
- Integrals Long Answer Type Questions
- Integrals Short Answer Type Questions
- Integrals Objective Type Questions
- Integrals Fill in the Blanks
Integrals Long Answer Type Questions
| Q1. |
|
|
| Q2. |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Kindly consider the following
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
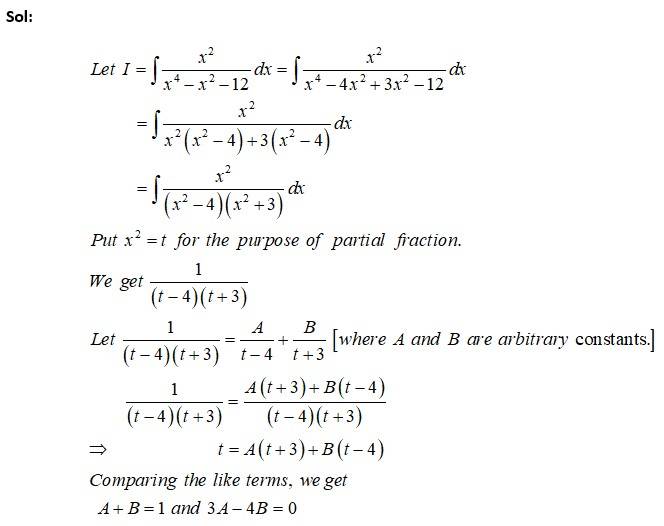
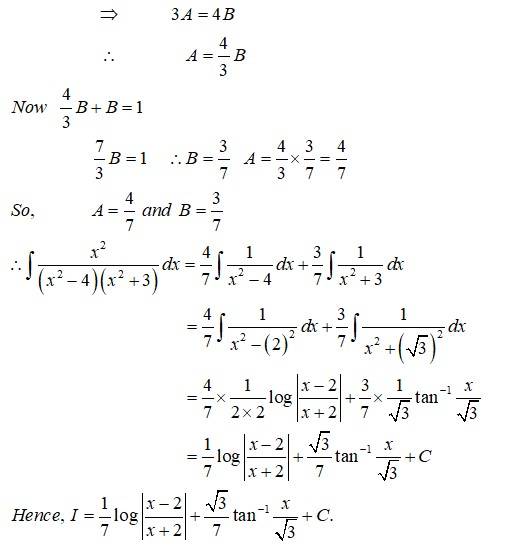
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
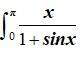
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
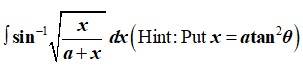
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

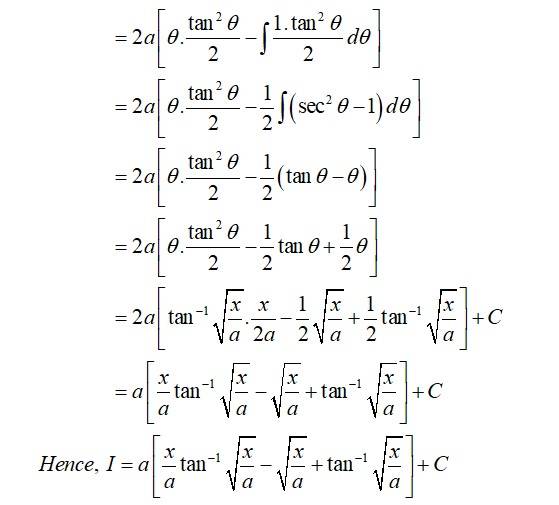
Kindly consider the following
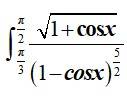
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Kindly consider the following
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

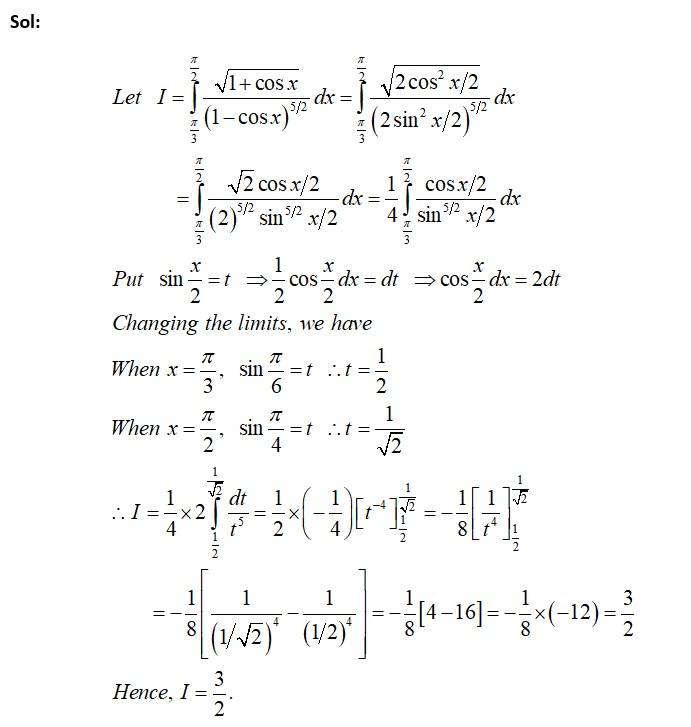
Kindly consider the following

This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
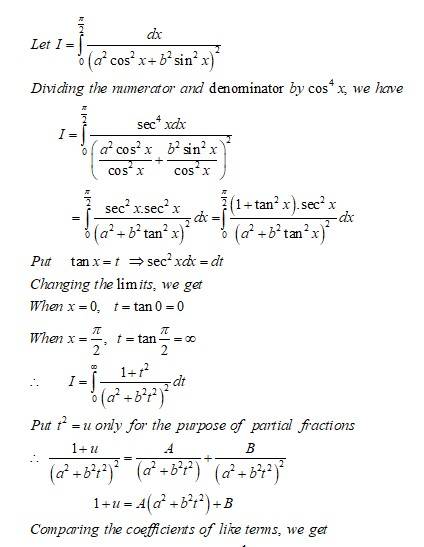
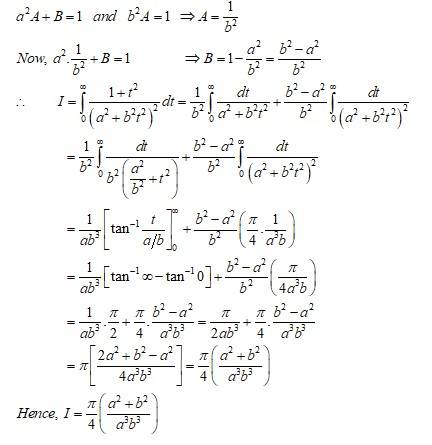
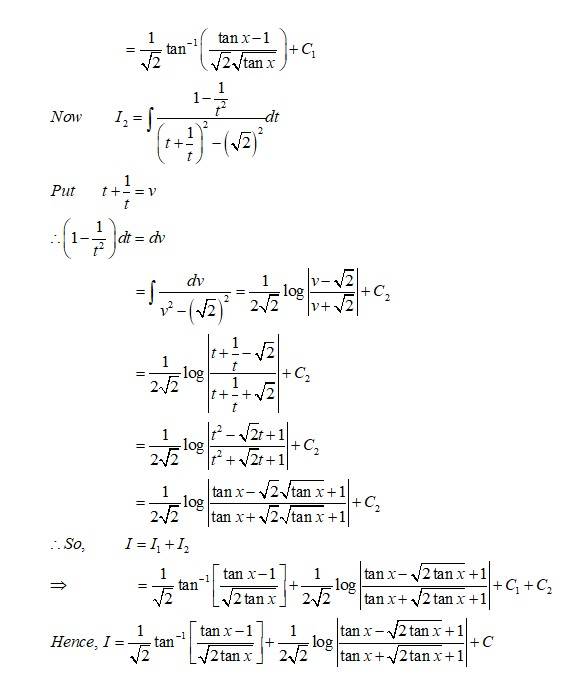
Kindly consider the following
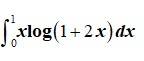
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
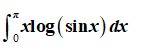
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
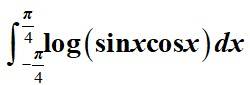
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Integrals Short Answer Type Questions
| Q1. |
| Sol:
|
| Q2. |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Evaluate the following:
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
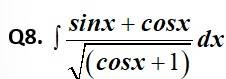
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
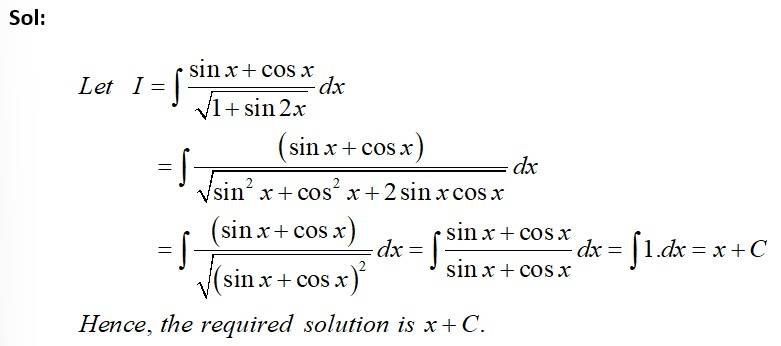
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
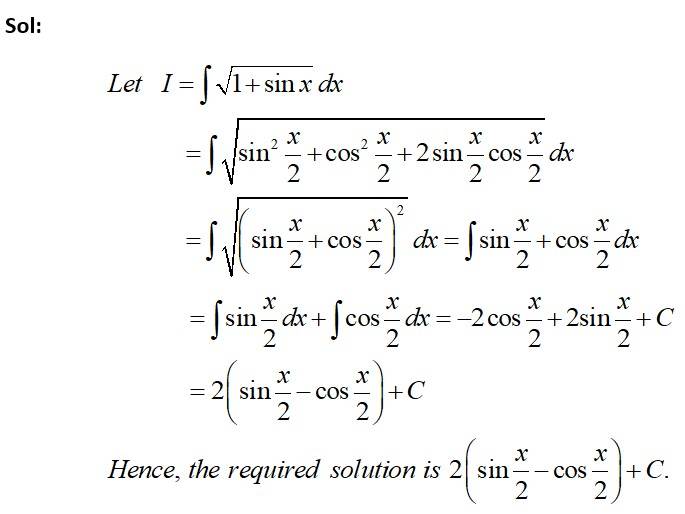
Kindly consider the following
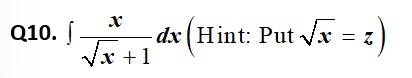
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

Kindly consider the following
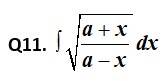
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
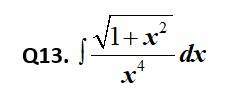
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
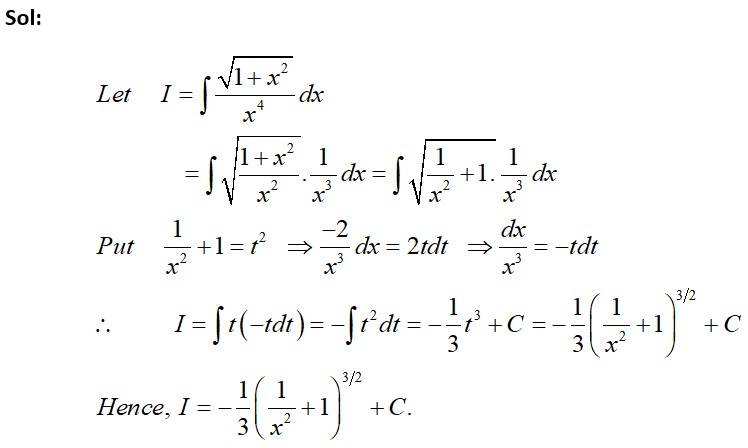
Kindly consider the following
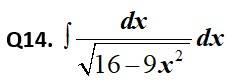
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
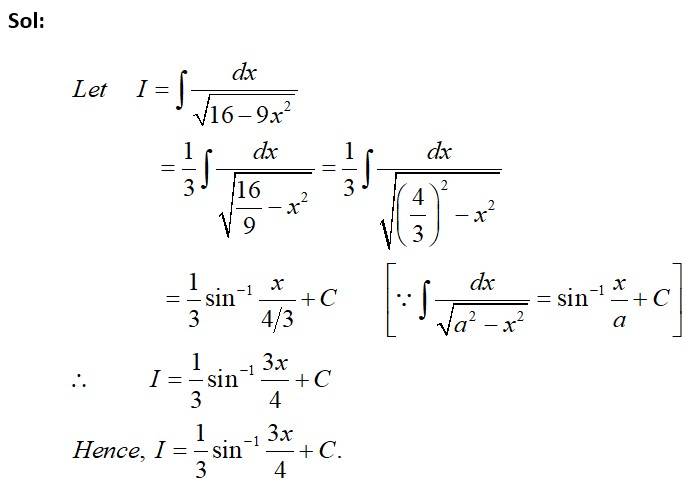
Kindly consider the following
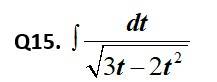
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
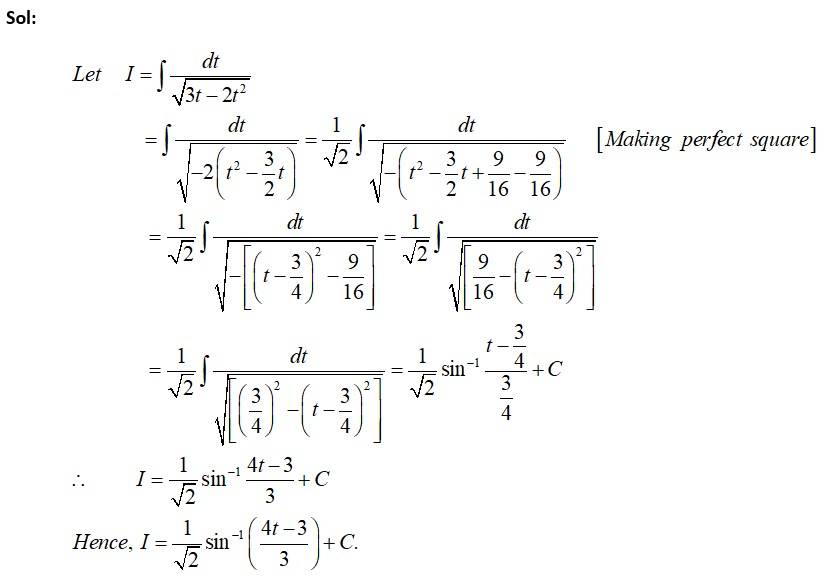
Kindly consider the following
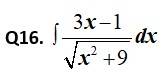
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

Kindly consider the following
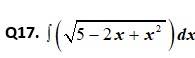
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
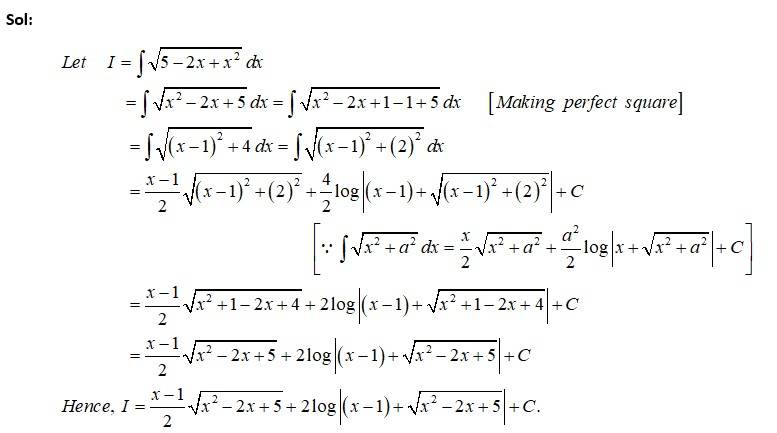
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
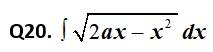
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
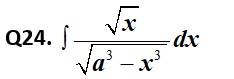
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
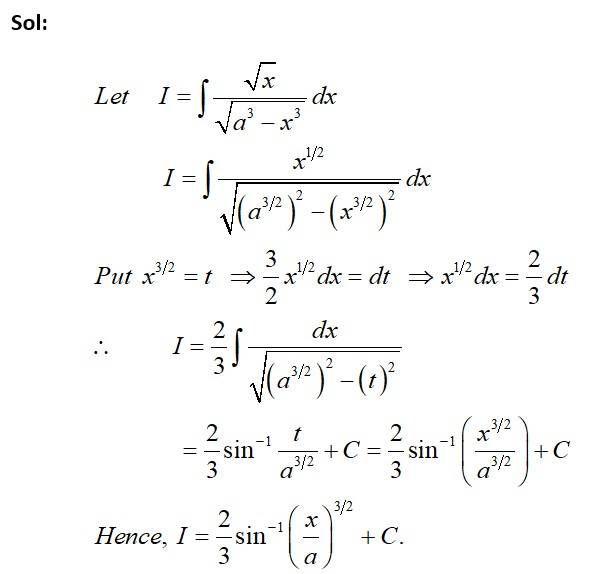
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
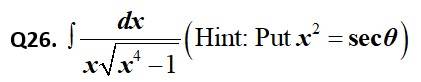
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
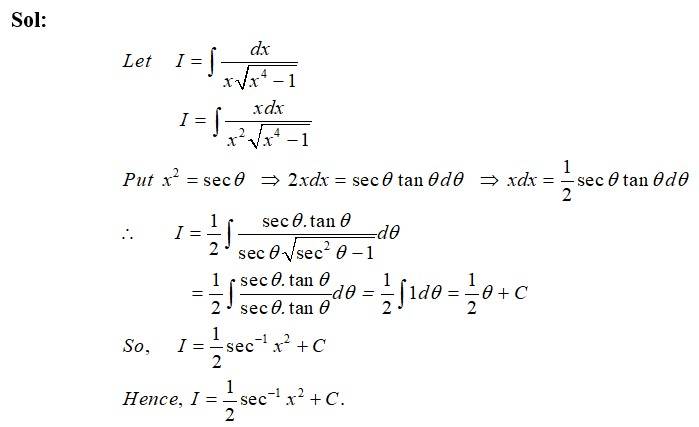
Evaluate the following as the limit of sums
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Evaluate the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
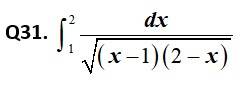
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
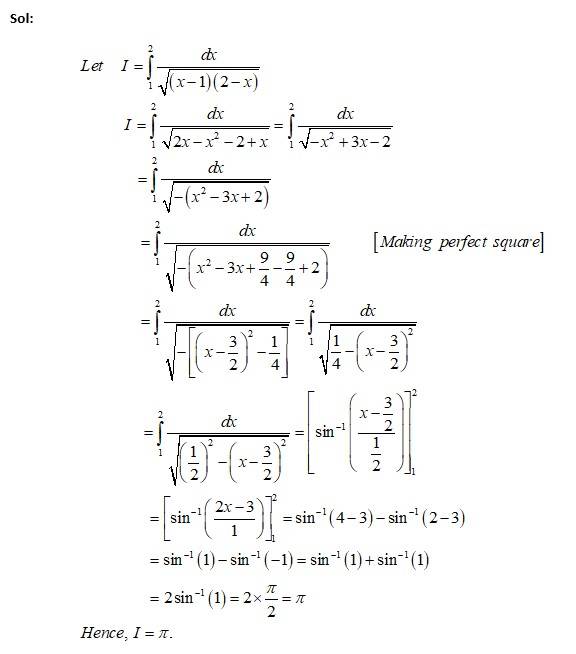
Kindly consider the following
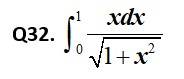
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
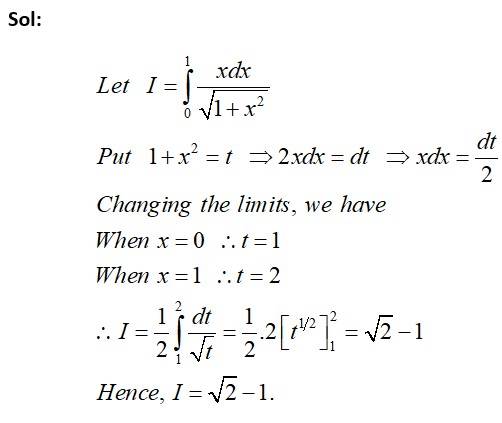
Kindly consider the following
sin x cos2xdx
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
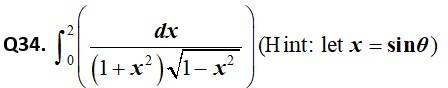
This is a Short answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
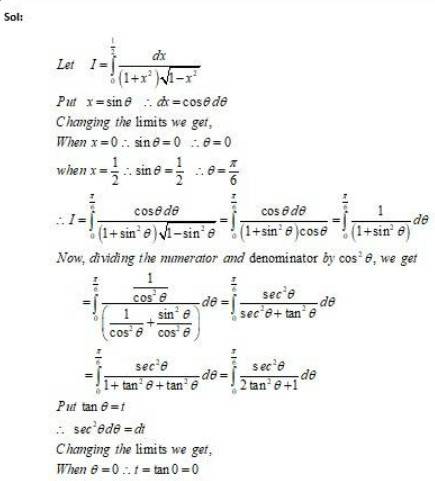
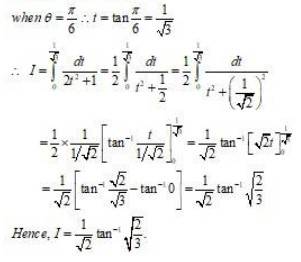
Integrals Objective Type Questions
| Choose the correct option from given four options in each of the Exercises from 1 to 11. Q1. is equal to (A) (B) (C) (D) |
| Sol:
|
| Q2. (A) (B) (C) (D) |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Choose the correct option from given four options in each of the Exercises from 1 to 11.
is equal to
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
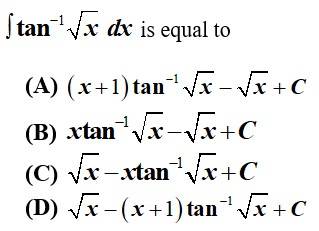
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar

(A) + C
(B) C
(C) + C
(D) + C
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
is equal to
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , then
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
is equal to
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
is equal to
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D) x
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
![]()
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
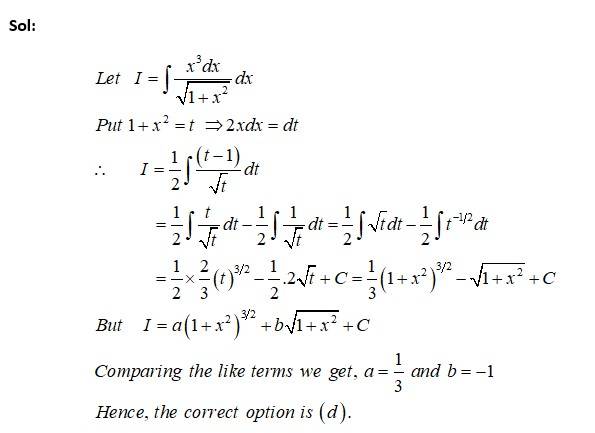
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
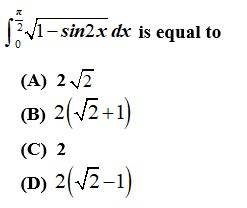
This is a Objective answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
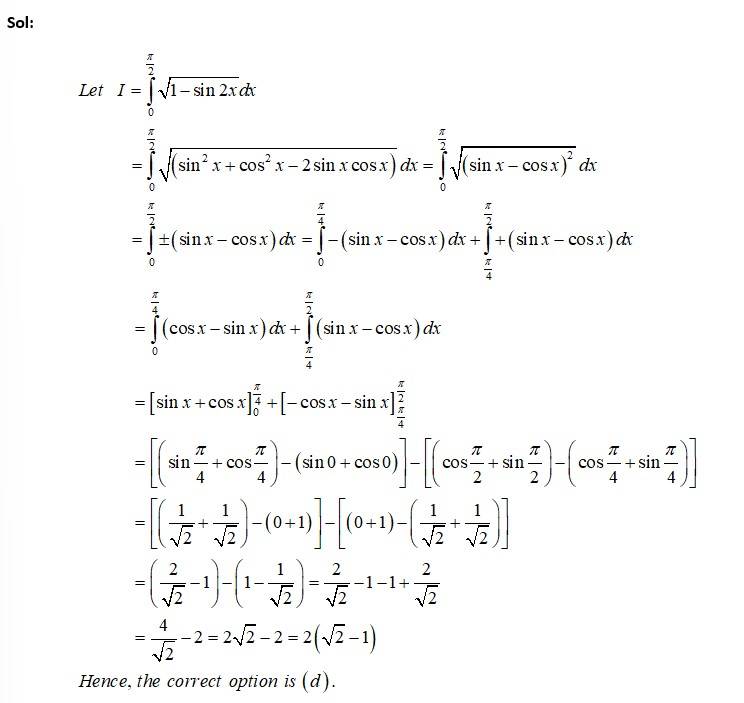
Integrals Fill in the Blanks
| Q1. is equal to _______. |
| Sol:
|
| Q2. =_______. |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Kindly consider the following
![]()
This is a Fill in the Blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
is equal to _______.
This is a Fill in the Blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
=_______.
This is a Fill in the Blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
If: ,then, _______.
This is a Fill in the Blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
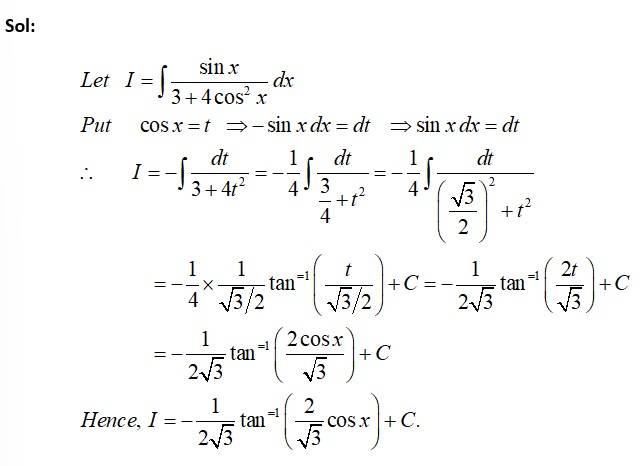
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
This is a Fill in the Blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Seven Exam
