which passes through
The equations of the sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle ABC are 2x + y = 0, x + py = 15a and x – y = 3 respectively. If its orthocenter is (2, a), then p is equal to…………
Slope of AH = slope of BC =
slope of HC =
slope of BC × slope of HC = -1 p = 3 or 5
hence p = 3 is only possible value.
Let the function f(x) = 2x2 – loge x, x > 0, be decreasing in (0, a) and increasing in (a, 4). A tangent to the parabola y2 = 4ax at a point P on it passes through the point (8a, 8a – 1) but does not pass through the point If the equation of the normal at P is then a + b is equal to…………….
so f (x) is decreasing in
Tangent at y2 = 2x is y = mx + it is passing through (4, 3) therefore we get m =
So tangent may be passes through (-2, 0) so rejected.
Equation of normal
Let Q and R be two points on the line at a distance from the point P(4, 2, 7). Then the surface of the area of the triangle PQR is……………
Let PT perpendicular to QR
therefore
Therefore square of = 153.
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,24th june , Maths, first shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,24th june , Maths, first shift
Commonly asked questions
Let A = and B = . Then, B :
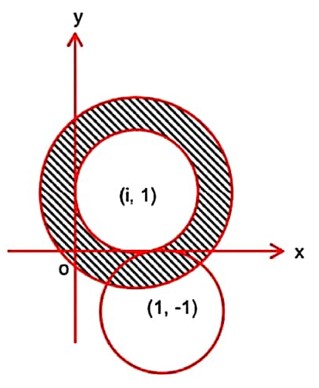
and
and also
hence B has infinite set.
The remainder when 32022 is divided by 5 is :
(3 * 3 * 3 * ………2022 times) ¸ 5
Remainder = (-1) (-1) (-1) ….1011 times)
Remainder = -1 + 5 = 4
The surface area of a balloon of spherical shape being inflated increases at a constant rate. If initially, the radius of balloon is 3 units and after 5 seconds, it becomes 7 units, then its radius after 9 seconds is :
Surface area, S = 4pr2
Initially t = 0, r = 3
c = 36 p
When t = 5, r = 7, k = 32p
When t = 9, r = r, r = 9
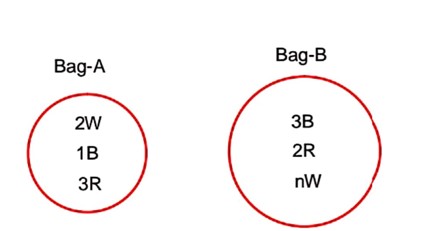
Bag A contains 2 white, 1 black and 3 red balls and bag B contains 3 black, 2 red and n white balls. One bag is chosen at random and 2 balls drawn from it at random are found to be 1 red and 1 black. If the probability that both balls come from Bag A is then n is equal to ________.
After solving, we get n = 4
Let x2 + y2 + Ax + By + C = 0 be a circle passing through (0, 6) and touching the parabola y = x2 at (2, 4). Then A + C is equal to
Equation of tangent to the circle at (2, 4) is
(4 + A) x + (8 + B) y + 2A + 2B + 2C = 0……. (i)
Also equation of tangent to parabola y = x2 at (2, 4) is
4x – y = 4 ………. (ii)
Comparing (i) and (ii) we get, A + C = 16
The number of values of a for which the system of equations :
x + y + z = a
ax + 2ay + 3z = -1
x + 3ay + 5z = 4
is inconsistent, is
For inconsistent,
a = 1
If the sum of the squares of the reciprocals of the roots a and b of the equation is 15, then is equal to :
The set of all values of k for which , is the interval :
Let S = .
Let If = 100l, then l is equal to :
S =
=
= 1 + a2
For the function f(x) = 4 loge(x – 1) – 2x2 + 4x + 5, x > 1, which one of the following is NOT correct?
f (x) = 4loge (x – 1) -2x2 + 4x + 5, x > 1
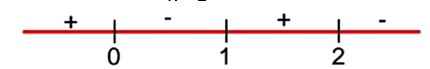
option (A) is correct.
(B) f (x) = -1, has two solution
option (B) is correct
option (C) is not correct
(D) f (e) = 4loge (e – 1) -2 (e2 – 2e + 1) + 7 > 0
f (e + 1) = 4 – 2 (e + 1)2 + 4 (e + 1) +5+ < 0
option (D) is correct
If the tangent at the point (x1, y1) on the curve y = x3 + 3x2 + 5 passes through the origin, then (x1, y1) does NOT lie on the curve:
f(x) =
f(1) = 3 + sin 1 cos 1 and
The sum of absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of the function f(x) = |2x2 + 3x + 2| + sin x cos x in the interval [0, 1] is :
f(x) =
f(1) = 3 + sin 1 cos 1 and
If where n is an even integer, is an arithmetic progression with common difference 1, and then n is equal to :
and
n (a2 + an) = 480 ……………… (ii)
n (a2 – a1) = 96
If x = x(y) is the solution of the differential equation ; then x(e) is equal to :
Equation (i) is in linear form, so I.F. = y-2
Let lx – 2y = µ be a tangent to the hyperbola Then is equal to
Let (x1, y1) be a point on the curve equation of tangent of eq (ii)
From (i) and (ii) are identical
Let and be unit vectors. If be vector such that the angle between and then is equal to :
If a random variable X follows the Binomial distribution B (33, p) such that 3P (X = 0) = P (X = 1) then the value of is equal to :L
n = 33, p = success, q = failure
3P (x = 0) = P (x = 1)
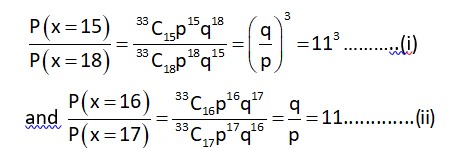
Subtracting, (ii) – (i), we get 1320
The domain of the function f(x) = is :
(x – 2) (x – 1) > 0 and
From (i) and (ii)
Let S = . If then T = n(S) is equal to
sinθ = 0 and 1 + sin θ = 2 cos2 θ = 2 – 2 sin2 θ ………….(i)
θ = np
θ = -p, p, 0
From (i), 2 sin2 θ + sin θ - 1 = 0
(2 sin θ - 1) (sin θ + 1) = 0
sin θ = -1,
is rejected.
T = cos (-2p) + cos 2p + cos θ + cos
T + n(s) = 4 + 5 = 9
The number of choices for , such that is a tautology, is :
Case I
When is same as
Then becomes
which is always true, so x becomes tautology.
Case II
When is same as
Then becomes is T, then is false, so x cannot be tautology.
Case III
When is same as
Then is same as which is true, so x becomes tautology.
Case IV
When is same as
Then
is true when p and q have same truth values both are false. Hence x cannot be tautology.
The number of one-one functions f:{a, b, c, d} ® {0, 1, 2, ……., 10} such that 2f (a) – f(b) + 3f(c) + f(d) = 0 is ___________.
f(b) = 2f(a) + 3f(c) + f(d)
Value of f(c) Value of f(a) Number of functions
1 7
2 5
0 3 3
4 2
0 6
1 2 2
3 1
2 0 3
1 1
3 0 1
Total number of function 31
In an examination, there are 5 multiple choice questions with 3 choices, out of which exactly one is correct. There are 3 marks for each correct answer, -2 marks for each wrong answer and 0 mark if the question is not attempted. Then, the number of ways a student appearing in the examination gets 5 marks is __________
Let x = correct answer, y = incorrect answer
only possible (x, y) is (3, 2)
Required number of ways = 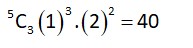
Let , be a fixed point in the xy-plane. The image of A in y-axis be B and the image of B in x-axis be C. If D (3 cos q, a sin q) is a point in the fourth quadrant such that the maximum area of is 12 square units, then a is equal to _________.
= 12
Let a line having direction ratios 1, -4, 2 intersect the lines and at the points A and B. Then (AB)2 is equal to _________.
and
AB2 = 84
f(-1) = 1
f(1) = 3
Hence f(x) will be discontinuous at x = 1 and also 4x2 – 1 = 0 , 1 , 2
The number of points where the function f(x) = [t] denotes the greatest integer t is discontinuous is __________-.
Let f (θ) = Then the value of is
f(q) = a sin q + b cos q
Solving (i) & (ii) we get a =
Let
If then is equal to __________.
Let f(x) =
a1 = 18, a2 = 16
a1 + a2 = 34
If two tangents drawn from a point (a, b) lying on the ellipse 25x2 + 4y2 = 1 to the parabola y2 = 4x are such that the slope of one tangent is four times the other, then the value of equals __________.
Equation of tangent to parabola y = mx + passes
though (a, b)
25(a2 + a) = 1 …………(iii)
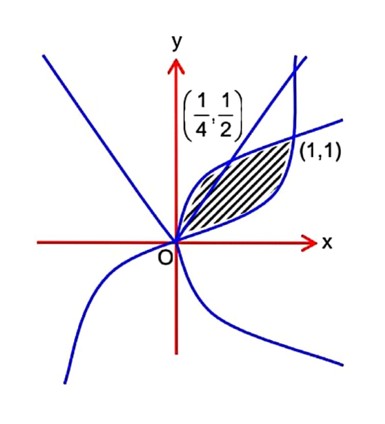
Let S be the region bonded by the curves y = x3 and y2 = x. The curve y = 2|x| divides S into two regions of areas R1, and R2 _________.
If max {R1, R2} = R2, then is equal to _________.
If the shortest distance between the lines is , then the integral value of ‘a’ is equal to __________.
=
Shortest distance =
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter One Exam