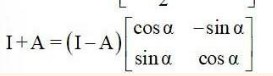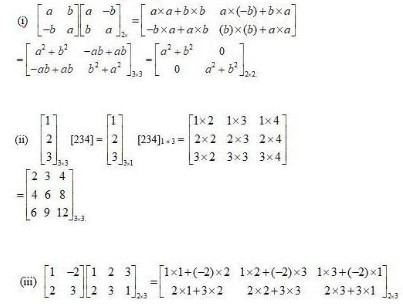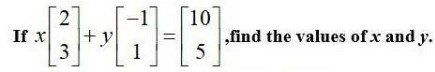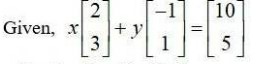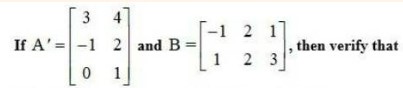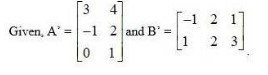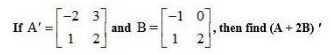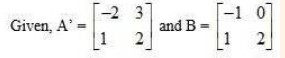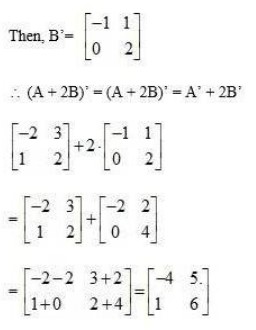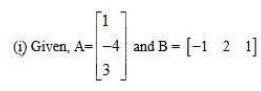Class 12 Math NCERT Solution Matrices is an important chapter, as Matrices are one of the most powerful tools in mathematics. Its knowledge is useful in various branches of mathematics. The concepts are used in the electronic spreadsheet programs for personal computers. It is also used in science and business, like sales projection, budgeting, cost estimation, analysing the results of an experiment, etc.
Matrices Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions are not only used in science but also in economics, genetics, modern psychology, sociology and industrial management. The chapter covers the types, operations and transpose of matrices. The experts at Shiksha have created the NCERT solutions to help students understand the concepts better. It will help them score high in the CBSE Board exam and other entrance tests like JEE Mains.
Explore the NCERT solutions for all chapters of Class 11 and Class 12 Maths, Physics, and Chemistry, and get the key topics and free PDFs.
- Key Concepts of Class 12 NCERT Maths Solutions Matrices at a Glance
- Class 12 Math Matrices Solution PDF: Free Download
- Class 12 Math Chapter 3 Matrices: Key Topics, Weightage
- Class 12 Math Ch 3 Matrices Exercise-wise Solutions
- Class 12 Math Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.1 Solutions
- Important Formulas of Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions Matrices
Key Concepts of Class 12 NCERT Maths Solutions Matrices at a Glance
Here is a quick summary of the main concepts covered in the Matrices Class 12:
- Class 12th Maths NCERT Solutions cover the definition of a matrix. It is an ordered rectangular array of functions or numbers. If a matrix has m rows and n columns, the matrix order is -
- It covers column matrix, row matrix, square matrix, diagonal matrix, scalar, and identity matrix.
- Also, the zero matrix, symmetric matrix, skew-symmetric matrix, and inverse of a square matrix.
Check here for NCERT solutions of all Class 12 Maths chapters with free PDF, important topics. You will also get the weightage information for the chapters.
Class 12 Math Matrices Solution PDF: Free Download
Those who are looking to download the free Matrices Class 12 NCERT PDF can find the link below. The students must download it for their exam preparation. The step-by-step solutions will help them understand the concepts clearly and score high in the exams.
Class 12 Math Chapter 3 Matrices Solution: Free PDF Download
Class 12 Math Chapter 3 Matrices: Key Topics, Weightage
While preparing the Class 12th Maths NCERT Solutions Matrices, students should focus on the core concepts of the matrices, including subtraction, addition, multiplication, and finding the determinant and inverse of matrices. See below the topics covered in Maths Class 12 NCERT Solutions Matrices:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Matrix |
| 3.3 | Types of Matrices |
| 3.4 | Operations on Matrices |
| 3.5 | Transpose of a Matrix |
| 3.6 | Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices |
| 3.7 | Invertible Matrices |
Maths Class 12 Matrices Weightage in JEE Mains
| Exam | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| JEE Main | 1-2 questions | 6-8% |
Related Links
| NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 | NCERT Class 12 Notes | Class 12 Maths Notes |
Class 12 Math Ch 3 Matrices Exercise-wise Solutions
The class 12 Matrices Chapter focuses on several important topics, such as the Type of Matrices, zero, symmetric, and asymmetric Matrices, the Transpose and Inverse of Matrices, and other Matrices operations. Students will encounter different problems based on these concepts in the exercises. Each exercise deals with different concepts, Class 12 Matrices Exercise 3.1 deals with the basics of Matrix, its types and fundamentals. Class 12 Matrices Exercise 3.2 deals with operations of Matrix, its multiplication both scaler and vector and more advanced concepts. Class 12 Matrices Exercise 3.3 deals with problems finding the transpose and inverse of Matrix. Students can check Exercise-wise Class 12 Chapter 3 Matrices NCERT Solutions below;
Class 12 Math Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.1 Solutions
Matrices exercise 3.1 solutions focuses on the basic concepts of matrices. Definition, types of Matrices, and basic operations of matrices are several topics discussed in the solutions of Matrices Class 12 Exercise 3.1. Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.1 includes 10 Questions (7 Short Answers, 3 MCQs). Students can find the solution of exercise 3.1 below;
Matrices Exercise 3.1 Solutions
| Q3.If a matrix has 18 elements, what are the possible orders it can have? What, if it has 5 elements? |
| A.3. As number of elements of matrix with order m × n (E) Possible order of matrix with 18 elements are (1 × 18), (2 × 9), (3 × 6), (6 × 3), (9 × 2) and (18 × 1) Similarly, possible order of matrix with 5 elements are (1 × 5) and (5 × 1) |
| Q4.Construct a 2 × 2 matrix, , whose elements are given by: (ii) (iii) |
| A.4. (E) (i) aij such that i = 1, 2 and j = 1 × 2 for 2 × 2 matrix Therefore a11 = A 2×2 = a12 = a21 a22 = |
Commonly asked questions
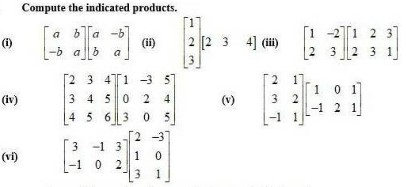
12.Compute the following:
(i) (ii)
(iii) (iv)
(I)
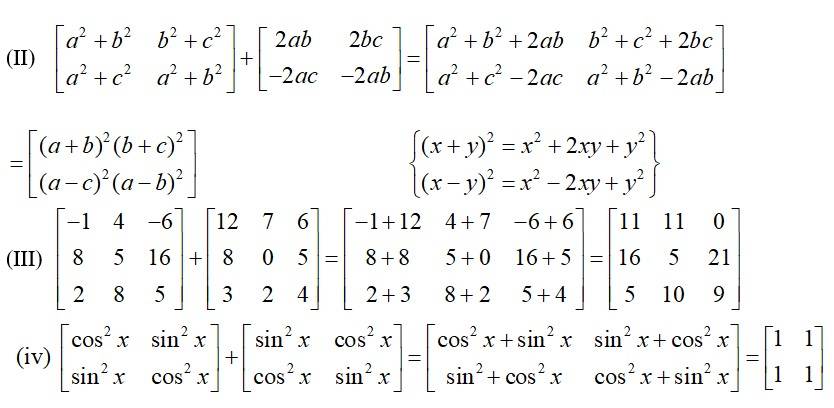
7. Find the value of a, b, c and d from the equation:
(5) Equating the corresponding elements of the matrices we get,
a - b = -1 - (i)
2a + c = 5 - (2)
2a - b = 0 - (3)
3c + d = 13 - (4)
Subtracting eqn (1) from (3) we get,
2a - b (a - b) = 0- (-1)
2a - b - a+ b = 0 + 1 = 1
[a= 1]
Put we get,
2 × 1 + c = 5 c = 5 - 2 [c = 3]
Put (4) we get,
3 × 3 + d = 13 => d = 13 - 9 [d = 4.]
put we get, 1 - b = -1 b = 1 + 1 [b= 2]
17.Find X and Y, if
(i) and
(ii) and
(i) x + y =
x - y =

(ii) 2x + 3y = ___ (1)
2x + 2y = _____ (2)
Multiplying eqn by 2 and
2 × (2x+ 3y) = 2 ×
4x + 6y =
4x + 6y =
3 × (3x+ 2y) = 3 ×
9x + 6y =
Subtracting eqn (iii) from (iv) we get,
4x+ 6y - (4x+ 6y) =
5x =
From eqn (u);
y
11 Let
Find each of the following:
(i) A + B (ii) A – B (iii) 3A – C (iv) AB (v) BA
A B C
(i) A + B =
(ii) A - B =
(iii) 3A - C = 3
=
(iv) AB =
=
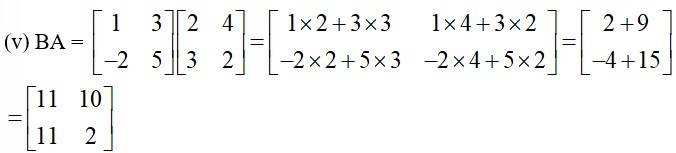
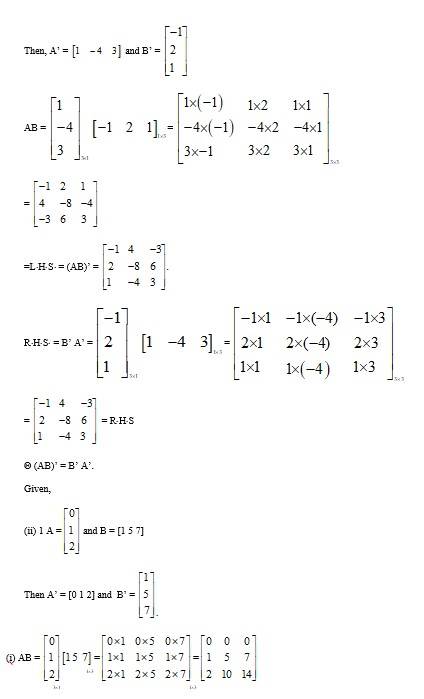
38. If (i) , then verify that A' A = I
(ii) If , then verify that A' A = I
(i) Given, A =
Then, A’ =
∴A’ A =
=
=
=
= A ’ A = 1.
Given,
(ii) 1 A =
Then, A’ =
∴A’ A =
=
=
=
A’ A. = I
6. Find the values of x, y and z from the following equations:
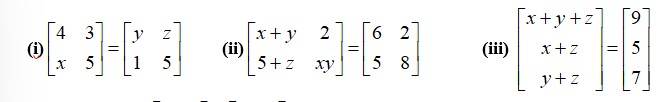
(i)
corresponding
By equating the elements of the matrices, we get,
x= 1
y= 4
z= 3.
(ii)
By equating the corresponding elements of the matrices we get,
x+ y = 6 (I)
5 + Z = 5
xy = 8
x
putting eq in (1) we get
+ y = 6.
8 + y2 = 6y
y2 6y + 8 = 0.
y2 - 4y - 2y + 8 = 0
y (y-4) -2 (y-4) = 0
(y-4) (y-2) = 0
y= 4 0r y = 2.
When y = 4,x= 6-y = 6-4 = and z = 0.
Wheny = 2,x = 6-y = 6-2 = 4 and z = 0.
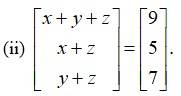
By equating the corresponding elements of the matrices we get,
x+ y + z = 9 -------(i)
x + z = 7 --------(ii)
y + z = 7 -------(iii)
Subtracting eqn (3) from (1) and (2) from (1) we get,
x + y + z -y - z = 9 - 7 and x + y + z - x - z = 9 - 5
x = 2 and y = 4 .
Putting x = 2 in eqn (2)
2 + z = 5
z = 5 - 2 = 3.
So, x = 2,y = 4, z = 3.
5.Construct a 3 × 4 matrix, whose elements are given by:
(i) (ii)
(E) (i) aij = such that i = 1, 2, 3 and j = 1, 2, 3, 4 for 3 × 4 matrix
So, a11= .
a12 =
a14 =
a21 =
a22 =
a23 =

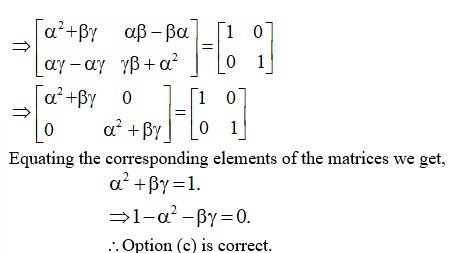
70. If A =[ ], show that A2 – 5A + 7I = 0.
Given A = [ ]
So;
∴ A2 - 5A + 7I =
Hence Showed.
26. If prove that
Given A =
A2 = AA =
A3 = A2A =
So, A3-6A2 + 7A + 2I
(2000 matrix )
Hence proud
9.Which of the given values of x and y make the following pair of matrices equal:
(B) Not possible to find (C) (D)
For the matrices to be equal, the corresponding elements
(B) heed to be equal so,
Fora11, 3x+ 7 = 0
3x = -7.
x =
fora12, 5 = y - 2
y = + 5 + 2 = 7.
For a21, y + 1 = 8
y = 8 - 1 = 7.
fora22, 2 - 3x = 4.
3x = 2 - 4
As the variable x and y has more than one value which is not peacetable.
Option B is correct.
10.The number of all possible matrices of order 3 × 3 with each entry 0 or 1 is:
(A) 27 (B) 18 (C) 81 (D) 512
A 3 × 3 order matrix will have 9 elements
(M) Since, the elements can be either 1 or number of choices for each element is 2 .
The required no. of arrangement = 29 (4,2 × 2 × 2 9 times ) 512
So, option D is correct.
8.A= is a square matrix, if
(A) m n (C) m = n (D) None of these
is a square matrix if m = n
(E) Option C is correct.
30. The bookshop of a particular school has 10 dozen chemistry books, 8 dozen physics books, 10 dozen economics books. Their selling prices are `80, `60 and`40 each respectively. Find the total amount the bookshop will receive from selling all the books using matrix algebra.
Assume X, Y, Z, W and P are matrices of order 2 × n, 3 × k, 2 × p, n × 3 and p × k, respectively. Choose the correct answer in Exercises 31 and 32.
Number of books matrix A =[10 dozen 8 dozen 10 dozen]
= (9600 + 5760 + 4800)
= ' 20160
Order of matrices,
40. For the matrix verify that
(i) (A + A') is a symmetric matrix
(ii) (A – A') is a skew symmetric matrix
Given, A =
Then, A’ =
Let P = A + A’ =
So, P’ = = P
i e, ( A + A’ )’ = A + A’.
Hence, A + A’ is symmetric matrix.
Let Q = A A’ =
So,Q1 = = (1) = (1) Q.
Q1 = Q.
i e, (A A’)’ = -(A - A’).
Have, A - A’ is a show symmetric matrix
Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
29. A trust fund has ? 30,000 that must be invested in two different types of bonds.
The first bond pays 5% interest per year, and the second bond pays 7% interest per year. Using matrix multiplication, determine how to divide ? 30,000 among the two types of bonds. If the trust fund must obtain an annual total interest of:
(a) 1800 (b) 2000
let x be the investment in the first bond out of total `30,000.
(M) then, investment use for the second bond = ` 30,000 - x.
Hence, investment matrix A =
As there is 5% and 7% interest paid the first and second , (per year)
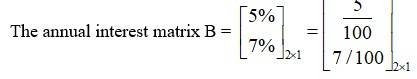
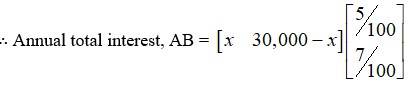
Manual total interest = `
(a) Given, manual total interest = ` 1800.
` 210.000 - `180,000 = 2x
x = ` 15, 000
∴investment in first and second bond is x = 15,000 and ` 30,000 –x = ` 30,000 - `15,000 - ` 15,000 respectively.
(b) Given ,Annual total interest = ` 2000.
` 2,10, 000 - ` 2,00,000
` 2,10, 000 - `2; 000 = 2x
x = ` 5,000
∴investment in first and second hand is x = 5,000 and. 30,000 - x = 30,000 - 5,000 = 25,000 respectively
15.If and then compute 3A – 5B.
3a - 5b = 3 × -
=
76.If the matrix A is both symmetric and skew symmetric, then
(A) A is a diagonal matrix (B) A is a zero matrix
(C) A is a square matrix (D) None of these
Given, A is both symmetric and skew-symmetric.
(E) Then, A' = A ____ (1) and A' = -A ____ (2)
So using (2), A' = -A.
A = -A {eqn (I)}
A + A = 0
2A = 0
A = 0.
A is a zero matrix
So, option B is correct.
23. If F , show that F(x) F(y) = F(x + y).
Given,
So, F (y)
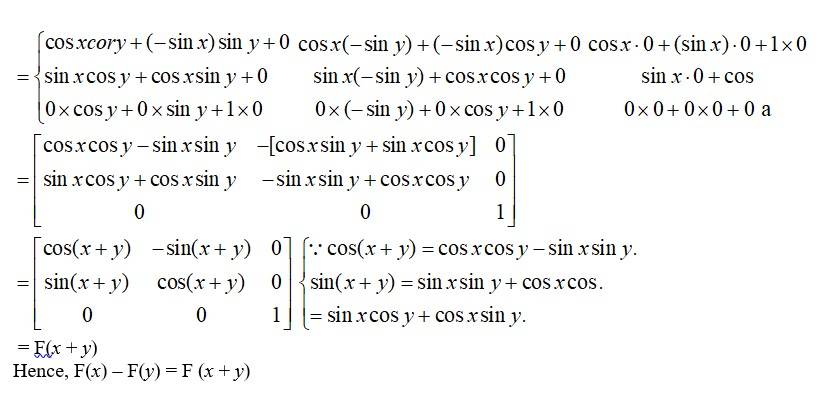
Kindly Consider the following
53.
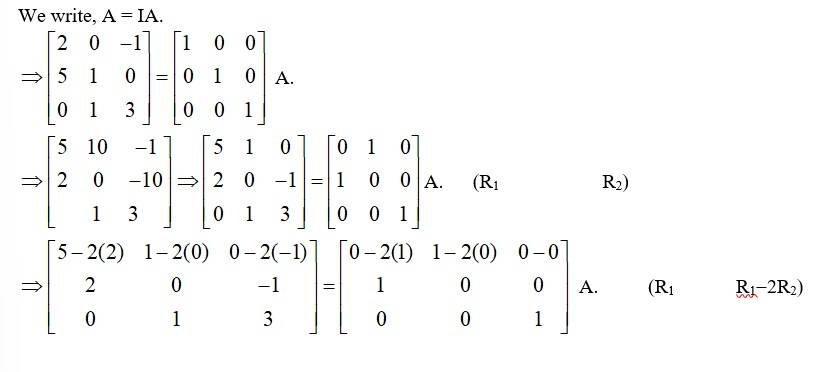
Let A =
We write, A = IA.
= A.
= A.
A.
= A. (R2→R2 - 2R1)
A.
= A.
= A.
∴ A-1 =
14.if and then compute
(A+B) and (B – C). Also, verify that A + (B – C) = (A + B) – C.
A + B =
Now
L.H.S. = a+ (b - c) =
R.H.S. = (a+ b) - c =
= L.H.S.
∴A + (B - C) = (A + B) - C
22. Given , find the values of x, y, z and w.
Given,
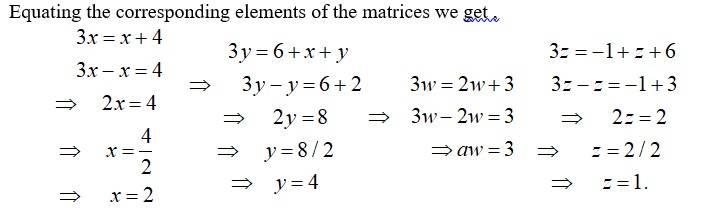
31. The restriction on n, k and p so that PY + WY will be defined are:
(A) k = 3, p = n (B) k is arbitrary, p = 2 (C) p is arbitrary, k = 3 (D) k = 2, p = 3
For, PY + WY to be defined
(E) P should be seen that number of columns of p
Should, be equal to no of nous of yi.e, [x = 3]
n × 3 and (PY) (p × x)
similarity, in W n×3Y 3×xwe see thatno of columns of
W = no of rows in Y and (WY) n × x.
Again, PY + WY is defined if order of (PY) p × k and (WY)n × u are the sameie, P = n
so, option a is correct .
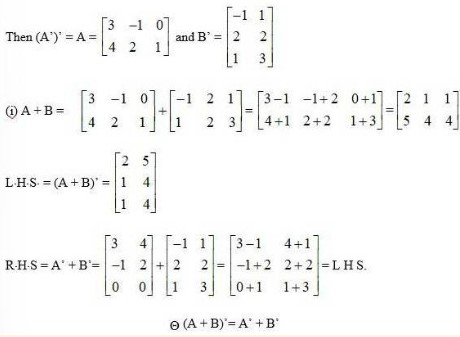
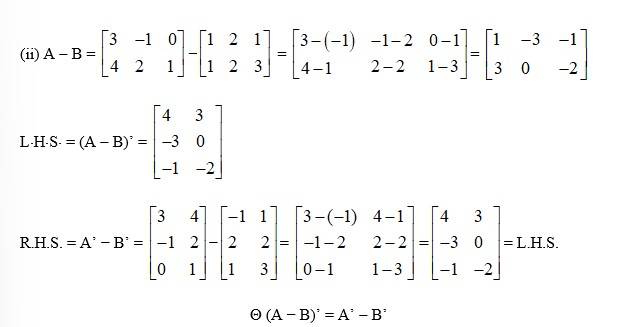
34. If and , then verify that
(i) (A + B)'= A'+ B' (ii) (A – B) '= A'– B'
(i) Given, A = and B =
Then, A’ = and B =
A + B = + = =
LHS. = (A + B)’ =
RHS = A’+ B’ = = = L H S
(A + B)’ = A’+ B’
(ii) A – B =
L.H.S. = (A − B)’ =
R.H.S. = A’ − B’ =
(A − B)’ = A’ − B’
Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
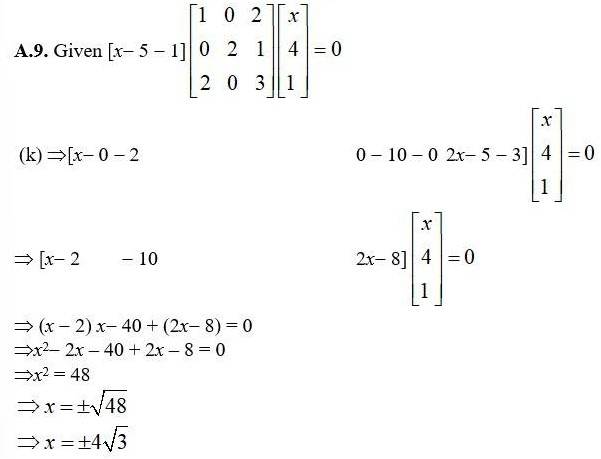
32. If n = p, then the order of the matrix 7X – 5Z is:
(A) p × 2 (B) 2 × n (C) n × 3 (D) p × n
The order of 7x - 5z will be same as order of x and z
as has order 2 × n and z has order 2 × p.and given n = p.
7x - 5z has order 2 × n
∴option b is correct.
13. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
65. If A = , then prove that An = , where n is any positive integer.
We have,
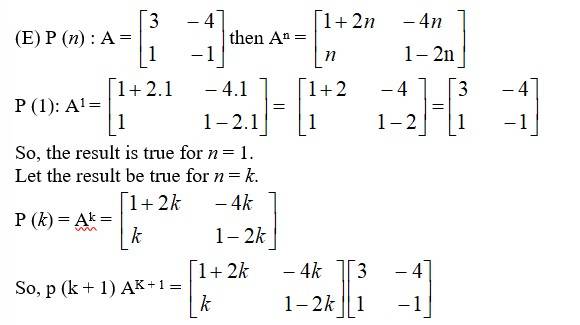
The results also holds for n = k + 1. Hence, An
Holds for all natural number n.
42. Express the following matrices as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric
matrix:
(i) (ii)
(iii) (iv)
(i) Let A =
Then, A’ =
Let P = (A + A’) =
=
Then, P’ = = P.
∴ P = (A + A’) is symmetric matrix
Let Q = (A + A’) =
=
Then Q.’ = = (-1) = (-1) Q.
Q.’ = Q,
∴ Q = (A - A’) is a symmetric matrix
Now, P + Q = (A + A’) + (A - A’)
P + Q = = A.
This A is represented as a sun of symmetric and skew symmetric matrix
Let A =
Then A’ =
Now, A + A’ =
= =
Let P = (A + A’) =
Then, P’ = = P’
∴ P = (A + A’) is asyntri matrix.
A - A’ =
Let Q = (A - A’) =
Q’ = (-1) = -Q.
Q’ = -Q.
∴ Q = (A - A’) is a skew symmetric matrix
Have P + Q = = A.
Then A is represented as a sum of symmetric & skew symmetric matrix
(iii) Let A =
Then, A’ =
Let P = (A + A’) =
=
=
Then P’ = = P.
∴ P = (A + A’ ) is symmetric matrix.
Let Q = (A - A’) =
=
=
Then Q’ = = (-1) = (-1) Q.
Q’ = Q.
∴ Q = (A - A’) is a skew symmetric matrix
∴ P + Q = symmetric
= ..
=
18. Find X, if and
Give, 2x + 4 =
y
39. (i) Show that the matrix is a symmetric matrix.
(ii) Show that the matrix is a skew symmetric matrix.
(i) Given A =
Then, A’ =
∴A’ = A.
Here, A is symmetric matrix
(ii) Given, A =
Then, A’ =
A’ = (1) A.
A’ = A.
Hers A is a show symmetric matrix.
2. If a matrix has 24 elements, what are the possible orders it can have? What, if it has 13 elements?
As, number of elements of matrix having order m * n = m.n.
(b) So, (possible) order of matrix with 24 elements are (1 * 24), (2 * 12), (3 * 8), (4 * 6), (6 * 4), (8 * 3), (12 * 2), 24 * 1).
Similarly, possible order of matrix with 13 elements are (1 * 13) and (13 * 1)
3.If a matrix has 18 elements, what are the possible orders it can have? What, if it has 5 elements?
As number of elements of matrix with order m * n
(E) Possible order of matrix with 18 elements are (1 * 18), (2 * 9), (3 * 6), (6 * 3), (9 * 2) and (18 * 1)
Similarly, possible order of matrix with 5 elements are (1 * 5) and (5 * 1)
Kindly Consider the following
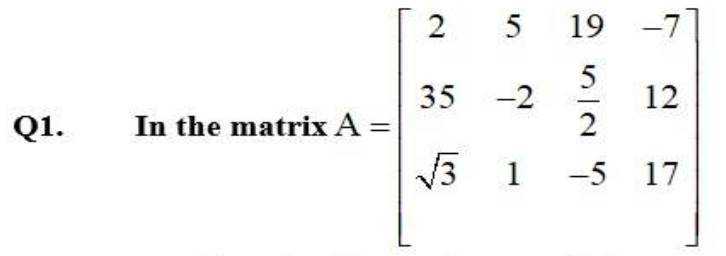
Kindly go through the solution
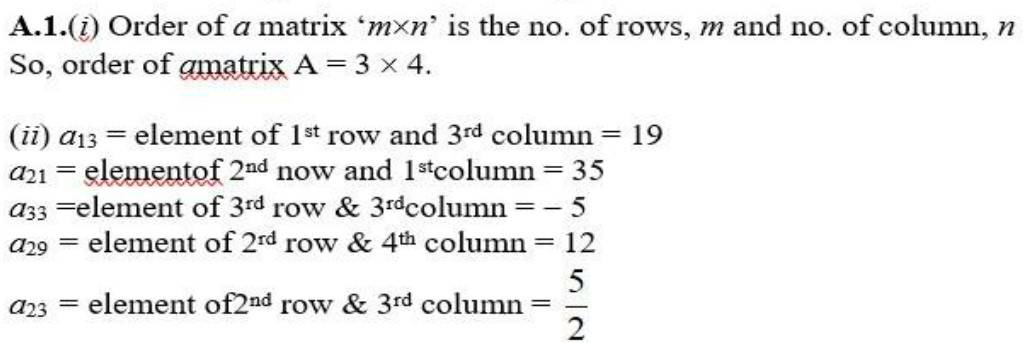
67. Show that the matrix B’AB is symmetric or skew symmetric according as A is symmetric or skew symmetric.
We have,
(E) (B'AB)' = [B' (AB]'
= (AB)' (B')'
= B'A'B.
When A is symmetric, A' = A
(B'AB)' = B'AB
ie, B'AB is symmetric.
And when A is skew-symmetric, A1 = -A
(B'AB)' = -B'AB.
ie, B'AB is skew-symmetric.
Kindly Consider the following
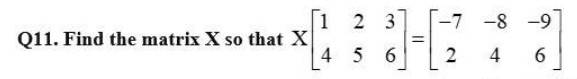
Kindly go through the solution


66. If A and B are symmetric matrices, prove that AB – BA is a skew symmetric matrix.
Given, A and B are symmetric matrices.
(E) Then A' = A and B' = B.
Now, (AB - BA)' = (AB)' - (BA)'
= B'A' - A'B'
= BA - AB
= - (AB - BA).
Hence, AB BA is skew-symmetric matrix
Kindly Consider the following
46.
Let A =
We write, A = IA.
= A.
= A (R1→R1–R2)
= A.
= = A (R2→R2–R1).
A.
∴ A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
55.
Let A =
We write, A = IA.
A.
(R1 R1 - R2)
A.
A. (R2 R2 --------- R1)
A.
A. (R2 -> R1)
A. (R1 R1 + 4R2)
A.
∴A-1 =
43. If A, B are symmetric matrices of same order, then AB – BA is a
(A) Skew symmetric matrix (B) Symmetric matrix
(C) Zero matrix (D) Identity matrix
Given A and B are symmetric matrices,
(E) Then, A’ = A and B’ = B.
Now, (AB - BA)’ = (AB)’- (BA)’
= B’A’ - A’B’.
= BA - AB
(AB - BA)’ = - (AB - BA)
AB - BA is a skew symmetric matrix
∴ Option A is correct.
77. If A is square such that A2 = A, then (I + A)3 – 7A is equal to
(A) A (B) I – A (C) I (D) 3A
Given, A2= A.
(E) we need to calculate,
(I + A)3- 7A = I3 + A3 + 3IA (I + A) - 7A { (x + y)3 = x3 + y3 + 3xy (a + y)}

4.Construct a 2 × 2 matrix, , whose elements are given by:
(ii) (iii)
(E) (i) aij such that i = 1, 2 and j = 1 × 2 for 2 × 2 matrix
Therefore a11 = A 2×2 =
a12 =
a21
a22 =
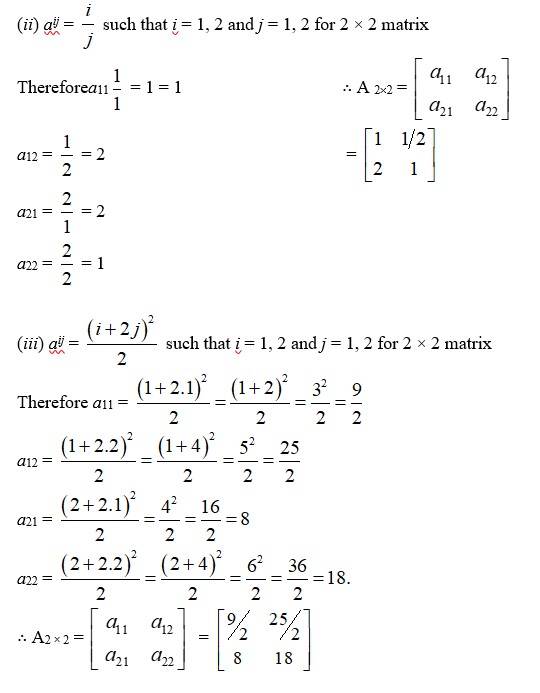
21. Kindly Consider the following
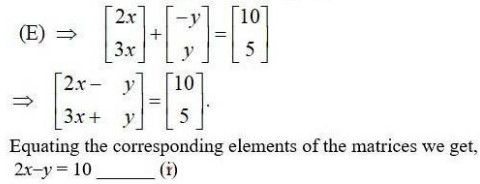
3x + y = 5 _____ (ii)
Adding (i) and (i) we get,
2x - y + 3x + y = 10 + 5.
5x = 15
=> x = 3
5x = 15
=> x = 3
Putting x = 3 in (i) we gel,
2 × 3 - y = 10
6 - 10 = y
y = -4
25. Find – 5A + 6I, if
Given, A =
A2 = AA2 =
=

27. If and , find k so that A
Given,A =
A2 = A. A =
So,A2= xA2I.
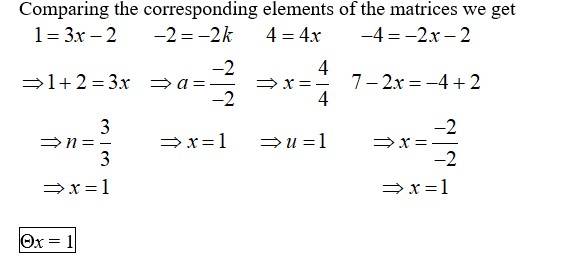
41. Find and , when A=
Given, A =
Then, A’ =
So, A + A’ =
(A + A’) =
And A - A’ =
=
(A - A’) = =
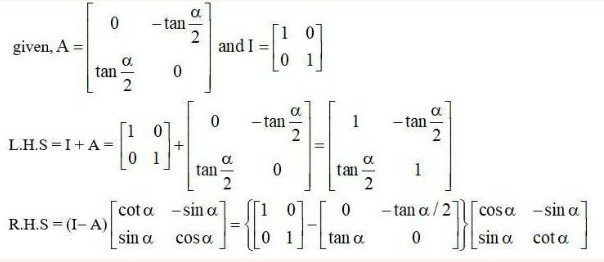
44 .If and A + A'?= I, then the value of is

Given, A = . Then, A’ =
and A + A’ = I.
+ =
=
=
Equating the corresponding element of the matrix we get,
2 cos = 1
cos
= cos - = cos-1
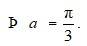
Option B is correct
Kindly Consider the following
45.
Let A=
We write A = IA.
(R2 → R2 –2R1)
∴ A-1 =
62.Matrices A and B will be inverse of each other only if
(A) AB = BA (B) AB = BA = 0
(C) AB = 0, BA = I (D) AB = BA = I
Matrices A and B will be inverse of each other if.
(E) AB = BA = I.
Here option D is correct.
63. Let A = , show that (aI + bA)n = anI + nan – 1 bA, where I is the identity matrix of order 2 and n N.
We shall prove the result by using principal of mathematical induction
we have,
P (n) :- If A = , then (a I + b A)n = an I + nan - 1b A where I is identity matrix of order 2, n∈N
P (1): (a I + b A)1 = a1I + 1 ´a1 - 1b A
= a I + a0bA
= a1I + b A {Qx0 = 1}
So the result is true for n = 1.
Let the result be true for n = k. So,
P (k): (a I + b A)u = auI + u. au-1b A. _____ (1)
Now, we prove that the result holds for n = k + 1,
P (k + 1): (a I + b A)k + 1 = (a I + b A). (a I + b A)k
= (a I + b A) (auI + k au 1b A){using eqn (1)}
= a.akI2 + k. a au - 1b IA + akb.AI + a zzk 1b2k A2
= ak + 1I2 + k au - 1+1b IA + ak b AI + ak - 1b2 k A2 _____ (2)
Now, I2 = = = I
IA = = A
AI = = A.
A2 = A.A = = 0.
Putting these values in eqn (2). We get,
P (k + 1) = ak + 1 I + kab A + ak + 1 - 1b A + 0.
= ak + 1 I + (k + 1) a(k + 1)-1b A.
The result is true for n = k + 1. Thus by principle of mathematical induction
(a I + b A)n = an I + nan -1bA for A =
holds true for all natural number n.
68. Find the values of x, y, z if the matrix A = satisfy the equation A’A = I.
Given, A1Then,
Since, we can write,
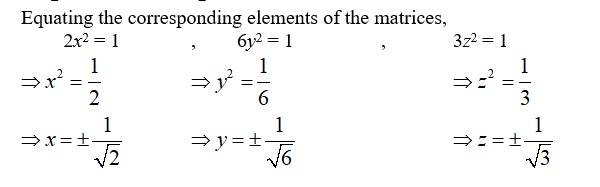
Kindly Consider the following
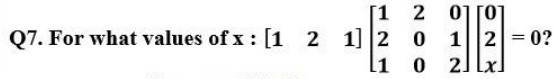
Kindly go through the solution
Kindly Consider the following

Kindly go through the solution

74. If A and B are square matrices of the same order such that AB = BA, then prove by induction that ABn = BnA. Further, prove that (AB)n = AnBn for all n Î N.
We have, AB = BA. (given)
(E) P (n):AB’ = B’A.
P (i):AB1 = B1A. Þ AB = BA
so, the result is true for n = 1.
Let the result be true for n = k.
P (k):ABk = BkA
Then,
P (k + 1) : ABk + 1 = A. Bk. B = BkA.B = Bk.BA
= Bk + 1.A .
So, ABk + 1 = Bk + 1A.
The result also holds for n = k + 1.
Hence, AB^n = B^n A^n holds for all natural number ‘n’.
Kindly Consider the following
47.
Let A =
We write, A = IA.
A.
A (R2→R2–2R1)
= A.
= A(R1→R1–3R2)
= A.
∴A-1 =
64. If A = , prove that An = , n ∈ N.
We have,
(E) P (n) : If A =
]. then An =
P (1) : A1=
So, the result holds true for n = 1.
Let the result be for n = k. So,
P (k): Au=
Then P (k+1): Ak + 1 = Ak. A =
=
= Ak + 1 =
The result holds for n = k + 1. Hence,
An =
16.Simplify
(E)
19. Find x and y, if
Given,
Equating the corresponding elements of the matrices we get,
2 + y = 5
y = 5 - 2 = 3
And 2x + 2 = 8
2x = 8 - 2
x = 3
∅x = 3, y - 3.
20. Solve the equation for x, y, z and t, if
Equating the corresponding elements of the matrices
2x + 3 = 9
2x = 9 - 3
x = 3
2z - 3 = 15
2z = 15 + 3
z = 9
2y = 12
2t + 6 = 18
2t = 18 - 6
2t = 12 => t =
24. Show that
(i)
(ii)
Kindly go through the solution
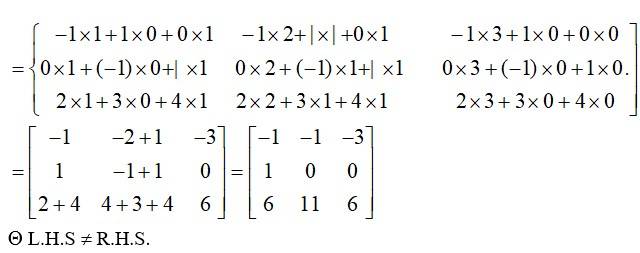
35. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
36. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
37. Kindly Consider the following
(i)
Kindly go through the solution
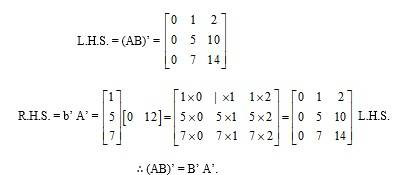
Kindly Consider the following
50.
Let A =
We write, A = IA
∴ A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
60.
Let A =
We write A = IA
∴A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following

Kindly go through the solution
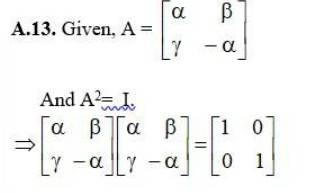
Kindly Consider the following
48.
Let A =
We write, A = 1A.
∴ A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
49.
Let A =
We write, A = IA,
∴A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
51.
Let A =
We write A = IA.
∴ A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
52.
Let A =
We write A = IA
∴ A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
54.
Let A =
We write A = IA.
∴ A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
56.
Let A =
We write A = IA.
As all the elements of 2nd row on the lift side matrix are 2000, A-1 does not exit .
Kindly Consider the following
57.
Let A =
We write A = IA.
∴A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
58.
Let A =
We write, A = IA.
∴A-1 does not exit
Kindly Consider the following
59.
Let A =
We write, A = IA
∴A-1 =
Kindly Consider the following
61.
Let A =
∴ A1 =
Important Formulas of Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions Matrices
Matrices Important Formulae for CBSE and Competitive Exams
Students can check important formulae and basic concepts of the Matrices chapter below for a better understanding of questions. Students can also use these formulae to solve exercises.
Matrix Basics
- Order of a Matrix:
- If a matrix has
m m n n m × n m \times n
- If a matrix has
- Elements:
-
A = [ a i j ] A = [a_{ij}] a i j a_{ij} i th i^{\text{th}} j th j^{\text{th}}
-
Matrix Operations
-
Addition/Subtraction:
( A ± B ) i j = a i j ± b i j (A \pm B)_{ij} = a_{ij} \pm b_{ij} -
Scalar Multiplication:
( k A ) i j = k ⋅ a i j (kA)_{ij} = k \cdot a_{ij} -
Matrix Multiplication:
( A B ) i j = ∑ k = 1 n a i k ⋅ b k j (AB)_{ij} = \sum_{k=1}^n a_{ik} \cdot b_{kj} - Condition: Number of columns in
A A B B
- Condition: Number of columns in
-
Transpose of a Matrix:
( A T ) i j = a j i (A^T)_{ij} = a_{ji}
Properties of Matrix Operations
-
Transpose Properties:
( A T ) T = A (A^T)^T = A ( A + B ) T = A T + B T (A + B)^T = A^T + B^T ( k A ) T = k A T (kA)^T = kA^T ( A B ) T = B T A T (AB)^T = B^T A^T -
Symmetry:
A T = A ( Symmetric ) A^T = A \quad (\text{Symmetric}) A T = − A ( Skew-Symmetric ) A^T = -A \quad (\text{Skew-Symmetric}) -
Identity Matrix Properties:
A I = I A = A AI = IA = A
Determinant and Inverse of Square Matrices
-
Adjoint Formula for Inverse:
A − 1 = Adj ( A ) det ( A ) A^{-1} = \frac{\text{Adj}(A)}{\det(A)} -
Determinant Property:
det ( A T ) = det ( A ) \det(A^T) = \det(A)
Applications of Matrcies
- Solving Linear Equations:
A X = B ⟹ X = A − 1 B AX = B \implies X = A^{-1}B - Consistency of Linear Equations:
- If
det ( A ) ≠ 0 \det(A) \neq 0
- If
Maths Ncert Solutions class 12th Exam