- General Principles and Isolation of Elements Long Answers Type Questions
- General Principles and Isolation of Elements Short Answers Type Questions
- 26th June 2022
- JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
General Principles and Isolation of Elements Long Answers Type Questions
| 1. Explain the following : (a) CO2 is a better reducing agent below 710 K whereas CO is a better reducing agent above 710 K. (b) Generally, sulfide ores are converted into oxides before reduction. (c) Silica is added to the sulfide ore of copper in the reverberatory furnace. (d) Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agents at high temperatures. (e) Vapor phase refining method is used for the purification of Ti. |
| Ans: (a). According to Ellingham diagram, the reaction of CO2 is more feasible at temperatures lower than 710 K and thus it is a better reducing agent below 710 K.
While the reaction of CO is more feasible at temperatures higher than 710 K and thus it is a better reducing agent at above 710 K.
(b). According to the Ellingham diagram, the more negative the Gibbs free energy of a particular reaction the more feasible it is to carry out. Since the oxides are easier to reduce, sulfide ores are converted into oxides before reduction.
(c). To extract copper, its sulfide ores are supposed to be heated in a reverberatory furnace. The sulfide ore may contain iron as an impurity. So, it is mixed with silica before heating. The oxide of iron slags off as iron silicate. In other words, the iron impurity is removed easily in the form of iron silicate.
(d). Carbon and hydrogen are good reducing agents. They are used preferably for reduction of oxides. They also form escapable gasses as by-products. However, at higher temperatures they form carbides and hydrides. Also, it is not convenient to maintain such high temperatures. Thus, electrolysis is used for this purpose.
(e). Ti is heated in an evacuated vessel along with iodine. Ti forms volatile compounds with iodine. The volatile compound formed decomposes easily. This makes the recovery of the metal convenient. Ti thus fulfills the requirements needed for carrying out vapor phase refining. Hence, this method is used for its purification. |
Commonly asked questions
1. Explain the following :
(a) CO2 is a better reducing agent below 710 K whereas CO is a better reducing agent above 710 K.
(b) Generally, sulfide ores are converted into oxides before reduction.
(c) Silica is added to the sulfide ore of copper in the reverberatory furnace.
(d) Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agents at high temperatures.
(e) Vapor phase refining method is used for the purification of Ti.
1. Ans:
(a). According to Ellingham diagram, the reaction of CO2 is more feasible at temperatures lower than 710 K and thus it is a better reducing agent below 710 K.
While the reaction of CO is more feasible at temperatures higher than 710 K and thus it is a better reducing agent at above 710 K.
(b). According to the Ellingham diagram, the more negative the Gibbs free energy of a particular reaction the more feasible it is to carry out. Since the oxides are easier to reduce, sulfide ores are converted into oxides before reduction.
(c). To extract copper, its sulfide ores are supposed to be heated in a reverberatory furnace. The sulfide ore may contain iron as an impurity. So, it is mixed with silica before heating. The oxide of iron slags off as iron silicate. In other words, the iron impurity is removed easily in the form of iron silicate.
(d). Carbon and hydrogen are good reducing agents. They are used preferably for reduction of oxides. They also form escapable gasses as by-products. However, at higher temperatures they form carbides and hydrides. Also, it is not convenient to maintain such high temperatures. Thus, electrolysis is used for this purpose.
(e). Ti is heated in an evacuated vessel along with iodine. Ti forms volatile compounds with iodine. The volatile compound formed decomposes easily. This makes the recovery of the metal convenient. Ti thus fulfills the requirements needed for carrying out vapor phase refining. Hence, this method is used for its purification.
4. Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulfur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron?
4. Iron oxides are mixed with limestone and coke in order to decompose carbonates and oxidize sulfides. This mixture is then fed into the blast furnace. Many reactions take place in different temperature ranges of the blast furnace. By oxidizing impurities from cast iron in a reverberatory furnace which is lined by hematite, wrought iron or malleable iron is obtained. This is the purest form of commercial iron. This can be shown with the following reaction:
Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO.
Sulfur, silicone and phosphorus are oxidized and passed into the slag and removed as impurities when limestone is added as a flux to it.
6. Write two basic requirements for refining of a metal by Mond process and by Van Arkel Method.
6. Both processes have two basic requirements:
(i) The metal should react with an available reagent to form a volatile compound.
(ii) The volatile compound should be easily decomposable, allowing for easy metal recovery.
12. Why are sulfide ores converted to oxide before reduction?
12. Sulfide ore of copper contains some types of impurities. Sulfide ores are not reduced easily, but oxide ores are easily reduced. It is necessary to make sulfide ores free from volatile impurities. This can be performed by a roasting method. In this moisture escape and impurities like sulfur, phosphorus, arsenic are oxidized to their volatile oxides. It is performed in a reverberatory furnace. After this process the mass becomes porous.
15. What is the role of flux in metallurgical processes?
15. In metallurgical processes, Flux works as various types of agents like chemical agents, cleaning/purifying agents.
Fluxes have many important properties such as corrosivity, cleanability, conductivity, volatility, etc.
Flux, when combined with gangue together, forms slag i.e. Flux + Gangue = Slag
As compared to gangue, slag separates much easily from the ore, in this way the removal of gangue also becomes much easier.
Flux is useful for making the molten mass more conducting which helps to remove impurities from metals through electrolytic metallurgical processes.
17. Write down the reactions taking place in Blast furnaces related to the metallurgy of iron in the temperature range 500-800 K.
17. The chemical reactions taking place in Blast furnace in the temperature range 500-800 K are:
3Fe2O3 + CO→ 2Fe3O4 + CO2
Fe3O4 + 4CO→ 3Fe + 4CO2
Fe2O3 + CO→ 2FeO + CO2
53. Assertion: Sulfide ores are concentrated by Froth Flotation method.
Reason: Cresols stabilize the froth in the Froth Flotation method.
53. (ii) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: Froth Flotation method is used to separate the hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic materials. In this method a mixture of palm oil, water and detergent is taken in a tank along with powdered sulfide ore. Compressed air is then passed through the pipe of the rotating agitator to create froth. The sulfide ore is then wetted by the palm oil mixture and it rises with the froth and the impurities or gauge settles at the bottom of the tank. The froth containing the sulfide is then cleaned and dried. Cresols or Aniline are used to stabilize the froth and in case of sulfides palm oil is used to collect non wet particles of the sulfide.
54. Assertion: Zone refining method is very useful for producing semiconductors.
Reason: Semiconductors are of high purity.
54. (ii) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: The zone refining method is very useful for producing high-purity semiconductors and other metals, such as germanium.
2. Why is an external emf of more than 2.2 V required for the extraction of Cl2 from the brine?
2. Extraction of chlorine from brine is an oxidation method. The reactions involved are:
2Cl− + 2H2O → 2OH− + H2 + Cl2
For this reaction, the value of ΔG°=+422 kJ, which is positive. Using the formula ΔG°=−nE°F, we get a negative value of E° =−2.2 V.
Since, E°=−2.2 V, it would naturally require an external voltage greater than 2.2 V for the reaction to occur.
3. At temperatures above 1073K coke can be used to reduce FeO to Fe. How can you justify this reduction with the Ellingham diagram?
3. From Ellingham diagram, we know that ΔG° (C, CO) < ΔG° (Fe, Fe), the following reactions are:
C+ O2→CO
2Fe+O2→2FeO
Therefore, FeO can be reduced to Fe by coke.
5. How is copper extracted from low grade copper ores?
5. Low-grade copper ores contain a small percentage of copper that is 0.27% copper. By hydrometallurgy, low-grade copper is leached by treating with acid when copper metal goes into solution as copper ions. The solution containing copper ions is treated with scrap iron or hydrogen gas. Since iron or hydrogen is more reactive than copper so they reduced copper ions from solution to copper metal.
7. Although carbon and hydrogen are better reducing agents, they are not used to reduce metallic oxides at high temperatures. Why?
7. The reduction is the removal of oxygen. Hydrogen and carbon both form oxides that are easy to remove both water and carbon dioxide which are produced as a gas at hot reactions. Although carbon and hydrogen are better reducing agents, they are not used to reduce metallic oxides at high temperatures because at high temperatures carbon and hydrogen react with metals to form carbide and hydrides respectively.
8. How do we separate two sulfide ores by the Froth Floatation Method? Explain with an example.
8. Separation of two sulfide ores can be accomplished by adjusting the proportion of oil to water or by using depressants. In the case of an ore containing ZnS and PbS, for example, the depressant NaCN is used. It forms a complex with ZnS and prevents it from coming into contact with froth, but PbS remains in contact with froth.
9. The purest form of iron is prepared by oxidizing impurities from cast iron in a reverberatory furnace. Which iron ore is used to line the furnace? Explain by giving a reaction
9. A metal is called Pure when it contains the highest concentration of itself and the least concentration of impurities. While refining of metal, these impurities are removed by various processes aided by the use of other compounds.
Hematite supplies oxygen and oxidizes carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus present in the cast iron to carbon monoxide, manganese oxide, phosphorus pentoxide respectively.
Fe2O3 + 3C 2Fe + 3CO
3Si + 2Fe2O3 → 4Fe + 3SiO2
3S + 2Fe2O3→3SO2 + 4Fe
Wrought iron is called the purest form of iron as it contains the highest percentage of Iron and the least impurities. It is prepared from cast iron by oxidizing impurities in a reverberatory furnace lined with Hematite.
10. The mixture of compounds A and B is passed through a column of Al2O3 by using alcohol as eluent. Compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Which of the compounds A or B, is more readily adsorbed on the column?
10. Column chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures based on differences in their affinity towards the stationary phase. If one molecule in a solute has more affinity towards the stationary phase, it would form bonds with the stationary phase and hence remain in the column, Whereas, if the other one has less affinity, it would not form bonds and hence will travel down and come out of the column faster.
As compound A is eluted in preference to compound B, compound B is more readily adsorbed on the column of Al2O3.
10. Why is sulfide ore of copper heated in a furnace after mixing with silica?
10. Sulfide ores are not reduced easily, but oxide ores are easily reduced. Sulfide ore of copper contains some types of impurities. This can cause by-product formation and degrade our final product. Iron oxide is present as a key impurity of concern in sulfide ore of copper. During the roasting process the temperature in the furnace is near about 1200°C. During such high temperatures iron oxide which is gangue (impurity) in ore forms slag. Slag is insoluble in molten metal and being lighter floats over the surface of molten metal. Here silica is used as flux.
FeO + SiO2 →FeSiO3
13. Which method is used for refining Zr and Ti? Explain with equations.
13. Vapor phase refining or Van Arkel's method is used for refining Zr and Ti.
Vapor refining or vapor phase process: The metal is collected in the form of volatile compound that decomposes to pure metal.
Van Arkel method: This method is useful for removing all Oxygen and nitrogen present in the form of impurity in metals like Zr and Ti. The crude metal is heated in an empty vessel with a small amount of iodine. The metal iodine being more covalent volatilises. Impure Zr reacts with iodine to form zirconium tera iodide.
The following reaction occurs Zr + 2I2? ZrI4 The metal iodide is decomposed on a tungsten filament electrically heated to about 1800 K. The pure metal is deposited on the filament and to maintain temperature the current is steadily raised, as the depositing continues.
14. What should be the considerations during the extraction of metals by electrochemical method?
14. The considerations during the extraction of metals by electrochemical method are :
a) Reactivity of metals: If the metals are reactive and are likely to react with water then the metals should be isolated by the electrolysis of their purified molten ore rather than their aqueous solution.
b) Suitability of electrodes:The electrode is carefully chosen so that they should not react with the product of electrolysis. If they react then the electrodes must be made of a material which is quite cheap so their replacement should not increase the cost of the process.
16. How are metals used as semiconductors refined? What is the principle of the method used?
16. Semiconducting metal is produced by the zone refining method.
Zone refining is centered on the principle that the impurities which are included in the metal ores are more soluble in the molten state as compared to the solid-state of metals.
Zone refining is mostly used for obtaining semiconductor and other metals which are highly pure, e.g., germanium, silicon, etc.
18. Give two requirements for vapor phase refining.
18. The two import requirements for performing the Vapor Phase Refining Method:
a) The metal which is to be refined should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
b) The volatile compound formed must be easily decomposable so that it is easy to recover the desired metal.
19. Write the chemical reactions involved in the extraction of gold by cyanide process. Also give the role of zinc in the extraction.
19. The metal gold is a nonreactive metal. It is found as a native metal in its free state.
So, it is not compulsory to separate it by a chemical process. Thus, gold is leached to get it in its pure form. In the metallurgy of gold (Au), the respective metal is leached with a dilute mixture of NaCN or KCN in the presence of air where Gold (Au) is oxidized by oxygen of the air to Au+cation which then merges with ions to form a soluble compound.
4Au (s)+8CN− (aq)+O2− (g)+2H2O− (aq)→4 [Au (CN)2]− (aq)+4OH− (aq)
Gold is then obtained from this soluble compound x by replacement method by using a much more electropositive Zinc metal.
In this method of Gold extraction, the metal Zinc (Zn) plays the role of a reducing agent and it reduces Au+to Au.
Zn itself gets oxidized to Zn+ions which combine with CN−ions to form another soluble complex. 2Na [Au (CN)2] (aq)+Zn→2Au+Na2 [Zn (CN)4].
20. In the extraction of chlorine by electrolysis of brine
(i) Oxidation of Cl−ion to chlorine gas occurs.
(ii) Reduction of Cl−ion to chlorine gas occurs.
(iii) For overall reaction ΔG? has a negative value.
(iv) A displacement reaction takes place.
20. Option (i)
Explanation: 2H2O + Cl−→2OH− + H2 + Cl2
The ΔG? is +422 kJ for this reaction. We get ΔE? = −2.2 V, when we convert it to ΔE? (using G? = E? F). It will, of course, require an external e.m.f. greater than 2.2 V. However, electrolysis necessitates an excess potential in order to overcome some other impeding reactions. Thus, Cl2 is obtained through electrolysis, which produces H2 and aqueous NaOH as byproducts. In addition, molten NaCl is electrolyzed. However, in that case, Na metal is formed rather than NaOH.
21. When copper ore is mixed with silica, in a reverberatory furnace copper matte is produced. The copper matte contains
(i) sulfides of copper (II) and iron (II)
(ii) sulfides of copper (II) and iron (III)
(iii) sulfides of copper (I) and iron (II)
(iv) sulfides of copper (I) and iron (III)
21. Option (iii)
Copper ore is mixed with silica before heating in a reverberatory furnace. When heated in a reverberatory furnace, the iron oxide slags of iron silicate and copper are produced. This product is produced in the form of copper matte in the furnace. Presence of Cu2S and FeS is observed in copper matte. In these compounds, we observe the sulfides of Copper (I) Cu2+ and Iron (II) Fe2+.
22. Which of the following reactions is an example of autoreduction?
(i) Fe3O4 + 4CO→3Fe + 4CO2
(ii) Cu2O + C→2Cu + CO
(iii) Cu2+(aq) + Fe(s)→Cu(s) + Fe2+(aq)
(iv) Cu2O + Cu2S → 3Cu + 12SO2
22. Option (iv)
Copper (I) oxide is reduced by copper (I) sulfide in this reaction. Because copper is reduced by itself in this process, it is referred to as auto reduction.
23. A number of elements are available in earth's crust but most abundant elements are
(i) Al and Fe
(ii) Al and Cu
(iii) Fe and Cu
(iv) Cu and Ag
23. Option (i)
Explanation: Aluminum is the third most abundant metal in the earth's crust (8.3 percent approximately by weight). It is found in a variety of igneous minerals, including mica and clays. The second most abundant metal in the earth's crust is iron.
24. Zone refining is based on the principle that
(i) Impurities of low boiling metals can be separated by distillation.
(ii) Impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal.
(iii) Different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
(iv) Vapors of volatile compounds can be decomposed in pure metal.
24. Option (ii)
Purification of metal crystals by making a thin region of crystal undergo melting is known as Zone refining. The molten crystal is then moved up along the crystal to get pure form of it. This process is used to get pure form of Silicon and Germanium. Basic principle of the zone refining process is that the impurities are more soluble in molten metal than solid metal to get pure form of metal.
25. In the extraction of copper from its sulfide ore, the metal is formed by the reduction of Cu2O with
(i) FeS
(ii) CO
(iii) Cu2S
(iv) SO2
25. Option (iii)
Reaction takes place as Cu2O + Cu2S?3Cu +12SO2 with a product as bristle copper. This type of reaction is called an auto-reduction reaction as copper is reducing itself with help of other copper compounds.
26. Brine is electrolysed by using inert electrodes. The reaction at anode is
(i) Cl−(aq)→ Cl2(g)+ e−;E cell =1.36 V
(ii) 2H2O(l)→O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e−, E cell = 1.23 V
(iii) Na+(aq.)+ e→Na(s); E cell = 2.71 V
(iv) H+(aq) + e−→12H2(g); E cell = 0.00 V
26. Correct option (i)
The reaction at the anode with a lower E value is preferred, but oxygen cannot be obtained in this process due to overvoltage.
27. In the metallurgy of aluminum
(i) Al3+ is oxidized to Al (s).
(ii) Graphite anode is oxidized to carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
(iii) Oxidation state of oxygen changes in the reaction at anode.
(iv) Oxidation state of oxygen changes in the overall reaction involved in the process.
27. Option (ii)
Reaction involved in the metallurgy of aluminum is 2Al2O3 + 3C→ 4Al + 3CO2.
The reaction at cathode is Al3+ + 3e−→ Al
The reaction at anode is
C+12O2 →CO + 2e and C+O2→CO2 + 4e−
Hence, from the reaction graphite anode is oxidized to carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
28. Electrolytic refining is used to purify which of the following metals?
(i) Cu and Zn
(ii) Ge and Si
(iii) Zr and Ti
(iv) Zn and Hg
28. Option (i)
The electrolytic method can be used to purify zinc and copper. The impure metal is used as an anode in this method. As the cathode, a pure strip of the same metal is used. They are immersed in an appropriate electrolytic bath containing a soluble salt of the same metal.
The more basic metals remain in the solution, while the less basic metals are transferred to the anode mud.
29. Extraction of gold and silver involves leaching the metal with CN−ion. The metal is recovered by
(i) Displacement of metal by some other metal from the complex ion.
(ii) Roasting of metal complexes.
(iii) Calcination followed by roasting.
(iv) Thermal decomposition of metal complexes.
29. Option (i)
The cyanide process involves 3 steps:
First step - The finely grounded ore of gold and silver are made to come in contact with the solution containing the cyanide,
Second step - it involves separation of gold and silver from the cyanide solution
Third step - it involves the recovery of gold and silver in their pure forms precipitating the remaining solution with zinc dust.
Thus, the metal is recovered by displacing Zn with the metal (Au or Ag) from metal ions.
Note : Answer the questions 11-13 on the basis of Fig. 6.1.
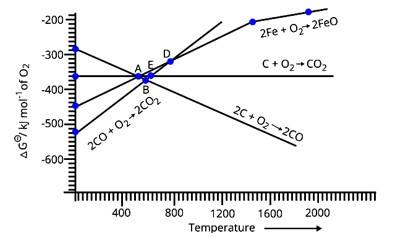
30. Choose the correct option of temperature at which carbon reduces FeO to iron and produces CO
(i) Below temperature at point A.
(ii) Approximately at the temperature corresponding to point A.
(iii) Above temperature at point A but below the temperature at point D.
(iv) Above temperature at point A.
30. Option (iv)
Above point A, ΔG (C, CO)<ΔG (Fe, FeO). Thus, carbon reduces FeO to iron i.e. Fe and in order carbon is oxidized to carbon monoxide i.e. CO. Both these lines intersect at Point A. As we can see in the figure above point A only carbon could reduce FeO in Fe and CO is being produced.
31. Below point ' A ' FeO can
(i) Be reduced by carbon monoxide only.
(ii) Be reduced by both carbon monoxide and carbon.
(iii) Be reduced by carbon only.
(iv) Not be reduced by both carbon and carbon monoxide.
31. Option (i)
Below point A, only the value of ΔG (CO, CO2) is less than the value of ΔG (Fe, FeO) at the corresponding temperatures. Thus, only carbon monoxide will be able to reduce FeO to Fe and will get itself oxidized into CO2.
32. For the reduction of FeO at the temperature corresponding to point D, which of the following statements is correct?
(i) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with carbon monoxide is zero.
(ii) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with a mixture of 1 mol carbon and 1 mol oxygen is positive.
(iii) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with a mixture of 2 mol carbon and 1 mol oxygen will be positive.
(iv) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with carbon monoxide is negative.
32. Option (i)
According to the above graph, at point D the equivalent value of ΔG for the reduction of FeO is approximately 330 units for the particular temperature. Also, for CO the equivalent value of Δ? at the particular temperature for point D is around −330 units. Thus, if we calculate the overall value of ΔG for the reduction of FeO with carbon monoxide then it is almost zero at point D.
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
33. At the temperature corresponding to which of the points in Fig.6.1, FeO will be reduced to Fe by coupling the reaction 2FeO→2Fe+O2with all of the following reactions?
(a) C+O2 → CO2
(b) 2C+O2 → 2CO and
(c) 2CO + O2 → 2CO2.
(i) Point A
(ii) Point B
(iii) Point D
(iv) Point E
33. Option (ii) and (iv)
From Fig.6.1, at point B, all three lines, i.e. for the lines for all three given reactions, are below that of the line of reduction of FeO. This means, that the value of ΔG for the equivalent temperature at point B for reduction of FeO is greater than (positive) that of values of ΔG for all three reactions (negative). Thus, FeO will get reduced by all three reactions at point B. Same is the case with point E as that of point B, the value of ΔG for reduction of FeO at E is greater than the value of ΔG for all three reactions at the equivalent temperature. Thus, FeO will get reduced by all three reactions at point E.
34. Which of the following options are correct?
(i) Cast iron is obtained by smelting pig iron with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast.
(ii) In extraction of silver, silver is extracted as a cationic complex.
(iii) Nickel is purified by zone refining.
(iv) Zr and Ti are purified by van Arkel method.
34. Option (i) and (iv)
Pig iron is the iron obtained from the blast that has many impurities (Mn, P, Si, etc.) and approximately 4% carbon content. When it is re-melted or cast with the help of scrap iron, then it has less carbon content i.e. 3% as compared to pig iron.
The Zr andTi are purified by the help of Arkel Method that contain the following reaction:
Zr (s) + 2I2 ZrI4 ( g) Zr Pure (s) + 2I2
Ti + 2I2 TiI4 Ti + 2I2
Here we obtain Zr and Ti as a pure form of solid when purified using the Arkel method.
35. In the extraction of aluminum by Hall-Heroult process, purified Al2O3 is mixed with CaF2 to
(i) Lower the melting point of Al2O3.
(ii) Increase the conductivity of molten mixture.
(iii) Reduce Al3+ into Al(s).
(iv) Acts as a catalyst.
35. Option (i) and (ii)
In the extraction of alumina by Hall-Heroult's process, alumina is mixed with cryolite with the mixture of fluorspar \& fluoride that increases the conductivity of electrical and lowers the melting point of Al2O3 .
36. Which of the following statements is correct about the role of substances added in the froth floatation process?
(i) Collectors enhance the non-wettability of the mineral particles.
(ii) Collectors enhance the wettability of gangue particles.
(iii) By using depressants in the process two sulfide ores can be separated.
(iv) Froth stabilizers decrease wettability of the gangue.
36. Option (i) and (iii)
A suspension of powdered ore is made with water during the froth floatation process. Collectors and froth stabilizers are added to it. Collectors (e.g., pine oils, fatty acids, xanthates, etc.) improve the non wettability of the mineral particles, while froth stabilizers (e.g., cresols, aniline) keep the froth stable
37. In the Froth Floatation process, zinc sulfide and lead sulfide can be separated by
(i) Using collectors.
(ii) Adjusting the proportion of oil to water.
(iii) Using depression.
(iv) Using froth stabilizers.
37. Option (ii) and (iii)
It is possible to separate two sulfide ores using the froth floatation process by adjusting the proportion of oil to water or by using 'depressants.' In the case of an ore containing ZnS and PbS, for example, the depressant used is NaCN.
38. Common impurities present in bauxite are
(i) CuO
(ii) ZnO
(iii) Fe2O3
(iv) SiO2
38. Option (iii) and (iv)
Bauxite consists of many impurities like hematite, goethite, Fe2O3, the sand SiO2, etc.'
39. Which of the following ores are concentrated by froth floatation?
(i) Haematite
(ii) Galena
(iii) Copper pyrites
(iv) Magnetite
39. Option (ii) and (iii)
The froth floatation method is most commonly used for sulfide ore. Sulfide ores galena (PbS) and copper pyrites (CuFeS2) are found here.
40. Which of the following reactions occur during calcination?
(i) CaCO3→CaO+CO2
(ii) 2FeS2 + O2→Fe2O3+4SO2
(iii) Al2O3⋅?H2O→Al2O3+ ? H2O
(iv) ZnS + O2→ZnO+SO2
40. Option (i) and (iii)
Calcination is the process of heating when the volatile matter escapes, leaving the metal oxide behind. It is usually done in the absence of air.
41. For the metallurgical process of which of the ores calcined ore can be reduced by carbon?
(i) Haematite
(ii) Calamine
(iii) Iron pyrites
(iv) Sphalerite
41. Option (i) and (iii)
Explanation: Haematite is an ore of iron that can be calcined and reduced by carbon. In the metallurgical process, calamine ore is calcined ore that can be reduced by carbon. Hence, option (i) and (ii) are correct.
42. The main reactions occurring in blast furnaces during extraction of iron from haematite are
(i) Fe2O3+3CO→2Fe+3CO2
(ii) FeO+SiO2→FeSiO3
(iii) Fe2O3+3C→2Fe+3CO
(iv) CaO+SiO2→CaSiO3
42. Option (i) and (iv)
(i) Carbon monoxide is the primary reducing agent in the furnace.
(ii) This is an endothermic reaction in which heat is absorbed from the furnace. As a result, it is critical not to add too much limestone, as this will cool the furnace. Calcium oxide is a basic oxide that reacts with acidic oxides in the rock, such as silicon dioxide. Calcium silicate is formed when calcium oxide reacts with silicon dioxide.
43. In which of the following methods of purification, metal is converted to its volatile compound which is decomposed to give pure metal?
(i) Heating with a stream of carbon monoxide.
(ii) Heating with iodine.
(iii) Liquation.
(iv) Distillation.
43. Option (i) and (ii)
In the vapor phase refining method, the metal is converted into its volatile compound and then is collected elsewhere. This involves two techniques:
1. Mond Process for refining Nickel: in this process, a volatile complex, nickel tetracarbonyl is formed when nickel is heated with a stream of carbon monoxide.
2. Van Arkel Method for refining Zirconium or Titanium: this method is basically used for removal of oxygen and nitrogen present as impurities in the Zr or Ti metal. These are heated in an evacuated metal with iodine. As iodine is more covalent than these metals, it volatilizes.
44. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) A depressant prevents a certain type of particle from coming to the froth.
(ii) Copper matte contains Cu2S and ZnS.
(iii) The solidified copper obtained from the reverberatory furnace has a blistered appearance due to evolution of SO2 during the extraction.
(iv) Zinc can be extracted by self-reduction.
44. Option (i) and (ii)
Explanation: Depressants are materials that are added for the separation of ores that prevent certain types of particles from coming to froth and forming bubbles. For example, an ore containing ZnS and PbS, NaCN is used as a depressant.
When sulfur ores are blown in hot air along with silica, the solidified metal which is obtained has a blistered appearance due to SO2 evolution.
45. In the extraction of chlorine from brine
(i) ΔG° for the overall reaction is negative.
(ii) ΔG° for the overall reaction is positive.
(iii) E° for overall reaction has negative value.
(iv) E° for overall reaction has positive value.
45. Option (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Using oxidation method for extraction of chlorine from brine. The reactions involved are:
2Cl− + 2H2O → 2OH− + H2 + Cl2
For this reaction, the value of ΔG°=+422 kJ, which is positive. Using the formula ΔG°=−nE°F, we get a negative value of E° =−2.2 V.
46. Match the items of Column I with items of Column II and assign the correct code:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(A) Pendulum |
(1) Chrome steel |
|
(B) Malachite |
(2) Nickel steel |
|
(C) Calamine |
(3) Na3AlF6 |
|
(D) Cryolite |
(4) CuCO3⋅Cu(OH)2 |
|
(5) ZnCO3 |
Code:
A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
A (2) B (4) C (5) D (3)
A (2) B (3) C (4) D (5)
A (4) B (5) C (3) D (2)
46. Option (ii) A (2) B (4) C (5) D (3)
Pendulum is always made of nickel steel.
Hence, option (A) from column I is matched with option (2) from column II. Malachite is the ore of copper.
Hence, option (B) from column I is matched with option (4) from column II. Calamine is the ore of zinc.
Hence, option (C) from column I is matched with option (5) from column II. Cryolite is an ore of aluminum.
Hence, option (D) from column I is matched with option (3) from column II.
47. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(A) Coloured bands |
(1) Zone refining |
|
(B) Impure metal to volatile complex |
(2) Fractional distillation |
|
(C) Purification of Ge and Si |
(3) Mond process |
|
(D) Purification of mercury |
(4) Chromatography |
|
(5) Liquation |
Code :
A (1) B (2) C (4) D (5)
A (4) B (3) C (1) D (2)
A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
47. Option (ii) A (4) B (3) C (1) D (2)
Coloured bands are found in chromatography.
Hence, option (A) from column I is matched with option (4) from column II. Impure metals are converted to volatile complexes in Mond's process.
Hence, option (B) from column I is matched with option (3) from column II. Purification of Ge and silicon is done using zone refining.
Hence, option (C) from column I is matched with option (1) from column II. Purification of mercury is done using fractional distillation.
Hence, option (D) from column I is matched with option (2) from column II.
48. Match items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code :
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(A) Cyanide process |
(1) Ultrapure Ge |
|
(B) Froth Floatation Process |
(2) Dressing of ZnS |
|
(C) Electrolytic reduction |
(3) Extraction of Al |
|
(D) Zone refining |
(4) Extraction of Au |
|
(5) Purification of Ni |
Code :
A (4) B (2) C (3) D (1)
A (2) B (3) C (1) D (5)
A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
A (3) B (4) C (5) D (1)
48. Correct code (i) A (4) B (2) C (3) D (1)
The cyanide process is used in the extraction of Au.
Hence, option (A) from column I is matched with option (4) from column II. Froth floatation process is used in the dressing of ZnS.
Hence, option (B) from column I is matched with option (2) from column II. Electrolytic reduction is used in the extraction of AI.
Hence, option (C) from column I is matched with option (3) from column II. Zone refining is used to get ultrapure Ge.
Hence, option (D) from column I is matched with option (1) from column II.
49. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code :
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(A) Sapphire |
(1) Al2O3 |
|
(B) Sphalerite |
(2) NaCN |
|
(C) Depressant |
(3) Co |
|
(D) Corundum |
(4) ZnS |
|
(5) Fe2O3 |
Code :
A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
A (2) B (3) C (4) D (5)
A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
49. Option (i) A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
Sapphire is a gemstone containing Co.
Hence, option (A) from column I is matched with option (3) from column II. The Sphalerite single is ZnS.
Hence, option (B) from column I is matched with option (4) from column II. NaCN is also used as a depressant.
Hence, option (C) from column I is matched with option (2) from column II. Al2O3 is also called corundum.
Hence, option (D) from column I is matched with option (1) from column II.
50. Match the items of Column I with items of Column II and assign the correct code :
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(A) Blistered Cu |
(1) Aluminum |
|
(B) Blast furnace |
(2) 2Cu2O+Cu2 S→6Cu+SO2 |
|
(C) Reverberatory furnace |
(3) Iron |
|
(D) Hall-Heroult process |
(4) FeO+SiO2→FeSiO3 |
|
(5) 2Cu2 S+3O2→2Cu2O+2SO2 |
Code :
A (2) B (3) C (4) D (1)
A (1) B (2) C (3) D (5)
A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
A (4) B (5) C (3) D (2)
50. Option (i) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (1)
Explanation: A solidified copper has a blistered appearance due to the evolution of SO2 Hence it is called blistered copper.
Hence, option (A) from column I is matched with option (2) from column II. Iron is extracted from a blast furnace.
Hence, option (B) from column I is matched with option (3) from column II. The iron ore is heated in the reverberatory furnace after mixing with silica. In the furnace, iron oxide slags of iron and copper are produced in the form of copper matte.
Hence, option (C) from column I is matched with option (4) from column II. The hall-Heroult process is used for the extraction of aluminum from its ore.
Hence, option (D) from column I is matched with option (1) from column II.
51. In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(i) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(iii) Assertion is true but the reason is false.
(iv) Assertion is false but the reason is true.
(v) Assertion and reason both are wrong.
1. Assertion: Nickel can be purified by the Mond process.
Reason: Ni(CO)4 is a volatile compound which decomposes at 460 K to give pure Ni.
51. (i) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: In the Mond process Nickel is reacted with carbon monoxide reversibly to give Nickel carbonyl, Ni (CO)4. Nickel carbonyl is a volatile compound. It decomposes to nickel and carbon monoxide at 460 K.
52. Assertion: Zirconium can be purified by Van Arkel method.
Reason: ZrI4 is volatile and decomposes at 1800 K.
52. (i) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: Van Arkel method is generally used to obtain pure forms of Zirconium (Zr) and Titanium (Ti).
The metal iodide is heated at 1800 K and is decomposed on a tungsten filament. The pure metal is dropped on the tungsten filament. This proves that ZrI4 is volatile and decomposes at 1800 K.
55. Assertion: Hydrometallurgy involves dissolving the ore in a suitable reagent followed by precipitation by a more electropositive metal.
Reason: Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy.
55. (ii) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: Hydrometallurgy is used to extract copper from low-grade ore. Hydrometallurgy entails dissolving the ore in a suitable reagent and then precipitating it. In this method, more electropositive metal is used, allowing pure metal to be displaced.
General Principles and Isolation of Elements Short Answers Type Questions
| 1. Why is an external emf of more than 2.2 V required for the extraction of Cl2 from the brine? |
| Ans: Extraction of chlorine from brine is an oxidation method. The reactions involved are: 2Cl− + 2H2O → 2OH− + H2 + Cl2 For this reaction, the value of ΔG°=+422 kJ, which is positive. Using the formula ΔG°=−nE°F, we get a negative value of E° =−2.2 V. Since, E°=−2.2 V, it would naturally require an external voltage greater than 2.2 V for the reaction to occur. |
| 2. At temperatures above 1073K coke can be used to reduce FeO to Fe. How can you justify this reduction with the Ellingham diagram? |
| Ans: From Ellingham diagram, we know that ΔG° (C,CO) < ΔG° (Fe,Fe), the following reactions are: C+ O2→CO 2Fe+O2→2FeO Therefore, FeO can be reduced to Fe by coke. |
| 3. Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulfur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron? |
| Ans: Iron oxides are mixed with limestone and coke in order to decompose carbonates and oxidize sulfides. This mixture is then fed into the blast furnace. Many reactions take place in different temperature ranges of the blast furnace. By oxidizing impurities from cast iron in a reverberatory furnace which is lined by hematite, wrought iron or malleable iron is obtained. This is the purest form of commercial iron. This can be shown with the following reaction: Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO. Sulfur, silicone and phosphorus are oxidized and passed into the slag and removed as impurities when limestone is added as a flux to it. |
26th June 2022
26th June 2022
Commonly asked questions
A commercially sold conc. HCl is 35% HCl by mass. If the density of this commercial acid is 1.46 g/mL, the molarity of this solution is
= 14.0 M
Consider the ions /molecule
For increasing bond order the correct option is
Hence Bond order for
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: According to the Ellingham diagram, any metal oxide with higher is more stable that the one with lower .
Statement II: The metal involved in the formation of oxide placed lower in the Ellingham diagram can reduce the oxide of a metal placed higher in the diagram.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer form the options given below
According to Ellingham diagram, the metal oxide with lower is more stable than metal oxide of higher at same temperature.
The correct order of melting points of hydrides of group 16 elements is
Due to H- bond in water, it has high melting point and melting point of other hydrides of the group are depending upon the molecular weight.
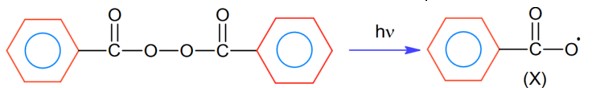
Consider the above reaction and identify the intermediate ‘X’
This is the formation of free radical mechanism, hence free radical will be formed
Which of the following sets are correct regarding polymer?
(A) Copolymer: Buna-S
(B) Condensation polymer: Nylon-6,6
(C) Fibres: Nylon-6,6
(D) Thermosetting polymer: Terylene
(E) Homopolymer: Buna-N
Choose the correct answer form given options below
Buna-S is the copolymer of butadiene and styrene, Nylon-6, 6 is the condensation polymer of adipic acid and diamine and having fibrous nature.
Which statement is not true with respect to nitrate ion test?
Brown ring is formed due to nitrosoferrous sulphate formation.
An evacuated glass vessel weights 40.0g when empty, 135.0g when filled with a liquid of density 0.95 g mL-1 and 40.5 g when filled with an ideal gas at 0.82 atm at 250 K. The molar mass of the gas in g mo-1 is:
(Given: R = 0.082 L atm K-1 mol-1)
Wt of liquid = 135 – 40 = 95 gm
Volume of liquid =
Hence volume of vessel = 100 ml = 0.1 lit from ideal gas equation,
If the radius of the 3rd Bohr’s orbit of hydrogen atom r3 and the radius of 4th Bohr’s orbit is r4. Then
Radius of Bohr’s orbit
Radius of Bohr’s orbit for hydrogen,
For third orbit (R3) = = r3 and
Fourth orbit (R4) =
The of different types of half cells are as follows:
(Where E is the electromotive force )
Which of the above half cells would be preferred to be used as reference electrode
is the temperature Co-efficient of cell. The cell having less variation of EMF, with respect to temperature have high efficiency.
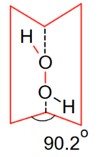
Consider the following reaction.
The dihedral angle in product A in its solid phase at 110 K is
During the electrolysis of dilute H2SO4
In the solid form of dihedral angle is equal to 90.2°.
The correct order of melting point is
Due to high crystallity Be has the highest M.P.
Be = 1560 K
Mg = 925 K
Ca = 1120 K
Sr = 1062 K
Consider the following reaction:
A + alkali → B(Major Product)
If B is an oxoacid of phosphorous with no P-H bond, then A is
Polar stratospheric clouds facilitate the formation of
HOCl produce in the stratospheric cloud, by the hydrolysis reaction of ClONO2.
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: In ‘Lassaigne’s Test’, when both nitrogen and sulphur are present in an organic compound, sodium thiocyanate is formed.
Statement II: If both nitrogen and sulphur are present in an organic compound, then the excess of sodium used in sodium fusion will decompose the sodium thiocyanate formed to given NaCN and Na2S.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the option given below
Regarding Lassaigne's Test, both statement are correct.
Which will have the highest enol content?
Aromaticity drives the highest enolic percentage of given structure:
Among the following structure, which will show the most stable enamine formation?
Enamines are inter conversible and have low stability with respect to imine. Among all C is most stable due to steric factor.
A chemical which stimulates the secretion of pepsin is
Histamine is the chemical which stimulates the secretion of pepsin in stomach.
For complete combustion of methanol
The amount of heat produced as measured by bomb calorimeter is 726 kJmol-1 at 27°C. The enthalpy of combustion for the reaction is -x kJ mol-1, where x is_________
(Nearest integer)
(Given : R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1).
Hence, x = 727 (the nearest integer)
A 0.5 percent solution of potassium choride was found to freeze at -0.24°C. The percentage dissociation of potassium chloride is__________. (Nearest integer)
(Molal depression constant for water is 1.80 K kg mol-1 and molar mass of KCl is 74.6 g mol-1)
0.5 % KCl solution has molality (m) =
1 - α α α
And I =
1.976 = 1 + α
% = 97.6%
the nearest 98.
50 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH is being titrated against 0.1 M NaOH. When 25 mL of NaOH has been added, the pH of the solution will be_________× 10-2. (Nearest integer)
(Given : pKa (CH3-COOH) = 4.76)
log 2 = 0.30
log 3 = 0.48
log 5 = 0.69
log 7 = 0.84
log 11 = 1.04
Here, total meq of acetic acid = 50 × 0.1 = 5
And total meq of NaOH = 25 × 0.1 = 2.5
After neutralization process
Meq of left acetic acid = 2.5
And meq of formed CH3COONa = 2.5
A flask is filled with equal moles of A and B. The half lives of A and B are 100s and 50s respectively and are independent of the initial concentration. The time required for the concentration of A to be four times that of B is ______________s.
(Given : In 2 = 0.693)
Process is based upon simultaneous disintegration hence,
………….(i)
and ………….(ii)
from equation (i) and (ii)
Here; A0 = B0 and
Therefore
2.0g of H2 gas is adsorbed on 2.5g platinum powder at 300K and 1 bar pressure. The volume of the gas adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent is ______________mL.
(Given : R = 0.083 L bar K-1 mol-1)
Volume of H2 adsorbed =
Therefore volume of gas adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent =
The spin- only magnetic moment value of the most basic oxide of vanadium among V2O3, V2O4 and V2O5 is _____________B. M (Nearest integer)
Most basic oxide V2O3
Here V has +3 O.S. Hence V+3
two unpaired e- in d- subshell
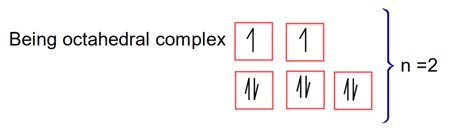
The spin only magnetic moment value of an octhahedral complex among CoCl3.4NH3, NiCl2.6H2O and PtCl4.2HCl, which upon reaction with excess of AgNO3 gives 2 moles of AgCl is____________B. M. (Nearest integer)
For precipitation of two moles of AgCl
Two Cl will produce as a free anion
CoCl3.4NH3 complex will Cl (will not give 2Cl)
complex will be H2 [PtCl6] will not any Cl
will produce two Cl ion.
precipitate formation
On complete combustion 0.30g of an organic compound gave 0.20g of carbon dioxide and 0.10 g of water. The percentage of carbon in the given organic compound is __________. (Nearest integer)
Complete combustion of compound produces 0.2 gm CO2
Hence wt of carbon in 0.2 gm CO2
Therefore % of carbon in compound
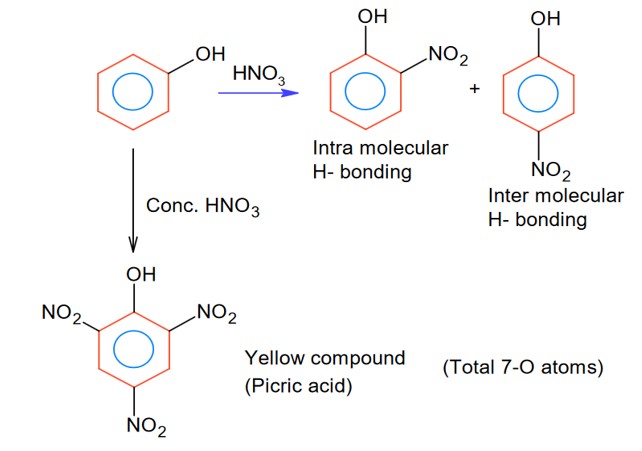
Compound ‘P’ on nitration with dil. HNO3 yields two isomers (A) and (B). These isomers can be separated by steam distillation. Isomers (A) and (B) show the intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonding respectively. Compound (P) on reaction with conc. HNO3 yields a yellow compound ‘C’___________
Intermolecular H- bonding and intra-molecular H- bonding producing compound may be the phenol derivatives.
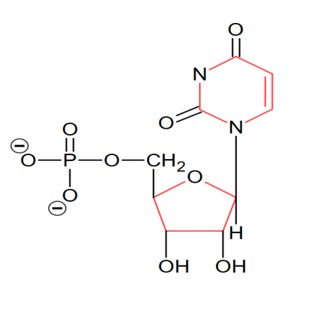
The number of oxygen’s present in a nucleotide formed from a base, that is present only in RNA is_______________.
Consider the following image
JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
JEE MAINS 25th Feb 2021
Commonly asked questions
Copper reduces into NO and NO2 depending upon the concentration of HNO3 in solution. (Assuming fixed ), the HNO3 concentration at which the thermodynamic tendency for reduction of NO and NO2by copper is same is 10x M. The value of 2x is…….. (rounded-off to the nearest integer).
For same thermodynamic tendency of reduction
Assume
Comparing x = 2.16 and 2x = 4.32
Nearest integer is 4.
The rate constant of a reaction increases by five times on increase in temperature from 27°C to 52°C. The value of activation energy in kJ mol-1 is……….. (Rounded-off to the nearest integer).
[R = 8.314JK-1mol-1]
log (5) =
Ea in kJ/mole =
the nearest integer is 52.
The unit cell of copper corresponds to a face centered cube of edge length 3.596 with one copper atom at each lattice point. The calculated density of copper in kg/m3 is……..
[Molar mass of Cu = 63.54g : Avogadro Number = 6.022 × 1023]
Density =
Five moles of an ideal gas at 293K is expanded isothermally from an initial pressure of 2.1 MPa to 1.3 MPa against at constant external pressure 4.3 MPa. The heat transferred in this process is…….. kJ mol-1. (Rounded-off to the nearest integer).
[Use R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1]
If
Q = W
W = -Pext
=
= 15347.70 K = 15.3 kJ
Q = 15 kJ
If a compound AB dissociates to the extent of 75% in an aqueous solution, the molality of the solution which shows a 2.5K rise in the boiling point of the solution is…….. molal.
(Rounded-off to the nearest integer).
[Kb = 0.52 K kg mol-1]
1-x x x
the nearest integer is 3.
Consider titration of NoOH solution versus 1.25M oxalic acid solution. At the end point following burette readings were obtained.
(i) 4.5mL (ii) 4.5mL
(iii) 4.44mL (iv) 4.4mL
(v) 4.44mL
If the volume of oxalic acid taken was 10.0mL then the molarity of the NaOH solution is……….M.
(Rounded-off to the nearest integer).
Meq of NaOH = Meq H2C2O4
4.44 × N = 1.25 × 2 × 10
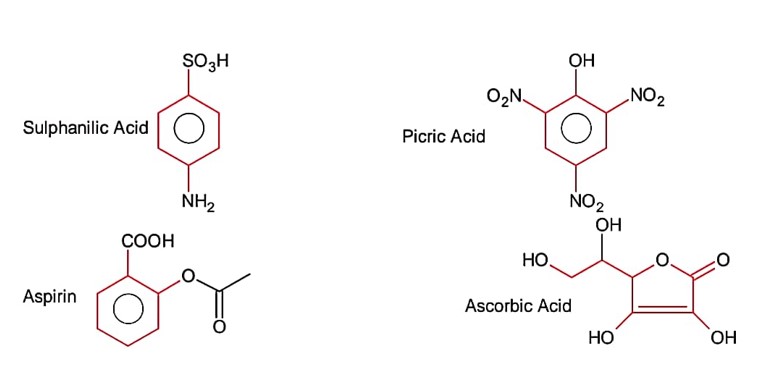
The number of compound/s given below which contain/s – COOH group is………….
(Integer answer)
(a) Sulphanilic acid (b) Picric acid
(c) Aspirin (d) Ascorbic acid
Please find the below image
Electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 663nm is just sufficient to ionize the atom of metal A. The ionization energy of metal A in kJ mol-1 is…………… (Rounded-off to the nearest integer)
[h = 6.63 × 10-34Js,c = 3.00 × 108ms-1, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol-1]
= 0.03 × 10-17 = 3.0 × 10-19 J/atom
= 18.06 × 101 kJ/mole = 180.6
The spin only magnetic moment of a divalent ion in aqueous solution (atomic number 29) is……..BM.
Cu+ = 3d9 4s0
n = 1
the nearest integer is 2.
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Six Exam