- Communication Systems Long Answer Type Questions
Communication Systems Long Answer Type Questions
| 1. The intensity of a light pulse travelling along a communication channel decreases exponentially with distance x according to the relation I = I0e-ax, where I0is the intensity at x = 0 and α is the attenuation constant. |
| Explanation- as we know that I= I0 And I= 25%of I0= I=I0/4 I0/4= I0 I0 cancel from both sides ¼= Taking log on both sides log1 -log4= - loge X= log4/ |
| 2. A 50 MHz sky wave takes 4.04 ms to reach a receiver via re-transmission from a satellite 600 km above Earth’s surface. Assuming re-transmission time by satellite negligible, find the distance between source and receiver. If communication between the two was to be done by Line of Sight (LOS) method, what should size and placement of receiving and transmitting antenna be? |
| Explanation- height of satellite hs= 600km 2x/4.0410-3 = 38 So x=606 km after solving So d= 85.06km so total distance will be double from receiver to transmitter = 170.1km |
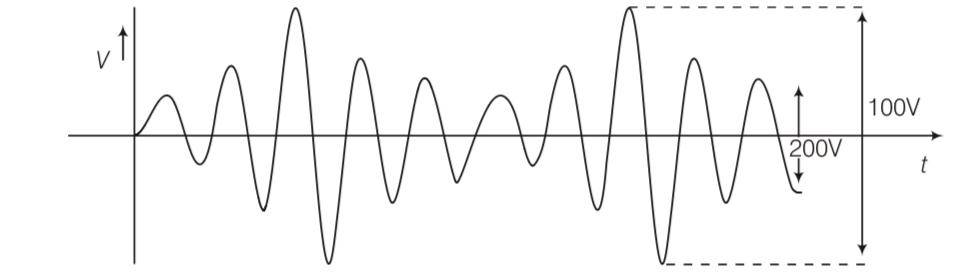
| 3. An amplitude modulated wave is as shown in figure. Calculate |
| Explanation- maximum voltage = 100/2 = 50V And minimum voltage = 20/2 = 10V Percentage modulation= max voltage -min voltage/ max voltage + min voltage = = 66.67% Peak carrier voltage= max voltage+ min voltage/2= 50+10/2=30V Peak value of information voltage= 66.67/100 30= 20V |
| 4. (i) Draw the plot of amplitude versus ω for an amplitude modulated wave whose carrier wave (ω > ωc) is carrying two modulating signals, ω1 and ω2(ω2> ω1). |
| Explanation- in first case crowding spectrum is visible If we want more wave to be modulated then more crowding will occur and more mixing up of signal. But we want to accommodate this we use higher band width and frequency carrier wave |
Commonly asked questions
The intensity of a light pulse travelling along a communication channel decreases exponentially with distance x according to the relation I = I0e-ax, where I0is the intensity at x = 0 and α is the attenuation constant.
(a) Show that the intensity reduces by 75% after a distance of (In4/α).
(b) Attenuation of a signal can be expressed in decibel (dB) according to the relation dB=10 log10(I/I0).What is the attenuation in dB/km for an optical fibre in which the intensity falls by 50% over a distance of 50 km?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
as we know that I= I0
And I= 25%of I0=
I=I0/4
I0/4= I0
I0 cancel from both sides
¼=
Taking log on both sides log1 -log4= - loge
X= log4/
A 50 MHz sky wave takes 4.04 ms to reach a receiver via re-transmission from a satellite 600 km above Earth’s surface. Assuming re-transmission time by satellite negligible, find the distance between source and receiver. If communication between the two was to be done by Line of Sight (LOS) method, what should size and placement of receiving and transmitting antenna be?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
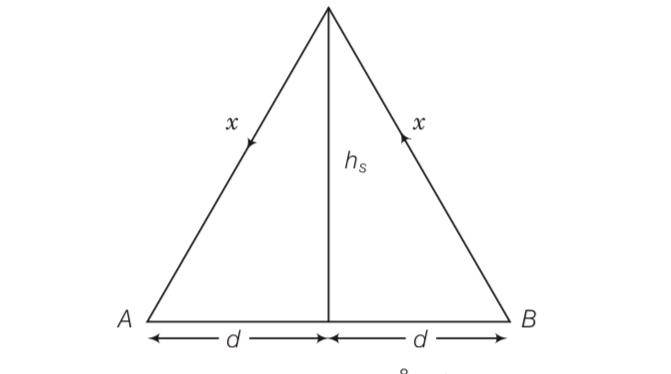
height of satellite hs= 600km
As we know velocity = distance/time
2x/4.0410-3 = 38
So x=606 km after solving
According to Pythagoras theorem d2=x2-h2= 6062-6002= 7236
So d= 85.06km so total distance will be double from receiver to transmitter = 170.1km
And d = √2Rh
h=7236/2×6400 = 565m
An amplitude modulated wave is as shown in figure. Calculate
(i) The percentage modulation,
(ii) Peak carrier voltage and
(iii) Peak value of information voltage
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Maximum voltage = 100/2 = 50V
And minimum voltage = 20/2 = 10V
Percentage modulation= max voltage -min voltage/ max voltage + min voltage
= = 66.67%
Peak career voltage= max voltage+ min voltage/2= 50+10/2=30V
Peak value of information voltage= 66.67/100 30= 20V
(i) Draw the plot of amplitude versus ω for an amplitude modulated wave whose carrier wave (ω > ωc) is carrying two modulating signals, ω1 and ω2(ω2> ω1).
(ii) Is the plot symmetrical about ωc? Comment especially about plot in region (ω < ωc ).
(iii) Extrapolate and predict the problems one can expect if more waves are to be modulated.
(iv) Suggest solutions to the above problem. In the process can one understand another advantage of modulation in terms of bandwidth?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
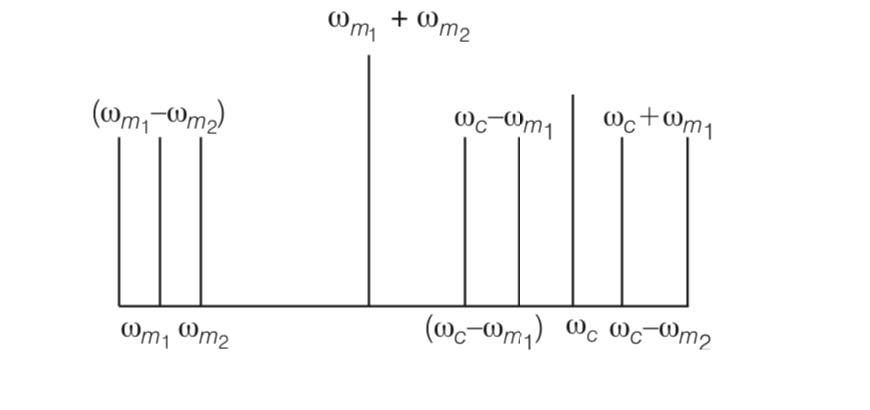
in first case crowding spectrum is visible
If we want more wave to be modulated then more crowding will occur and more mixing up of signal.
But we want to accommodate this we use higher band width and frequency career wave
An audio signal is modulated by a carrier wave of 20 MHz such that the bandwidth required for modulation is 3 kHz. Could this wave be demodulated by a diode detector which has the values of R and C as
(i) R = 1 kΩ, C= 0.01 µF?
(ii) R= 10 kΩ, C=0.01 µF?
(iii) R = 10 kΩ, C = 0.1 µF?
Frequency of career wave is 20MHz
Bandwidth require for modulation is 3kHz/2= 1.5kHz
For demodulating we need to reciprocal it
1/f= 1/20MHz= 0.5 10-7s
For modulation = 1/1.5KHz= 0.7 103s
According to first option =RC= 1 0.01= 10-5s
So it will demodulated
According to 2nd option- RC= 10-4s
So it can also be demodulated
According to third option – RC= 10-8s
So it cannot be modulated
Would sky waves be suitable for transmission of TV signals of 60 MHz frequency?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When we send a signal to be transmitted through sky waves must have a frequency range of 1710 kHz to 40 MHz.
But, the frequency of TV signals are 60 MHz which is beyond the required range.
So, sky waves will not be suitable for transmission of TV signals of 60 MHz frequency.
Two waves A and B of frequencies 2 MHz and 3 MHz, respectively are beamed in the same direction for communication via sky wave. Which one of these is likely to travel longer distance in the ionosphere before suffering total internal reflection?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As frequency of B is more than A so it has more refractive index also and if a wave have higher refractive index then it has less angle of refraction. So wave B travel more in ionosphere.
The maximum amplitude of an AM wave is found to be 15 V while its minimum amplitude is found to be 3 V. What is the modulation index?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Maximum amplitude = Am+Ac =12 while minimum amplitude is Ac-Am=3
Using elimination method = 2Ac= 18
Ac=9 and Am= 6V
So modulating index m = 6/9= 2/3
Compute the LC product of a tuned amplifier circuit required to generate a carrier wave of 1 MHz for amplitude modulation.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Frequency tuned amplifier is
=1/2
Why is an AM signal likely to be more noisy than a FM signal upon transmission through a channel?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In modulating signal we add career wave or noise signal to send it to receiver end and this wave is varied from time to time that is why more noise appear.
But in frequency modulation frequency is not varied so less noise appear.
Figure shows a communication system. What is the output power when input signal is of 1.01 mW? [Gain in dB= 10 log10 (P0 / P1)]

This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Total distance = 5km and loss is 2 dB/km
So total loss = 5 (2)= 10 dB
Total gain in amplifier 10+20= 30dB and gain in signal is 20dB
So by the formula 20= 10log10
log10 = 2
so po/pi= 102
so Po= Pi (100)= 101mW
A TV transmission tower antenna is at a height of 20 m. How much service area can it cover if the receiving antenna is (i) At ground level, (ii) At a height of 25 m? Calculate the percentage increase in area covered in case (ii) Relative to case (i).
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Range =
Area = =803.84km2
When H= 25 m
Range = = 33.9km
Area= 3.14 2
percentage increase = %
If the whole earth is to be connected by LOS communication using space waves (no restriction of antenna size or tower height), what is the minimum number of antennas required? Calculate the tower height of these antennas in terms of earth’s radius.?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
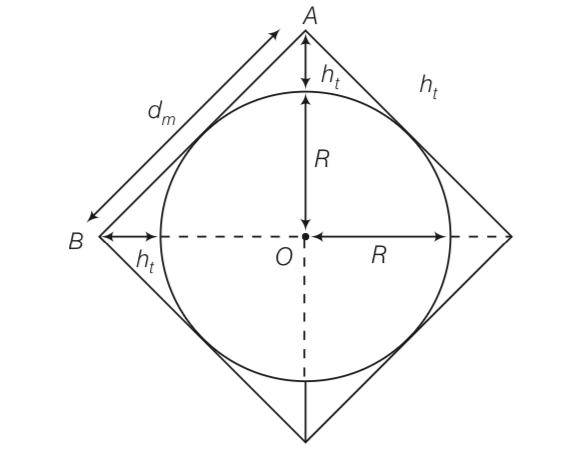
dm2= (R+h)2+ (R+h)2= 2 (R+h)2
So dm=
8hR= R2+2Rh+h2
R-h=0
R=h so frequency of space wave Is less than height of tower. So it is also keep in consideration. for 3 dimension coverage 2 antennna each side means total 6 antenna required.
The maximum frequency for reflection of sky waves from a certain layer of the ionosphere is found to be fmax= 9(Nmax)1/2, where Nmaxis the maximum electron density at that layer of the ionosphere.
On a certain day it is observed that signals of frequencies higher than 5 MHz are not received by reflection from the F1 layer of the ionosphere while signals of frequencies higher than 8 MHz are not received by reflection from the F2 layer of the ionosphere. Estimate the maximum electron densities of the F1 and F2 layers on that day.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Frequency, fmax= 9 (Nmax)1/2
For F1 layer frequency is 5MHz
So 5 1/2
Nmax= (5/9 )2= 3.086 1011/m3
For F2 layer 8MHz
8 1/2
Nmax= (8/9 )2= 7.9 1011/m3
On radiating (sending out) and AM modulated signal, the total radiated power is due to energy carried by ωc, (ωc– ωm) and (ωc + ωm). Suggest ways to minimise cost of radiation without compromising on information.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In amplitude modulated wave side frequency contain the information and from the question the power will be ωc, (ωc – ωm) and (ωc + ωm)
So to minimise cost of radiation we use both (ωc – ωm) and (ωc + ωm)
Three waves A, B and C of frequencies 1600 kHz, 5 MHz and 60 MHz respectively are to be transmitted from one place to another. Which of the following is the most appropriate mode of communication?
(a) A is transmitted via space wave while B and C are transmitted via sky wave
(b) A is transmitted via ground wave, B via sky wave and C via space wave
(c) B and C are transmitted via ground wave while A is transmitted via sky wave
(d) B is transmitted via ground wave while A and C are transmitted via space wave
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Ground wave propagation – 530KHz to 1710KHz
Sky wave propagation- 1710KHz- 40MHz
Space wave propagation- 54MHz to 42GHz
A loom long antenna is mounted on a 500 m tall building. The complex can become a transmission tower for waves with λ.
(a) ~400m (b) -25 m (c) -150 m (d) -2400 m
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a
length of building is given by l= 500m
And 4l= 4 100 =400mf
A1 kW signal is transmitted using a communication channel which provides attenuation at the rate of -2dB per km. If the communication channel has a total length of 5 km, the power of the signal received is [gain in dB=10 log10(p0/pi)]
(a) 900 W (b) 100 W (c) 990 W (d) 1010 W
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-b
p = 1kW= 1000W
Attenuation of signal = -2dB/km and total path length = 5km
Gain in dB= 5
Gain in dB= 10 log (p0/pi)……. (i)
-10=10 log (p0/pi)= -10log (pi/po)
logPi/po=1 = log (pi/po)= log10
pi/p0=10= 1000W= 10p0
p0=100W
A speech signal of 3 kHz is used to modulate a carrier signal of frequency 1 MHz, using amplitude modulation. The frequencies of the side bands will be
(a) 1.003 MHz and 0.997 MHz (b) 3001 kHz and 2997 kHz
(c) 1003 kHz and 1000 kHz (d) 1 MHz and 0.997 MHz
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a
Frequency of career signal = 1MHz and frequency = 3KHz= 0.003MHz
So frequency of side bands = 1 0.003
So 1.003MHz and 0.997MHz
A message signal of frequency ωmis superposed on a carrier wave of frequency ωc to get an Amplitude Modulated Wave (AM). The frequency of the AM wave will be
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation- frequency of career wave and frequency of amplitude modulated wave is same which is wc .
I-V Characteristics of 4 devices are shown in figure.
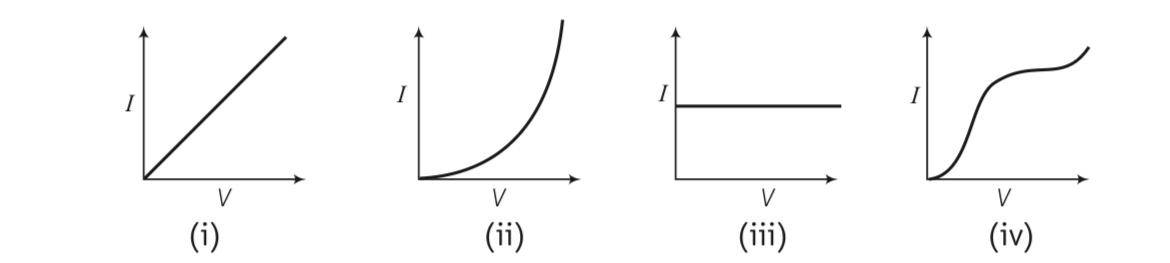
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- c
Explanation- The device which follows square law is used for modulation purpose. Characteristics shown by (i) and (iii) corresponds to linear devices.
Characteristics shown by (ii) corresponds to square law device. Some part of (i) also
Follow square law.
Hence, (ii)and (iv) can be used for modulation.
A male voice after modulation-transmission sounds like that of a female to the receiver. The problem is due to
(a) Poor selection of modulation index (selected 0 < m <1)
(b) Poor bandwidth selection of amplifiers
(c) Poor selection of carrier frequency
(d) Loss of energy in transmission.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation- Here, in this question, the frequency of modulated signal received becomes more, which is possible with the poor bandwidth selection of amplifiers.
This happens because bandwidth in amplitude modulation is equal to twice the
Frequency of modulating signal. But, the frequency of male voice is less than that of a female.
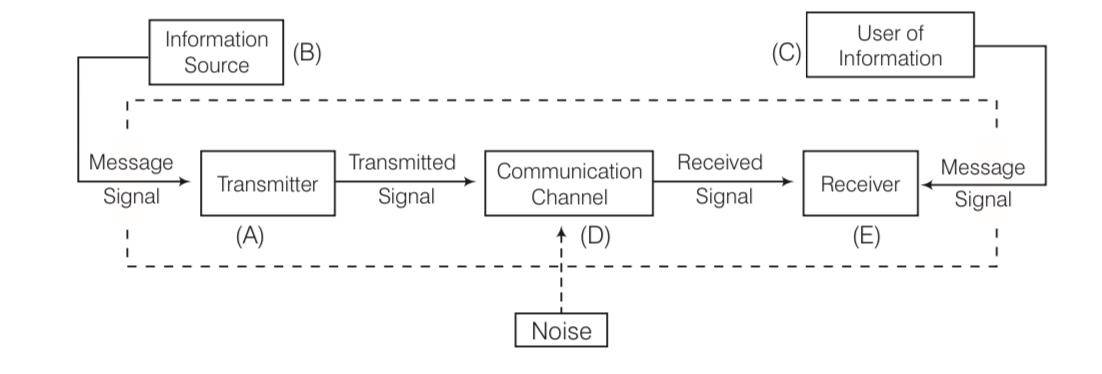
A basic communication system consists of transmitter.
B. Information source.
C. User of information.
D. Channel.
E. Receiver.
Choose the correct sequence in which these are arranged in a basic communication system.
(a) ABCDE (b) BADEC (c) BDACE (d) BEADC
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation- it is represented by a diagram given below
Identify the mathematical expression for amplitude modulated wave,
(a) Acsin[{wc+K1Vm(t)}t+ ]
(b) Acsin[{wct+ K2Vm(t)]
(c) Ac+K2Vmt}+sinwct+ ]
(d) Ac Vm(t)sin[{wct+ )
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-equation of modulating wave is, m (t)= Amsinwmt
Carrier wave equation is Cm (t)= (Ac+Amsinwmt)sinwct
= Ac [1+ ]sinwct
Also = M
Cmt= (Ac+Ac )sinwct
Ac =K
Sinwmt= Vm
equation having phase
so equation is Ac+K2Vmt}+sinwct+ ]
An audio signal of 15 kHz frequency cannot be transmitted over long distances without modulation, because
(a) The size of the required antenna would be at least 5 km which is not convenient
(b) The audio signal cannot be transmitted through sky waves
(c) The size of the required antenna would be at least 20 km, which is not convenient
(d) Effective power transmitted would be very low, if the size of the antenna is less than 5 km
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b, d
Explanation- frequency is given by Vm=15KHz
So wavelength is given by
Also we know that l = = 5km
The audio signals are of low frequency waves. Thus, they cannot be transmitted through sky
Waves as they are absorbed by atmosphere.
If the size of the antenna is less than 5 km, the effective power transmission would be very
Low because of deviation from resonance wavelength of wave and antenna length.
Audio sine waves of 3 kHz frequency are used to amplitude modulate a carrier signal of 1.5 MHz. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) The side band frequencies are 1506 kHz and 1494 kHz
(b) The bandwidth required for amplitude modulation is 6 kHz
(c) The bandwidth required for amplitude modulation is 3 MHz
(d) The side band frequencies are 1503 kHz and 1497 kHz
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b, d
Explanation- wm=3KHz
And wc= 1.5MHz= 1500KHz
By using these two 1500 3= 1503 and 1497
Bandwidth = 2wm= 2 = 6KHz
A TV transmission tower has a height of 240 m. Signals broadcast from this tower will be received by LOS communication at a distance of (assume the radius of earth to be (6.4 x 106m)
(a) 100 km (b) 24 km (c) 55 km (d) 50 km
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-b, c, d
Explanation- height of tower= 240m
For line of sight communication maximum distance would be d=
So d= = 55.4km
So distance under this are communicable
The frequency response curve (figure) for the filter circuit used for production of AM wave should be
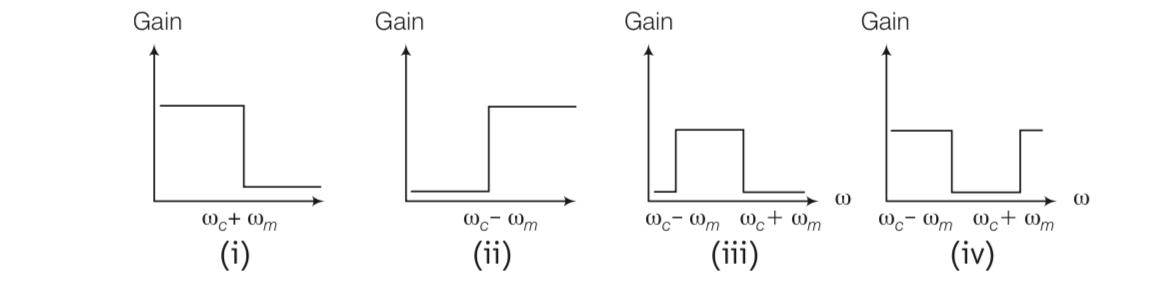
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b, c
Explanation- production of modulated wave is given by frequency of upper side band – frequency of lower side band so in first three cases it is clearly visible.
In amplitude modulation, the modulation index m is kept less than or equal to 1 because
(a) m> 1, will result in interference between carrier frequency and message frequency, resulting into distortion.
(b) m > 1, will result in overlapping of both side bands resulting into loss of information
(c) m > 1, will result in change in phase between carrier signal and message signal.
(d) m > 1, indicates amplitude of message signal greater than amplitude of carrier signal resulting into distortion.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b, d
Explanation- modulation index m= Am/Ac
If m>1 then Am>Ac
maximum modulation frequency mf= frequency deviation / maximum frequency of modulating wave
here if m>1 then it means overlapping of both sides resulting loss of information.
Which of the following would produce analog signals and which would produce digital signals?
(a) A vibrating tuning fork
(b) Musical sound due to a vibrating sitar string
(c) Light pulse
(d) Output of NAND gate
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Analog and digital signals are used to transmit information, usually through electric signals. In both these technologies, the information such as any audio or video is
transformed into electric signals.
The difference between analog and digital technologies is that in analog technology, information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude. In digital technology, translation of information is into binary formal (zero or one) where each bit is representative of two distinct amplitudes.
Thus, (a) and (b) would produce analog signal and (c) and (d) would produce digital
signals.
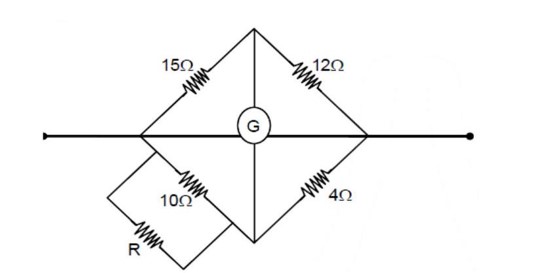
Four resistances of and respectively in cyclic order to form Whetstone's network. The resistance that is to be connected in parallel with the resistance of to balance the network is
A particle is moving along the -axis with its coordinate with time ' ' given by . Another particle is moving along the -axis with its coordinate a function of time given by . At , the speed of the second particle as measured in the frame of the first particle is given as . Then (in ) is
A body , of mass has an initial velocity of . It collides elastically with another body, of the same mass which has an initial velocity of . After collision, A moves with a velocity . The energy of after collision is written as . The value of is
For elastic collision
A one metre long (both ends open) organ pipe is kept in a gas that has double the density of air at STP. Assuming the speed of sound in air at STP is , the frequency difference between the fundamental and second harmonic of this pipe is
(If )
(If )
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fifteen Exam