- Relations and Functions Short Answer Type Questions
- Relations and Functions Long Answer Type Questions
- Relations and Functions Objective Type Questions
- Relations and Functions Fill in the blanks Type Questions
- Relations and Function True or False Type Questions
- JEE Mains 2022
Relations and Functions Short Answer Type Questions
| 1. Let A = {–1, 2, 3} and B = {1, 3}. Determine (i) A × B (ii) B × A (iii) B × B (iv) A × A |
| Sol. |
| 2. If P = {x: x < 3, x ∈ N}, Q = {x: x ≤ 2, x ∈ W}. Find (P ∪ Q) × (P ∩ Q), where W is the set of whole numbers. |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
Let A = {–1, 2, 3} and B = {1, 3}. Determine
(i) A × B
(ii) B × A
(iii) B × B
(iv) A × A
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If P = {x: x < 3, x ∈ N}, Q = {x: x ≤ 2, x ∈ W}. Find (P ∪ Q) × (P ∩ Q), where W is the set of whole numbers.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If A = {x: x ∈ W, x < 2} B = {x: x ∈ N, 1 < x < 5} C = {3, 5} find
(i) A × (B ∩ C)
(ii) A × (B ∪ C)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In each of the following cases, find a and b.
(i) (2a + b, a – b) = (8, 3)
(ii)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, S = {(x, y): x ∈ A, y ∈ A}. Find the ordered pairs which satisfy the conditions given below:
(i) x + y = 5
(ii) x + y < 5
(iii) x + y > 8
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given R = {(x, y): x, y ∈ W, }. Find the domain and Range of R.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If is a relation. Then find the domain and Range of .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If is a relation. Then find .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If is a relation. Then find the domain and range of .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Is the given relation a function? Give reasons for your answer.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If and are real functions defined by and , find each of the following
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let and be real functions defined by and .
(a) For what real numbers ,
(b) For what real numbers ,
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If and are two real valued functions defined as , , then find:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Express the following functions as a set of ordered pairs and determine their range.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the values of for which the functions and are equal.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Suppose that a function f: R → R satisfies f(x + y) = f(x)f(y) for all x, y ∈ R and f(1) = 3. If Σ???? f(i) = 363, then n is equal to
Given f (1) = a = 3, and assuming the function form is f (x) = a?
So f (x) = 3?
∑? f (i) = 363
⇒ 3 + 3² + . + 3? = 363
This is a geometric progression. The sum is S? = a (r? -1)/ (r-1).
3 (3? -1)/ (3-1) = 363
3 (3? -1)/2 = 363
3? - 1 = 242
3? = 243
3? = 3? ⇒ n = 5
The sum of distinct values of λ for which the system of equations
(λ – 1)x + (3λ + 1)y + 2λz = 0
(λ – 1)x + (4λ – 2)y + (λ + 3)z = 0
2x + (3λ + 1)y + 3(λ – 1)z = 0,
has non-zero solutions, is
|λ-1 3λ+1 2λ|
|λ-1 4λ-2 λ+3| = 0
|2 3λ+1 3 (λ-1)|
R? → R? - R? and R? → R? - R? (from a similar matrix setup, applying operations to simplify)
The provided solution uses a slightly different matrix but let's follow the subsequent steps.
A different matrix from the image is used in the calculation:
|λ-1 3λ+1 2λ|
|0 λ-3 -λ+3|
|3-λ 0 λ-3 |
C? → C? + C?
|3λ-1 3λ+1 2λ |
|3-λ λ-3-λ | = 0
|0 λ-3 |
⇒ (λ-3) [ (3λ-1) (λ-3) - (3λ+1) (3-λ)] = 0
⇒ (λ-3) [ (λ-3) (3λ-1) + (λ-3) (3λ+1)] = 0
⇒ (λ-3)² [3λ-1 + 3λ+1] = 0
⇒ (λ-3)² [6λ] = 0 ⇒ λ = 0, 3
Sum of values of λ = 3
1If x? and ? be two non-zero vectors such that |x? + ?| = |x?| and 2x? + λ? is perpendicular to ?, then the value of λ is
|x + y|² = |x|²
(x+y)· (x+y) = x·x
|x|² + 2x·y + |y|² = |x|²
|y|² + 2x·y = 0 (1)
and (2x + λy)·y = 0
2x·y + λ|y|² = 0 (2)
From (1), 2x·y = -|y|².
Substitute into (2):
-|y|² + λ|y|² = 0
(λ-1)|y|² = 0
Assuming y is a non-zero vector, |y|² ≠ 0, therefore λ=1.
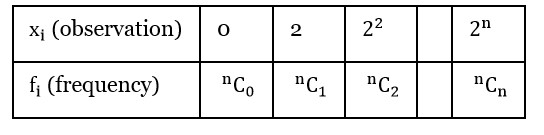
Consider the data on x taking the values 0,2,4,8, ..., 2? with frequencies ?C?, ?C?, ?C?, ..., ?C? respectively. If the mean of this data is 728/2?, then n is equal to
The number of words (with or without meaning) that can be formed from all the letters of the word "LETTER" in which vowels never come together is
The word is 'LETTER'.
Consonants are L, T, R.
Vowels are E, E.
Total number of words (with or without meaning) from the letters of the word 'LETTER' is:
6! / (2! 2!) = 720 / 4 = 180.
Total number of words (with or without meaning) from the letters of the word 'LETTER' if vowels are together:
Treat (EE) as a single unit. We now arrange {L, T, R, (EE)}. This is 5 units.
Number of arrangements = 5! / 2! (for the two T's) = 120 / 2 = 60.
∴ The number of words where vowels are not together = Total words - Words with vowels together
Required = 180 - 60 = 120.
Let cr denote the binomial coefficient of xr in the expansion of (1 + x)10. If for a, b c1 + 3.2C2 + 5.3C3 + ….upto 10 terms = then the value of a + b is equal to………..
S = 29 . 110 – 10.29 = 29 . 100
S = 29 . 100
The number of 3-digit odd numbers, whose sum of digits is a multiple of 7, is……….
= 63
Let q be the angle between the vectors where and . Then is equal to…………
=
=4 × 16 × 9 = 576
Let the abscissae of the two points P and Q be the roots of 2x2 – rx + p = 0 and the ordinates of P and Q be the roots of x2 – sx – q = 0. If the equation of the circle described on PQ as diameter is 2(x2 + y2) – 11x – 14y – 22 = 0, then 2r + s – 2q + is equal to…..
r = 11, s = 7, p – 2q = -22
For a natural number n, let an = 19n – 12n. Then, the value of
Let f : R ® R be a function defined by f(x) If the function g(x) = then the greatest integer less than or equal to g(1) is……..
g (1) =?
3 > 1
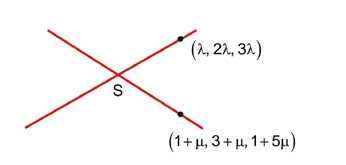
Let the lines
L1 :
L2 :
intersects at the point. S. If a plane ax + by – z + d = 0 passes through S and is parallel to both lines L1 and L2, then the value of a + b + d is equal to…………
7x – 2y – z + d = 0
(2, 4, 6) Þ d = -14 + 8 + 6
d = 0
7x – 2y – z = 0
7 – 2 = 5
Let A be a 3 × 3 matrix having entries from the set {-1, 0, 1}. The number of all such matrices A having sum of all the entries equal to 5, is……….
Total = 414
The greatest integer less than or equal to the sum of first 100 terms of the sequence
Total number of 3-digit numbers whose product is 12 is ______.
Single digit factor of
where ,
Total 15 Ways
Image of point (2, 1, 3) in the plane containing lines r = i + λj, r = i + mk (where, λ, m ∈ R) is (α,β,γ) then (α + β + γ) = ______.
Plane containing both line
Image of point in the plane
If tangent to the curve y = log x at (e², λ) and normal to the parabola y² = 8x at (2, 4) cuts the y axis at the same point on T. Then λ is ______.
Equation of tangent of at at is
It cuts y axis at
Also normal to at is
Cuts y axis at SO ATQ
If 2, a?, a?, a?,....,a??, 5 are in AP and 2, H?, H?, H?,....,H??, 5 are in H.P. then a?H? is ______.
By property
If first and Last term of Andhra Pradesh and HP are equal (of n
If
Let 's' be the set of all integral solutions of (x, y, z) the system of equations
x - 2y - 6z = 0
-2x + 3y + 9z = 0
3x - 5y - 15z = 0
and 10 ≤ x² + y² + z² ≤ 200 then number of element in the set ‘s’ ______.
Clearly all equations can be form where
So for
So (as )
ATQ
Number of three digit numbers that can be formed by digits 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 such that number is divisible by 3. (Repetition of digits allowed) ______.
I = ∫??⁄??⁄? [cos³x(1+cos x) + sin³x(1+sin x)] dx. Then 24I - 18π = ______.
(1 + 2x + 3x² + 4x³ + ....)?² = a? + a?x + a?x² + ...a?x?. Then |a? - a?| = ______.
Number of solutions of the equation cot?¹x = 1 - |x| is ______.
Kindly consider the following Image
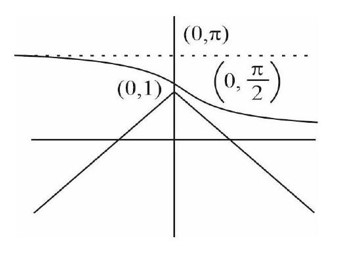
|z - i| = Im(z) represents a conic with foci (α,β) then α + β = ______. a conic with foci (α,β) then α + β = ______.
Foci (0,1)
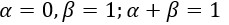
Relations and Functions Long Answer Type Questions
| 1. Is a function? Justify. If this is described by the relation, , then what values should be assigned to and ? |
| Sol. |
| 2. Find the domain of each of the following functions given by (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
Is a function? Justify. If this is described by the relation, , then what values should be assigned to and ?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the domain of each of the following functions given by
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the range of the following functions given by
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(Hint:-
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Redefine the function
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then show that
(i)
(ii)
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let and be two functions defined in the domain .
Find
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Find the domain and range of the function .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then prove that .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Relations and Functions Objective Type Questions
| 1. Let , and . Then the total number of non-empty relations that can be defined from to is: (a) (b) (c) (d) |
| Sol. |
| 2. If , where [.] denotes the greatest integer function, then (a) (b) (c) (d) |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
Domain of ( ) is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let , and . Then the total number of non-empty relations that can be defined from to is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , where [.] denotes the greatest integer function, then
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Range of is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let then
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , where and are integers, and , then and are equal to
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The domain of the function defined by is equal to
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The domain and range of the real function defined by is given by
(a) Domain = , Range = {-1, 1}
(b) Domain = , Range =
(c) Domain = , Range = {-1}
(d) Domain = , Range = {-1, 1}.
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The domain and range of real function defined by is given by
(a) Domain = , Range =
(b) Domain = , Range =
(c) Domain = , Range =
(d) Domain = , Range =
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The domain of the function given by is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The domain and range of the function given by is
(a) Domain = , Range =
(b) Domain = Range =
(c) Domain = Range =
(d) Domain = , Range =
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The domain for which the functions defined by and are equal is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is an Objective Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Relations and Functions Fill in the blanks Type Questions
| 1. Let f and g be two real functions given by then the domain of is given by _________. |
| Sol. |
| 2. Let be two real functions. Then Match the following: (a) (i) (b) (ii) (c) (iii) (d) (iv) |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
Let f and g be two real functions given by then the domain of is given by _________.
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let be two real functions. Then Match the following:
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Relations and Function True or False Type Questions
| 1. The ordered pair belongs to the relation . |
| Sol. |
| 2. If , then . |
| Sol. |
Commonly asked questions
The ordered pair belongs to the relation .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If are two equal ordered pairs, then , .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
If , then , .
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
Let cr denote the binomial coefficient of xr in the expansion of (1 + x)10. If for α, β c1 + 3.2C2 + 5.3C3 + ….upto 10 terms = then the value of a + b is equal to………..
S = 29 . 110 – 10.29 = 29 . 100
S = 29 . 100
The number of 3-digit odd numbers, whose sum of digits is a multiple of 7, is……….
=63
Let θ be the angle between the vectors where and . Then is equal to…………
= 4 × 16 × 9 = 576
Let the abscissae of the two points P and Q be the roots of 2x2 – rx + p = 0 and the ordinates of P and Q be the roots of x2 – sx – q = 0. If the equation of the circle described on PQ as diameter is 2(x2 + y2) – 11x – 14y – 22 = 0, then 2r + s – 2q + is equal to…..
r = 11, s = 7, p – 2q = -22
The number of values of x in the interval for which 14 cosec2x – 2sin2 x = 21 – 4cos2x holds, is………
Kindly consider the following answer
No. of solutions = 4
For a natural number n, let an = 19n – 12n. Then, the value of
Let f : R -> R be a function defined by f(x) If the function g(x) = then the greatest integer less than or equal to g(1) is……..
g(1) = ?
3 > 1
Let the lines
L1 :
L2 :
intersects at the point. S. If a plane ax + by – z + d = 0 passes through S and is parallel to both lines L1 and L2, then the value of a + b + d is equal to…………
7x – 2y – z + d = 0
(2, 4, 6) Þ d = -14 + 8 + 6
d = 0
7x – 2y – z = 0
7 – 2 = 5
Let A be a 3 × 3 matrix having entries from the set {-1, 0, 1}. The number of all such matrices A having sum of all the entries equal to 5, is……….
Total = 414
The greatest integer less than or equal to the sum of first 100 terms of the sequence
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Two Exam