Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter contains the solutions to all the questions given in the Exemplar Book Chapter 11. Students must practice these questions to score high in the CBSE Board exams and the entrance exams like NEET and JEE. The solutions are given in a step-by-step method, hence students get a clear understanding of when and why the concept and formula are used. It improves their problem-solving skills. The questions cover all the main topics of Chapter 11, which deepens students' understanding of the key concepts.
Students must download the Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter NCERT PDF from Shiksha's page and read it from anywhere, whenever they want, without the requirement of an internet connection. The PDF has multiple-choice questions, long answer questions, short answer questions, and very short answer questions. The PDF is well-structured and highly reliable. It helps students to prepare for their examinations. The PDF is a great preparation tool available at no cost; students must practice from it to score high in examinations.
The students should also read the NCERT Solutions Chapter Eleven Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter and must also check the NCERT Solutions on Shiksha's page.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Eleven Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Very Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Short Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Eleven Long Answer Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Objective Type Questions
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter Eleven NCERT Exemplar
- Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Physics Exemplar Chapter Eleven
- FAQs Related to Physics Chapter 11 NCERT Exemplar
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Eleven Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Dual Nature Of Matter and Radiation PDF is an excellent practice material. Students can download it from this page and study it without any internet connection. This gives them access to important questions, solved examples, and explanations without the need for internet connectivity. The PDF serves as a comprehensive practice resource. It helps students strengthen their conceptual understanding. Practice all the MCQs, LA, SA, and VSA questions to prepare well for the CBSE Board exam and the entrance exams like NEET and JEE.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Very Short Answer Type Questions
VSA questions are concept-based and require answers generally in one-line or one-word. It evaluates students' understanding of the fundamental ideas on the work function, the nature of light, units and values, and threshold frequency.
See Below VSA
Commonly asked questions
A proton and an a-particle are accelerated, using the same potential difference. How are the de-Broglie wavelengths λp and λαrelated to each other?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
=
So wavelength of proton is times of alpha particle
(i) In the explanation of photoeletric effect, we assume one photon of frequency v collides with an electron and transfers its energy. This leads . to the equation for the maximum energy Emaxof the emitted electron as Emax = hv – ɸ0
where ɸ0 is the work function of the metal. If an electron absorbs 2 photons (each of frequency v), what will be the maximum energy for the emitted electron?
(ii) Why is this fact (two photon absorption) not taken into consideration in our discussion of the stopping potential?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- (i) Here it is given that, an electron absorbs 2 photons each of frequency ν then ν where, v′ is the frequency of emitted electron.
Given, Emax= hv-
Now, maximum energy for emitted electrons is Emax= h2v-
(ii) The probability of absorbing 2 photons by the same electron is very low. Hence, such emission will be negligible
There are materials which absorb photons of shorter wavelength and emit photons of longer wavelength. Can there be stable substances which absorb photons of larger wavelength and emit light of shorter wavelength?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- According to first statement, when the materials which absorb photons of shorter wavelength has the energy of the incident photon on the material is high and the energy ofemitted photon is low when it has a longer wavelength.
But in second statement, the energy of the incident photon is low for the substances which has to absorb photons of larger wavelength and energy of emitted photon is high to emit light of shorter wavelength. This means in this statement material has to supply the energy for the emission of photons.But this is not possible for a stable substances.
Do all the electrons that absorb a photon come out as photo electrons
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- In photoelectric effect, we can observe that most electrons get scattered into the metal by absorbing a photon.Thus, all the electrons that absorb a photon doesn't come out as photoelectron. Only a few come out of metal whose energy becomes greater than the work function of metal.
There are two sources of light, each emitting with a power of 100 W. One emits X-rays of wavelength 1 nm and the other visible light at 500 nm. Find the ratio of number of photons of X-rays to the photons of visible light of the given wavelength.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- p=100W
1= 1nm
2= 500nm
Also n1and n2 represent number of photon of x-rays and visible light emitted from the two sources per sec
E/t=P=n1hc/ 1=n2hc/ 2
So n1/ 1 = n2/ 2
So n1/n2= 1/500
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Short Answer Type Questions
The SA questions require concise explanations or calculations based on de Broglie wavelength and its applications, Einstein’s photoelectric equation, simple numerical problems on kinetic energy of photoelectrons, and photoelectric emission and factors affecting it. These questions are to evaluate the students' conceptual clarity and how they apply formulas to practical situations.
Following Are Short-Answer Type Questions
Commonly asked questions
Consider figure for photoemission. How would you reconcile with momentum conservation ? note light have momentum in a different direction than the emitted electrons.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- during photoelectric emission the momentum is transferred to metal. metal absorbs absorb the photon and its momentum is transferred, and excited electron emitted.
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength 600 nm. The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used. Find the work function in eV.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
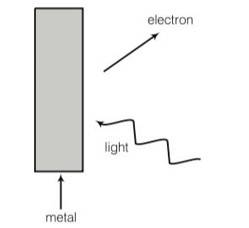
Explanation- During photoelectric emission, the momentum of incident photon is transferred to the metal. At microscopic level, atoms of a metal absorb the photon and its momentum is transferred mainly to the nucleus and electrons.
The excited electron is emitted. Therefore, the conservation of momentum is to be Considered as the momentum of incident photon transferred to the nucleus and electrons.
Assuming an electron is confined to a 1 nm wide region, find the uncertainty in momentum using Heisenberg uncertainty principle (∆x x∆p=h). You can assume the uncertainty in position ∆x as 1 nm. Assuming p = ∆p, find the energy of the electron in electron volts.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-
= kgm/s
E= p2/2m= J= 3.8 eV
Two monochromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then, what inference can you make about their frequencies?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Suppose nA is the number of photons falling per second of beam A and nB is the number of photons falling per second of beam B.
NA=2nB
energy of falling photon A=hvA
B=hvB
as we know intensities are same
nAhvA=nBhvB
va/vb=nB/nA=1/2
vB=2vA
Two particles A and B of de-Broglie wavelengths A, and combine to form a particle C. The process conserves momentum. Find the de-Broglie wavelength of the particle C. (The motion is one-dimensional)
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- from conservation of momentum
Pc=PA+PB
=
=
Case 1 when both momentum are positive
=
Case 2 when both momentum are negative
=
Case 3 when 1 is negative and 2 is positive
=
Case4 when 1 is positive and 2 is negative
=
A neutron beam of energy E scatters from atoms on a surface with a spacing d = 0.1 nm. The first maximum intensity in the reflected beam occurs at θ= 30°. What is the kinetic energy E of the beam in eV?
Explanation- given d= 0.1nm, =300 and n=1
According to bragg's law
2dsin = n
2
P=h/ = = 6.62 kgm/s
k.E= 1/2mv2= = = 0.21eV
Consider a metal exposed to light the wavelength of 600 nm. The maximum energy of electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used.Find the work function in eV?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- k’max= 2kmax
K’max= hc/
2Kmax= hc/
2 (1230/600- )= (1230/400- )
So =1.02eV
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Eleven Long Answer Type Questions
The LA questions require detailed explanations, derivations and problem-solving. The topics may include - a comparative analysis of classical and quantum interpretations of light, applications of de Broglie’s hypothesis in electron diffraction, experimental verification of the photoelectric effect, and derivation of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Here Are LA Questions
| 1. A neutron beam of energy E scatters from atoms on a surface with a spacing d = 0.1 nm. The first maximum intensity in the reflected beam occurs at θ= 30°. What is the kinetic energy E of the beam in eV? |
| Explanation- given d= 0.1nm, =300 and n=1 According to bragg’s law 2dsin = n 2
P=h/ = = 6.62 kgm/s k.E= 1/2mv2= = = 0.21eV
|
| 4. Consider a thin target (10–2m square, 10–3m thickness) of sodium, which produces a photocurrent of 100μA when a light of intensity 100W/m2(λ = 660nm) falls on it. Find the probability that a photoelectron is produced when a photons strikes a sodium atom. [Take density of Na = 0.97 kg/m3] |
| Explanation- A= 10-4m2 So d= 10-3 and i= 100-4A I= 100W/m2
10-4(10-3)=10-7m3
So volume Na atoms=23/0.97m3 Volume occupied by one Na atom= Number of Na atoms in target So energy falling per sec= So n= = N=P I = 100 A I=Ne= ( A) P= 7.48 it is less than 1. |
| 5. Consider an electron in front of metallic surface of a distance d. Assume the force of attraction by the plate is given as . Calculate work in taking the to an infinite distance from the plate .Taking d=0.1 nm. find the work done in electron volts? |
| Explanation- Fx= W= = = = J= 3.6eV |
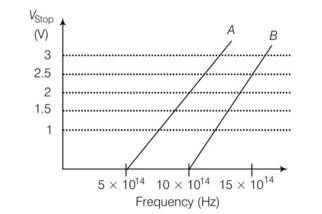
| 6. A student performs an experiment on photoelectric effect, using two materials A and B. A plot of Vstopversus v is given in figure. Which has higher work function?
|
| Explanation -Given threshold frequency of A is given by v0A= 5 hz VOB= 10 1014hz
< for metal A slope=h/e= = 6.4 js slope=h/e= = 8 js
|
| 7. A particle A with a mass mA is moving with a velocity v and hits a particle B (mass mB) at rest (one dimensional motion). Find the change in the de-Broglie wavelength of the particle A. Treat the collision as elastic. |
| Explanation- according to law of conservation of momentum S0 mAv+mb0=mAv1+mBv2 So mA(v-v1)= mBv2 according to law of conservation of kinetic energy 1/2mAv2=1/2mAv12+1/2mBv22 So mA(v2-v12)= mBv22 From above eqn we can say that v+v1=v2 or v=v2-v1 So v1= v and v2= v initial=h/mAv final=h/mAv1= = final- initial=
|
| 8. Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å. (iii) How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)? |
| Explanation-number of photon emitted per second n=
(ii) E=hc = this enegy is greater than 2 so emission is possible (iii) work function = = = = (iv) N= = =2 (v) as the time of emission is 11.04s so photoelectric is not spontaneous. |
Commonly asked questions
A neutron beam of energy E scatters from atoms on a surface with a spacing d = 0.1 nm. The first maximum intensity in the reflected beam occurs at θ= 30°. What is the kinetic energy E of the beam in eV?
Explanation- given d= 0.1nm, =300 and n=1
According to bragg's law
2dsin = n
2
P=h/ = = 6.62 kgm/s
k.E= 1/2mv2= = = 0.21eV
Consider a thin target (10–2m square, 10–3m thickness) of sodium, which produces a photocurrent of 100μA when a light of intensity 100W/m2(λ = 660nm) falls on it. Find the probability that a photoelectron is produced when a photons strikes a sodium atom. [Take density of Na = 0.97 kg/m3]
Explanation- A= 10-4m2
So d= 10-3 and i= 100-4A
I= 100W/m2
10-4(10-3)=10-7m3
So volume Na atoms=23/0.97m3
Volume occupied by one Na atom=
Number of Na atoms in target
So energy falling per sec=
So n= =
N=P
I = 100 A
I=Ne= ( A)
P= 7.48 it is less than 1.
Consider an electron in front of metallic surface of a distance d. Assume the force of attraction by the plate is given as . Calculate work in taking the to an infinite distance from the plate .Taking d=0.1 nm. find the work done in electron volts?
Explanation- Fx=
W= =
=
= J= 3.6eV
A student performs an experiment on photoelectric effect, using two materials A and B. A plot of Vstopversus v is given in figure. Which has higher work function?
Explanation -Given threshold frequency of A is given by v0A= 5 hz
VOB= 10 1014hz
<
for metal A slope=h/e=
= 6.4 js
slope=h/e= = 8 js
A particle A with a mass mA is moving with a velocity v and hits a particle B (mass mB) at rest (one dimensional motion). Find the change in the de-Broglie wavelength of the particle A. Treat the collision as elastic.
Explanation- according to law of conservation of momentum
S0 mAv+mb0=mAv1+mBv2
So mA(v-v1)= mBv2
according to law of conservation of kinetic energy
1/2mAv2=1/2mAv12+1/2mBv22
So mA(v2-v12)= mBv22
From above eqn we can say that v+v1=v2 or v=v2-v1
So v1= v and v2= v
initial=h/mAv
final=h/mAv1=
= final- initial=
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
(i) Estimate number of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
(ii) Will there be photoelectric emission?
(iii) How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
(iv) How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
(v) Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
Explanation-number of photon emitted per second n=
(ii) E=hc = this enegy is greater than 2 so emission is possible
(iii) work function = =
= =
(iv) N=
= =2
(v) as the time of emission is 11.04s so photoelectric is not spontaneous.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Objective Type Questions
These include multiple choice and assertion-reason type questions aimed at identifying the correct interpretations of experimental results, testing quick reasoning and application of formulas, and distinguishing between related physical quantities such as frequency vs threshold frequency.
Following Are MCQs Of Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
| 1. A particle is dropped from a height H. The de-Broglie wavelength of the particle as a function of height is proportional to (a) H (b) H1/2 (c) H0 (d) H-1/2 |
| Explanation- velocity of a freely falling body is v= And -1 |
| 2. The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly a) 1.2 nm (b) 1.2 x 10-3 nm (c) 1.2 x 10-6 nm (d). 1.2 x 10 nm |
| Answer –(b) Explanation- E=hc/ And l = hc/E= 1240/106= 1.24 10-3nm |
| 3. Consider a beam of electrons (each electron with energy E0) incident on a metal surface kept in an evacuated chamber. Then, |
| answer-(d) explanation- When a beam of electrons of energy E0 is incident on a metal surface kept in an evacuated chamber electrons can be emitted with maximum energy E0 (due to elastic collision) and with any energy less than E0, when part of incident energy of electron is used in liberating the electrons from the surface of metal. |
| 4. Consider the figure given below. Suppose the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that (a) will be larger than the earlier value |
| Answer-(c) Explanation- In Davisson-Germer experiment, the de-Broglie wavelength associated with electron is λ = 12.27/Å ...(i)where V is the applied voltage. If there is a maxima of the diffracted electrons at an angle θ, then 2dsinθ = λ …(ii) From Eq.(i),we note that if V is inversely proportional to the wavelength λ. i.e., V will increase with the decrease in the λ. From Eq.(ii),we note that wavelength λ is directly proportional to sinθ and hence θ. So, with the decrease in λ, θ will also decrease. Thus, when the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the Maximum at a value of θ that will be less than the earlier value. |
| 5. A proton, a neutron, an electron and an a-particle have same energy. Then, their de-Broglie wavelengths compare as (a) λp= λn > λe > λα (b) λα < λp = λn > λe |
| answer-(b) Explanation-as we know that so inversely proportional to so from the above conclusion we can say that alpha p n e |
| 6. An electron is moving with an initial velocity v = v0i and is in a magnetic field B = B0 Then, its de-Broglie wavelength |
| Answer-(a) Explanation- v=v0i and B =B0j Force on moving electron F= e(v ) = e(v0i )=-eV0B0k |
| 7. An electron mass m with an initial velocity v=voi is in an electric field E=-Eoi. its debroglie wavelength at time t is given by (a) (b) (c) (d) |
| Answer- a Explanation- Force F= -eE=-e[Eoi]=eEoi So a=f/m=eEoi/m V=Voi+ eEoit/m h/ m Voi+ eEoit/m |
| 8. An electron mass m with initial velocity v=v0i is an electric field E=Eo if its debroglie wavelength at time t is given by (a) (b) (c) (d) |
| Answer- c Explanation- Force F= -eE=-e[Eoi]=eEoi So a=f/m=eEoi/m Velocity at xaxis=Voi Velocity at yaxis= eEotj/m Net velocity v=
|
| 9. Relativistic corrections become necessary when the expression for the kinetic energy 1/2 mv2, becomes comparable with mc2. where m is the mass of the |
| Answer-(c,d) Explanation- V= h/m V1=
V1=
V1=
V1= |
| 10. Two particles A1and A2 of masses m1 , m2 ( m1> m2) have the same de-Broglie (b) their energies are the same Answer-(a,c) |
| Explanation- as debroglie wavelength is P=h/ P1/p2= If wavelength are equal then ratio is 1:1 so P1=P2 E= 1/2mv2= p2/2m E inversely proportional to m So = <1 E1
|
| 11. De-Broglie wavelength associated with uncharged particles: For Neutron efe-Broglie wavelength is given as ve=c/100.Then (a) = 10-4 (b) = 10-2 (c) (d) Answer- (b,c) |
| Explanation- = Ee=1/2meve2 Meve=
Ee= h2/2 e2me For photon Ep= hc/ = hc/2 = 100
Pe=meve= me
|
| 12. Photons absorbed in a matter are converted to heat. A source emitting v photon/sec of frequency v is used to convert 1 kg of ice at 0°C to water at 0°C. Then, the time T taken for the conversion (a) decreases with increasing n. with v fixed Answer-(a,b,c) |
| Explanation- energy spent to convert into water = mass latent heat = mL= 1000g 80cal/g = 80000cal Energy of phtons used= nT E=nT So nTh =mL T= mL/nhv T 1/n where v is constant T when n is fixed T 1/nv |
| 13. A particle moves in a closed orbit around the origin, due to a force which is directed towards the origin. The de-BrOglie wavelength of the particle varies cyclically between two values λ1, λ2 with λ1> λ2 Which of the following statements are true? (a) The particle could be moving in a circular orbit with origin as centre (b) The particle could be moving in an elliptic orbit with origin as its focus (c) When the de-Broglie wavetength is λ1the particle is nearer the origin than when its value is λ2 Answer-(b,d) |
| Explanation- the debroglie wavelength of the particle can be varying cyclically between two values and , if particle is moving in an elliptical orbit with origin as its focus.
|
Commonly asked questions
A particle is dropped from a height H. The de-Broglie wavelength of the particle as a function of height is proportional to (a) H (b) H1/2 (c) H0 (d) H-1/2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- velocity of a freely falling body is v=
And
-1
The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly
(a) 1.2 nm
(b) 1.2 x 10-3 nm
(c) 1.2 x 10-6 nm
(d). 1.2 x 10 nm
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (b)
Explanation- E=hc/
And l = hc/E= 1240/106= 1.24 10-3nm
Consider a beam of electrons (each electron with energy E0) incident on a metal surface kept in an evacuated chamber. Then,
(a) No electrons will be emitted as only photons can emit electrons
(b) Electrons can be emitted but all with an energy, E0
(c) Electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0– ɸ (ɸ is the work function)
(d) Electron can be omitted with energy ,with a maximum of E0
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (d)
explanation- When a beam of electrons of energy E0 is incident on a metal surface kept in an
evacuated chamber electrons can be emitted with maximum energy E0 (due to elastic
collision) and with any energy less than E0, when part of incident energy of electron is
used in liberating the electrons from the surface of metal.
Consider the figure given below. Suppose the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that
(a) Will be larger than the earlier value
(b) Will be the same as the earlier value
(c) Will be less than the earlier value
(d) Will depend on the target
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (c)
Explanation- In Davisson-Germer experiment, the de-Broglie wavelength associated with electron is
λ = 12.27/
Å . (i)where V is the applied voltage.
If there is a maxima of the diffracted electrons at an angle θ, then
2dsinθ = λ … (ii)
From Eq. (i), we note that if V is inversely proportional to the wavelength λ.
i.e., V will increase with the decrease in the λ.
From Eq. (ii), we note that wavelength λ is directly proportional to sinθ and hence θ.
So, with the decrease in λ, θ will also decrease.
Thus, when the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the
Maximum at a value of θ that will be less than the earlier value.
A proton, a neutron, an electron and an a-particle have same energy. Then, their de-Broglie wavelengths compare as
(a) λp= λn > λe > λα
(b) λα < λp = λn > λe
(c) λe< λp = λn> λα
(d) λe = λp = λn = λα
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b)
Explanation-as we know that
so inversely proportional to
so from the above conclusion we can say that alpha p n e
An electron is moving with an initial velocity v = v0i and is in a magnetic field B = B0 Then, its de-Broglie wavelength
(a) Remains constant
(b) Increases with time
(c) Decreases with time
(d) Increases and decreases periodically
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a)
Explanation- v=v0i and B =B0j
Force on moving electron F= e (v )
= e (v0i )=-eV0B0k
An electron mass m with an initial velocity v=voi is in an electric field E=-Eoi. its debroglie wavelength at time t is given by
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a
Explanation-
Force F= -eE=-e [Eoi]=eEoi
So a=f/m=eEoi/m
V=Voi+ eEoit/m
h/ m Voi+ eEoit/m
An electron mass m with initial velocity v=v0i is an electric field E=Eo if its debroglie wavelength at time t is given by
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- c
Explanation-
Force F= -eE=-e [Eoi]=eEoi
So a=f/m=eEoi/m
Velocity at xaxis=Voi
Velocity at yaxis= eEotj/m
Net velocity v=
Relativistic corrections become necessary when the expression for the kinetic energy 1/2 mv2, becomes comparable with mc2. where m is the mass of the
At what de-Broglie wavelength, will relativistic corrections become important for an electron?
(a) A=10nm (b) A =10-1 nm (c) A=10-4 nm (d) A=10-6 nm
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-(c,d)
Explanation-
V= h/m
V1=
V1=
V1=
V1=
Two particles A1and A2 of masses m1 , m2 ( m1> m2) have the same de-Broglie
Then,
(a) their momenta are the same
(b) their energies are the same
(c) energy of A1 is less than the energy of A2
(d) energy of A1 is more than the energy of A2
Answer-(a,c)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as debroglie wavelength is
P=h/
P1/p2=
If wavelength are equal then ratio is 1:1 so P1=P2
E= 1/2mv2= p2/2m
E inversely proportional to m
So = <1
E1
. De-Broglie wavelength associated with uncharged particles: For Neutron efe-Broglie wavelength is given as ve=c/100.Then
(a) = 10-4 (b) = 10-2 (c) (d)
Answer- (b,c)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- =
Ee=1/2meve2
Meve=
Ee= h2/2 e2me
For photon
Ep= hc/ = hc/2
= 100
Pe=meve= me
Photons absorbed in a matter are converted to heat. A source emitting v photon/sec of frequency v is used to convert 1 kg of ice at 0°C to water at 0°C. Then, the time T taken for the conversion
(a) Decreases with increasing n. with v fixed
(b) Decreases with n fixed, v increasing
(c) Remains constant with n and v changing such that nv = constant
(d) Increases when the product nv increases
Answer-(a,b,c)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- energy spent to convert into water = mass latent heat
= mL= 1000g 80cal/g
= 80000cal
Energy of phtons used= nT E=nT
So nTh =mL
T= mL/nhv
T 1/n where v is constant
T when n is fixed
T 1/nv
A particle moves in a closed orbit around the origin, due to a force which is directed towards the origin. The de-BrOglie wavelength of the particle varies cyclically between two values λ1, λ2 with λ1> λ2 Which of the following statements are true?
(a) The particle could be moving in a circular orbit with origin as centre
(b) The particle could be moving in an elliptic orbit with origin as its focus
(c) When the de-Broglie wavetength is λ1the particle is nearer the origin than when its value is λ2
(d) When the de-Broglie wavelength is λ2 the particle is nearer the origin than when its value is λ1
Answer-(b,d)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the debroglie wavelength of the particle can be varying cyclically between two values and , if particle is moving in an elliptical orbit with origin as its focus.
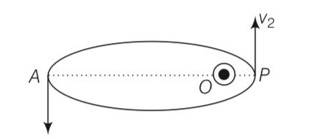
Let v1, v2, be the speed of particle at A and B respectively and origin is at focus O. If and are the de-Broglie wavelengths associated with particle while moving at A and B
respectively. Then,
=h/mv1
=h/mv2
>
So v2>v1
By law of conservation of angular momentum, the particle moves faster when it is closer to
focus.
From figure, we note that origin O is closed to P than A
A particle is dropped from a height H. The de-Broglie wavelength of the particle as a function of height is proportional to (a) H (b) H1/2 (c) H0 (d) H-1/2
Explanation- velocity of a freely falling body is v=
And
-1
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter Eleven NCERT Exemplar
See below the important formulas of the NCERT Exemplar Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
de Broglie Wavelength
Kinetic Energy in terms of de Broglie Wavelength
Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation
Stopping Potential and Kinetic Energy
Threshold Frequency
Photoelectric Current ∝ Intensity
Momentum of Photon
For a deeper understanding of key concepts of Physics and creating a strong foundation for advanced physics, students should also read - Class 11 Physics Notes and NCERT Class 12 Physics Notes for CBSE.
Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Physics Exemplar Chapter Eleven
See below the common mistakes and tips for Chapter Eleven Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:
- Students often confuse the de Broglie wavelength with the electromagnetic wavelength. They think that the de Broglie wavelength is only for electromagnetic radiation or light. Tip: The students must understand that the de Broglie wavelength applies to all matter with momentum, including protons, electrons, neutrons, and even macroscopic objects (in theory).
While calculating de Broglie wavelength, students often do not convert the velocity to m/s or mass to kg. Tip: Always use SI Units: - Students sometimes misapply Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation and they forget that the work function is not the incident light and is a property of the metal. Tip:
- They use the wrong formula for kinetic energy. Some mix Kinetic energy with photoelectric kinetic energy. The formula for K.E. is the following - and for the photoelectric kinetic energy, it is:
- Sometimes, students assume the photoelectric current increases with frequency. Students must understand that the Photoelectric current does not depend on the frequency but on the intensity. The intensity affects the number of photoelectrons and the frequency affects the energy.
The following are some general tips to avoid common mistakes while practicing questions of Class 12 Physics Chapter 11:
- Students should understand the difference between quantum and classical views.
- They should practice unit conversions frequently.
- Solve numerical problems involving stopping potential, work function, and wavelength carefully.
- For conceptual clarity, review graphs of current vs intensity and K.E. vs frequency.
FAQs Related to Physics Chapter 11 NCERT Exemplar
Commonly asked questions
In modern physics, what is the significance of de Broglie’s hypothesis?
According to de Broglie's hypothesis, all matter exhibits wave-like behavior. It laid the foundation for quantum mechanics by introducing the concept of matter waves. The dual nature of particles (both wave and particle) is essential in designing technologies like electron microscopes and helps explain phenomena like electron diffraction.
Why regardless of the intensity of light, the photoelectric emission not occur below the threshold frequency?
Photons do not have enough energy ( )to overcome the work function (? ) of the material below the threshold frequency.The energy per photon remains too low to liberate electrons even if the light intensity is increased, so photoelectric emission cannot occur.
What factors affect the de Broglie wavelength of a particle?
The de Broglie wavelength depends on:
Planck's constant h (a universal constant),
velocity v of the particle
mass m of the particle.
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven Exam