- Applications of Derivatives Questions and Answers
- 26th June 2022 (First Shift)
- JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
Applications of Derivatives Questions and Answers
| 1. If the sum of the lengths of the hypotenuse and a side of a right-angled triangle is given, show that the area of the triangle is maximum when the angle between them is . |
| Sol: |
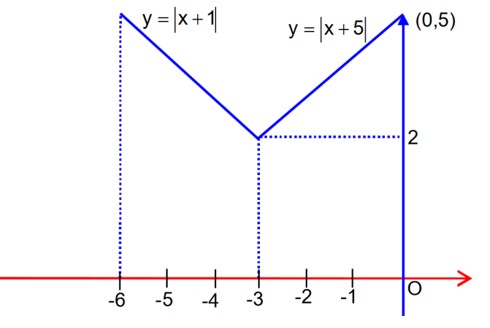
| 2. Find the points of local maxima, local minima, and the points of inflection of the function f(x) = Also, find the corresponding local maximum and local minimum values. |
| Sol:
|
| 3.A telephone company in a town has 500 subscribers on its list and collects fixed charges of Rs 300/- per subscriber per year. The company proposes to increase the annual subscription, and it is believed that for every increase of Re 1/-, one subscriber will discontinue the service. Find what increase will bring maximum profit. |
| Sol:
|
| 4. If the straight-line x cosα + y sinα = p touches the curve, , then prove that a² cos²α + b² sin²α =p². |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
If the sum of the lengths of the hypotenuse and a side of a right-angled triangle is given, show that the area of the triangle is maximum when the angle between them is .
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:


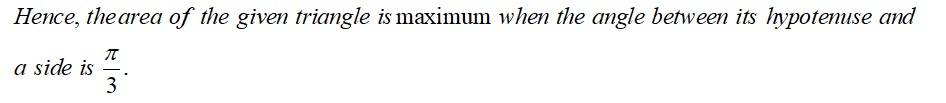
Find the points of local maxima, local minima, and the points of inflection of the function f(x) = Also, find the corresponding local maximum and local minimum values.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
A telephone company in a town has 500 subscribers on its list and collects fixed charges of Rs 300/- per subscriber per year. The company proposes to increase the annual subscription, and it is believed that for every increase of Re 1/-, one subscriber will discontinue the service. Find what increase will bring maximum profit.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If the straight-line x cosα + y sinα = p touches the curve, , then prove that a² cos²α + b² sin²α =p².
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
An open box with a square base is to be made of a given quantity of cardboard of area c². Show that the maximum volume of the box is cubic units.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
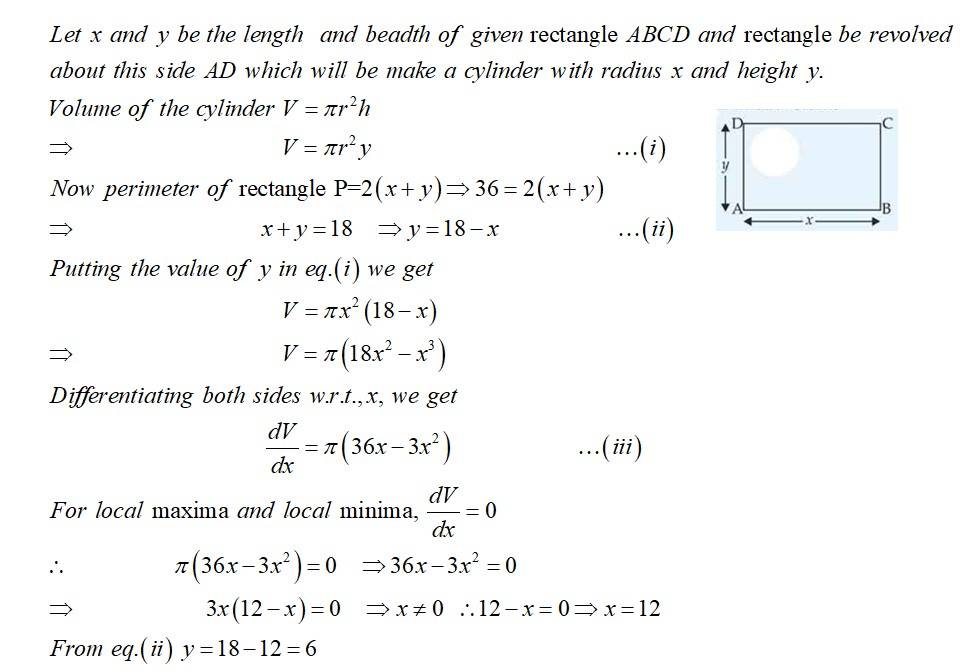
Find the dimensions of the rectangle of perimeter 36 cm which will sweep out a volume as large as possible when revolved about one of its sides. Also, find the maximum volume.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

If the sum of the surface areas of a cube and a sphere is constant, what is the ratio of an edge of the cube to the diameter of the sphere, when the sum of their volumes is minimum?
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

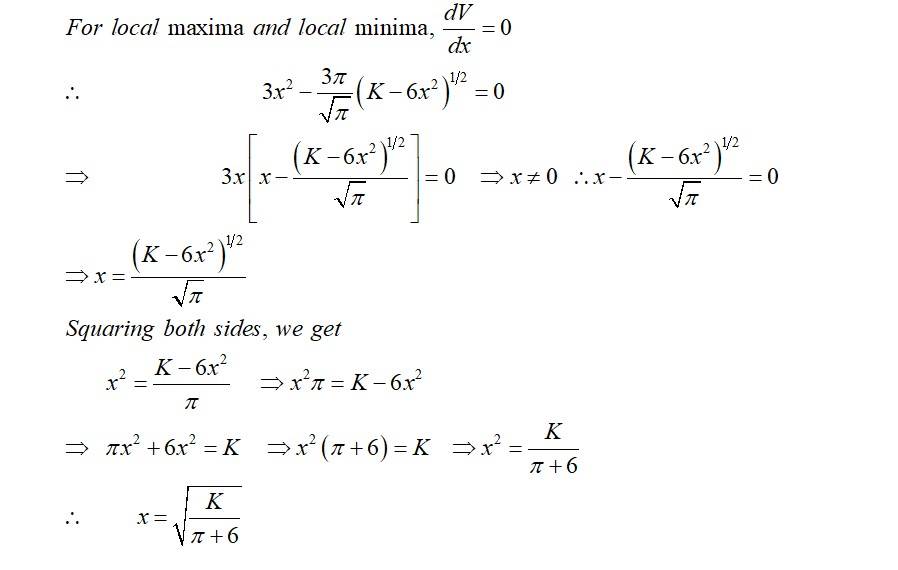
Minimum
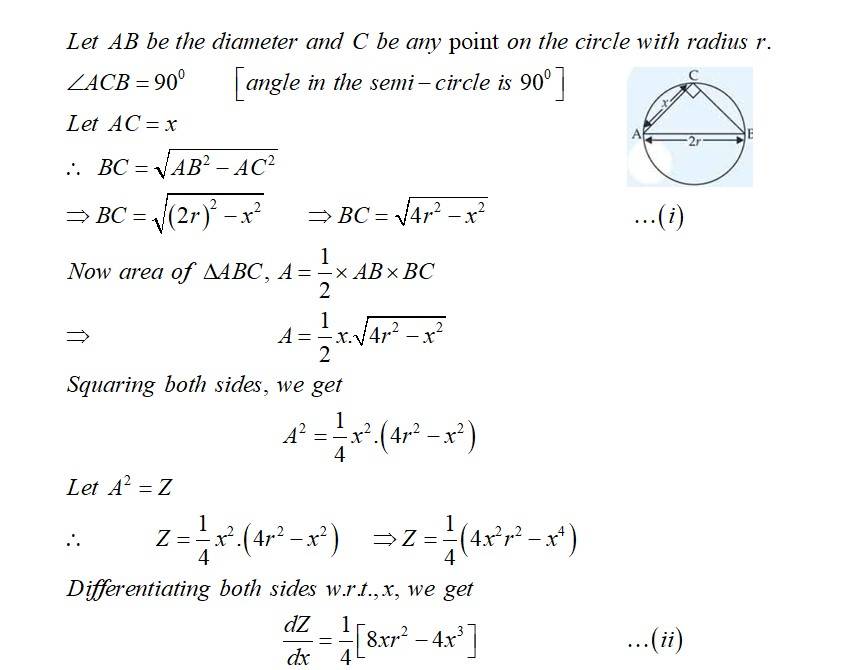
AB is a diameter of a circle and C is any point on the circle. Show that the area of ?ABC is maximum when it is isosceles.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

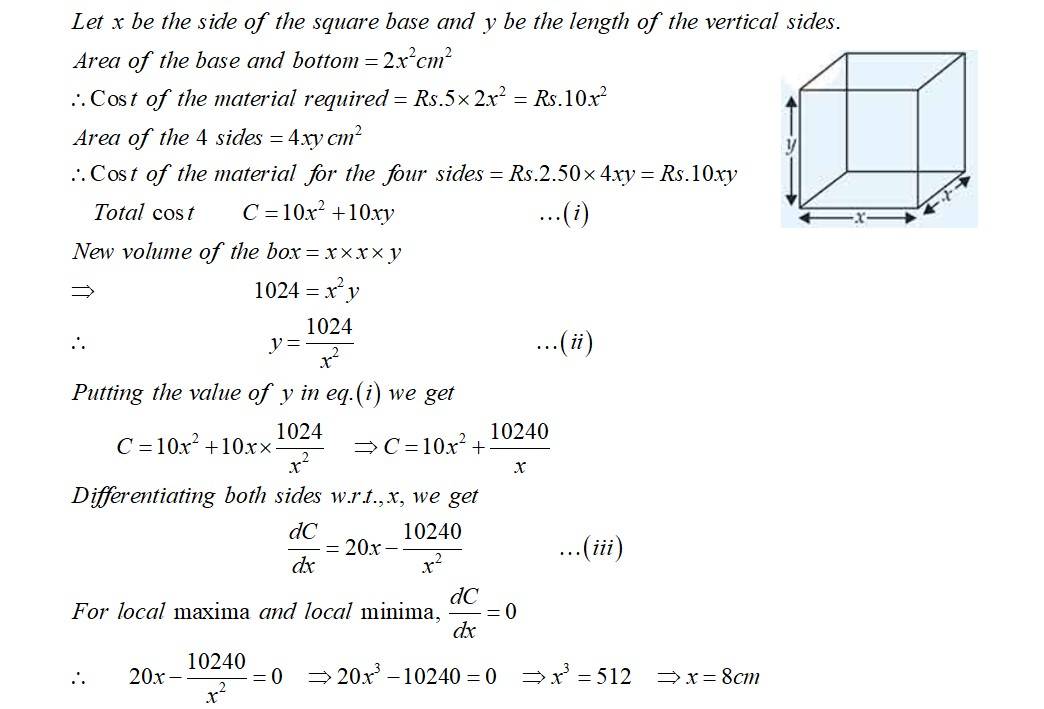
A metal box with a square base and vertical sides is to contain 1024 cm³. The material for the top and bottom costs Rs 5/cm² and the material for the sides costs Rs 2.50/cm². Find the least cost of the box
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

The sum of the surface areas of a rectangular parallelepiped with sides x, 2x, and and a sphere is given to be constant. Prove that the sum of their volumes is minimum if x is equal to three times the radius of the sphere. Also, find the minimum value of the sum of their volumes.
This is a Long Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
A spherical ball of salt is dissolving in water in such a manner that the rate of decrease of the volume at any instant is proportional to the surface. Prove that the radius is decreasing at a constant rate.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
If the area of a circle increases at a uniform rate, then prove that the perimeter varies inversely as the radius.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find an angle θ, 0 < θ < , which increases twice as fast as its sine.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the approximate value of (1.999) ?.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the approximate volume of metal in a hollow spherical shell whose internal and external radii are 3 cm and 3.0005 cm, respectively.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
A swimming pool is to be drained for cleaning. If L represents the number of liters of water in the pool t seconds after the pool has been plugged off to drain and L = 200(10 – t)², how fast is the water running out at the end of 5 seconds? What is the average rate at which the water flows out during the first 5 seconds?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The volume of a cube increases at a constant rate. Prove that the increase in its surface area varies inversely as the length of the side.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
x and y are the sides of two squares such that y = x – . Find the rate of change of the area of the second square with respect to the area of the first square.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the condition that the curves 2x = and 2xy = k intersect orthogonally.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
Prove that the curves xy = 4 and x² + y² = 8 touch each other.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the coordinates of the point on the curve √x + √y = 4 at which the tangent is equally inclined to the axes
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:


Prove that the curves y² = 4x and x² + y² – 6x + 1 = 0 touch each other at the point (1, 2).
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the equation of the normal lines to the curve 3x² – y² = 8 which are parallel to the line x + 3y = 4.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
At what points on the curve x² + y² – 2x – 4y + 1 = 0 are the tangents parallel to the y-axis?
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Show that the line x/a + y/b = 1 touches the curve y = b(-x/a) at the point where the curve intersects the y-axis.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Kindly consider the following
![]()
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
Kindly consider the following
![]()
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Show that f(x) = tan?¹(sinx + cosx) is an increasing function in (0, ).
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
At what point is the slope of the curve y = –x³ + 3x² + 9x – 27 maximum? Also, find the maximum slope.
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
Prove that f(x) = sinx + cosx has a maximum value at x = , .
This is a Short Answer Type Question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

The sides of an equilateral triangle are increasing at the rate of 2 cm/sec. The rate at which the area increases when the side is 10 cm is:
(A) 10 cm²/s
(B) √3 cm²/s
(C) 10 cm²/s
(D) 10/3 cm²/s
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

The curve y = x1/? has at (0, 0):
(A) A vertical tangent (parallel to y-axis)
(B) A horizontal tangent (parallel to x-axis)
(C) An oblique tangent
(D) No tangent
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The equation of the normal to the curve *3x² – y² = 8, which is parallel to the line *x + 3y = 8, is:
(A) 3x – y = 8
(B) 3x + y + 8 = 0
(C) x + 3y ± 8 = 0
(D) x + 3y = 0
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If the curves ay + x² = 7 and x³ = y cut orthogonally at (1, 1), then the value of a is:
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) –6
(D) 6
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If the curves ay + x² = 7 and x³ = y cut orthogonally at (1, 1), then the value of a is:
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) –6
(D) 6
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If y = x? – 10 and x changes from 2 to 1.99, what is the change in *y
(A) 0.32
(B) 0.032
(C) 5.68
(D) 5.968
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The equation of the tangent to the curve y(1 + x²) = 2 – x, where it crosses the x-axis, is:
(A) x + 5y = 2
(B) x – 5y = 2
(C) 5x – y = 2
(D) 5x + y = 2
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The points at which the tangents to the curve y = x³ – 12x + 18 are parallel to the x-axis are:
(A) (2, –2), (–2, –34)
(B) (2, 34), (–2, 0)
(C) (0, 34), (–2, 0)
(D) (2, 2), (–2, 34)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The tangent to the curve y = e²? at the point (0,1) meets the x-axis at:
(A) (0, 1)
(B) (–1/2, 0)
(C) (2, 0)
(D) (0, 2)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The slope of the tangent to the curve x = t² + 3t – 8, y = 2t² – 2t – 5 at the point (2, –1) is:
(A) 22/7
(B) 6/7
(C) -6/7
(D) –6
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The two curves x³ – 3xy² + 2 = 0 and 3x²y – y³ – 2 = 0 intersect at an angle of:
(A) π/4
(B) π/3
(C) π/2
(D) π/6
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The interval on which the function f(x) = 2x³ + 9x² + 12x – 1 is decreasing is:
(A) [–1, ∞)
(B) [–2, –1]
(C) (–∞, –2]
(D) [–1, 1]
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 2x + cosx, then f:
(A) Has a minimum at x = π
(B) Has a maximum at x = 0
(C) Is a decreasing function
(D) Is an increasing function
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The function y = x (x – 3) ² decreases for the values of x given by:
(A) 1 < x < 3
(B) x < 0
(C) x > 0
(D) 0 < x < 3/2
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The function f(x) = 4 sin³x – 6 sin²x + 12 sinx + 100 is strictly decreasing in:
(A) Increasing in (π, 3π/2)
(B) Decreasing in ( π/2,π)
(C) Decreasing in (-π/2,π/2 )
(D) Decreasing in (0, π/2)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Which of the following functions is decreasing in (0,) π/2 )?
(A) sin2x
(B) tanx
(C) cosx
(D) cos3x
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The function f(x) = tanx – x:
(A) Always increases
(B) Always decreases
(C) Never increases
(D) Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If x is real, the minimum value of x² – 8x + 17 is:
(A) –1
(B) 0
(C) 1
(D) 2
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The smallest value of the polynomial x³ – 18x² + 96x in [0, 9] is:
(A) 126
(B) 0
(C) 135
(D) 160
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The function f(x) = 2x³ – 3x² – 12x + 4 has:
(A) Two points of local maximum
(B) Two points of local minimum
(C) One maximum and one minimum
(D) No maximum or minimum
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The maximum value of sinx –cosx is:
(A) 1/4
(B) 1/2
(C) √2
(D) 2√2
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
![]()
At the function f(x) = 2sin³x + 3cos³x is:
(A) Maximum
(B) Minimum
(C) Zero
(D) Neither maximum nor minimum
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The maximum slope of the curve y = –x³ + 3x² + 9x – 27 is:
(A) 0
(B) 12
(C) 16
(D) 32
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The function f(x) = xˣ has a stationary point at:
(A) x = e
(B) x = 1/e
(C) x = 1
(D) x =√e
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The maximum value of (1/x)x is:
(A) e
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The curves y = 4x² + 2x – 8 and y = x³ – x + 13 touch each other at the point ___.
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The equation of the normal to the curve y = tanx at (0, 0) is ____.
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The values of a for which the function f(x) = sinx – ax + b increases on R are __.
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol.
The function f(x) = , x > 0 decreases in the interval ___.
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The least value of the function f(x) = ax + ( ), where a > 0, b > 0, x > 0, is ___.
This is a Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:

26th June 2022 (First Shift)
26th June 2022 (First Shift)
Commonly asked questions
Let f(x) = If then f6 (6) + f7 (7) is equal a to
=
Let A be a 3 × 3 invertible matrix. If is equal to
The ordered pair (a, b), for which the system of linear equations
3x – 2y + z = b
5x – 8y + 9z = 3
2x + y + az = -1
has no solution, is
System of equation can be written as
for no solution
3a + 9 = 0 but
The remainder when (2021)2023 is divided by 7 is
mod (7)
…… (i)
Now,
……. (ii)
(i) & (ii)
Remainder = 5
is equal to
let
=
Let f, g : R → R be two real valued function defined as f(x) = and , where k1 and k2 are real constants. If (gof) is differentiable at x = 0, then (gof)(-4) is equal to
GOF is differentiable at x = 0
So R.H.D = L.H.D.
⇒ 4 = 6 – k1 Þ k1 = 2
Now g (f (-4) + g (f (4)
= 2 (2e4 – 1)
The sum of the absolute minimum and the absolute maximum values of the friction f(x) = in the interval [1, 2] is
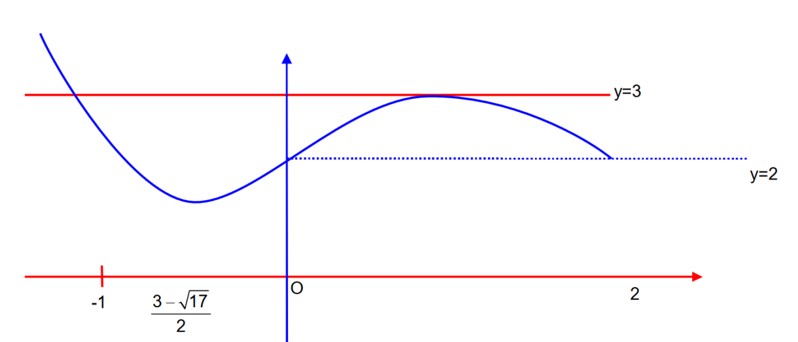
absolute minimum
absolute maximum = 3
Let S be the set of all the natural numbers, for which the line is a tangent to the curve at the point (a, b), ab Then
So line always touches the given curve.
The area bounded by the curve y = and the line y = 3 is :
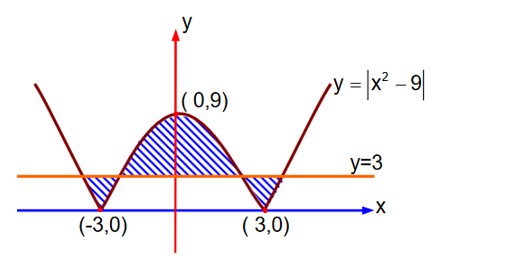
Required area = A
Note : No option in the question paper is correct.
Let R be the point (3, 7) and let P and Q be two points on the line x + y = 5 such that PQR is an equilateral triangle. Then the area of is
RM =
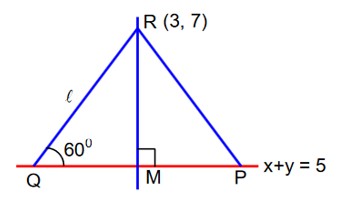
=25/2√3
Let C be a circle passing through the points A(2, 1) and B(3, 4). The line segment AB is not a diameter of C. If r is the radius of C and its centre lies on the circle , then r2 is equal to
Equation of perpendicular bisector of AB is
Solving it with equation of given circle,
But
because AB is not the diameter.
So, centre will be
Now,
Let the normal at the point P on the parabola y2 = 6x pass through the point (5, 8). If the tangent at P to the parabola intersects its directrix at the point Q, then the ordinate of the point Q is
Let P (at2, 2 at) where
T : yt = x + at2 so point Q is
N : y = -tx + 2at + at3 passes through (5, -8)
⇒
⇒ t = -2
So ordinate of point Q is
If the two lines are perpendicular, then an angle between the lines
are perpendicular, so
a = 3
Now angle between ,
Let the plane 2x + 3y + z + 20 = 0 be rotated through a right angle about its line of intersection with the plane x – 3y + 5z = 8. If the mirror image of the point in the rotated plane in B(a, b, c), then
Consider the equation of plane,
Plane P is perpendicular to 2x + 3y + z + 20 = 0
So,
0
P : 9x – 18y + 36z – 36 = 0
Or P : x – 2y + 4z = 4
If image of
In plane P is (a, b, c) then
and
clearly
So, a : b : c = 8 : 5 : 4
If then the value of
so vectors
are coplanar, hence their Scalar triple product will be zero.
Let a biased coin be tossed 5 times. If the probability of getting 4 heads is equal to the probability of getting 5 heads, then the probability of getting atmost two heads is
P (H) = x . P (T) = 1 – x
P (4H. 1T) = P (5H)
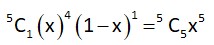
6x = 5 = 0
P (atmost 2H)
The mean of the numbers a, b, 8, 5, 10 is 6 and their variance is 6.8. If M is the mean deviation of the numbers about the mean, then 25 M is equal to
…… (i)
and
a2 + b2 = 25 ……. (ii)
From (i) and (ii) (a, b) = (3, 4) or (4, 3)
Now mean deviation about mean
25M = 60
Let f(x) = is the range of the function f, then 4a – b is equal to
So, f (x) is decreasing function and range of f (x) is
which is
Now 4a – b = 4 ( + 5) (5 + 9) = 11 - π
Let be such that is a tautology. Then is logically equivalent to
Case – I
it can be false if r is false,
so not a tautology
Case – II If
tautology
then
Case – III If
then
Not a tautology
Case – IV If
Not a tautology
The sum of the cubes of all the roots of the equation is
and let, are roots of x2 – 3x – 1 = 0
= 27 + 3 (3) = 36
There are ten boys B1, B2,….., B10 and five girls G1, G2,….., G5 in a class. Then the number of ways of forming a group consisting of three boys and three girls, if both B1 and B2 together should not be the members of a group, is………….
Boys (10) Girls (5)
(3) (3)
B1 & B2 should not be selected together
Total number of ways
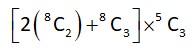
= (56 + 56) × 10 = 1120
LE the common tangents to the curves and y2 = 4x intersect at the point Q. Let an ellipse, centered at the origin O, has lengths of semi-minor and semi-major axes equal to OQ and 6, respectively. If e and respectively denote the eccentricity and the length of the latus rectum of this ellipse, then is equal to
Let y = mx + c is the common tangent
so equation of common tangents will be
which intersects at Q (3, 0)
Major axis and minor axis of ellipse are 12 and 6. So eccentricity
and length of latus rectum
Hence
Let f(x) = is equal to
Let the solution curve y = y(x) of the differential equation (4 + x2)dy – 2x(x2 + 3y + 4)dx = 0 pass through the origin. They y(2) is equal to
So
When x = 0, y = 0 gives
So, for x = 2, y = 12
If then 16 + 1 is equal to
Clearly
Hence 16 + a-1 = 80
Let A = and Let B = Then the sum of all the elements of
Sum of all elements of [Sum of natural number upto 100 which are neither divisible by 3 nor by 5]
= 10100 – 3366 – 2100 + 630
= 5264
The value of the integral is equal to
Using
we get
Adding these two equations, we get
Let Then A + B is equal to
Each element of ordered pair (i, j) is either present in A or in B.
So, A + B = Sum of all elements of all ordered pairs {i, j} for and
= 20 (1 + 2 + 3 + … + 10) = 1100
Let S = (0, 2) – Let y = y(x), be the solution curve of the differential equation If the sum of abscissas of all the points of intersection of the curve y = y(x) with the curve then k is equal to
When
gives c = 1
So
sum of all solutions =
Hence k = 42
JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
Commonly asked questions
A line ‘I’ passing through origin is perpendicular to the lines
If the co-ordinates of the point in the first octant on at a distance of from the point of intersection of and (a,b,c), then 18(a + b + c) is equal to……..
Point of intersection is P (2, 3, 2)
Point Q on is (3 + 2s, 3 + 2s, 2 + s).
If exists and is equal to b, then the value of a – 2b is……..
use of L’ Hospital rule implies
a – 2b = 4 – (1) = 5
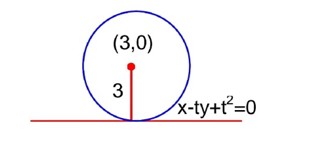
A line is a common tangent circle and the parabola y2 = 4x. If the two point of contact (a, b) and (c, d) are distinct and lie in the first quadrant, then 2(a + c) is equal to………
A tangent to y2 = 4x is x – ty + t2 = 0
(3 + t2)2 = 9 (1 + t2)
Point of contact
&
If the curve, y = y(x) represented by the solution of the differential equation passes through the intersection of the lines, 2x – 3y = 1 and 3x + 2y = 8, then is equal to………….
Then
Point (2, 1) c = 2 – 4 = 2 y =
The value of
A function f is defined on as
where [x] denotes the greatest integer The number of points, where f is not differentiable in (3, 3) is………
Number of points where f is not differentiable = 5
If the curves x = y4 and xy = k cut at right angles, then (4k)6 equal to………….
P (x1, y1)
where
Let It the area of the parallelogram shoes adjacent sides are represented by the vectors square units, then is equal to……….
322 + 64 = 192
2 =
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Six Exam