GD Topic - Union Budget 2024: Are the New Income Tax Slabs a Win for the Middle Class?
Read article below to find details on new income tax slabs under Union Budget 2024 and their impact on middle class people.
Management of Business Studies is one of most opted postgraduate courses. MBA admission process includes entrance exams like CAT, XAT, SNAP, NMAT and MAH MBA CET. Once entrance exam is over, selected candidates are eligible for Group Discussion Round. Candidates who will achieve a good score in Group Discussion will be able to participate in next stage of MBA admission process.
Students planning to gain admission at top Bussiness schools, like IIM, XLRI Jamshedpur, SBIM Pune, etc., must prepare well for GD/PI round. To do well in this round, one must work on their speaking and reasoning skills, maintain eye contact with group during discussion, use relevant points to prove their statement, listen attentively, avoid interrupting others and work on their body language.
Check Out: Top MBA Colleges in India
- Union Budget 2024: Changes in Income Tax Slab under New Tax Regime
- What is Income Tax?
- Income Tax Slabs: Old Regime vs New Regime (Effective from FY 2024-25)
- Changes under New Tax Regime for FY 2024-25
- Is New Income Tax Slab Good for Middle Class?
- Top GD Topics for MBA Admission Process
Union Budget 2024: Changes in Income Tax Slab under New Tax Regime
The Union Finance Minister of India, Nirmala Sitharaman, presented Union Budget for FY 2024-25 on 23rd July 2024. This was her seventh consecutive budget presentation. This budget holds much importance for nation as it was the first budget formulated after 2024 general elections.
Our Hon’ble Prime Minister Narendra Modi has praised this budget. According to him, Union Budget 2024 caters to all sections of society. It will help India achieve vision of a Viksit Bharat by 2047, marking 100 years of independence. But, former Finance Minister P. Chidambaram criticized this budget, stating, This budget fails to assure people of India how inflation would be controlled in this country and this budget gives too little room for improving condition of unemployment.
Many experts praised different aspects of this budget. While others criticized Union Budget 2024, stating that it missed certain opportunities and gave insufficient attention to some sections of society.
What is Income Tax?
Income Tax is direct tax imposed on an individual's or an entity's income during a financial year. It is directly paid to government. The amount of tax to be paid per person or company depends on income tax slab applicable to their income.
Income Tax Slabs are different tax rates applied to different income brackets. This system of charging different tax rates ensures that as taxable income of a taxpayer increases, tax rate also increases. This practice makes sure that high income earners contribute a larger portion of their income in taxes.
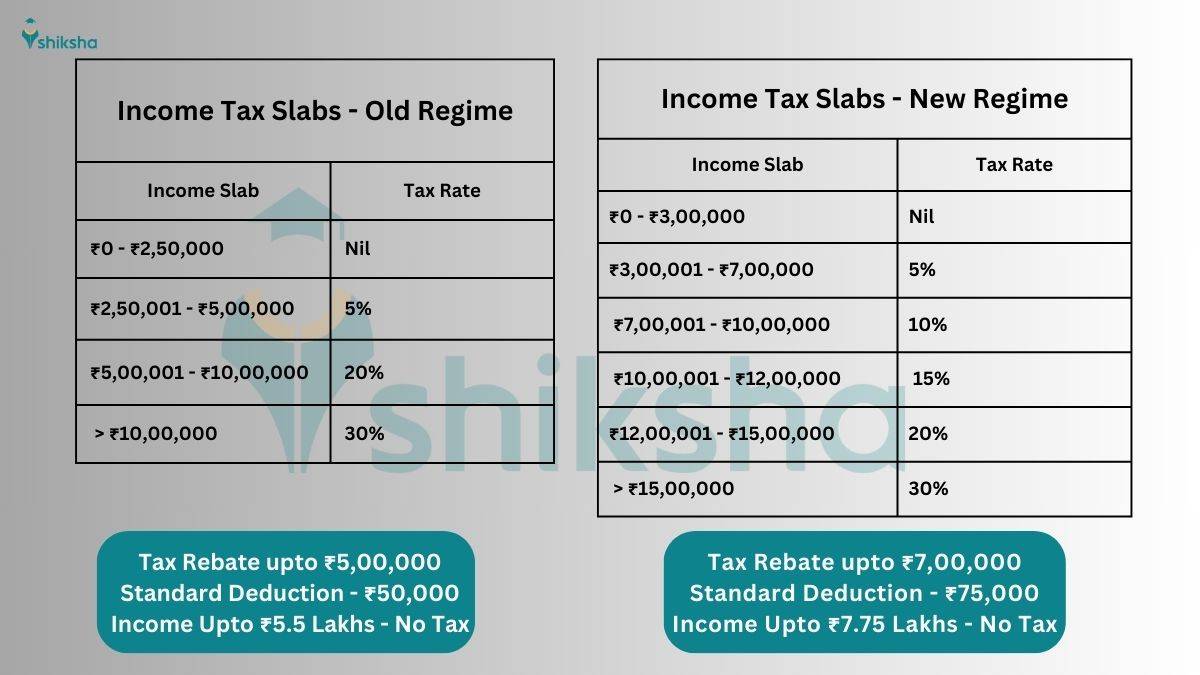
Income Tax Slabs: Old Regime vs New Regime (Effective from FY 2024-25)
Changes under New Tax Regime for FY 2024-25
Finance Minister of India, Nirmala Sitharaman, announced following changes in new tax regime under Union Budget 2024.
- Increased Standard Deduction: From ₹50,000 to ₹75,000
- Higher Tax Rebate: Applicable for incomes up to ₹7,00,000.
- Revised Income Tax Slab: Lower tax rates for certain income brackets.
- Family Pension Deduction: Increased from ₹15,000 to ₹25,000.
- Enhanced NPS Deduction: Employer contribution to NPS increased from 10% to 14% in case of private companies, PSUs and private banks.
Also Read: GST Rate Changes After the 55th GST Council Meeting: Simplification or Complexity?
Is New Income Tax Slab Good for Middle Class?
To determine whether revised income tax slab is beneficial for middle class or not, we have to check impact of tax rates across income levels. Let us take an example and determine net taxable income and tax amount to be paid under Old Tax Regime and New Tax Regime.
Tax under Old Tax Regime
| Gross Salary Range | Gross Salary (₹) | Standard Deduction | Extra Deductions* | Net Taxable Income | Tax to be Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ₹ 0 - 2.5 Lakhs | ₹2,40,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹0 | ₹1,90,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 2.5 - 3 Lakhs | ₹2,80,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹0 | ₹2,30,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 3 - 5 Lakhs | ₹4,70,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹0 | ₹4,20,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 5 - 7 Lakhs | ₹5,60,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹4,60,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 7 - 10 Lakhs | ₹8,80,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹2,50,000 | ₹5,80,000 | ₹28,500 |
| ₹ 10 - 12 Lakhs | ₹11,50,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹3,00,000 | ₹8,00,000 | ₹72,500 |
| ₹ 12 - 15 Lakhs | ₹14,00,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹3,50,000 | ₹10,00,000 | ₹1,12,500 |
| > ₹ 15 Lakhs | ₹17,00,000 | ₹50,000 | ₹4,00,000 | ₹12,50,000 | ₹1,87,500 |
Notes
- Tax has been calculated without Surcharge and Cess.
- *Extra Deductions include HRA Exemption, Loss on House Property, Interest on Home Loans, Deductions under Section 80C, Deductions under Section 80D and NPS contribution from employer (up to 10% of Basic + DA)
Tax under New Tax Regime
| Gross Salary Range | Gross Salary (₹) | Standard Deduction | NPS Deductions * | Net Taxable Income | Tax to be Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ₹ 0 - 2.5 Lakhs | ₹2,40,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹1,65,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 2.5 - 3 Lakhs | ₹2,80,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹2,05,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 3 - 5 Lakhs | ₹4,70,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹3,95,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 5 - 7 Lakhs | ₹5,60,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹4,85,000 | ₹0 |
| ₹ 7 - 10 Lakhs | ₹8,80,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹8,05,000 | ₹30,500 |
| ₹ 10 - 12 Lakhs | ₹11,50,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹10,75,000 | ₹61,250 |
| ₹ 12 - 15 Lakhs | ₹14,00,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹13,25,000 | ₹1,05,000 |
| > ₹ 15 Lakhs | ₹17,00,000 | ₹75,000 | - | ₹16,25,000 | ₹1,77,500 |
Note: *NPS Contribution is not mandatory. Therefore, in this example, we will take NPS as zero.
With above example, we can see that individuals earning up to ₹7,00,000 pay no tax, under old tax regime as well as new tax regime, due to higher standard deduction and tax rebate. This offers relief to individuals selecting new tax regime, as they do not have to invest to save tax, giving them more disposable income. It will also give them additional financial flexibility for savings and important expenditures.
Individuals earning more than ₹7,00,000 will have to pay tax under old and new tax regimes. Individuals earning between ₹7,00,000 and ₹10,00,000 might find old tax regime better. While individuals earning more than ₹10,00,000 might prefer new tax regime due to lower tax amount. The old regime is better for those who either claim higher HRA or have overall deductions more than benefits of new regime.
Top GD Topics for MBA Admission Process
Below listed are some important GD Topics for reference.
- Importance of Statue of Unity
- Citizenship Amendment Act - What and Why
- Making Aadhaar mandatory is not a good idea- for or against
- Implications of CAA-NCR
- Cashless Economy – Is India ready for it?
- All you need to know about Right To Information
- How can we control banking frauds to reduce NPAs?
- Statue of Unity - Symbol of Pride or Wastage of Public Money?
- Rural vs Urban India
- Environment and us
- Self Motivation
- First impression is the last impression
- Funding Democracy: Are Electoral Bonds a Boon or Bane?
- Quick Commerce: A Step Toward Progress or a Wasteful Luxury?
- Crime Against Women in India: Who Bears the Responsibility?
- Innovation Vs Invention: What does the world need?
- PM Internship Scheme: How Effective is it in Enhancing Youth Employability?
- Job Reservation in Private Sector: A Boon or a Barrier?
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS): Reforming Criminal Law for Better or Worse?
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) in India: Dream or Reality?
- India’s Historic Performance at the Paris Paralympics 2024
- Global Innovation Index 2024: India Jumps from 81st to 39th Rank in 9 Years
- UCPMP 2024: Strengthening Ethical Standards in Pharmaceutical Marketing
- Global Food and Hunger Crisis: India Ranks 105 at Global Hunger Index 2024
- Making India a Semiconductor Powerhouse: The SEMICON India Programme
- Monkeypox Outbreak: A Wake-Up Call for Better Disease Surveillance


Nupur Jain started with a passion for educational content writing, which soon grew into a meaningful journey of helping students through reliable guidance. A commerce graduate from Delhi University, she has spent ov
Read Full Bio