- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Questions and Answers
- JEE Mains 02 MT
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Questions and Answers
| 1. Discuss the factors affecting electron gain enthalpy and the trend in its variation in the periodic table. |
| Ans: The factors that affects electron gain enthalpy are as follows: (a) Effective nuclear charge with its increase the electron gain enthalpy also increases (b) Atomic size with its increase the electron gain enthalpy decreases (c) The e- -e - repulsion with its increase the electron gain enthalpy decreases (d) Whenever there exists half filled or completely filled orbital than it lead to decrease the electron gain enthalpy because it leads to give extra stability to the atom due to symmetry The electron gain enthalpy decreases down the group and increases across the period. |
| 2. Define ionisation enthalpy. Discuss the factors affecting ionisation enthalpy of the elements and its trends in the periodic table. |
| Ans: The amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state is said to be ionisation enthalpy. The factors that affect ionization enthalpy of the elements are as follows: (a) Effective nuclear charge with its increase the ionization enthalpy also increases (b) Atomic size with its increase the ionization enthalpy decreases (c) The e- -e - repulsion with its increase the ionization enthalpy decreases (d) Whenever there exists half filled or completely filled orbital than it lead to increase the ionization enthalpy because it leads to give extra stability to the atom due to symmetry The ionization enthalpy decreases down the group and increases across the period. |
| 3. Justify the given statement with suitable examples— “the Properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers”. |
| Ans: The chemical properties and physical properties of the elements depends upon its outer electron configuration which ultimately is the periodic function of the atomic number. The elements which possess the same outer electron configuration belong to the same group or family showing similar properties. |
| 4. Write down the outermost electronic configuration of alkali metals. How will you justify their placement in group 1 of the periodic table? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ans: The group 1 elements are called alkali metals which possess outermost electronic configuration as ns1 .All the elements that have same outermost electron configuration possess similar properties and are placed in the same group.
|
| 5. Write the drawbacks in Mendeleev’s periodic table that led to its modification. |
| Ans: Mendeleev’s arranged the elements as the periodicity of their atomic weights. The drawbacks of Mendeleev’s periodic table are as follows:- (a) The position of hydrogen in the periodic table is not specified (b) Isotopes are not included in the periodic table (c) Elements with higher atomic mass are placed before the elements with lower atomic mass. For e.g- Co & Ni (d) Gaps are left in his table considering the fact that more elements are yet to be discovered (e) Inappropriate position of group VII. |
| 6. In what manner is the long form of periodic table better than Mendeleev’s periodic table? Explain with examples. |
| Ans: The following points make long form of periodic table better than Mendeleev’s periodic table :- (a) It is a periodic function of atomic number (b) Elements are grouped as per there outermost electronic configuration (c) Proper segregation of metals and non-metals (d) More appropriate position of group VII. |
| 7. Discuss and compare the trend in ionisation enthalpy of the elements of group1 with those of group17 elements. |
| Ans: As we move across the periodic table the ionization energy increases because of the increase in the effective nuclear charge and decrease of the shielding effect as more and more electrons get added in the same orbital. Thus group 1 has lower ionization enthalpy compared to that of group 17 and also group 1 by losing one electron it will acquire the nearest noble gas electronic configuration which also contributes towards its lower ionization enthalpy. |
Commonly asked questions
Discuss the factors affecting electron gain enthalpy and the trend in its variation in the periodic table.
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The factors that affects electron gain enthalpy are as follows:
(a) Effective nuclear charge with its increase the electron gain enthalpy also increases
(b) Atomic size with its increase the electron gain enthalpy decreases
(c) The e-e - repulsion with its increase the electron gain enthalpy decreases
(d) Whenever there exists half filled or completely filled orbital than it lead to decrease the electron gain enthalpy because it leads to give extra stability to the atom due to symmetry
The electron gain enthalpy decreases down the group and increases across the period.
Define ionisation enthalpy. Discuss the factors affecting ionisation enthalpy of the elements and its trends in the periodic table.
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state is said to be ionisation enthalpy.
The factors that affect ionization enthalpy of the elements are as follows:
(a) Effective nuclear charge with its increase the ionization enthalpy also increases
(b) Atomic size with its increase the ionization enthalpy decreases
(c) The e-e - repulsion with its increase the ionization enthalpy decreases
(d) Whenever there exists half filled or completely filled orbital than it lead to increase the ionization enthalpy because it leads to give extra stability to the atom due to symmetry
The ionization enthalpy decreases down the group and increases across the period.
Justify the given statement with suitable examples— “the Properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers”.
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The chemical properties and physical properties of the elements depends upon its outer electron configuration which ultimately is the periodic function of the atomic number. The elements which possess the same outer electron configuration belong to the same group or family showing similar properties.
Write down the outermost electronic configuration of alkali metals. How will you justify their placement in group 1 of the periodic table?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The group 1 elements are called alkali metals which possess outermost electronic configuration as ns1 .All the elements that have same outermost electron configuration possess similar properties and are placed in the same group.
Atomic number | Symbol | Electronic Configuration |
|
3 | Li | 1s2 2s1 | [He]2s1 |
11 | Na | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 | [Ne]3S1 |
19 | K | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 4s1 | [Ar]4S1 |
37 | Rb | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3d10 4s2 4p6 5s1 | [Kr]5S1 |
55 87 | Cs Fr | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3d10 4s2 4p6 5d10 5s2 5p6 6s1 | [Xe]6s1 [Rn]7s1 |
Write the drawbacks in Mendeleev’s periodic table that led to its modification.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Mendeleev's arranged the elements as the periodicity of their atomic weights.
The drawbacks of Mendeleev's periodic table are as follows:-
(a) The position of hydrogen in the periodic table is not specified
(b) Isotopes are not included in the periodic table
(c) Elements with higher atomic mass are placed before the elements with lower atomic mass. For e.g- Co & Ni
(d) Gaps are left in his table considering the fact that more elements are yet to be discovered
(e) Inappropriate position of group VII.
In what manner is the long form of periodic table better than Mendeleev’s periodic table? Explain with examples.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The following points make long form of periodic table better than Mendeleev's periodic table :-
(a) It is a periodic function of atomic number
(b) Elements are grouped as per there outermost electronic configuration
(c) Proper segregation of metals and non-metals
(d) More appropriate position of group VII.
Discuss and compare the trend in ionisation enthalpy of the elements of group1 with those of group17 elements.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: As we move across the periodic table the ionization energy increases because of the increase in the effective nuclear charge and decrease of the shielding effect as more and more electrons get added in the same orbital.
Thus group 1 has lower ionization enthalpy compared to that of group 17 and also group 1 by losing one electron it will acquire the nearest noble gas electronic configuration which also contributes towards its lower ionization enthalpy.
Explain why the electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative than that of chlorine.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the atomic size of F is much smaller which leads to high e- - e - repulsion upon addition of electrons thus its electron gain enthalpy is less than that of Cl.
All transition elements are d-block elements, but all d-block elements are not transition elements. Explain.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Transition elements are named so because they form a bridge between s-block elements and p-block elements. Zn, Cd and Hg are among those elements that are dblock elements but they do not exhibit most of the properties of transition elements.
Identify the group and valency of the element having atomic number 119. Also predict the outermost electronic configuration and write the general formula of its oxide.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Group | 1 |
Valency | 1 |
Outermost electronic configuration | 8s1 |
Formula of Oxide | M2O |
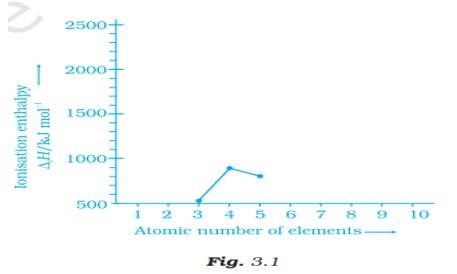
Ionisation enthalpies of elements of second period are given below :
Ionisation enthalpy/ k cal mol–1 : 520, 899, 801, 1086, 1402, 1314, 1681, 2080.
Match the correct enthalpy with the elements and complete the graph given in Fig. 3.1. Also write symbols of elements with their atomic number.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
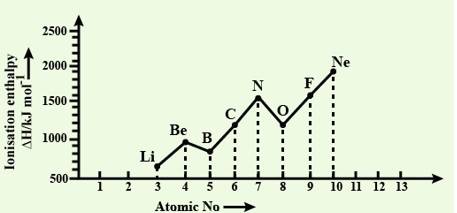
Among the elements B, Al, C and Si
(i) Which element has the highest first ionisation enthalpy ?
(ii) Which element has the most metallic character? Justify your answer in each case
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) C has the highest ionization energy among the given elements as along the period ionization enthalpy increases whereas it decreases down the group.
(ii) Al is the most metallic element among the given elements because down the group metallic character increases
Write four characteristic properties of p-block elements.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The characteristics properties of p-block elements are as follows:-
(i) It contain metals, nonmetals and metalloids
(ii) Mostly involved in covalent bonding
(iii) Some elements show variable oxidation state
(iv) It possesses relatively higher ionization enthalpy compared to the s-block elements.
Choose the correct order of atomic radii of fluorine and neon (in pm) out of the options given below and justify your answer.
(i) 72, 160
(ii) 160, 160
(iii) 72, 72
(iv) 160, 72
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)
As across the period the atomic radius decreases due to the increase of effective nuclear charge.
Illustrate by taking examples of transition elements and non-transition elements that oxidation states of elements are largely based on electronic configuration.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electronic configuration of Cr= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10
The electronic configuration of Cr after losing one electron= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10
The electronic configuration of F= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
The electronic configuration of F after gaining one electron= 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
From the above electronic configuration, we can see that chromium will achieve stable electronic configuration after losing one 4s electron and fluorine will achieve stable electronic configuration after gaining one electron. So, the oxidation of chromium will be +1 and that of fluorine will be -1.
Nitrogen has positive electron gain enthalpy whereas oxygen has negative. However, oxygen has lower ionisation enthalpy than nitrogen. Explain.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The N possesses a half filled p-orbital which provides it extra stability due to symmetry due to which its electron gain enthalpy is positive and its ionization enthalpy is larger than that of O.
First member of each group of representative elements (i.e., s and p-block elements) shows anomalous behaviour. Illustrate with two examples.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The anomalous behaviour of the first member of each group of representative elements i.e. of second period can be attributed to their small size, high charge/radius ratio, high electronegativity and absence of vacant d-orbitals to expand their oxidation state.The first member of each group of p-Block elements displays their greater ability to form multiple bond with itself, e.g. C=C, O=O, N=N and to other second periodic elements, e.g. C=O, C=N, N=N.
P-Block elements form acidic, basic and amphoteric oxides. Explain each property by giving two examples and also write the reactions of these oxides with water.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In the p block, some elements are metallic some elements are non-metallic while some elements are metalloids in nature. The oxides of metals are basic in nature and that of oxides of nonmetals are acidic in nature.
Acidic oxide SO2 + H2O →H2SO3
Basic oxide Tl2O + 2HCl → 2TlCl +H2O
Amphoteric oxide
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 +2 NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Reaction with water
B3O2 +3H2O → 2H3BO3
P4O11 + 6H2O → 4H4PO3
Cl2 O7 + H2O → HClO4
How would you explain the fact that first ionisation enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium but its second ionisation enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electronic configuration of Na is [Ne]3s1 while that of Mg is [Ne]3s2 as Mg possesses a fully filled 3s orbital thus its first ionisation enthalpy is higher than that of Na.
After losing one electron Na obtained the electronic configuration of Ne while Mg acquired the electronic configuration of Na thus the second ionisation energy of Na is higher than that of Mg.
What do you understand by exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction? Give one example of each type.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Exothermic reaction- The reaction in which heat is released
For example- CaO + CO2 → CaCO3 + Heat
Endothermic reaction- The reaction in which heat is absorbed.
For example- 2NH3 + heat → N2 +3H2
Arrange the elements N, P, O and S in the order of-
(i) Increasing first ionisation enthalpy.
(ii) Increasing non metallic character.
Give reason for the arrangement assigned.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) S
The ionization enthalpy increases across the period and decreases down the group. N possesses a half filled 2p orbital which provides it extra stability due to symmetry.
(ii)P
The non-metallic character increases across the period
Explain the deviation in ionisation enthalpy of some elements from the general trend by using Fig. 3.2.
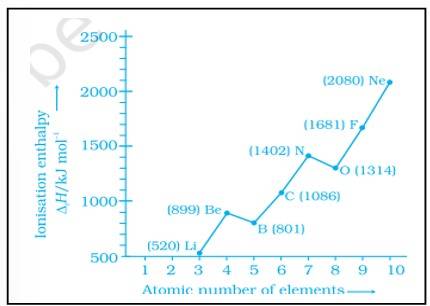
The deviation in the ionization enthalpy of some elements from the general trend can be explained by the points as given below:-
(i) The fully filled and half filled orbital provide extra stability due to the symmetry
(ii) The effective nuclear charge
(iii) The e- - e- repulsion which lead to instability
Explain the following:
(a) Electronegativity of elements increase on moving from left to right in the periodic table.
(b) Ionisation enthalpy decrease in a group from top to bottom?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) As the effective nuclear charge increases and shielding effect decreases across the periods thus the electronegativity increases on moving from left to right in the periodic table.
(b) As the number of shells increases down the group thus its ionisation enthalpy decreases down the group.
How does the metallic and non metallic character vary on moving from left to right in a period?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Metallic character- Tendency to lose electrons.
Non-Metallic character- Tendency to accept electrons.
Across the period the metallic character decreases whereas non-metallic character increases across the period.
The radius of Na+ cation is less than that of Na atom. Give reason.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The radius of Na+ ion is smaller than that of Na is due to the following reasons:-
(i) The effective nuclear charge of Na+
(ii) The disappearance of 3s orbital from its outermost shell electronic configuration.
Among alkali metals which element do you expect to be least electronegative and why?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electronegativity of the alkali metals decreases down the group due to the increase of the shells thus Cs (Caesium) is the least electronegative metal in the alkali metals.
Consider the isoelectronic species, Na+, Mg2+, F– and O2–. The correct order of increasing length of their radii is _________.
(i) F- < O2– < Mg2+ < Na+
(ii) Mg2+ < Na+ < F– < O2–
(iii) O2– < F– < Na+ < Mg2+
(iv) O2– < F– < Mg2+ < Na
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii)
All the given ions are isoelectronic species thus their radii depend upon the charge more the negative charge higher would be the atomic radii and higher the positive charge lesser would be the atomic radii.
Which of the following is not an actinoid?
(i) Curium (Z = 96)
(ii) Californium (Z = 98)
(iii) Uranium (Z = 92)
(iv) Terbium (Z = 65)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv)
Actinoids possess Z=90-103
Terbium is lanthanoid.
The order of screening effect of electrons of s, p, d and f orbitals of a given shell of an atom on its outer shell electrons is:
(i) s > p > d > f
(ii) f > d > p > s
(iii) p < d < s > f
(iv) f > p > s > d
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)
The orbitals nearer to the nucleus possess more shielding effect.
The first ionisation enthalpies of Na, Mg, Al and Si are in the order:
(i) Na < Mg > Al < Si
(ii) Na > Mg > Al > Si
(iii) Na < Mg < Al < Si
(iv) Na > Mg > Al < Si
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)
As Mg contains fully filled 3s orbital thus its ionisation is higher than that of Na and Al.
The electronic configuration of gadolinium (Atomic number 64) is
(i) [Xe] 4f 3 5d5 6s2
(ii) [Xe] 4f7 5d2 6s1
(iii) [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
(iv) [Xe] 4f8 5d6 6s2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
Gadolinium is a lanthanoid which belongs to the f-block elements with electronic configuration (n-2)f14 (n-1)d0-1ns2
The statement that is not correct for periodic classification of elements is:
(i) The properties of elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers.
(ii) Non metallic elements are less in number than metallic elements.
(iii) For transition elements, the 3d-orbitals are filled with electrons after 3p-orbitals and before 4s-orbitals.
(iv) The first ionisation enthalpies of elements generally increase with increase in atomic number as we go along a period.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
As per Aufbau principle 3d orbitals are filled first than 4s as due to lower n value.
Among halogens, the correct order of amount of energy released in electron gain (electron gain enthalpy) is:
(i) F > Cl > Br > I
(ii) F < Cl < Br < I
(iii) F < Cl > Br > I
(iv) F < Cl < Br < I
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)
The electron gain enthalpy decreases down the group, however as the size of F atom is much smaller thus it leads to repulsion upon addition of electrons on its 2p orbital for this electron gain enthalpy of Cl is higher than that of F.
The period number in the long form of the periodic table is equal to
(i) Magnetic quantum number of any element of the period.
(ii) Atomic number of any element of the period.
(iii) Maximum Principal quantum number of any element of the period.
(iv) Maximum Azimuthal quantum number of any element of the period.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
Period number indicates the maximum value of principal quantum number
The elements in which electrons are progressively filled in 4f-orbital are called
(i) Actinoids
(ii) Transition elements
(iii) Lanthanoids
(iv) Halogens
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
The lanthanoids which belong to the f-block elements are the elements where 4forbitals are filled progressively.
Which of the following is the correct order of size of the given species:
(i) I > I – > I +
(ii) I + > I – > I
(iii) I > I + > I –
(iv) I – > I > I+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iv)
I+ possess the highest effective nuclear charge whereas I- possess the least among the given species.
The formation of the oxide ion, O2– (g), from oxygen atom requires first an exothermic and then an endothermic step as shown below:
O(g) + e– → O– (g) ; ∆ Hᶱ = – 141 kJ mol–1
O– (g) + e– → O2– (g); ∆ Hᶱ = + 780 kJ mol–1
Thus process of formation of O2– in gas phase is unfavourable even though O2– is isoelectronic with neon. It is due to the fact that,
(i) Oxygen is more electronegative.
(ii) Addition of electron in oxygen results in larger size of the ion.
(iii) Electron repulsion outweighs the stability gained by achieving noble gas configuration.
(iv) O– ion has comparatively smaller size than oxygen atom.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
High amount of energy has to be supplied in order to overcome the e- - e - repulsion that arises when O- gets converted to O2- by accepting an electron
Comprehension given below is followed by some multiple choice questions. Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option.
In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers which is related to the electronic configuration. Depending upon the type of orbitals receiving the last electron, the elements in the periodic table have been divided into four blocks, viz, s, p, d and f. The modern periodic table consists of 7 periods and 18 groups. Each period begins with the filling of a new energy shell. In accordance with the Arfbau principle, the seven periods (1 to 7) have 2, 8, 8, 18, 18, 32 and 32 elements respectively. The seventh period is still incomplete. To avoid the periodic table being too long, the two series of f-block elements, called lanthanoids and actinoids are placed at the bottom of the main body of the periodic table.
(a) The element with atomic number 57 belongs to
(i) s-block
(ii) p-block
(iii) d-block
(iv) f-block
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii) d-block
Lanthanum is the element with the atomic number 57 and it belongs to the d-block.
Electronic configurations of four elements A, B, C and D are given below:
(A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 (B) 1s2 2s2 2p4
(C) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 (D) 1s2 2s2 2p5
Which of the following is the correct order of increasing tendency to gain electron :
(i) A < C < B < D
(ii) A < B < C < D
(iii) D < B < C < A
(iv) D < A < B < C
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)
The electron gain enthalpy of 2p orbital is higher than that of the 3s orbital
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Which of the following elements can show covalency greater than 4?
(i) Be
(ii) P
(iii) S
(iv) B
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii) & (iii)
Both P and S have vacant d-orbital for which they execute extended covalency.
Those elements impart colour to the flame on heating in it, the atoms of which require low energy for the ionisation (i.e., absorb energy in the visible region of spectrum). The elements of which of the following groups will impart colour to the flame?
(i) 2
(ii) 13
(iii) 1
(iv) 17
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i) & (iii)
Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals have low ionization enthalpy.
Which of the following sequences contain atomic numbers of only representative elements?
(i) 3, 33, 53, 87
(ii) 2, 10, 22, 36
(iii) 7, 17, 25, 37, 48
(iv) 9, 35, 51, 88
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)& (iv)
The s-block elements and p-block elements together are called representative elements.
Which of the following elements will gain one electron more readily in comparison to other elements of their group?
(i) S (g)
(ii) Na (g)
(iii) O (g)
(iv) Cl (g)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)& (iv)
Both S and Cl have the higher tendency to gain electrons in order to attain stable the nearest noble gas configuration i.e. of Argon.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Helium has the highest first ionisation enthalpy in the periodic table.
(ii) Chlorine has less negative electron gain enthalpy than fluorine.
(iii) Mercury and bromine are liquids at room temperature.
(iv) In any period, atomic radius of alkali metal is the highest.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i), (iii)& (iv)
He with 1s2 electronic configuration has the highest electron gain enthalpy in the periodic table. In any period the alkali metals have the lowest effective nuclear charge in that particular period for which its atomic radius is the highest in that period.
Which of the following sets contain only isoelectronic ions?
(i) Zn2+, Ca2+, Ga3+, Al3+
(ii) K+ , Ca2+, Sc3+, Cl –
(iii) P3–, S2–, Cl– , K+
(iv) Ti 4+, Ar, Cr3+, V5+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
option (ii)& (iii)
Isoelectronic species/ions are those species that possess the same number of electrons.
In which of the following options order of arrangement does not agree with the variation of property indicated against it?
(i) Al3+ < Mg2+ < Na+ < F– (increasing ionic size)
(ii) B < C < N < O (increasing first ionisation enthalpy)
(iii) I < Br < Cl < F (increasing electron gain enthalpy)
(iv) Li < Na < K < Rb (increasing metallic radius)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii)& (iii)
The ionization enthalpy of N is higher than that of F because it possess half filled orbital which provide it extra stability due to symmetry.
As the atomic size of F is much smaller thus its electron gain enthalpy is lower than that of the Cl
Which of the following have no unit?
(i) Electronegativity
(ii) Electron gain enthalpy
(iii) Ionisation enthalpy
(iv) Metallic character
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)& (iv)
Both electronegativity and metallic character do not possess units as they both are qualitative properties not a quantitative property.
Ionic radii vary in
(i) Inverse proportion to the effective nuclear charge.
(ii) Inverse proportion to the square of effective nuclear charge.
(iii) Direct proportion to the screening effect
(iv) Direct proportion to the square of screening effect.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)& (iii)
Ionic radii decreases with the increase of the effective nuclear charge and increases with the increase of shielding effect or e- - e - repulsion as it outweighs the effective nuclear charge effect.
An element belongs to 3rd period and group-13 of the periodic table. Which of the following properties will be shown by the element?
(i) Good conductor of electricity
(ii) Liquid, metallic
(iii) Solid, metallic
(iv) Solid, non metallic
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (i)& (iii)
Aluminium is the element which is a metal and good conductor of electricity.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Generally, ionisation enthalpy increases from left to right in a period.
Reason (R) : When successive electrons are added to the orbitals in the same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate.
(i) Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(iii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iv) Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii)
The ionization energy depends upon two factors
(a) The effective nuclear charge.
(b)The e- -e – repulsions.
Assertion (A) : Boron has a smaller first ionisation enthalpy than beryllium.
Reason (R) : The penetration of a 2s electron to the nucleus is more than the 2p electron hence 2p electron is more shielded by the inner core of electrons than the 2s electrons.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(ii) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(iii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(iv) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (iii)
The Be has the electronic configuration of [He]2s2 while B has the electronic configuration of [He]2s22p1 . As in Be the outermost orbital i.e. 2s is fully filled thus it provides extra stability to the Be compared to B. Apart from this 2s electron is more penetrated compared to the 2p electron for which 2p electron faces more shielding effect than that of 2s electron.
Assertion (A) : Electron gain enthalpy becomes less negative as we go down a group.
Reason (R) : Size of the atom increases on going down the group and the added electron would be farther from the nucleus.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(iii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iv) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Option (ii)
The electron gain enthalpy decreases down the group due to the increase in the atomic size which leads to decrease in the effective nuclear charge.
Match the correct atomic radius with the element.
|
Element |
Atomic Radius (pm) |
|
Be |
74 |
|
C |
88 |
|
O |
111 |
|
B |
77 |
|
N |
66 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Be 111
C 77
O 66
B 88
N 74
Match the correct ionisation enthalpies and electron gain enthalpies of the following elements.
|
Elements |
|
?H1 |
? H2 |
?egH |
|
(i) Most reactive non metal |
A |
419 |
3051 |
– 48 |
|
(ii) Most reactive metal |
B |
i b |
i b |
i b |
|
(iii) Least reactive element |
C |
738 |
1451 |
– 40 |
|
(iv) Metal forming binary halide |
D |
2372 |
5251 |
+ 48 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
i ) b 1681 3374 – 328
ii ) a 419 3051 – 48
iii) d 2372 5251 + 48
iv) c 738 1451 – 40
Electronic configuration of some elements is given in Column I and their electron gain enthalpies are given in Column II. Match the electronic configuration with electron gain enthalpy.
|
Column (I) |
Column (II) |
|
Electronic configuration |
Electron gain enthalpy/kJ mol–1 |
|
(i) 1s2 2s2 sp6 |
(A) – 53 |
|
(ii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 |
(B) – 328 |
|
(iii) 1s2 2s2 2p5 |
(C) – 141 |
|
(iv) 1s2 2s2 2p4 |
(D) + 48 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
i d + 48
ii a – 53
iii b – 328
iv c – 141
120g of an organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen gives 330g of CO2 and 270g of water on complete combustion. The percentage of carbon and hydrogen, respectively are
Number of moles of C = Number of moles of CO2 =
Number of moles of H = 2 × no. of moles of H2O =
Mass of C =
Mass of H =
The energy of one mole of photons of radiation of wavelength 300nm is (Given: h = 6.63 × 1034 Js,NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol-1 c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
Energy of 1 photon =
Energy of 1 mole of photon =
= 0.399 × 106 J = 399 KJ
The correct order of bond orders of is , respectively
Bond order of
Bond order of
Bond order of
NB = No. of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals.
NA = No. of electron is Anti bonding molecular orbitals
For a first order reaction, the time required for completion of 90% reaction is ‘x’ times the half life of the reaction. The value of ‘x’ is
(Given : In 10 = 2.303 and log 2 = 0.3010)
Metals generally melt at very high temperature. Amongst the following, the metal with the highest melting point will be
Metal Ag Ga Cs Hg
Melting point 961°C 29.7°C 28.5°C -38.3°C
Which of the following chemical reaction represents Hall-Heroult process
In Hall Heroult process electrolysis is carried out using carbon anode. The liberated
O2 at anode reacts with anode.
Cathode :
Anode :
Net Reaction 2Al2O3 + 3C
In the industrial production of which of the following, molecular hydrogen is obtained as a by product?
NaOH is obtained by electrolysis of NaCl. Solution of NaCl using Hg cathode
Which one of the following compounds is used as a chemical in certain type of fire extinguishers?
Fire extinguisher contains sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3), also known as baking soda.
PCl5 is well known, but NCl5 is not. Because
(a) Nitrogen is less reactive than phosphorous
(b) Nitrogen doesn’t have d-orbitals in its valence shell.
(c) catenation tendency is weaker in nitrogen than phosphorous
(d) size of phosphorous is larger than nitrogen
Phosphorous can expand its covalency beyond 4, as it has vacant 3d orbitals. Nitrogen can't expand its covelency beyond 4, as it does not posses vacant 3d- orbitals.
Transition metal complex with highest value of crystal field splitting will be
The value of crystal field spilitting energy increases down the group. 5d series member will have more compared to 3d series or 4d series member.
Some gases are responsible for heating of atmosphere (green house effect). Identify from following the gaseous species which does not cause it.
CH4, O3 & H2O are green-house gases.
Given below are two statements.
Statement I : The presence of weaker p-bonds make alkenes less stable than alkanes.
Statement II : The strength of the double bond is greater than that of carbon-carbon single bond.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Both Statements I and Statement II are correct.
(b) Both Statements I and Statement II are incorrect.
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Bond is weaker then - bond.
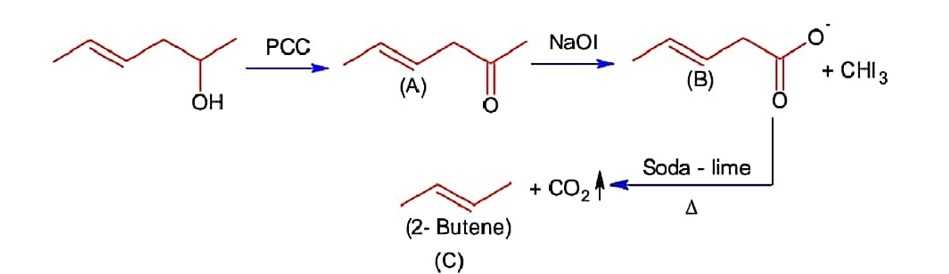
Hex-4- ene- 2-ol on treatment with PCC gives ‘A’ on reaction with sodium hypolodite gives ‘B’, which on further heating with soda lime gives ‘C’. The compound ‘C’ is
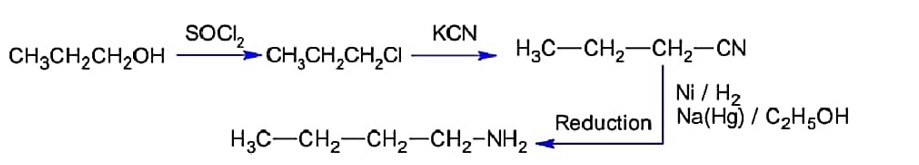
The conversion of propan-1- ol to n- butylamine involves the sequential addition of reagents. The correct sequential order of reagent is
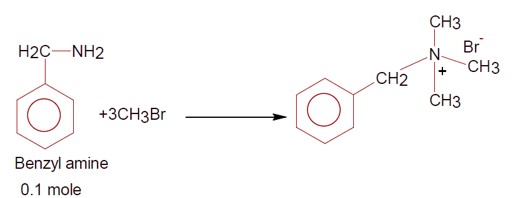
A reaction of 0.1 mole of Benzylamine with bromomethane gave 23g of Benzyl trimethyl ammonium bromide. The number of moles of bromomethane consumed in this reaction are n x 10?¹, when n=_____. (Round off to the nearest integer).
[Given: Atomic masses: C=12.0u, H:1.0u, N:14.0u, Br:80.0u]
For the reaction C?H? → C?H? + H? the reaction enthalpy ?rH = ____ kJ mol?¹. (Round off to the nearest integer).
[ Given: Bond enthalpies in kJ mol?¹ : C-C: 347, C=C:611; C-H:414,H-H:436]
For the reaction C? H? → C? H? + H? , calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH).
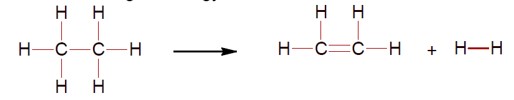
ΔH = [Bond energy (C-C) + 6 × Bond energy (C-H)] - [Bond energy (C=C) + 4 × Bond energy (C-H) + Bond energy (H-H)]
ΔH = 347 + 2 (414) - 611 - 436 = 128 kJ/mol.
In order to prepare a buffer solution of pH 5.74, sodium acetate is added to acetic acid. If the concentration of acetic acid in the buffer is 1.0 M, the concentration of sodium acetate in the buffer is _____ M. (Round off to the nearest integer).
[Given: pKa (acetic acid) = 4.74]
For an acidic buffer solution, pH = pKa + log ( [Base]/ [Acid]).
Given pH = 5.74 and pKa = 4.74.
5.74 = 4.74 + log ( [Base]/1).
1 = log ( [Base]).
[Base] = 10M.
AX is a covalent diatomic molecule where A and X are second row elements of periodic table. Based on molecular orbital theory, the bond order of AX is 2.5. The total number of electrons in AX is _____. (Round off to the nearest integer).
AX is a diatomic molecule with a bond order of 2.5.
The compound is NO. The total number of electrons = 15 (7+8).
For the reaction
2Fe³?(aq) + 2I?(aq) → 2Fe²?(aq) + I?(s)
The magnitude of the standard molar free energy change, ?rG° = ____ kJ (Round off to the nearest integer).
[Given: E°(Fe²?/Fe(s)) = -0.440V; E°(Fe³?/Fe(s)) = -0.036V; E°(I?/2I?) = 0.539V; F = 96500C]
Please consider the following Image
_____ grams of 3-Hydroxy propanal (MW = 74) must be dehydrated to produce 7.8g of acrolein (MW = 56) (C?H?O) if the percentage yield is 64. (Round off to the nearest integer).
[Given: Atomic masses: C: 12.0u, H:1.0u, O:16.0u]
3-Hydroxy propanal
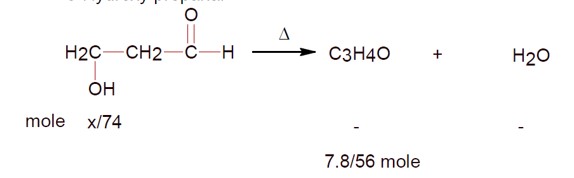
If 7.8g of C? H? O (molar mass 56 g/mol ) is formed, calculate the initial weight of 3-hydroxy propanal (molar mass 74 g/mol ).
Weight = (7.8/56) × 74 × (100/64) [Assuming 64% yield, though the number seems out of place].
Ans ≈ 16 g.
2NO(g) + Cl?(g) ? 2NOCl(s)
This reaction was studied at -10°C and the following data was obtained
[NO]? and [Cl?]? are the initial concentrations and r? is the initial reaction rate. The overall order of the reaction is _____. (Round off to the nearest integer).
Please consider the following Image
2 molal solution of a weak acid HA has a freezing point of 3.885°C. The degree of dissociation of this acid is _____ × 10?³. (Round off to the nearest integer).
[ Given : Molal depression constant of water = 1.85 K kg mol?¹, Freezing point of pure water = 0°C]
Given K_f = 1.85 K kg mol? ¹ for a solution with molality of 2 m.
ΔT_f = I * K_f * m
3.885 = I * 1.85 * 2
The van't Hoff factor, I = 1.05.
i = 1 + (n-1)α. For an electrolyte dissociating into 2 ions, n=2.
1.05 = 1 + (2-1)α.
The degree of dissociation, α = 0.05 or 50 × 10? ³.
Complete combustion of 3 g of ethane gives x×10²² molecules of water. The value of x is _____. (Round off to the nearest integer).
[ Use : NA = 6.023 ×10²³; Atomic masses in u: C:12.0,O:16.0; H:1.0]
Combustion of ethane: C? H? + 7/2 O? → 2CO? + 3H? O.
Moles of C? H? = 3g / 30 g/mol = 0.1 mol.
Moles of H? O produced = 0.3 mol.
Number of H? O molecules = 0.3 × 6.023 × 10²³ ≈ 18.06 × 10²².
So, x = 18.
The total number of unpaired electrons present in the complex K?[Cr(oxalate)?] is _____.
For the complex K? [Cr (oxalate)? ], the central metal ion is Cr³?
Electronic configuration of Cr (24) is [Ar] 4s¹3d?
Electronic configuration of Cr³? is [Ar] 4s?3d³.
The number of unpaired electrons in Cr³? is 3.
JEE Mains 02 MT
JEE Mains 02 MT
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Three Exam