- Sequence and Series Short Answer Type Questions
- Sequence and Series Long Answers Type Questions
- Sequence and Series Objective Type Questions
- Sequence and Series Fill in the blanks Type Questions
- Sequence and Series True or False Type Questions
- Sequence and Series Matching Type Questions
- JEE Mains 2020
- JEE Mains 2025
Sequence and Series Short Answer Type Questions
| 1. The first term of an A.P. is , and the sum of the first terms is zero, show that the sum of its next terms is . [Hint: Required sum = ] |
| Sol:
|
| 2. A man saved Rs 66000 in 20 years. In each succeeding year after the first year, he saved Rs 200 more than what he saved in the previous year. How much did he save in the first year? |
| Sol:
|
Sequence and Series Long Answers Type Questions
| 1. If is the arithmetic mean and be two geometric means between any two numbers, then prove that
|
| Sol:
|
| 2. If are in A.P., whose common difference is , show that |
| Sol:
|
Sequence and Series Objective Type Questions
| 1. If the sum of terms of an A.P. is given by , then the common difference of the A.P. is (a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 6 (d) 4 |
| Sol:
|
| 2. The third term of a G.P. is 4. The product of its first 5 terms is (a) (b) (c) (d) None of these |
| Sol:
|
Sequence and Series Fill in the blanks Type Questions
| 1. For to be in G.P., the value of is equal to .............. . For to be in G.P., the value of is equal to .... |
| Sol:
|
| 2. The sum of terms equidistant from the beginning and end in an A.P. is equal to ............ . |
| Sol:
|
Sequence and Series True or False Type Questions
| State whether the statements are True or False: 1. Two sequences cannot be in both A.P. and G.P. together. |
| Sol:
|
| 2. Every progression is a sequence but the converse, i.e., every sequence is also a progression, need not necessarily be true. |
| Sol:
|
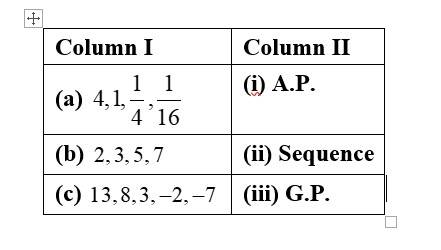
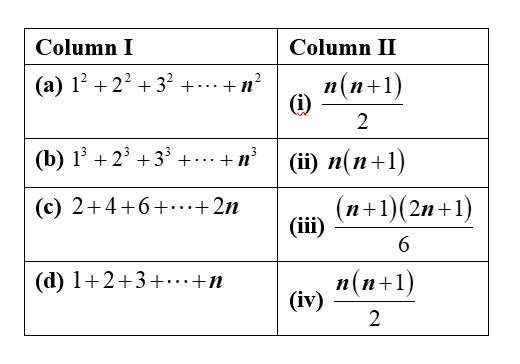
Sequence and Series Matching Type Questions
| Sol:
|
|
|
| Sol:
|
JEE Mains 2020
JEE Mains 2020
JEE Mains 2025
JEE Mains 2025
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine Exam