- Probability Short Answer Type Questions
- Probability Long Answer Type Questions
- Probability Objective Type Questions
- Probability True or False Type Questions
- Probability Fill in the blank Type Questions
- Probability Matching Type Questions
Probability Short Answer Type Questions
| 1. If the letters of the word ALGORITHM are arranged at random in a row, what is the probability that the letters GOR must remain together as a unit? |
| Sol. |
| 2. Six new employees, two of whom are married to each other, are to be assigned six desks that are lined up in a row. If the assignment of employees to desks is made randomly, what is the probability that the married couple will have nonadjacent desks? [Hint: First find the probability that the couple has adjacent desks, and then subtract it from 1.] |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
Six new employees, two of whom are married to each other, are to be assigned six desks that are lined up in a row. If the assignment of employees to desks is made randomly, what is the probability that the married couple will have nonadjacent desks?
[Hint: First find the probability that the couple has adjacent desks, and then subtract it from 1.]
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the letters of the word ALGORITHM are arranged at random in a row, what is the probability that the letters GOR must remain together as a unit?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Suppose an integer from 1 through 1000 is chosen at random. Find the probability that the integer is a multiple of 2 or a multiple of 9.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
An experiment consists of rolling a die until a 2 appears.
(i) How many elements of the sample space correspond to the event that the 2 appears on the roll of the die?
(ii) How many elements of the sample space correspond to the event that the 2 appears not later than the roll of the die?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A die is loaded in such a way that each odd number is twice as likely to occur as each even number. Find , where is the event that a number greater than 3 occurs on a single roll of the die.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In a large metropolitan area, the probabilities are 0.87, 0.36, 0.30 that a family (randomly chosen for a sample survey) owns a colour television set, a black and white television set, or both kinds of sets. What is the probability that a family owns either any one or both kinds of sets?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If and are mutually exclusive events, and , find:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A team of medical students doing their internship has to assist during surgeries at a city hospital. The probabilities of surgeries rated as very complex, complex, routine, simple, or very simple are respectively, 0.15, 0.20, 0.31, 0.26, 0.08. Find the probabilities that a particular surgery will be rated:
(a) complex or very complex;
(b) neither very complex nor very simple;
(c) routine or complex;
(d) routine or simple.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Four candidates have applied for the assignment to coach a school cricket team. If is twice as likely to be selected as , and and are given about the same chance of being selected, while is twice as likely to be selected as , what are the probabilities that:
(a) C will be selected?
(b) A will not be selected?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
One of the four persons, John, Rita, Aslam, or Gurpreet, will be promoted next month. Consequently, the sample space consists of four elementary outcomes:
S = {John promoted, Rita promoted, Aslam promoted, Gurpreet promoted}
You are told that the chances of John’s promotion are the same as that of Gurpreet. Rita’s chances of promotion are twice as likely as John’s. Aslam’s chances are four times that of John.
(a) Determine P (John promoted),
P (Rita promoted),
P (Aslam promoted), and
P (Gurpreet promoted).
(b) If A = {John promoted or Gurpreet promoted}, find P(A).
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
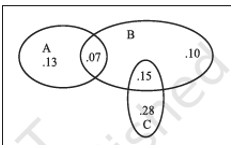
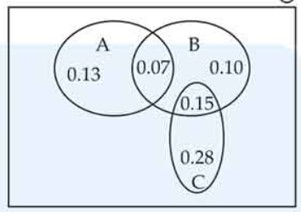
The accompanying Venn diagram shows three events, A, B, and C, and also the probabilities of the various intersections (for instance, P (A ∩ B) = .07). Determine
(a) P (A)
(b) P (B ∩ C )
(c) P (A ∪ B)
(d) P (A ∩ B )
(e) P (B ∩ C)
(f) Probability of exactly one of the three occurs.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Probability Long Answer Type Questions
| 1. One urn contains two black balls (labeled and ) and one white ball. A second urn contains one black ball and two white balls (labeled and ). Suppose the following experiment is performed: one of the two urns is chosen at random. Next, a ball is randomly chosen from the urn. Then a second ball is chosen at random from the same urn without replacing the first ball. (a) Write the sample space showing all possible outcomes. (b) What is the probability that two black balls are chosen? (c) What is the probability that two balls of opposite color are chosen? |
| Sol. |
| 2. A bag contains 8 red and 5 white balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Find the probability that: (a) All the three balls are white. (b) All the three balls are red. (c) One ball is red and two balls are white. |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
One urn contains two black balls (labeled and ) and one white ball. A second urn contains one black ball and two white balls (labeled and ). Suppose the following experiment is performed: one of the two urns is chosen at random. Next, a ball is randomly chosen from the urn. Then a second ball is chosen at random from the same urn without replacing the first ball.
(a) Write the sample space showing all possible outcomes.
(b) What is the probability that two black balls are chosen?
(c) What is the probability that two balls of opposite color are chosen?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A bag contains 8 red and 5 white balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Find the probability that:
(a) All the three balls are white.
(b) All the three balls are red.
(c) One ball is red and two balls are white.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the letters of the word ASSASSINATION are arranged at random, find the probability that:
(a) Four S’s come consecutively in the word.
(b) Two I’s and two N’s come together.
(c) All A’s are not coming together.
(d) No two A’s are coming together.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A card is drawn from a deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a king or a heart or a red card.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A sample space consists of 9 elementary outcomes whose probabilities are:
, , , .
Suppose , .
(a) Calculate , , and .
(b) Using the addition law of probability, calculate .
(c) List the composition of the event , and calculate by adding the probabilities of the elementary outcomes.
(d) Calculate from , also calculate directly from the elementary outcomes of .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Determine the probability p, for each of the following events.
(a) An odd number appears in a single toss of a fair die.
(b) At least one head appears in two tosses of a fair coin.
(c) A king, 9 of hearts, or 3 of spades appears in drawing a single card from a well shuffled ordinary deck of 52 cards.
(d) The sum of 6 appears in a single toss of a pair of fair dice.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Probability Objective Type Questions
| 1. In a non-leap year, the probability of having 53 Tuesdays or 53 Wednesdays is: (a) (b) (c) (d) None of these |
| Sol. |
| 2. Three numbers are chosen from 1 to 20. Find the probability that they are not consecutive: (a) (b) (c) (d) 18/20C3 |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
A single letter is selected at random from the word “PROBABILITY.” The probability that it is a vowel is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these.
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In a non-leap year, the probability of having 53 Tuesdays or 53 Wednesdays is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Three numbers are chosen from 1 to 20. Find the probability that they are not consecutive:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) 18/20C3
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
While shuffling a pack of 52 playing cards, 2 are accidentally dropped. Find the probability that the missing cards are of different colors
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Seven persons are to be seated in a row. The probability that two particular persons sit next to each other is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If P(A ∪ B) = P(A ∩ B) for any two events A and B, then:
(a) P(A) = P(B)
(b) P(A) > P(B)
(c) P(A) < P(B)
(d) None of these.
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Six boys and six girls sit in a row at random. The probability that all the girls sit together is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these.
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If the probabilities for A to fail in an examination are 0.2 and for B are 0.3, then the probability that either A or B fails is:
(a) > 0.5
(b) 0.5
(c) ≤ 0.5
(d) 0
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probability that at least one of the events A and B occurs is 0.6. If A and B occur simultaneously with a probability of 0.2, then P(A) + P(B) is:
(a) 0.4
(b) 0.8
(c) 1.2
(d) 1.6
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If M and N are any two events, the probability that at least one of them occurs is:
(a) P(M) + P(N) – 2P(M ∩ N)
(b) P(M) + P(N) – P(M ∩ N)
(c) P(M) + P(N) + P(M ∩ N)
(d) P(M) + P(N) + 2P(M ∩ N)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Without repetition of the numbers, four-digit numbers are formed with the numbers 0, 2, 3, 5. The probability of such a number divisible by 5 is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then: (A) P
(a) ≤ P(B)
(b) P(A) ≥ P(B)
(c) P(A) < P(B)
(d) None of these.
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Probability True or False Type Questions
| 1. The probability that a person visiting a zoo will see the giraffe is 0.72, the probability that he will see the bears is 0.84, and the probability that he will see both is 0.52. |
| Sol. |
| 2. The probability that a student will pass his examination is 0.73, the probability of the student getting a compartment is 0.13, and the probability that the student will either pass or get a compartment is 0.96. |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
The probability that a person visiting a zoo will see the giraffe is 0.72, the probability that he will see the bears is 0.84, and the probability that he will see both is 0.52.
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probability that a student will pass his examination is 0.73, the probability of the student getting a compartment is 0.13, and the probability that the student will either pass or get a compartment is 0.96.
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probabilities that a typist will make 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 or more mistakes in typing a report are, respectively, 0.12, 0.25, 0.36, 0.14, 0.08, 0.11.
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If A and B are two candidates seeking admission in an engineering college, the probability that A is selected is 0.5, and the probability that both A and B are selected is at most 0.3. Is it possible that the probability of B getting selected is 0.7?
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probability of the occurrence of event A is 0.7 and that of the occurrence of event B is 0.3, but the probability of the occurrence of both is 0.4.
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probability of the intersection of two events A and B is always less than or equal to the probability of A.
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The sum of probabilities of two students getting distinction in their final examinations is 1.2.
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Probability Fill in the blank Type Questions
| 1. The probability that the home team will win an upcoming football game is 0.77, the probability that it will tie the game is 0.08, and the probability that it will lose the game is ___. |
| Sol. |
| 2. If e₁, e₂, e₃, e₄ are the four elementary outcomes in a sample space and P(e₁) = 0.1, P(e₂) = 0.5, P(e₃) = 0.1, then the probability of e₄ is __. |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
The probability that a person visiting a zoo will see the giraffe is 0.72, the probability that he will see the bears is 0.84, and the probability that he will see both is 0.52.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probability that a student will pass his examination is 0.73, the probability of the student getting a compartment is 0.13, and the probability that the student will either pass or get a compartment is 0.96.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If A and B are two events associated with a random experiment such that P(A) = 0.3, P(B) = 0.2, and P(A ∩ B) = 0.1, then the value of P(A ∩ B') is ___.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The probability of happening of event A is 0.5, and that of B is 0.3. If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then the probability of neither A nor B is ____.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} and E = {1, 3, 5}. Then E is ___.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Probability Matching Type Questions
| 1. Match the proposed probability under Column C1 with the appropriate written description under column C2 : C1 C2 Probability Written Description (a) 0.95 (i) An incorrect assignment (b) 0.02 (ii) No chance of happening (c) – 0.3 (iii) As much chance of happening as not. (d) 0.5 (iv) Very likely to happen (e) 0 (v) Very little chance of happening |
| Sol. |
| 2. Match the following (a) If E1 and E2 are the two mutually (i) E1 ∩ E2 = E1 exclusive events (b) If E1 and E2 are the mutually (ii) (E1 – E2) ∪ (E1 ∩ E2) = E1 exclusive and exhaustive events (c) If E1 and E2 have common (iii) E1 ∩ E2 = φ, E1 ∪ E2 = S outcomes, then (d) If E1 and E2 are two events (iv) E1 ∩ E2 = φ such that E1 ⊂ E2 |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
Match the following
(a) If E1 and E2 are the two mutually (i) E1 ∩ E2 = E1 exclusive events
(b) If E1 and E2 are the mutually (ii) (E1 – E2) ∪ (E1 ∩ E2) = E1
exclusive and exhaustive events
(c) If E1 and E2 have common (iii) E1 ∩ E2 = φ, E1 ∪ E2 = S
outcomes, then
(d) If E1 and E2 are two events (iv) E1 ∩ E2 = φ
such that E1 ⊂ E2
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Match the proposed probability under Column C1 with the appropriate written description under column C2 :
C1 C2
Probability Written Description
(a) 0.95 (i) An incorrect assignment
(b) 0.02 (ii) No chance of happening
(c) – 0.3 (iii) As much chance of happening as not.
(d) 0.5 (iv) Very likely to happen
(e) 0 (v) Very little chance of happening
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Sixteen Exam