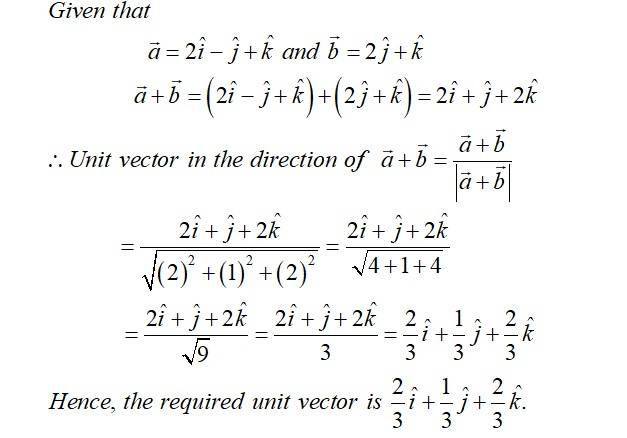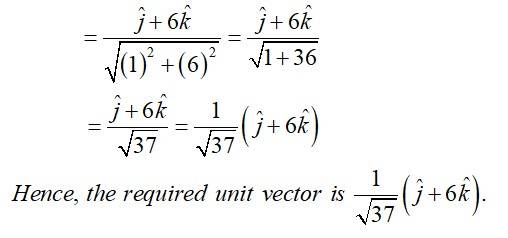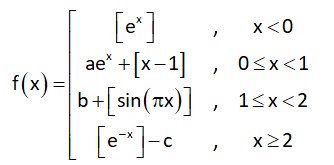- Vector Algebra Short Answer Type Questions
- Vector Algebra Long Answer Type Questions
- Vector Algebra Objective Type Questions
- Vector Algebra Fill in the blanks
- Vector Algebra True or False Type Question
- 28th June 2022 (First Shift)
- JEE Mains 2022
Vector Algebra Short Answer Type Questions
| 1. Find the unit vector in the direction of the sum of vectors = î − 2ĵ + k̂ and = ĵ + 2k̂. |
| Sol:
|
| 2. If â = î + ĵ + 2k̂ and b̂ = î + 2ĵ − 2k̂, find the unit vector in the direction of |
| Sol: |
Commonly asked questions
Find the unit vector in the direction of the sum of vectors = î − 2ĵ + k̂ and = ĵ + 2k̂.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If â = î + ĵ + 2k̂ and b̂ = î + 2ĵ − 2k̂, find the unit vector in the direction of
(i) 6
(ii) 2 − .
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find a unit vector in the direction of , where P and Q have coordinates (5, 0, 8) and (3, 3, 2), respectively.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If and . are the position vectors of A and B, respectively, find the position vector of a point C in BA produced such that BC = 1.5 BA.
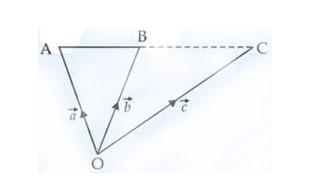
Using vectors, find the value of k such that the points (k, –10, 3), (1, –1, 3), and (3, 5, 3) are collinear.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
A vector . is inclined at equal angles to the three axes. If the magnitude of . is 2 units, find .
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
A vector has magnitude 14 and direction ratios 2, 3, –6. Find the direction cosines and components of r?, given that makes an acute angle with the x-axis.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find a vector of magnitude 6, which is perpendicular to both the vectors 2î − 2ĵ + k̂ and 4î − 3ĵ + k̂.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the angle between the vectors 2î − ĵ + k̂ and 3î + 4ĵ − k̂.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If + + = 0, show that × = × = × . Interpret the result geometrically.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the sine of the angle between the vectors = 3î + 2ĵ + k̂ and = −î + 2ĵ + 4k̂.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If A, B, C, D are the points with position vectors î + ĵ − k̂, 2î − 3ĵ + k̂, 2î − 3k̂, and 3î + 2ĵ − k̂, respectively, find the projection of along
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Using vectors, find the area of the triangle ABC with vertices A(1, 2, 3), B(2, –1, 4), C(4, 5, –1).
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
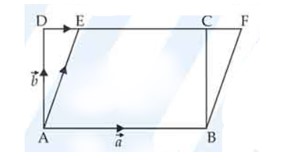
Using vectors, prove that parallelograms on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area.
This is a Short Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Vector Algebra Long Answer Type Questions
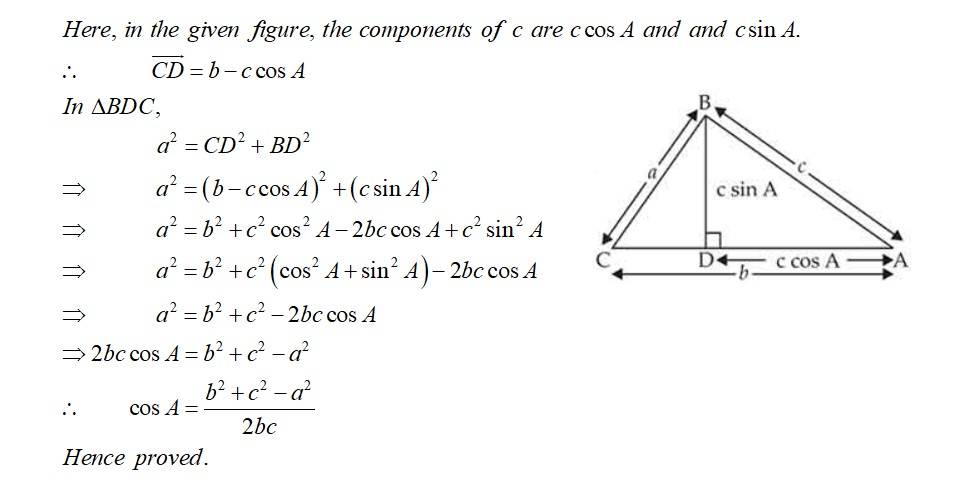
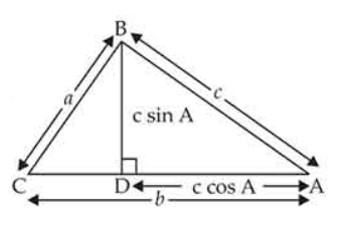
| 1. Prove that in any triangle ABC, where a, b, c are the magnitudes of the sides opposite to the vertices A, B, C, respectively. |
| Sol:
|
| 2. If determine the vertices of a triangle, show that gives the vector area of the triangle. Hence deduce the condition that the three points are collinear. Also, find the unit vector normal to the plane of the triangle. |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Prove that in any triangle ABC, where a, b, c are the magnitudes of the sides opposite to the vertices A, B, C, respectively.
This is a Long Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If determine the vertices of a triangle, show that gives the vector area of the triangle. Hence deduce the condition that the three points are collinear. Also, find the unit vector normal to the plane of the triangle.
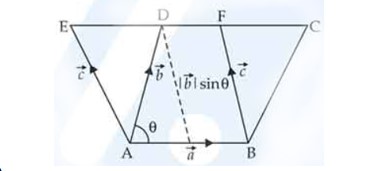
Show that the area of the parallelogram whose diagonals are given by and is Also, find the area of the parallelogram whose diagonals are 2î − ĵ + k̂ and î + 3ĵ − k̂.
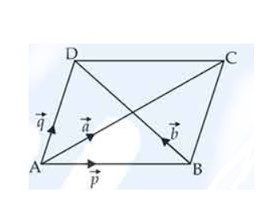
If = î + ĵ + k̂ and b̂ = ĵ − k̂, find a vector such that = and = 3.
This is a Long Answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Vector Algebra Objective Type Questions
| Choose the correct answer from the given four options in each of the Exercises 19 to 33: 1. The vector in the direction of the vector î − 2ĵ + 2k̂ that has magnitude 9 is: (A) î − 2ĵ + 2k̂ (B) (C) 9(î − 2ĵ + 2k̂) (D) (î − 2ĵ + 2k̂)/3 |
| Sol:
|
| 2. The position vector of the point that divides the join of points 2â − 3b̂ and â + b̂ in the ratio 3:1 is: (A) (B) (C) (D) |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options in each of the Exercises 19 to 33:
The vector in the direction of the vector î − 2? + 2k? that has magnitude 9 is:
(A) î − 2ĵ + 2k̂
(B)
(C) 9(î − 2ĵ + 2k̂)
(D) (î − 2ĵ + 2k̂)/3
This is a Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The position vector of the point that divides the join of points 2â − 3b̂ and â + b̂ in the ratio 3:1 is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The vector having initial and terminal points as (2, 5, 0) and (–3, 7, 4), respectively, is
(A) –î + 12ĵ + 4k̂
(B) 5î − 2ĵ − 4k̂
(C) −5î + 2ĵ + 4k̂
(D) î + ĵ + k̂
This is a Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The angle between two vectors , with magnitudes √3 and 4, respectively, and . = 2√3 is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is a Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Find the value of λ such that the vectors = 2î + λĵ + k̂ and = î + 2ĵ + 3k̂ are orthogonal.
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C)
(D) −
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The value of λ for which the vectors 3î − 6? + k? and 2î − 4? + λk? are parallel is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The vectors from the origin to the points A and B are: respectively. Then the area of triangle OAB is:
(A) 340
(B) 25
(C) 229
(D)
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
For any vector , the value of is equal to:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If , , and , then the value of is:
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 14
(D) 16
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The vectors are coplanar if:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If are unit vectors such that then the value of is:
(A) 1
(B) 3
(C)
(D) None of these
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The projection vector of on is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If are three vectors such that and , then the value of is:
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C)
(D) 38
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If and , then the range of is:
(A) [0, 8]
(B) [-12, 8]
(C) [0, 12]
(D) [8, 12]
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The number of unit vectors perpendicular to both is:
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Infinite
This is an Objective type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Vector Algebra Fill in the blanks
| 1. The vector + bisects the angle between the non-collinear vectors and if ________. |
| Sol:
|
| 2. If . = 0, . = 0, . = 0 for some non-zero vector r̂, then the value of ( × ) ĉ is ________. |
| Sol:
|
Commonly asked questions
The vector + bisects the angle between the non-collinear vectors and if ________.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If . = 0, . = 0, . = 0 for some non-zero vector r̂, then the value of
( × ) ĉ is ________.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The vectors = 3î − 2ĵ + 2k̂ and b̂ = î − 2k̂ are the adjacent sides of a parallelogram. The acute angle between its diagonals is ________.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The values of k for which |k <| | and k is parallel to holds true are ________.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The value of the expression + is ________.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If then b is equal to _______.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If a is any non-zero vector, then equals _______.
This is a Fill in the blanks type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
Vector Algebra True or False Type Question
| 1. If | =| , then necessarily it implies = ± |
|
Sol:
|
| 2. The position vector of a point P is a vector whose initial point is the origin. |
| Sol: |
Commonly asked questions
State True or False for the statement in each of the Exercises 41 to 45.
If | =| , then necessarily it implies = ±
This is a True or False type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The position vector of a point P is a vector whose initial point is the origin.
This is a True or False type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If + = - , then the vectors and are orthogonal.
This is a True or False type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
The formula is valid for non-zero vectors and .
This is a True or False type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
If and are adjacent sides of a rhombus, then = 0.
This is a True or False type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sol:
28th June 2022 (First Shift)
28th June 2022 (First Shift)
Commonly asked questions
If the system of linear equations
2x + 3y – z = 2
x + y + z = 4
where has no solution, then
System of equation is
R1 – 2 R2, R3 – R2
System of equation will have no solution for = 7.
Let [t] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then, the value of the integral is equal to
Let f (x) = -8x2 + 6x – 1
f (0) = -1, f (1) = -3
max f (x) =
=
=
Let f : R → R be defined as
where a, b, c R and [t] denotes greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then, which of the following statements is true?
For x < 0 0 < ex < 1 Þ [ex] = 0
= a ex – 1 b + [sin px]
For f to be continuous at x = 0
a – 1 = 0 ⇒ a = 1
Let the solution curve y = y(x) of the differential equation pass through the points (1, 0) and (2α, α), α > 0. Then a is equal to
Integrating
Passes (1, 0)
1 = c
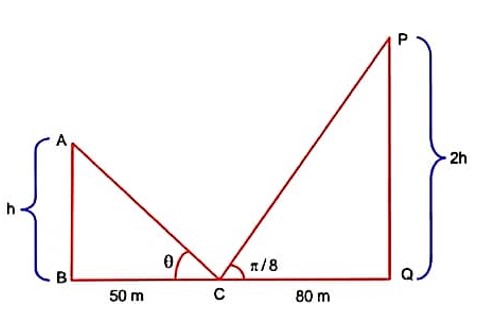
Let AB and PQ be two vertical poles, 160m apart from each other. Let C be the middle points of B and Q, which are feet of these two poles. Let and q be the angles of elevation from C to P and A, respectively. If the height of pole PQ is twice the height of pole AB, then tan2q is equal to
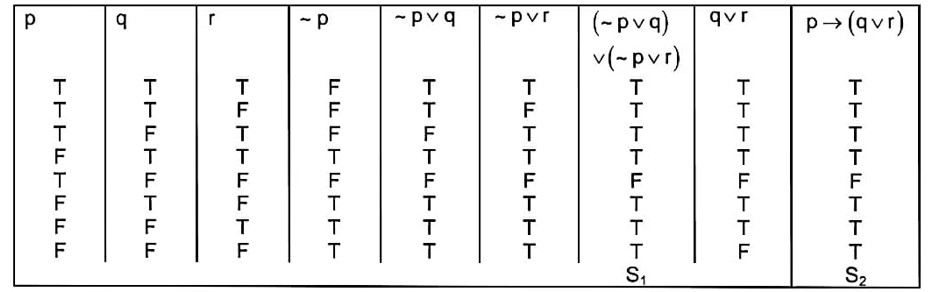
Let p, q, r be three logical statements. Consider the compound statements
Then, which of the following is NOT true?
Consider the following image
Let R1 and R2 be relations on the set {1,2,…., 50} such that
R1 =
R2 =
Then, the number of elements in R1 – R2 is…………
A = {1, 2, 3, ….50}
R1 = (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 4)…. (2, 32)
(3, 1) (3, 3) (3, 9) (3, 27)
(13, 1) (13, 13) etc.
R2 = { (2, 1), (2, 2), (3, 1), (3, 3), (5, 1), (5, 5), (7, 1), (7, 7), (1, 1), (11, 11)…}
contains only 9 elements.
The mean and standard deviation of 15 observations are found to be 8 and 3 respectively. On rechecking it was found that, in the observations, 20 was misread as 5. Then, the correct variance is equal to…………….
S.D = 3
Given 20 has misread as 5
in new case
mean in new case
ariance in new case
If are coplanar vectors and is equal to……….
Solving (i), (ii), (iii)
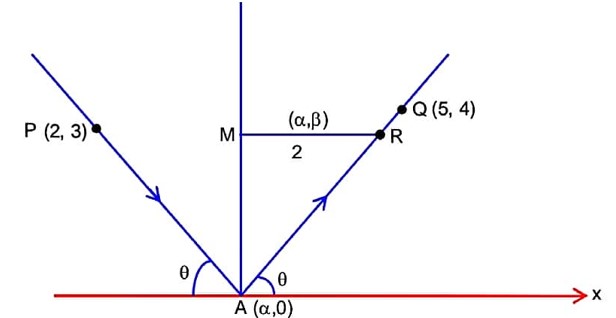
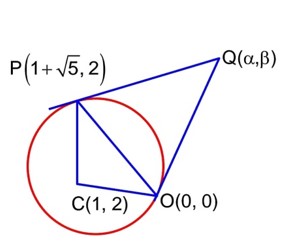
A ray of light passing through the point P(2, 3) reflects on the x-axis at point A and the reflected ray passes through the point Q(5, 4). Let R be the point that divides the line segment AQ internally into the ration 2 : 1. Let the co-ordinates of the foot of the perpendicular M from R on the bisector of the angle PAQ be (a, b). Then the value of 7a + 3b is equal to………..
Let be a line which is normal to the curve y = 2x2 + x + 2 at a point P on the curve. If the point Q(6, 4) lies on the line and O is origin, then the area of the triangle OPQ is equal to
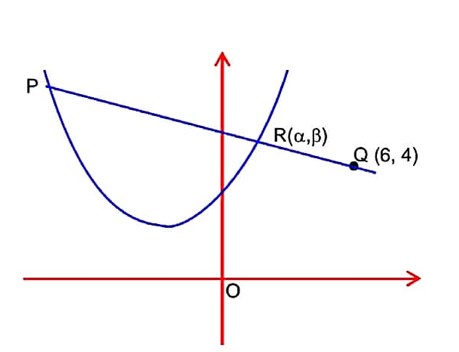
Slope of normal
Equation of PQ y - β =
It passes (6, 4)
Let A = be a set of integers with 1 < a1 < a2 < … < a18 < 77. Let the set A + A = contains exactly 39 elements. Then, the value of a1 + a2 +….. + a18 is equal to
1 < a1 < a2 ……18 < 77
77 = 1 + (20 – 1) . d If n numbers are in A.P.
76 = 19 × d ⇒ d = 4
⇒ a1 = 5
The number of elements in the set is
⇒ 1 < (a – 3)2 + (b + 2)2 < 16
in equivalent to 1 < α2 + β2 < 16
Total 40 such points are possible
Let the lines y + 2x = and be normal to a circle C : If the line is tangent to the circle C, then the value of is equal to
……… (i)
……… (ii)
……… (iii)
Centre of the circle given by solving (i) & (ii)
Again is tangent to the circle.
If 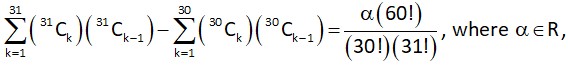
Let a function f : N → N be defined by
then, f is
for n = 2, 4, 6 ……
f (n) = 4, 8, 12, ….4 (n) form
for n = 3, 7, 11, 15, ….
f (n) = 1, 3, 5, 7, …. (4n + 1) or, (4n + 3) from
f is one and onto.
Let A be matrix of order 3 × 3 and det(A) = 2. Then is equal to
|A| = 2
=
The total number of 5-digit numbers, formed by using the digits 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 without repetition, which are multiple of 6, is
Sum of digits
1 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 24
So, either 3 or 6 rejected at a time
Case 1 Last digit is 2
……….2
no. of cases = 2C1 × 4! = 48
Case 2 Last digit is 6
……….6
= 4! = 24
Total cases = 72
Let A1, A2, A3,…. be an increasing geometric progression of positive real numbers. If A1A3A5A7 = and A2 + A4 = then, the value of A6 + A8 + A10 is equal to
Let
Again, A2 + A4 =
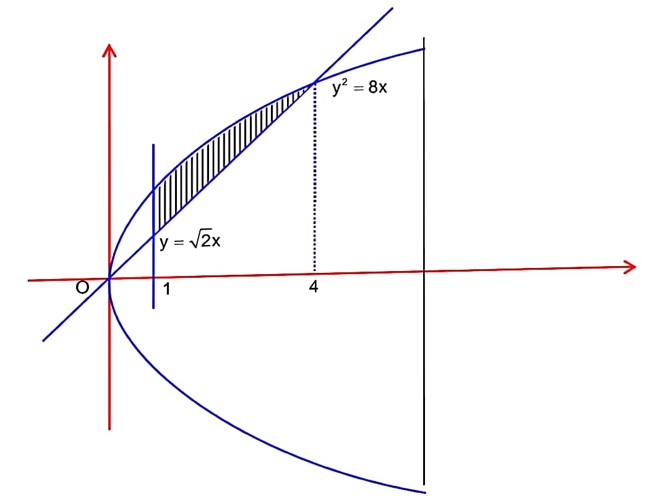
The area of the region S = is
Let y = y(x) be the solution of the differential equation Then y(3) is equal to
Let the eccentricity of the hyperbola and length of its latus rectum be is a tangent to the hyperbola H, then the value of c2 is equal to
Length of latus rectum
y = 2x + c is tangent to hyperbola
If the tangents drawn at the points O(0, 0) and on the circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 4y = 0 intersect at the point Q, then the area of the triangle OPQ is equal to
Equation of OQ is x . 0 + y . 0 – (x + 0) – 2 (y + 0) = 0
⇒ x + 2y = 0 ……… (i)
Equation of PQ is
Solving (i) & (ii),
If two distinct points Q, R lie on the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y – z = 0 and 3x 5y + 2z = 0 and PQ = PR = where the point P is (1, 2, 3), then the area of the triangle PQR is equal to
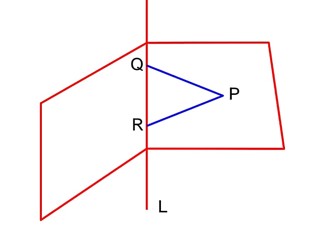
Let vector along L is
=
Area of
The acute angle between the planes P1 and P2, when P1 and P2 are the planes passing through the intersection of the planes 5x + 8y + 13z – 29 = 0 and 8x – 7y + z – 20 = 0 and the points (2, 1, 3) and (0, 1, 2), respectively, is
P1 passing (2, 1, 3)
(10 + 8 + 39 – 29) +
2X – Y + Z – 6 = 0 …..(i)
For P2 passes (0, 1, 2)
Acute angle between the planes
Let the plane contains the line of intersection of two planes and If the plane P passes through the point , then the value of is equal to
Passes
The probability, that in a randomly selected 3-digit number at least two digits are odd, is
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
The number of real solutions of the equation e4x + 4e3x – 58e2x + 4ex + 1 = 0, is……………
The number of positive integers k such that the constant term in the binomial expansion of is an odd integer, is………..
gen term = 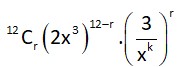
For constant term
36 – 3r – rk = 0
for r = 1, 2, 4
12Cr212-r>28
Possible values of k = 3, 1
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
The sum, of all real values of x for which is equal to…………….
Let S be the set of all passwords which are six to eight characters long, where each character is either an alphabet form or a number from with the repetition of characters allowed. If the number of passwords in S whose at least one character is a number from then is equal to………….
Required number = Total – no character from {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
= 7073
Let and be the vertices of the rhombus PQRS. If the direction ratios of the diagonal RS are a, -1, b where both a and b are integers of minimum absolute values, then α2 + β2 is equal to………..
Let f: [0, 1] R be a twice differentiable function in (0, 1) such that f(0) = 3 and f(1) = 5. If the line y =2x + 3 intersects the graph of f at only two distinct points in (0, 1), then the least number of points at which is…………….
f’’ (x) is zero for atleast
If where a, b are integers, then α + β is equal to………..
Put
Put (1 + t) = u2
dt = 2u du
Let Let a1 be the value of a which satisfies be the value of a which satisfies (A + B)2 = B2. Then is equal to…………….
= 1 = 1
For p, q consider the real valued function f(x) = (x – p)2 – q, and q > 0. Let a1, a2, a3 and a4 be in an arithmetic progression with mean p and positive common difference. If for all I = 1, 2, 3, 4, then the absolute difference between the roots of f(x) = 0 is………….
Roots are
Now,
=> …….(i)
and
From equation (i)
and
For the hyperbola H: x2 – y2 = 1 and the ellipse E : a > b > 0, let the
(1) eccentricity of E be reciprocal of the eccentricity of H, and
(2) the line y = be a common tangent of E and H.
Then 4(a2 + b2) is equal to……………..
Let x1, x2, x3,……..x20 be in geometric progression with x1 = 3 and the common ratio A new data is constructed replacing each xi by (xi – i)2. If is the mean of new data, then the greatest integer less than or equal to is………….
Now,
is equal to………….
, using L.H.L Rule, e0 = 1
Sum of roots = 6, no solution.
Commonly asked questions
The sum, of all real values of x for which is equal to…………….
Let S be the set of all passwords which are six to eight characters long, where each character is either an alphabet form or a number from with the repetition of characters allowed. If the number of passwords in S whose at least one character is a number from then is equal to………….
Required number = Total – no character from {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
= 7073
Let and be the vertices of the rhombus PQRS. If the direction ratios of the diagonal RS are a, -1, b where both a and b are integers of minimum absolute values, then α2 + β2 is equal to………..
Let f: [0, 1] R be a twice differentiable function in (0, 1) such that f(0) = 3 and f(1) = 5. If the line y =2x + 3 intersects the graph of f at only two distinct points in (0, 1), then the least number of points at which is…………….
f’’ (x) is zero for atleast
If where a, b are integers, then α + β is equal to………..
Put
Put (1 + t) = u2
dt = 2u du
Let Let a1 be the value of a which satisfies be the value of a which satisfies (A + B)2 = B2. Then is equal to…………….
= 1 = 1
For p, q consider the real valued function f(x) = (x – p)2 – q, and q > 0. Let a1, a2, a3 and a4 be in an arithmetic progression with mean p and positive common difference. If for all I = 1, 2, 3, 4, then the absolute difference between the roots of f(x) = 0 is………….
Roots are
Now,
=> …….(i)
and
From equation (i)
and
For the hyperbola H: x2 – y2 = 1 and the ellipse E : a > b > 0, let the
(1) eccentricity of E be reciprocal of the eccentricity of H, and
(2) the line y = be a common tangent of E and H.
Then 4(a2 + b2) is equal to……………..
Let x1, x2, x3,……..x20 be in geometric progression with x1 = 3 and the common ratio A new data is constructed replacing each xi by (xi – i)2. If is the mean of new data, then the greatest integer less than or equal to is………….
Now,
is equal to………….
, using L.H.L Rule, e0 = 1
Sum of roots = 6, no solution.
Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Ten Exam