NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Physics Chapter Eight Electromagnetic Waves provides solutions to all the questions of the NCERT Class 12 Physics Exemplar book. It includes various multiple-choice questions, short answer type questions, very short answer type questions, and long answer type questions.
To practice all these questions, students can download NCERT Class 12 Physics Exemplar for Chapter 8 PDF from here. PDF is designed by Shiksha's subject matter experts. It has well-structured content and all the solutions are given in a step-by-step method. Students can understand each step of the solutions, that is, why and when to use any formula and concept while solving a complex problem.
The students should also check NCERT solutions given on the Shiksha's page. They must also refer to the NCERT Solution for Chapter Eight Electromagnetic Waves.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Eight Electromagnetic Waves
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 8 NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Waves – Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Waves – Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Waves – Objective Type Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Long Answers Type Questions
- JEE Main 27th June 2022 (Second Shift)
- JEE Mains 2021
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Eight Electromagnetic Waves
The students can download the Chapter Eight Electromagnetic Waves NCERT Exemplar PDF from here. They can study from this PDF offline without the requirement of an internet connection. The PDF has all types of questions from MCQ, SA, VSA, and LA around all the key concepts of Chapter 8 Class 12 Physics. It offers self-paced learning and exam-oriented preparation. It is given free of cost and is great for concept reinforcement.
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 8 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of the Physics Class 12 Chapter 8:
Speed of Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum
Relationship Between Electric and Magnetic Fields
Average Energy Density
a. Simple Form:
b. Detailed Form:
Intensity of Electromagnetic Wave
Electromagnetic Wave Equation (E field)
Speed of Light in Medium
Poynting Vector (Energy Flux)
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Waves – Short Answer Type Questions
Find below the solutions:
Commonly asked questions
Show that the magnetic field B at a point in between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor during charging is (symbols having usual meaning).
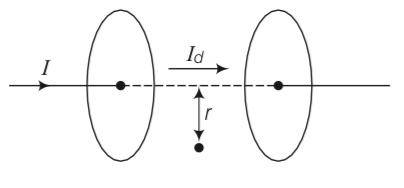
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Magnetic field induction at a point in a region between two plates of a parallel plate capacitor is
B= = = 0
= (E ) = (E)
B= (E)
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
(i) λ1, is used in satellite communication.
(ii) λ2, is used to kill germs in water purifier.
(iii) λ3, is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines.
(iv) λ4, is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
(a) Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
(b) Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
(c) Write one more application of each.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Microwave is used in satellite communications. So, λ1 is the wavelength of microwave.
(ii) Ultraviolet rays are used to kill germs in water purifier. So, λ2 is the wavelength of UV rays.
(iii) X-rays are used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines. So, λ3 wavelength of X-rays.
(iv) Infrared is used to improve visibility on runways during fog and mist conditions. So, it is the wavelength of infrared waves.
(b) Wavelength of X-rays < wavelength of UV < wavelength of infrared < wavelength of microwave.
⇒ λ3 < λ2 < λ4< λ1
(c) (i) Microwave is used in radar.
(ii) UV is used in LASIK eye surgery.
(iii) X-ray is used to detect a fracture in bones.
(iv) Infrared is used in optical communication.
Show that average value of radiant flux density S over a single period T is given by S= .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As we know radiant flux density S= (E )= c2 0(E )
Suppose electromagnetic waves be propagating along x-axis. The electric field vector of
Electromagnetic wave be along y-axis and magnetic field vector be along z-axis. Therefore,
E=E0cos (kx-wt)
B=B0cos (kx-wt)
E B= (E0B0)cos2(kx-wt)
S= c2 (E )
Radiant flux density over a complete cycle is
Sav= c2 0|E0 B0|
= c2 0|E0B0|
= 0E0( )
= 0E02= E02
=
You are given a 2 μF parallel plate capacitor. How would you establish an instantaneous displacement current of 1 mA in the space between its plates?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
q=CV
And we know q=It
Then Iddt= cdV
Id= Cdv/dt
1 = 2 10-6 dV/dt
DV/dt= 500V/s, this will produce the desired result.
Show that the radiation pressure exerted by an EM wave of intensity I on a surface kept in vacuum is I/C.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Pressure = force/area
Force =dp/dt
U=p.C or p= U/c
Pressure =
Pressure = I/C
What happens to the intensity of light from a bulb if the distance from the bulb is doubled? As a laser beam travels across the length of room, its intensity essentially remains constant. What geometrical characteristic of LASER beam is responsible for the constant intensity which is missing in the case of light from the bulb?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the distance is doubled, the area of spherical region ( 4πr2 )
will become four times, so the intensity becomes one fourth the initial value but in case of laser it does not spread, so its intensity remain same.
Geometrical characteristic of LASER beam which is responsible for the constant intensity are as following
(i) Unidirectional
(ii) Monochromatic
(iii) Coherent light
(iv) Highly collimated
These characteristic are missing in the case of light from the bulb.
Even though an electric field E exerts a force qE on a charged particle yet electric field of an EM wave does not contribute to the radiation pressure (but transfers energy). Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since, electric field of an EM wave is an oscillating field and so is the electric force caused by it on a charged particle. This electric force averaged over an integral number of cycles is zero, since its direction changes every half cycle.
Hence, electric field is not responsible for radiation pressure.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Waves – Very Short Answer Type Questions
See below the VSA questions:
Commonly asked questions
Why is the orientation of the portable radio with respect to broadcasting station important?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The orientation of the portable radio with respect to broadcasting station is important because the electromagnetic waves are plane polarised, so the receiving antenna should be parallel to the vibration of the electric or magnetic field of the wave.
Why does microwave oven heats up a food item containing water molecules most efficiently?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Microwave oven heats up the food items containing water molecules most efficiently because the frequency of microwaves matches the resonant frequency of water molecules.
The charge on a parallel plate capacitor varies as q=q0 cos 2πvt. The plates are very large and close together (area = A, separation = d). Neglecting the edge effects, find the displacement current through the capacitor.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Id=Ic= dq/dt
And q=q0 cos 2πvt
By putting this in above equation Id=Ic= q0 sin2πvt 2
A variable frequency AC source is connected to a capacitor. How will the displacement current change with decrease in frequency?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Xc=1/2
And displacement current is inversely proportional to Xc so when capacitive reactance increases then displacement current will decrease.
The magnetic field of a beam emerging from a fitter facing a flood light is given by B0= 12 x 10-8sin (1.2 x 107z- 3.60 x 1015 t) T What is the average intensity of the beam?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Aaverage magnetic energy density Iav= c
From eqn we know that B=12
= = 1.71W/m2
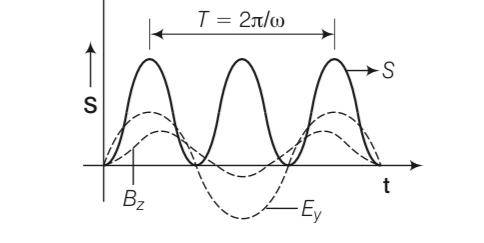
Poynting vectors S is defined as a vector whose magnitude is equal to the wave intensity and whose direction is along the direction of wave propogation. Mathematically, it is given by S= E Show the nature of S versus t graph.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider and electromagnetic waves, let E be varying along y-axis, B is along z-axis and propagation of wave be along x-axis. Then E×B will tell the direction of propagation of
energy flow in electromagnetic wave, along x-axis.
E= E0sin (wt-kx)j
B=B0sin (wt=kx)k
So S will become sin2 (wt-kx)i
And its variation with time is given below
Professor CV Raman surprised his students by suspending freely a tiny light ball in a transparent vacuum chamber by shining a laser beam on it. Which property of EM waves was he exhibiting? Give one more example of this property.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
An electromagnetic wave carries energy and momentum like other waves.
Since, it carries momentum, an electromagnetic wave also exerts pressure called radiation pressure. This property of electromagnetic waves helped professor CV Raman surprised his students by suspending freely a tiny light ball in a transparent vacuum chamber by shining a laser beam on it. The tails of the camets are also due to radiation pressure.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Electromagnetic Waves – Objective Type Questions
Here are the questions:
Commonly asked questions
One requires 11 eV of energy to dissociate a carbon monoxide molecule into carbon and oxygen atoms. The minimum frequency of the appropriate electromagnetic radiation to achieve the dissociation lies in
(a) Visible region
(b) Infrared region
(c) Ultraviolet region
(d) Microwave region
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) E=hv
V= = 2.65 1015hz this belongs to uv region
A linearly polarised electromagnetic wave given as E= E0icos(kz-wt) is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at z=a. assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
(a) Er=Eoi(kz-wt)
(b) Er =Eoicos(kz+wt
(c) Er = -Eoicos(kz+wt)
(d) Er = Eoisin(kz-wt)
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) the electromagnetic wave is
Er = Eoicos (kz-wt)
And reflected wave is given by
Er = -E0 (-i)cos (k (-z)+wt+ )
Light with an energy flux of 20 W/cm2 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 30 cm2, the total momentum delivered (for complete absorption) during 30 min is
(a) 36 x 10-5 kg-m/s
(b) 36 x 10-4 kg-m/s
(c) 108 x 104 kg-m/s
(d) 1.08 x 107 kg-m/s
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) as we know momentum = energy transferred/speed of light
= = 36 10-4kgms-1
Momentum of reflected light =0
So momentum delivered is = 36 10-4kgms-1
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from a 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is
(a) E/2
(b) 2E
(c) E/√2
(d) E
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) E
= =
2= E/
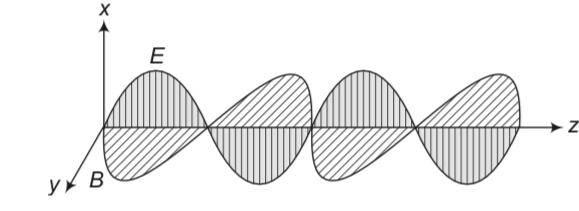
If E and B represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the direction of propagation of electromagnetic wave is along
(a) E
(b) B
(c) B×E
(d) E×B
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) The direction of propagation of electromagnetic wave is perpendicular to both electric field vector E and magnetic field vector B, i.e., in the direction of E×B .
This can be seen by the diagram given below
The ratio of contributions made by the electric field and magnetic field components to the intensity of an EM wave is
(a) C:1
(b) c2:1
(c) 1:1
(d) :1
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) As from the relation that electric and magnetic energy density are equal to one another so there ratio will be always 1:1
An EM wave radiates outwards from a dipole antenna, with E0as the amplitude of its electric field vector. The electric field E0 which transports significant energy from the source falls off as
(a) 1/r3
(b) 1/r2
(c) 1/r
(d) Remains constant
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) From a diode antenna, the electromagnetic waves are radiated outwards.The amplitude of electric field vector Eo which transports significant energy from the source falls off intensity inversely as the distance from the antenna, i.e. 1/r
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction E= (E1iE2j)cos(kz-wt). Choose the correct options from the following
(a) The associated magnetic field is given as B= (E1i-E2j)cos(kz-wt)
(b) The associated magnetic field is given as B= (E1i-E2j)cos(kz-wt)
(c) The given electro magnetic field is circularly polarised
(d) The given electromagnetic wave is plane polarised
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) as the electric and magnetic field in electromagnetic wave are perpendicular to each other also they are perpendicular to wave propagation so they are plane polarised.
An electromagnetic wave travelling along z-axis is given as E=E0cos(kz-wt).choose the correct options from the following
(a) Tha associated magnetic field is given as B=1/ck E=1/w(k )
(b) The electromagnetic field can be written in terms of associated magnetic field as E=c(b )
(c) E=0,k.B=0
(d) K E=0,k
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, c) electromagnetic wave traveling along the z direction is given by
E=E0cos (kz-wt)
The associated magnetic field B in electromagnetic wave is along xaxis along k
B0=E0/c=1/c (k )
E=c (B ) .As the angle is 90 so value is zero.
A plane electromagnetic wave propagating along x-direction can have the following pairs of E and B.
(a) Ex, By
(b) Ey, Bz
(c) Bx,Ey
(d) Ez,By
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, d) As electric and magnetic field vectors E and B are perpendicular to each other as well as Perpendicular to the direction of propagation of electromagnetic wave.
Here in the question electromagnetic wave is propagating along x-direction. So, electric and Magnetic field vectors should have either y-direction or z-direction.
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium position with a frequency of 109 The electromagnetic waves produced
(a) Will have frequency of 109Hz
(b) Will have frequency of 2 x 109 Hz
(c) Will have wavelength of 0.3 m
(d) Fall in the region of radio waves
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, c, d) as we know that = = 0.3m and it is fall in region of radio wave.
The source of electromagnetic waves can be a charge
(a) Moving with a constant velocity
(b) Moving in a circular orbit
(c) At rest
(d) Falling in an electric field
(b, d) Here, in option (b) charge is moving in a circular orbit.
In circular motion, the direction of the motion of charge is changing continuously, thus it is an accelerated motion and this option is correct.
Also, we know that a charge starts accelerating when it falls in an electric field.
An EM wave of intensity I falls on a surface kept in vacuum and exerts radiation pressure p on it. Which of the following are true?
(a) Radiation pressure is I/c if the wave is totally absorbed
(b) Radiation pressure is —I/c if the wave is totally reflected
(c) Radiation pressure is 2I/c if the wave is totally reflected
(d) Radiation pressure is in the range I/c < p < 2I/c for real surfaces
This is a multiple choice answer as classied in NCERT Exemplar
momentum per unit time per unit area = intensity/ speed of wave
= I/c= radiation pressure (p)
Momentum is always double when a light gets reflected back as in that case the momentum which is positive to one side added to momentum which is negative to other side so momentum is always double
So it becomes 2I/c
Electromagnetic Waves Long Answers Type Questions
| 1. An infinitely long thin wire carrying a uniform linear static charge density λ is placed along the z-axis (figure). The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity v = v zk . Calculate the pointing vector S = (E ) |
| 2. Sea water at frequency v = 4×108 Hz has permittivity ε≈80 , permeability µ≈ and resistivity ρ = 0.25 m. Imagine a parallel plate capacitor immersed in sea water and driven by an alternating voltage source V (t)= V0sin(2 ). What fraction of the conduction current density is the displacement current density? |
| Explanation- suppose the distance between the plates is d and applied voltage is Vt= V02 Then electric field is E= sin(2 ) Jc= = = Jd= = = cos(2 ) = J0d cos 2 J0d= = 2 = 2 v 0.25 = 4 v =4/9 |
| 3. A long straight cable of length l is placed symmetrically along z-axis and has radius a(<0 The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current I(t) = Io sin (2πνt) flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance s from the wire inside the cable is E(s,t)= μoIovcos (2πνt) In (s/a)k. (i) Calculate the displacement current density inside the cable. (iI) Integrate the displacement current density across the cross section of the cable to find the total displacement current Id. (iii) Compare the conduction current Io with the displacement current I0d . |
| Explanation- E(s,t)= Now displacement current Jd=eo = = = ina/s sin2 Id= =( )2 = After solving this we get Id= Id= Iod= (
|
| 4. A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z direction is given by E= Eosin(kz-wt)i and B=Bosin(kz-wt)j (i) Evaluate over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in figure (ii) Evaluate over the surface bounded by loop 1234. (iii) Use equation (iv) By using similar process and the equation |
| Explanation-(i) = = Eoh[sin(kz2-wt)-sin(kz1-gwt)] (ii) = (iv) =- =Eoh[sin(kz2-wt)-sin(kz1-wt)] =- Eo=Bow/k=Byc Eo/Bo=c |
Commonly asked questions
An infinitely long thin wire carrying a uniform linear static charge density λ is placed along the z-axis (figure). The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity v = v zk . Calculate the pointing vector S = (E )
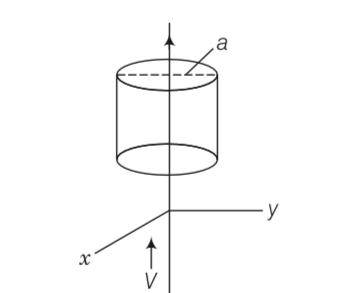
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
E=
And B= i= i
Then S= {E }=
=
Sea water at frequency v = 4×108 Hz has permittivity ε≈80 , permeability µ≈ and resistivity ρ = 0.25 m. Imagine a parallel plate capacitor immersed in sea water and driven by an alternating voltage source V (t)= V0sin(2 ). What fraction of the conduction current density is the displacement current density?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Suppose the distance between the plates is d and applied voltage is Vt= V02
Then electric field is E= sin(2 )
Jc=
=
=
Jd= =
= cos(2 )
= J0d cos 2
J0d=
= 2 = 2 v 0.25 = 4 v =4/9
A long straight cable of length l is placed symmetrically along z-axis and has radius a(<0
The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current I(t) = Io sin (2πνt) flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance s from the wire inside the cable is E(s,t)= μoIovcos (2πνt) In (s/a)k.
(i) Calculate the displacement current density inside the cable.
(ii) Integrate the displacement current density across the cross section of the cable to find the total displacement current Id.
(iii) Compare the conduction current Io with the displacement current I0d .
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
E(s,t)=
Now displacement current Jd=eo
=
=
= ina/s sin2
Id=
=( )2
=
After solving this we get
Id=
Id=
Iod= (
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z direction is given by E= Eosin(kz-wt)i and B=Bosin(kz-wt)j
(i) Evaluate over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in figure
(ii) Evaluate over the surface bounded by loop 1234.
(iii) Use equation
(iv) By using similar process and the equation
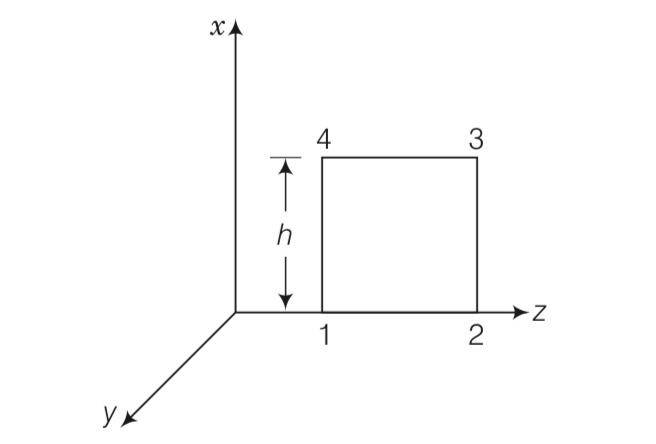
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) =
= Eoh[sin(kz2-wt)-sin(kz1-gwt)]
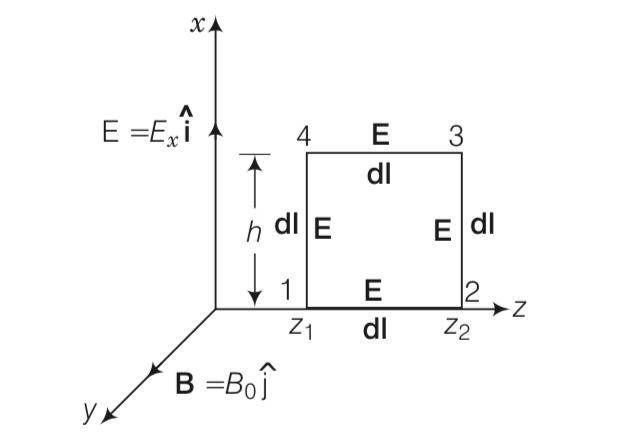
(ii)
=
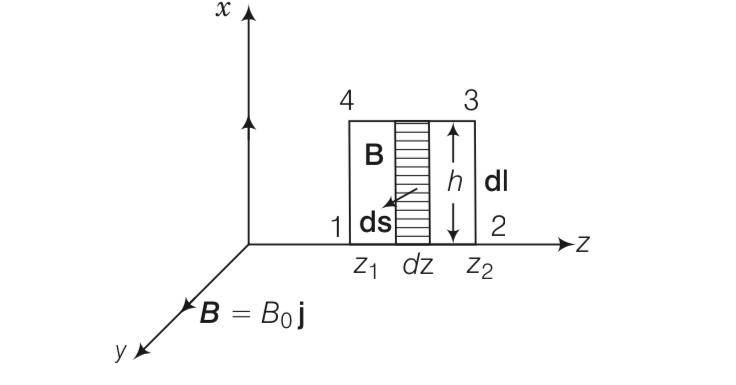
(iv) =-
=Eoh[sin(kz2-wt)-sin(kz1-wt)]
=-
Eo=Bow/k=Byc
Eo/Bo=c
A plane EM wave travelling along z direction is described by E=Eosin(kz-wt)i and B=Bosin(kz-wt)j . show that
(i) The average energy density of the wave is given by Uav=1/4 +1/4Bo2/ o
(ii) The time averaged intensity of the wave is given by Iav=1/2c
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) UE=
UB=
So total energy density = UE+ UB= +
E= Eo/ and B=Bo/
Uav= +
(ii) We know Eo=cBo and c = 1/
= 1/4 2
UE= UB
JEE Main 27th June 2022 (Second Shift)
JEE Main 27th June 2022 (Second Shift)
Commonly asked questions
The SI unit of a physical quantity is pascal-second. The dimensional formula of this quantity will be:
S. I. unit Pascal – second
=
=
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : In hydrogen atom, the frequency of radiation emitted when an electron jumps from lower energy orbit (E1) to higher energy orbit (E2), is given as hf = E1 = E2
Statement II : The jumping of electron from higher energy orbit (E2) to lower energy orbit (E1) is associated with frequency of radiation given as f = (E2 – E1) / h
This condition is Bohr’s frequency condition.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
For statement 1
hf = E1 - E2
Since, E2 > E1
So, it should be
hf = E2 – E1
Therefore statement 1 is wrong
For statement 2
For the jumping of electron from higher energy orbit
(E2) to lower energy orbit (E1)
hf = E2 – E1
Statement (2) is correct
The distance of the Sun from earth is 1.5 × 1011 m and its angular diameter is (2000) s when observed from the earth. The diameter of the Sun will be
1° → 60’
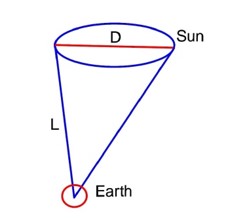
⇒ 60’ → 10°
L = 1.5 × 1011 m
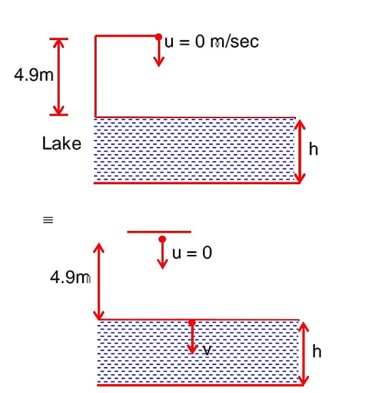
When a ball is dropped into a lake form a height 4.9 m above the water level, it hits the water with a velocity v and then sinks to the bottom with the constant velocity v. It reaches the bottom of the lake 4.0 s after it is dropped. The approximate depth of the lake is
Total time (T) = 4 sec
Given u = 0 m/sec
a = g = 9.8 m/sec2
h = 4.9 m, t =?
t = 1 sec
‘v’ be the velocity with which ball hits the water v = u + at
= 0 + 9.8 × 1 = 9.8 m/sec
Time taken to reach the bottom of the lake from surface of the lake
= 4 – 1 = 3 sec
v = 9.8 m/sec
29.4 + 4.9 × 9 = 29.4 + 44.1
H = 73.5 m
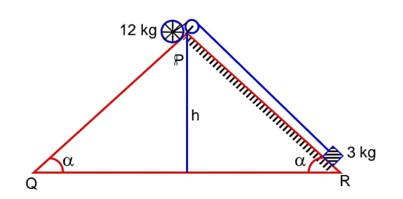
A rolling wheel of 12kg is on an inclined plane at position P and connected to a mass of 3kg through a string of fixed length and pulley as shown in figure.
Consider PR as friction free surface. The velocity of centre of mass of the wheel when it reaches at the bottom Q of the inclined plane PQ will be The value of x is…………
By conservation of Energy
3gh
A diatomic gas does 400 J of work when it is expanded isobarically. The heat given to the gas in the process is……………..J.
Q = 1400 J
A particle executives simple harmonic motion. Its amplitude is 8cm and time period is 6s. The time it will take to travel from its position of maximum displacement to the point corresponding to half of its amplitude, is………… s.
A = 8 cm
T = 6 sec
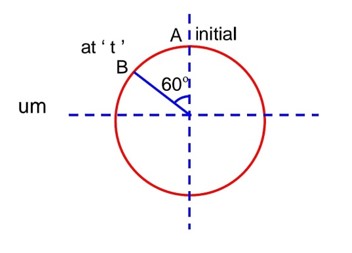
q = 60° from A to B
During reaching the point its maximum amplitude from point (A)
t = 1 sec
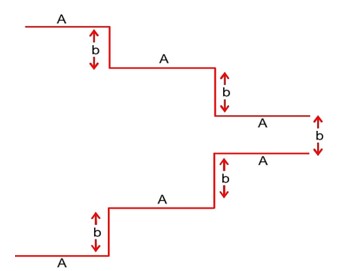
A parallel plate capacitor is made up of stair like structure with a plate area A of each stair and that is connected with a wire of length b, as shown in the figure. The capacitance of the arrangement is the value of x is……………
A deuteron and a proton moving with equal kinetic energy enter into to a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the field. If rd and rp are the radii of their circular paths respectively, then the ratio will be where x is……….
rd = (Radius of deuteron)
A metallic rod of length 20 cm is placed in North-South direction and is moved at a constant speed of 20 m/s towards East. The horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field at that place is 4 × 10-3 T and the angle of dip is 45°. The emf induced in the rod is………….mV.
= 4 × 10-3
emf induced in the rod is =
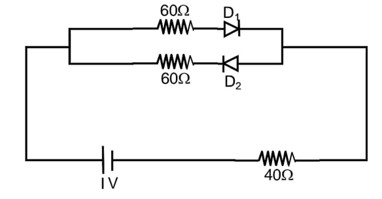
The cut-off voltage of the diodes (shown in figure) in forward bias is 0.6 V. The current through the resister of 40 is………….mA
D1 → forward biased
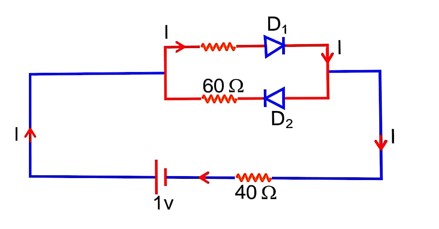
D2 → Reversed biased
So, current will flow through only D1
= 4 × 10-3 A
= 4mA
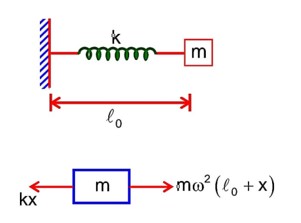
One end of a massless spring of spring constant k and natural length is fixed while the other end is connected to a small object of mass m lying on a frictionless table. The spring remains horizontal on the table. If the object is made to rotate at an angular velocity about an axis passing through fixed end, then the elongation of the spring will be
A stone tide to a string of length L is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string at the centre. At a certain instant of time, the stone is at its lowest position and has a speed u. The magnitude of change in its velocity, as it reaches a position where the string is horizontal, is The value of x is
Conservation of Energy b/w (1) & (2)
x = 2
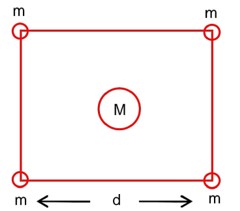
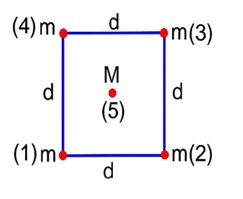
Four spheres each of mass m form a square of side d (as shown in figure). A fifth sphere of mass M is situated at the centre of square. The total gravitational potential energy of the system is
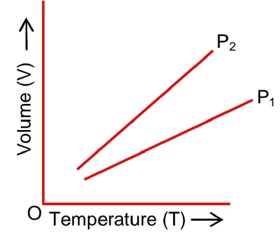
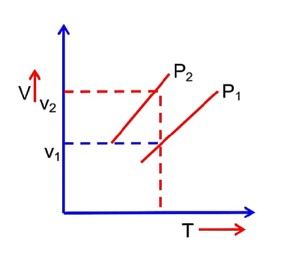
For a perfect gas, two pressures P1 and P2 are shown in figure. The graph shows:
At constant Temp
v2 > v1
⇒ P1 > P2
According to kinetic theory of gases,
A. The motion of the gas molecules freezes at 0°C.
B. The mean free path of gas molecules decreases if the density of molecules is increased.
C. The mean free path of gas molecules increases if temperature is increased keeping pressure constant.
D. Average kinetic energy per molecules per degree of freedom is (for monoatomic gases).
Choose the most appropriate answer form the options given below
(mean free path) =
n → No. of moles in volume v NA ® Avogadro’s Number
The motion of the gas molecules freezes at 0K not 0° C
Average kinetic Energy per molecule per degree of freedom is (for Mono atomic gases)
A lead bullet penetrates into a solid object and melts. Assuming that 40% of its kinetic energy is used to heat it, the initial speed of bullet is:
(Given, initial temperature of the bullet = 127°C,
Melting point of the bullet = 327°C,
Latent heat of fusion of lead = 2.5 × 104 J kg-1,
Specific heat capacity of lead = 125 J/kg K)
40% of K.E. =
v = 5 × 100
v = 500 m/sec
The equation of a particle executing simple harmonic motion is given by x = sin . At t = 1s, the speed of particle will be
(Given : p = 3.14)
Speed = 157 cm/sec
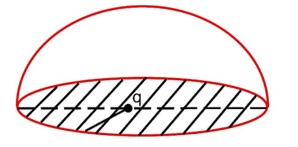
If a charge q is placed at the centre of a closed hemispherical non-conducting surface, the total flux passing through the flat surface would be:
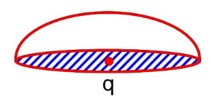
When, ‘q’ is at the centre of the flat surface then,
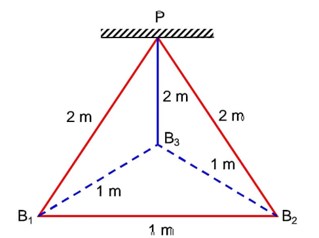
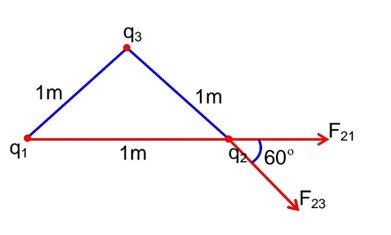
Three identical charged balls each of charge 2 C are suspended from a common point P by silk threads of 2 m each (as shown in figure). They form an equilateral triangle of side 1 m. The ratio of net force on a charged ball to the force between any two charged balls will be
Net force on q2 = FR =
=
=
Force b/w (1) & (2) F21 = 4k – (2)p
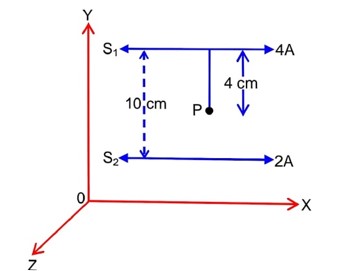
Two long parallel conductors S1 and S2 are separated by a distance 10 cm and carrying currents of 4A and 2A respectively. The conductors are placed along x-axis in X-Y plane. There is a point P located between the conductors (as shown in figure).
A charge particle of 3p coulomb is passing through the point P with velocity m/s; where represents unit vector along x & y axis respectively. The force acting on the charge particle is 4p × 10-5 The value of x is
q = 3πc
=
x = 3
If L, C and R are the self inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively, which of the following does not have the dimension of time?
Dimension
RC → [T]
dimensionless
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : A time varying electric field is a source of changing magnetic field and vice-versa. Thus a disturbance in electric or magnetic field creates EM waves.
Statement II : In a material medium, the EM wave travels with speed v = In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer for the options given below
Statement 1 is true
Speed of EM ware in vaccum is given by,
Speed of EM wave in a material medium
So, statement (2) is false.
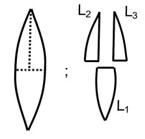
A convex lens has power P. It is cut into two halves along its principal axis. Further one piece (out of the two halves) is cut into two halves perpendicular to the principal axis (as shown in figures). Choose the incorrect option for the reported pieces.
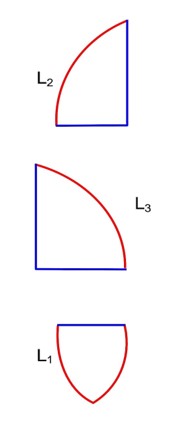
L2
R1 = R
R2 = -R
Power of
Power of
If a wave gets refracted into a denser medium, then which of the following is true?
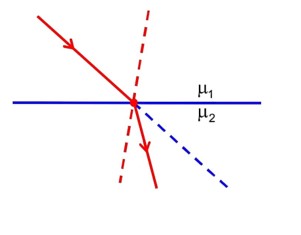
Frequency remains constant while refraction since energy is constant
decreases
wavelength and speed decreases but frequency remains constant
For a transistor to act as a switch, it must be operated in
For Transistor
to act as a switch → Saturation & cut – off state
to act as an amplifier → Active Region
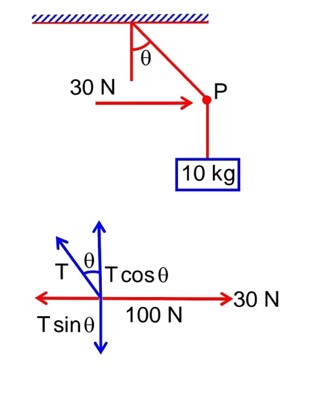
A mass of 10kg is suspended vertically by a rope of length 5m from the roof. A force of 30 N is applied at the middle point of rope in horizontal direction. The angle made by upper half of the rope with vertical is q = tan-1 (x × 10-1). The value of x is……………..
(Given, g = 10 m/s2)
F.B.D. of point ‘P’
- (1)
- (2)
JEE Mains 2021
Commonly asked questions
A parallel plate capacitor whose capacitance C is 14 pF is charged by a battery to a potential difference V = 12V between its plates. The charging battery is now disconnected and a porcelain plate with k = 7 is inserted between the plates, then the plate would oscillate back and forth between the plates with a constant mechanical energy of .......... pJ. (Assume no friction)
Initial charge Q = CV = 14 × 10? ¹² × 12 = 168 × 10? ¹² C
Initial energy U_in = ½ CV² = ½ (14 × 10? ¹²) × 12² = 1008 pJ
When the battery is disconnected and a dielectric (k=7) is inserted, the new capacitance is C' = kC.
The charge Q remains constant.
Final energy U_f = Q²/2C' = Q²/ (2kC) = (CV)²/ (2kC) = CV²/ (2k)
U_f = (14 × 10? ¹² × 12²) / (2 × 7) = 144 pJ
Mechanical energy available for oscillation
The following bodies,
(1) a ring
(2) a disc
(3) a solid cylinder
(4) a solid sphere
of same mass 'm' and radius 'R' are allowed to roll down without slipping simultaneously from the top of the inclined plane. The body which will reach first at the bottom of the inclined plane is ---.
[Mark the body as per their respective numbering given in the question]
The equations for an object rolling down an inclined plane without slipping are:
· Force equation: mg sinθ - f_s = ma
· Torque equation: f_s R = Iα
Since a = αR, we can write f_s = Iα/R = Ia/R².
Substituting this into the force equation:
mg sinθ - Ia/R² = ma
mg sinθ = a (m + I/R²)
a = (mg sinθ) / (m + I/R²)
The time taken to travel a distance S is given by S = ½ at², which means t ∝ 1/√a. Therefore, the object with the largest acceleration (a) will arrive first.
The problem is analyzed for different bodies:
· Ring: I = mR², a = (g sinθ) / (m + mR²/R²) = (g sinθ) / 2 = 0.50 g sinθ
· Disc / Solid Cylinder: I = ½ mR², a = (g sinθ) / (m + ½mR²/R²) = (2g sinθ) / 3 ≈ 0.67 g sinθ
· Solid Sphere: I = (2/5)mR², a = (g sinθ) / (m + (2/5)mR²/R²) = (5g sinθ) / 7 ≈ 0.71 g sinθ
Conclusion: The solid sphere has the greatest acceleration, so it will come down first.
The angular speed of truck wheel is increased from 900 rpm to 2460 rpm in 26 seconds. The number of revolutions by the truck engine during this time is --------. (Assuming the acceleration to be uniform).
The number of revolutions can be found using the rotational kinematic equation for angular displacement (θ):
θ = (ω_initial + ω_final)/2 * t
Number of revolutions = θ / 2π
Number of revolutions = [ (ω_final + ω_initial) * t] / (2 * 2π)
Based on the numerical values provided in the document, the calculation is:
Number of revolution = [ (2π × 3360/60 + 0) × t] / (2 * 2π) . with further calculation yielding the result:
Number of revolution = 728
For VHF signal broadcasting........ km2 of maximum service area will be covered by an antenna tower of height 30m, if the receiving antenna is placed at ground. Let radius of the earth be 6400km. (Round off to the Nearest Integer) (Take π as 3.14)
Kindly consider the following figure
The radius in kilometre to which the radius of earth (R = 6400 km) to be compressed so that the escape velocity is increased 10 times is ................
The formula for escape velocity (v_e) is v_e = √ (2GM/R).
According to the question, the new escape velocity (v_e') from a new radius R' is related to the original escape velocity by 10v_e' = v_e.
10 * √ (2GM/R') = √ (2GM/R)
Squaring both sides:
100 * (2GM/R') = (2GM/R)
100/R' = 1/R
R' = R/100
If R is the radius of Earth (6400 km), then:
R' = 6400 km / 100 = 64 km
If 2.5×10-9 N average force is exerted by a light wave on a non- reflecting surface of 30 cm2 area during 40 minutes of time span, the energy flux of light just before it falls on the surface is ................ W / cm2. (Round off to the Nearest Integer) (Assume complete absorption and normal incidence conditions are there)
The force (F) exerted by radiation is the rate of change of momentum (p).
F = Δp/Δt
For photons, p = E/c. So, F = (1/c) * (ΔE/Δt).
Since Power (P) is ΔE/Δt, F = P/c.
Intensity (I) is Power per unit Area (P/A).
The formula provided in the document is F/A = (nE)/ (Δt c A) which leads to a final calculated value of 25 W/cm².
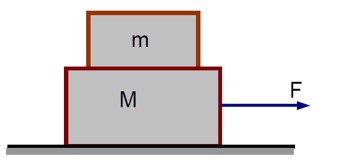
Two blocks (m = 0.5kg and M = 4.5kg) are arranged on a horizontal frictionless table as shown in figure. The coefficient of static friction between the two blocks is 3/7. Then the maximum horizontal force that can be applied on the block so that blocks move together is ---------N. (Round off to the Nearest Integer) [ Take g as 9.8 ms-2]
For the combined system of mass M and m, the acceleration under an applied force F is:
a = F / (M + m)
The static friction force (f_s) on the top block (m) provides its acceleration:
f_s = MA = m * [F / (M + m)] = mF / (M + m)
For the top block not to slip, the required static friction must be less than or equal to the maximum possible static friction (μmg):
f_s ≤ μmg
mF / (M + m) ≤ μmg
F ≤ μ (M + m)g
Using the values implied in the solution:
F ≤ 21 N
The equivalent resistance of series combination of two resistors is 's'. When they are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is 'p'. If s = np, then the minimum value for n is .............. (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
For series combination: s = R? + R?
For parallel combination: p = (R? ) / (R? + R? )
Given the condition s = np:
R? + R? = n * (R? ) / (R? + R? )
(R? + R? )² = nR? R?
R? ² + 2R? R? + R? ² = nR? R?
R? ² - 2R? R? + R? ² + 4R? R? = nR? R?
(R? - R? )² = (n - 4)R?
(R? - R? )² / (R? ) = n - 4
n = 4 + (R? - R? )² / (R? )
Since (R? - R? )² is always non-negative, the minimum value of the term (R? - R? )² / (R? ) is 0. This occurs when R? = R?
Therefore, the minimum value of n is 4.
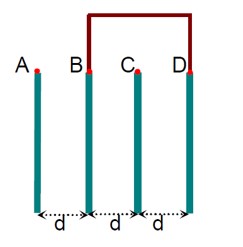
Four identical rectangular plates with length, l = 2cm and breadth, b = 3/2 cm are arranged as shown in figure. The equivalent capacitance between A and C is xε0A/d. The value of x is ----------. (Round off to the nearest integer)
Kindly consider the following figure
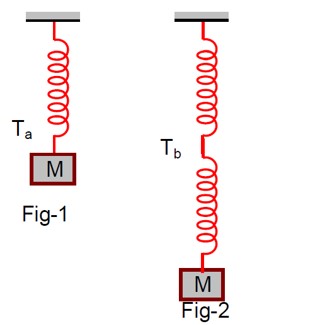
Consider two identical springs each of spring constant k and negligible mass compared to the mass M as shown. Fig. 1 shows one of them and Fig. 2 shows their series combination. The ratios of time period of oscillation of the two SHM is T_b / T_a = √x, where value of x is ................... (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
Kindly consider the following figure
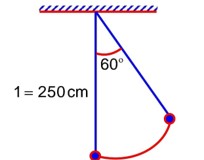
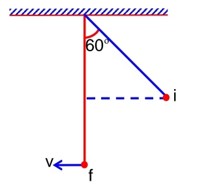
A pendulum is suspended by a string of length 250 cm. The mass of the bob of the pendulum is 200g. The bob is pulled aside until the string is at 60° with vertical as shown in the figure. After releasing the bob, the maximum velocity attained by the bob will be_________ ms-1. (if g = 10m/s2)
From conservation of Energy:
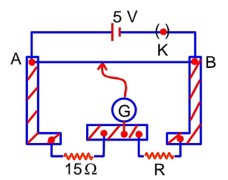
A meter bridge setup is shown in the figure. It is used to determine an unknown resistance R using a given resistor of 15 . The galvanometer (G) shows null deflection when tapping key is at 43cm mark from end A. If the end correction for end A is 2cm. Then the determined value of R will be ________ .
At null point:
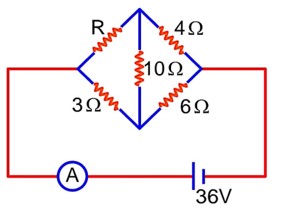
Current measured by the ammeter (A) in the reported circuit when no current flows through resistance, will be A.
Using whetstone
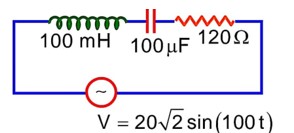
An AC source is connected to an inductance of 100 mH, a capacitance of 100 and a resistance of 120 as shown in figure. The time in which the resistance having a thermal capacity 2 J/°C will get heated by 16°C is________ s.
= 150
The position vector of 1kg object is and its velocity The magnitude of is angular momentum is where x is________.
=
A man of 60kg is running on the road and suddenly jumps into stationary trolly car of mass 120kg. Then, the trolly car starts moving with velocity 2ms-1. The velocity of the running man was _________ ms-1, when he jumps into the car:
Using conservation of momentum:
60 × v = (60 + 120) × 2
⇒v = 6m/s
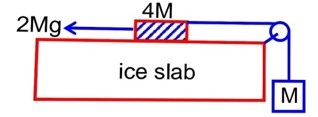
A hanging mass M is connected to a four times bigger mass by using a string-pulley arrangement, as shown in the figure. The bigger mass is placed on a horizontal ice-slab and being pulled by 2 Mg force. In this situation, tension in the string is for x_________. Neglect mass of the string and fiction of the block (bigger mass) with ice slab.
Using newton’s law:
2mg – T = 4ma - (1)
T – mg = ma - (2)
From (1) & (2) :
The total internal energy of two mole mono atomic ideal gas at temperature T = 300K will be __________J. (Given R = 8.31 J/mol.K)
A singly ionized magnesium atom (A = 24) ion is accelerated to kinetic energy 5 ke V, and is projected perpendicularly into a magnetic field B of the magnitude 0.5 T. The radius of path formed will be ________cm.
= 9.975 × 10-2 cm
= 9.975 cm
cm
A telegraph line of length 100km has a capacity of and it carries an alternating current at 0.5 kilo cycle per second. If minimum impedance is required, then the value of the inductance that need to be introduced in series is _________mH.
(if p = )
C = 10-6 f
f = 0.5 × 103 = 500
for minimum impedance :
xL = xC
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eight Exam