
Coordination Chemistry Class 12 talks about the Coordination Compounds, which is an important and challenging area of modern inorganic chemistry. A variety of industrial catalysts, metallurgical processes, and analytical reagents use coordination compounds. It also finds applications in textile dyeing, electroplating, and medicinal chemistry.
Coordination Compounds NCERT Solutions help students to understand the key concepts of the chapter, which include - Werner's theory of coordination compounds, meaning of terms such as central atom/ion, coordination entity, coordination number, ligand, coordination polyhedron, coordination sphere, homoleptic, oxidation number and heteroleptic. It also covers the rules, formulas, and names of the coordination compounds.
Related Links
| NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Notes for CBSE | NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 |
| Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions | NCERT Solutions Class 11 and 12 for Maths, Physics, Chemistry |
- Quick Summary of Coordination Compounds NCERT
- Topics Covered in NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Coordination Compounds Chapter
- Important Formulas of Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds
- Class 12 Coordination Compounds NCERT Solution PDF: Download PDF For Free
- Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Solutions for Intex Questions
- Benefit of using NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5
- NCERT Chemistry Chapter 5 Coordination Compounds – FAQs
Quick Summary of Coordination Compounds NCERT
Here is a walkthrough of the Class 12 Coordination Compounds NCERT Solutions:
- The recent advances in coordination compounds have provided the development of new concepts, molecular structure, models of bonding, vital insights and novel breakthroughs.
- The Valence Bond Theory (VBT) explains the creation, magnetic behavior, and geometrical shapes of coordination compounds.
- The Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is dependent on the effect of different crystal fields and the d orbital energies of the central metal atom/ion's degeneracy.
- Coordination Compounds is an important chapter. It provides insight into the functioning and structures of vital components of biological systems. Moreover, it has applications in analytical and medicinal chemistry and metallurgical processes.
Topics Covered in NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Coordination Compounds Chapter
NCERT Solutions Coordination Compounds offer deep insights into how metals and ligands interact with each other to form complex structures. The chapter helps students to understand molecular bonding, geometry, and isomerism, which are important for studies in higher education in medicine, pharmacy, chemistry, and materials science.
See the table below for the topics covered in the Coordination Compounds:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 5.1 | Werner's Theory of Coordination Compounds |
| 5.2 | Definitions of Some Important Terms Pertaining to Coordination Compounds |
| 5.3 | Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds |
| 5.4 | Isomerism in Coordination Compounds |
| 5.5 | Bonding in Coordination Compounds |
| 5.6 | Bonding in Metal Carbonyls |
| 5.7 | Importance and Applications of Coordination Compounds |
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Coordination Compounds Weightage in NEET, JEE Main Exam
| Exam | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| NEET | 2-3 questions | 3-6% |
| JEE Main | 2-3 questions | 3-10% |
Important Formulas of Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds
Class 12 Coordination Compounds: Important Formulae and Applications
| Concept | Formula |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Moment | |
| Crystal Field Splitting | |
| Oxidation State |
Class 12 Coordination Compounds NCERT Solution PDF: Download PDF For Free
Students can download the Coordination Compounds NCERT PDF from the link given below. The well-structured NCERT solutions are easy to understand. It is prepared by the subject matter experts to improve students' problem-solving skills. It can help students in exam preparation and scoring high in the CBSE Board exam and competitive exams like NEET and JEE Main.
Download Here: NCERT Solution for Class XII Chemistry Coordination Compounds PDF
Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Solutions for Intex Questions
Students can find here the NCERT Solutions for Coordination Compounds Intext questions below. Verify your answers and know how well you have understood the topics.
| Q 9.1 Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds: (i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt(III) chloride (ii) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II) (iii) Tris(ethane–1,2–diamine) chromium(III) chloride (iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II) (v) Dichloridobis(ethane–1,2–diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate (vi) Iron(III) hexacyanidoferrate(II) |
| Ans (i) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)2]Cl3 (ii) K2[Ni(CN)4] (iii) [Pt(en)3]NO3 (iv) [Pt(NH3)BrCl(NO2)] (v) [Pt(Cl)2(en)2](NO3)2 (vi) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 |
| Q 9.2 Write the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds: (i) [Co(NH3 )6 ]Cl3 (ii) [Co(NH3 )5Cl]Cl2 (iii) K3 [Fe(CN)6 ] (iv) K3 [Fe(C2O4 )3 ] (v) K2 [PdCl4 ] (vi) [Pt(NH3 )2Cl(NH2CH3 )] |
| Ans (i) Hexaminecobalt(III)chloride (ii) Pentaaminechloridecobalt(III)chloride (iii) Potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) (iv) Potassium trioxalatoferrate(III) (v) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II) (vi) Diaminechloride(methylamine)platinum(II)chloride |
| Q 9.3 Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structures for these isomers: (i) K[Cr(H2O)2 (C2O4 )2 (ii) [Co(en)3 ]Cl3 (iii) [Co(NH3 )5 (NO2 )](NO3 )2 (iv) [Pt(NH3 )(H2O)Cl2 ] |
| Ans (i) K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2 exhibits geometrical isomerism (Cis and trans) and optical isomerism of cis and trans (ii) Optical isomerism exhibiting mirror (iii) Ionisation isomerism- [Co(NH3)5(NO3)](NO3)(NO2) and Linkage isomerism-[Co(NH3)5(ONO)](NO3)2 (iv) Geometrical isomers are seen in [Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2] |
| Q 9.4 Give evidence that [Co(NH3 )5Cl]SO4 and [Co(NH3 )5 (SO4 )]Cl are ionisation isomers. |
| Ans These compounds give different ions in aqueous solution. This can be tested by using AgNO3 solution and BaCl2 [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(ppt) [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → no reaction [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Cl(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → no reaction [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl(ppt) Hence, they give different precipitates with different solutions. Thus, they are ionisation isomers. |
Commonly asked questions
9.5 Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4 ] 2– ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4 ] 2– ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
According to the valence band theory, the central metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n-1)d, ns, np (inner orbital complex) or ns, np, and (outer orbital complex)orbitals for hybridisation to form equivalent set of orbitals of definite geometry.
In [Ni (CN)4]2-, oxidation state of Ni can be calculated as :
Using overall charge balance as the whole ion has overall -2 charge:
x + 4 (-1) = -2 (? CN- has -1 negative charge) x = + 2
Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Ni is: [Ar]3d84s2 Where, [Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Ni+2 = [Ar]3d8 Outer electronic configuration of Ni+2 = 3d8
Since there are 4 CN ions so they can either form tetrahedral or square planar geometry. And CN- is a strong field ligand (according to experimental data of spectro-chemical series) it causes pairing of the 2 unpaired electrons.
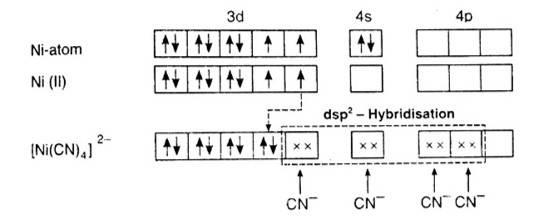
It undergoes dsp2 (one d orbital, one s and two p orbitals used by the ligands) hybridization and forms square planar structure.
Since all the electrons are paired so it is diamagnetic.
Paramagnetic compounds- those compounds which have one or more no. of unpaired electrons in their atomic orbitals.
Diamagnetic compounds-those compounds in which all the electrons in their atomic orbitals are paired.
Co-ordination number | Type of hybridisation | Distribution of hybrid orbitals in space |
4 | sp3 | Tetrahedral |
4 | dsp3 | Square planar |
5 | sp3d | Trigonalbipyramidal |
6 | sp3d2 | Octahedral |
6 | d2sp3 | octahedral |
In case of [Ni (Cl)4]2- ion, Cl- is a weak field ligand so it will not pair the unpaired electrons of Ni+2 ion. Therefore it undergoes sp3 hybridization.
Overall charge balance: X + 4 (-1) = -2
X = + 2.
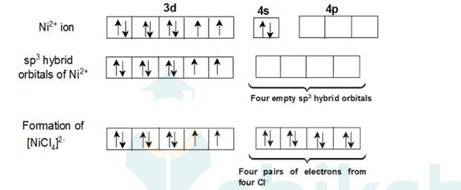
Since there are 2 unpaired electrons in the d orbital so it is a paramagnetic compound.
9.15 Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities:
(i) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2] 2+
(ii) [CoBr2(en)2] +
(iii) [PtCl4] 2–
(iv) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(v) [Cr(NH3)3Cl3]
(i) Let Oxidation of Co be x and charge on the complex is given as + 2
H2O has Oxidation Number: 0
CN has Oxidation Number: -1
en has Oxidation Number :0
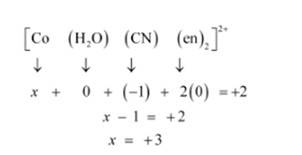
(ii) Let Oxidation number of Co be x and charge on the complex is given as + 1
Br has Oxidation number: 1
en has oxidation number : 0
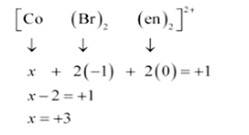
(iii) Let Oxidation number of Pt be x and charge on the complex is given as -2
Cl has oxidation number : -1
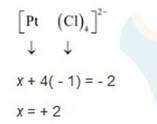
(iv) This complex can also be seen as [Fe (CN)6]3-
Let Oxidation number of Fe be x and charge given on the complex is given as -3
CN has oxidation number : -1
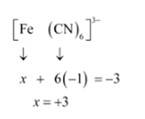
(v) Let Oxidation number of Cr be x and charge given on the complex is given as 0
NH3 has oxidation number : 0
Cl has oxidation number: -1
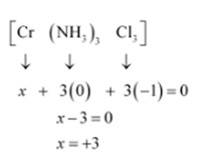
9.8 Explain [Co(NH3 )6 ] 3+ is an inner orbital complex whereas [Ni(NH3 )6 ] 2+ is an outer orbital complex.
[Co (NH3)6]3+ | [Ni (NH3)6]2+ |
Oxidation state of cobalt: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (0) = 3 X = + 3 | Oxidation state of nickel: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (0) = 2 X = + 2 |
Outer electronic configuration of cobalt = d6 | Outer electronic configuration of nickel = d8 |
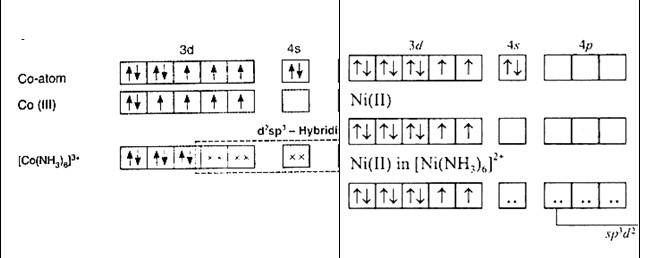
NH3 is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of electron. Therefore cobalt undergoes d2sp3 hybridisation. As in the hybridisation d2 orbitals are used from the (n-1)d orbitals (inner orbitals as n = 4 being quantum number) . hence it is a inner orbital complex. | NH3 is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of electron. Therefore, nickel undergoes sp3 d2 hybridisation. As in the hybridisation, d2 orbitals are used from the and orbitals (outer orbitals as n = 4 being quantum number). Hence, it is an outer orbital complex |
9.6 [NiCl4 ] 2– is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4 ] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why?
In [Ni (Cl)4]2- ion, Cl- is a weak field ligand so it will not pair the unpaired electrons of Ni+2 ion. Electronic configuration of Ni is: [Ar]3d84s2 where [Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Ni+2 = [Ar]3d8 Outer electronic configuration of Ni+2 = 3d8 Overall charge balance:
X + 4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2.
Therefore it undergoes sp3 hybridization. So it will have tetrahedral geometry.

Since there are 2 unpaired electrons in the d orbital so it is a paramagnetic compound. In [Ni (Co)4]:
Overall charge is neutral and oxidation state of Ni can be calculated as:
X + 4 (0) = 0
x = 0
Ni is in zero oxidation state.
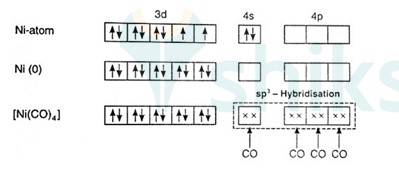
Co is a strong field ligand it causes pairing of the 4 unpaired electrons in d orbital. Also, it causes the 4s electrons to shift to the 3d orbital, thereby undergoes sp3 hybridisation forming tetrahedral geometry. Since it has no unpaired electron, therefore it is diamagnetic compound.
9.3 Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structures for these isomers:
(i) K[Cr(H2O)2 (C2O4 )2
(ii) [Co(en)3 ]Cl3
(iii) [Co(NH3 )5 (NO2 )](NO3 )2
(iv) [Pt(NH3 )(H2O)Cl2 ]
(i) K [Cr (H2O)2 (C2O4)2 exhibits geometrical isomerism (Cis and trans) and optical isomerism of cis and trans
(ii) Optical isomerism exhibiting mirror
(iii) Ionisation isomerism- [Co (NH3)5 (NO3)] (NO3) (NO2) and Linkage isomerism- [Co (NH3)5 (ONO)] (NO3)2
(iv) Geometrical isomers are seen in [Pt (NH3) (H2O)Cl2]
9.12 FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1:1 molar ratio gives the test of Fe2+ ion but CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1:4 molar ratio does not give the test of Cu2+ ion. Explain why?
The reaction is given below:
FeSO4 + (NH4)2SO4 + 6H2O → FeSO4 (NH4)2SO4.6H2O (Mohr Salt)
FeSO4, when reacted with (NH4)SO4, does not form any complex whereas they form a double salt, FeSO4. (NH4)2SO4.6H2O - (Mohr salt) which dissociates into ions in the solution. So, it gives the test of Fe2+ ions.
CuSO4 + 4NH3 + 5H2O→ [Cu (NH3)4SO4].5H2O
CuSO4 solution when mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1: 4 molar ratio forms a complex with formula [Cu (NH3)]SO4 in which the complex ion, [Cu (NH3)4]2+ does not dissociate to give Cu2+ ions. Therefore, it does not give the tests of the Cu2+ ion.
9.16 Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following:
(i) Tetrahydroxidozincate(II)
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum(II)
(iv) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II)
(v) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III)
(vi) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(vii) Potassium tri(oxalato)chromate(III)
(viii) Hexaammineplatinum(IV)
(ix) Tetrabromidocuprate(II)
(x) Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III)
(i) Tetrahydroxidozincate (II) = [Zn (OH)4]-2
Tetrahydroxi means 4 hydroxide ions with zinc in + 2 oxidation state. Hydroxide ions have a negative charge of -1, so balancing the overall charge of the coordination compound to be zero we get the formula as : [Zn (OH)4]-2
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate (II) = K3 [PdCl4].
Tetrachlorido means 3 Chloride ions each having a negative charge. Platinum is in + 2 state. Balance overall charge as 0, no. Of potassium ions are 3. Formula: K3 [PdCl4].
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) = [Pt (NH3)Cl2]2+
Diammine means 2 ammonia molecules, dichlorido means 2 chloride ions, platinum in + 2 state. Formula: [Pt (NH3)Cl2]2+
(iv) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate (II) = K2 [Ni (CN)4].
tetracyanido means 4 cyanide ions each with a unit negative charge and nickel atom with + 2 state. Formula: K2 [Ni (CN)4].
(v) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt (III) = [Co (ONO) (NH3)5]+2
penataammine means 5 ammonia molecules, nitrito-O means nitrate ion which is bonded to central atom via oxygen and cobalt in + 3 state. Formula: [Co (ONO) (NH3)5]+2
(vi) Hexaamminecobalt (III) sulphate = [Co (NH3)6]2 (SO4)3
Hexaammine means six ammonia molecules and cobalt in + 3 state. Sulphate have a negative charge of-2 Balance overall charge as 0. Formula: [Co (NH3)6]2 (SO4)3
(vii) Potassium tri (oxalato)chromate (III) = K3 [Cr (C2O4)3].
trioxolato means 3 oxolate ions and chromium in + 3 state. Balance overall charge as 0. Formula: K3 [Cr (C2O4)3].
(viii) Hexaammineplatinum (IV) = [Pt (NH3)6]4+
hexaammine means 6 neutral ammonia molecules and platinum in + 4 state. Balance overall charge as 0. Formula: [Pt (NH3)6]4+
(ix) Tetrabromidocuprate (II) = [Cu (Br)4]2-
tetrabromido means 4 bromide ions with a unit negative charge each and copper in + 2 state. Balance overall charge as 0. Formula: [Cu (Br)4]2-
(x) Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt (III) = [Co (NO2) (NH3)5]2+
pentaammine means 5 neutral ammonia molecules, nitrito-N means nitro group bonded to central atom via the lone pair of electron of nitrogen and cobalt in + 3 state. Balance overall charge as 0. Formula: [Co (NO2) (NH3)5]2+
9.9 Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4 ] 2– ion.
In Pt [ (CN)4]2- ion:
Overall charge balance:
X + 4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2.
The oxidation state of Pt is + 2.
Since CN- is a strong field ligand, it causes pairing of the unpaired electrons.
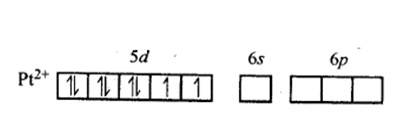
Therefore, now the 2 unpaired electrons from 5d orbital get paired and it undergoes dsp2 hybridisation. It forms square planar geometry. Since all the electrons are paired,
No. of unpaired electrons = 0.
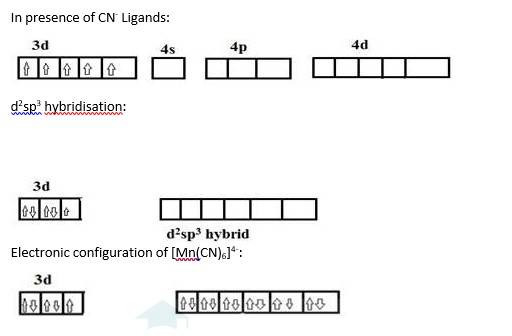
9.10 The hexaquomanganese(II) ion contains five unpaired electrons, while the hexacyanoion contains only one unpaired electron. Explain using Crystal Field Theory.
[Mn (H2O)6]+2 | [Mn (CN)6]4- |
Oxidation state of manganese: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (0) = 2 X = + 2 | Oxidation state of manganese: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (-1) = -4 X = + 2 |
Outer electronic configuration of Mn = d5 | Outer electronic configuration of Mn = d5 |
H2O is a weak field ligand so it does not cause pairing of the electron. Therefore Mn undergoes sp3d2 hybridization. Geometry is octahedral. Therefore the 5 unpaired electrons from the d orbital remain as it is. | CN is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of the electron (5 electrons get paired to form 2 pairs and one unpaired electron). Therefore Mn undergoes d2sp3 hybridization. Geometry is octahedral. |
Mn in + 2 oxidation state:
9.13 Explain with two examples each of the following: coordination entity, ligand, coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
(1) Coordination Entity: Coordination entity is a charged entity having positive or negative charge in which the central atom is surrounded by molecules which may be neutral/negatively charged called Ligands
Examples:
i. Cationic Complexes: [Cu (H2O)6]2+, [Al (H2O)6]3+
ii. Anionic Complexes: [CuCl4]2-, [Al (H2O)2 (OH)4]-
iii. Neutral Complexes: [Co (NH3)4 Cl2], [Ni (CO)4]
(2) Ligands: Ligands are the neutral or negatively charged entities surrounding the central metal atom of the coordination complex which possesses at least one unshared pair of electrons
Example: F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, H20, and NH3
(3) Coordination Number: Coordination Number which is also called as Ligancy is the total number of ligands that are attached to the central metal atom of the coordination
Example: [Cr (NH3)2Cl2Br2]? has Cr3+ as its central cation, and has a coordination number of 6
Al3+ has coordination number 4 in [AlCl4]- but 6 in [AlF6]3-.
(4) Coordination polyhedron: Coordination polyhedron is defined as the spatial arrangement of the ligands around the central atom of a coordination
Example:
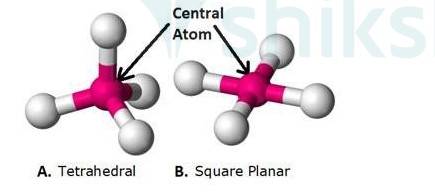
In the figure: The pink Sphere depicts the central atom of the coordination entity.
(5) Homoleptic complexes: Complexes in which the central metal atom is surrounded only by the same kind of donor groups which are the ligands.
Example: [Ag (CN)2]-, [Fe (CN6)]4+ etc.
(6) Heteroleptic complexes: Complexes in which the central metal atom is surrounded by more than one kind of donor groups which are the ligands.
Example: [Co (NH3)4 Cl2] +, [Co (NH3)5 Cl]2+
9.7 [Fe(H2O)6 ] 3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe(CN)6 ] 3– is weakly paramagnetic. Explain.
In [Fe (H2O)6]3+
Electronic configuration of Fe is: [Ar]3d64s2
[Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Fe+3 = [Ar]3d5
Outer electronic configuration of Fe+3 = 3d5
Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (0) = 3
X = + 3
In [Fe (CN)6]3-
Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (-1) = -3
X = + 3
In both the compounds Fe is in + 3 oxidation state.
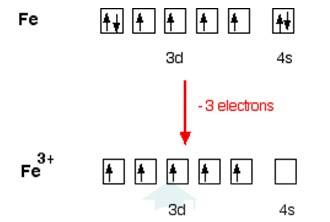
In case of [Fe (H2O)6]3+
H2O is weak field ligand so it does not pair the unpaired electron. Total no. of the unpaired electron, n =5, Spin only magnetic moment is given by:
μ = [n (n + 2)]1/2
μ = [5×7]1/2
μ = 5.916BM
In case of [Fe (CN)6]3-
CN- is a strong field ligand so it pairs up the electron.
Total no. of unpaired electrons = 1
Spin only magnetic moment is given by:
μ = [n (n + 2)]1/2
μ = [1×3]1/2
μ = 1.732BM
as we can see spin only magnetic moment of [Fe (H2O)6]3+ is more than [Fe (CN)6]3- .
so, [Fe (H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe (CN)6]3 weakly paramagnetic.
Fe in ground state
Fe in + 3 oxidation state
Electrons from 5 CN- ligands
9.20 Draw the structures of optical isomers of: (i) [Cr(C2O4)3] 3– (ii) [PtCl2(en)2] 2+ (iii) [Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+
Optical isomers are the one which rotate the plane polarized light by a certain angle when passed through them and are mirror images of each other, also called as stereoisomer.
(i) C2O4 2- is a bidentate ligand so it can attach to central atom at two sites, forming a chelate ring. In the complexes of this type, three symmetrical bidentate chelating ligands AA are coordinated to the central metal atom M. Such complexes do not possess any element of symmetry and are optically active. Moreover, these complexes can be resolved into optical
(ii) In this complex Cl is an unidentate ligand with one site of attachment whereas -en (ethylenediamine) is bidentate ligand with two sites of attachment. The complexes in which two symmetrical bidentate chelating ligands AA and two monodentate ligands a, are coordinated to central metal atom M, exhibit the phenomenon of optical isomerism and can be resolved into their optical
An example of this type of complexes is given as shows both geometrical as well as optical isomerism. Its cis form is unsymmetrical, while the trans form is symmetrical because it contains a plane of symmetry. Hence, optical isomerism is shown by cis form.
(iii) In this there are three types of ligands. One is ammonia which is neutral (nitrogen donates the lone pair of electron to metal), Cl - ligand is unidentate and -en is bidentate ligand. Coordination number is 6. Two optical isomers are possible due to presence of 3 types of
9.28 What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of ?o decide the actual configuration of d orbitals in a coordination entity?
The difference between the energies of the two set of the d orbitals is called as crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). The degenerate d orbitals split into two levels i.e t2g and eg level due to the presence of the ligands. This splitting of the degenerate orbitals due to the ligand is called as crystal field splitting and the energy difference between the two levels is called as crystal field splitting energy.
After the splitting of the degenerate orbitals has taken place the filling of the electrons takes place. Now first 3 electrons goes into the lower energy three t2g orbitals. The fourth electron can be filled in two ways:
It can enter the t2g orbitals causing pairing up of the electron (giving rise to t2g4e 0 electronic configuration) or it can enter into higher energy eg orbital (giving rise to t2g3e 1 electronic configuration). If the CFSE value of ligand is more than energy required for the pairing up of the electron then it will result in the pairing of electron (2 case) but if the CFSE value of ligand is less than the pairing energy of the electron then it will cause the electron to enter in higher energy eg orbital. (1 case)
9.17 Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following:
(i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl
(iii) [Ti(H2O)6] 3+
(iv) [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl
(v) [Mn(H2O)6] 2+
(vi) [NiCl4] 2–
(vii) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(viii) [Co(en)3] 3+
(ix) [Ni(CO)4]
(i) Starting with cation, the complex ion contains six ammonia molecules with cobalt in + 3 oxidation The name of compound: [Co (NH3)6]Cl3 is hexaamminecobalt (III) chloride.
(ii) The complex ion is cation, so there are 2 ammonia molecules, one chloride ion and methyammine molecule qith platinum in + 2 state. Going in alphabetical order, the name of compound: [Pt (NH3)2Cl (NH2CH3)]Cl is diamminechloridomethylammineplatinum (II)
(iii) It is a complex cation with six water molecules and titanium atom in + 3 state. The name of the compound: [Ti (H2O)6]3+ is hexaaquatitanium (III) ion
(iv) The complex ion is cation with cobalt in + 3 state and with four ammonia molecules etetraammine, one chloride ion and nitrate ion. The name of the compound: [Co (NH3)4Cl (NO2)]Cl is tetraamminechloridonitritocobalt (III) chloride.
(v) The complex ion is cation with manganese in + 2 state and six water The name of compound: [Mn (H2O)6]2+ is hexaaquamanganese (II) ion.
(vi) The complex is anion with nickel in + 2 state and with four chloride ions. The name of the compound: [NiCl4]2– is tetrachloridonickeltate (II)
(vii) The complex is cation with nickel in + 2 state and six ammonia molecules. The name of compound: [Ni (NH3)6]Cl2 is hexaamminenickel (II) chloride.
(viii) The complex is cationwithcobalt in + 3 stateand there is a bidentate ligand called as The name of compound : [Co (en)3]3+ is tris (ethylenediamine)cobalt (III) ion.
(ix) It is neutral complex with four carbonyl molecules and cobalt in 0 state. The name of compound: [Ni (CO)4] is tetracarbonylcobalt (0).
9.2 Write the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds:
(i) [Co(NH3 )6 ]Cl3
(ii) [Co(NH3 )5Cl]Cl2
(iii) K3 [Fe(CN)6 ]
(iv) K3 [Fe(C2O4 )3 ]
(v) K2 [PdCl4 ]
(vi) [Pt(NH3 )2Cl(NH2CH3 )]
(i) Hexaminecobalt (III)chloride
(ii) Pentaaminechloridecobalt (III)chloride
(iii) Potassium hexacyanoferrate (III)
(iv) Potassium trioxalatoferrate (III)
(v) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate (II)
(vi) Diaminechloride (methylamine)platinum (II)chloride
9.18 List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
Isomers are the compounds which have same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms in space. There are principle two types of isomerism:
(i) Stereo isomerism
(ii) Geometrical isomerism
(iii) Optical isomerism
(iv) Structural isomerism
(v) Ionisation isomerism
(vi) Linkage isomerism
(vii) Coordination isomerism
(viii) Solvate isomerism
Geometrical isomerism comes into existence by the different spatial arrangement of groups around the central metal atom. Similar groups may either be arranged on the same side or on opposite sides of the central metal atom. This gives rise to two types of isomers called cis and trans isomers. When groups under consideration are arranged on the same side of the central metal atom, isomers are called cis isomers and when the groups under consideration are spatially placed on the opposite sides, isomers are called trans isomer.
9.19 How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities? (i) [Cr(C2O4)3] 3– (ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
(i) No geometrical isomer is possible for [Cr (C2O4)3]3– because the ligand C2O 2- is bidentate ligand (which have two sites of attachment to the central atom) and also in the coordination sphere it is the only ligand bond to it.
(ii) In the coordination sphere of [Co (NH3)3Cl3] there are two types of ligands present i.e NH3 and Cl- . Coordination number is There are 2 isomers possible for the complex:
Facial: In this isomer one type of ligand say NH3 forms the face of the square bipyramidal (triangular) structure.
Meridional: In this isomer one type of ligand are along the central axis of the pyramidal structure.
9.34 Write down the IUPAC name for each of the following complexes and indicate the oxidation state, electronic configuration and coordination number. Also give stereochemistry and magnetic moment of the complex:
The complex is an anion with chromium as central atom, 2 water molecules and 2 oxolate ions with -2 negative charge Balance overall charge as 0, we get oxidation state of Cr as:
X + 2 (0) + 2 (-2) = -1 X = + 3.
Name of compound: potassium diaquadioxolatochromate (III) trihydrate. Electronic configuration of Cr: 3d3, t2g3
9.33 Give the oxidation state, d orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complexes:
(i) K3[Co(C2O4)3]
(ii) cis-[CrCl2(en)2]Cl
(iii) (NH4)2[CoF4]
(iv) [Mn(H2O)6]SO4
(i) Overall charge balance:
X + 3 (-2) = -3 X = + 3
Oxidation state of Co is + 3.
As there are 3 oxolate ion and being bidentate, coordination no. Of complex is 6. So it is octahedral complex.
d orbital occupation: t2g6eg0 (oxolate ion is weak field ligand, does not cause pairing of electron as the energy required for pairing of electron is more than CFSE).
(ii) Overall charge balance:
X + balance4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2
Oxidation state of Co is + 2.
As there are 4 fluoride ion, coordination no. Of complex is 4 i.e. Tetrahedral complex.
d orbital occupation: eg4t2g3 (fluoride ion is weak field ligand, does not cause pairing of electron as the energy required for pairing of electron is more than CFSE).
(iii) Overall charge balance:
X + 2 (-1) + 2 (0) = + 1 X = + 3
Oxidation state of Cr is + 3
Coordination no. Of complex is 6. (-en is a bidentate ligand). Octahedral complex. d orbital complex: t2g3
(iv) Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (0) = + 2 X = + 2
Oxidation state of Mn is + 2.
Coordination no. Of complex is 6. Octahedral complex.
d orbital occupation: t2g3e 2 (water is weak field ligand, does not cause pairing of the electron).
9.21 Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of:
(i) [CoCl2(en)2] +
(ii) [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2] 2+
(iii) [Co(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+
Two types of ligand : chloride ion is unidentate ligand and -en (ethylenediamine) is bidentate ligand with two sites of attachment. The complexes in which two symmetrical bidentate chelating ligands AA and two monodentate ligands a, are coordinated to central metal atom M, exhibit the phenomenon of optical isomerism and can be resolved into their optical isomers.
An example of this type of complexes is given as shows both geometrical as well as optical isomerism. Its cis form is unsymmetrical, while the trans form is symmetrical because it contains a plane of symmetry. Hence, optical isomerism is shown by cis form.
9.23 Aqueous copper sulphate solution (blue in colour) gives: (i) a green precipitate with aqueous potassium fluoride and (ii) a bright green solution with aqueous potassium chloride. Explain these experimental results.
Copper sulphate exists as [Cu (H2O)4]SO4 . It is blue in colour due to presence of the [Cu (H2O)4]2+ ions.
When KF is added water is replaced by fluoride ion and green colour is due to [Cu (F)4]2- ions.
When KCl is added water is replaced by chloride ion and bright green colour is due to presence of [CuCl4]2- ions.
In both the cases water, weak field ligand is replaced by fluoride and chloride ions.
9.11 Explain the bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner’s postulates.
Bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner's postulates is explained as:
(a) Metals can show two types of valencies which are Primary valency and Secondary
1. Primary Valency: Primary Valency shows Oxidation Primary valencies are ionizable.
2. Secondary Valency: Secondary Valency shows coordination These are non-ionizable.
(b) Both Primary and secondary valency of the metal are to be satisfied which is done by negative ions in case of primary valency and negative or neutral species in case of secondary
(c) Metals have a fixed number of secondary valencies/ Coordination number around the central atom, these secondary valencies are placed in such a way which leads to a specific geometry of the coordination
9.4 Give evidence that [Co(NH3 )5Cl]SO4 and [Co(NH3 )5 (SO4 )]Cl are ionisation isomers.
These compounds give different ions in aqueous solution. This can be tested by using AgNO3 solution and BaCl2
[Co (NH3)5Cl]SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (ppt)
[Co (NH3)5Cl]SO4 (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → no reaction
[Co (NH3)5 (SO4)]Cl (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → no reaction
[Co (NH3)5 (SO4)]Cl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgCl (ppt)
Hence, they give different precipitates with different solutions. Thus, they are ionisation isomers.
9.14 What is meant by unidentate, didentate and ambidentate ligands? Give two examples for each.
Ligands are the neutral or negatively charged entities surrounding the central metal atom of the coordination complex which possesses at least one unshared pair of electrons.
Based on the number of donor sites of these ligands, Ligands are classified as:
Unidentate ligands: These Ligands which have only one donor site are called unidentate ligands.
Example: F-, Cl – etc.
Didentate ligands: These Ligands which have only two donor site are called didentate ligands.
Example: Ethane-1,2-diamine, Oxalate ion etc.
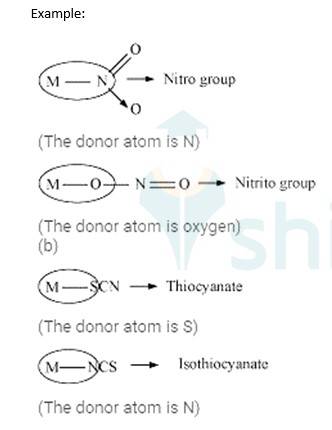
Ambidentate ligands: These ligands which can attach them with the central metal atom by two different atoms are called as ambidentate ligands.
9.22 Write all the geometrical isomers of [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py)] and how many of these optical isomers?
There are four different types of ligands present in the complex. So, by fixing the position of 2 ligands we get 2 geometrical isomers and by changing the position of fixed isomer we get one more geometrical isomer.
Since it is tetrahedral complex so it should be optically active . But however it has not been possible to resolve optically active d and l forms of such a complex due to its complicated nature.
9.24 What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when H2S(g) is passed through this solution?
CuSO4 + KCN? K2 [Cu (CN)4] + K2SO4
[Cu (H2O)4]2+ + 4CN-? [Cu (CN)4]2- + 4H2O
The coordination entity formed is K2 [Cu (CN)4] .
IUPAC name of the coordination entity is potassium tetracyanocuprate (II). It is a very stable complex. The copper atom present inside the coordination sphere does not separate out to form copper ions and cyanide ions due to strong bond between them.It does not ionize to give Cu2+ ions and hence on adding H2S, since there are no copper ions present so no precipitate of copper sulfide is formed.
9.25 Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory:
(i) [Fe(CN)6] 4–
(ii) [FeF6] 3–
(iii) [Co(C2O4)3] 3–
(iv) [CoF6] 3–
(i) In the coordination entity iron exists in + 2 oxidation state. Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (-1) = -4 X = + 2.
Its electronic configuration is: 3d6
CN- is strong field ligand so it causes pairing of the unpaired electron and undergoes hybridisation to form 6 d2sp3 hybrid orbitals to be filled by the six cyanide ions. It's geometry is octahedral with no unpaired electrons and hence is diamagnetic complex.
9.26 Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
In octahedral complex the splitting of the d orbital will be such a way that the dx2-y2 and dz2 orbitals which face towards the axes along the direction of the ligand will experience more repulsion and will be raised in the energy and the other three orbitals which are directed between the axes are lowered in energy.
9.29 [Cr(NH3)6] 3+ is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4] 2– is diamagnetic. Explain why?
Overall charge balance in [Cr (NH3)6]3+ complex:
X + 6 (0) = + 3 X = + 3
Cr is in + 3 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Cr in + 2 state: 3d3 . Now ammonia is a weak field ligand so it not causes pairing of the unpaired electron and undergoes hybridisation to form 6 sp3d2 hybrid orbitals filled by the six ammonia ligands. It's geometry is octahedral with unpaired electrons and hence is paramagnetic complex.
In case of [Ni (CN)4]2– ion :
Overall charge balance in [Ni (CN)4]2–complex:
X + 4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2
Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Ni in + 2 state: 3d8. Now cyanide ion is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of the unpaired electron and undergoes hybridisation to form 4 dsp2 hybrid orbitals filled by the four cyanide ligands. It's geometry is square planar with no unpaired electrons and hence is diamagnetic complex.
9.1 Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt(III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane–1,2–diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane–1,2–diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanidoferrate(II)
(i) [Co (NH3)4 (H2O)2]Cl3
(ii) K2 [Ni (CN)4]
(iii) [Pt (en)3]NO3
(iv) [Pt (NH3)BrCl (NO2)]
(v) [Pt (Cl)2 (en)2] (NO3)2
(vi) Fe4 [Fe (CN)6]3
9.27 What is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand.
The strong ligands have higher splitting power of d orbitals of the central metal ion, whereas weak ligand has relatively lower splitting power of d orbitals of the central metal ion. The energy difference between t2g and eg sets of d orbitals is CFSE. The strength of the ligands depend on the magnitude of Δ . Strong ligands have larger value of CFSE and in case of weak ligands the CFSE values are smaller. The common ligands can be arranged in a series in the order of their decreasing field strength, as follows.
This series depends on the power of splitting the d orbitals and is called spectrochemical series, The order of field strength of the common ligands neither depends on the geometry of the complex the nature of central metal ion.
9.30 A solution of [Ni(H2O)6] 2+ is green but a solution of [Ni(CN)4] 2– is colourless. Explain.
In case of [Ni (H2O)6]2+ H2O is a weak field ligand, so it does not cause the pairing of the unpaired electron of Ni2+ ion. Thus there is possibility of the intra d-d transition from the d orbital of lower energy to that of higher energy. Thus the light is absorbed from the visible region and complimentary colour is observed. But in case of [Ni (CN)4]2– CN- is strong field ligand.
Therefore it will cause pairing of the unpaired electrons of Ni2+ ion. There are no unpaired electrons present, so there is no d-d transition and hence it is colourless.
9.31 [Fe(CN)6] 4– and [Fe(H2O)6] 2+ are of different colours in dilute solutions. Why?
The colour of the particular complex compound depends on the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). This CFSE depends on the nature of the ligand attached to the metal atom. In case of [Fe (CN)6]4– and [Fe (H2O)6]2+ the colour differs due to differences in CFSE .
CN- is a strong field ligand so will have high CFSE than H2O with a low value of CFSE. There is absorption of the energy from the visible region for the d-d transition and corresponding complimentary colour is observed. Thus there is the colour difference.
9.32 Discuss the nature of bonding in metal carbonyls.
Compounds containing carbonyl
Ligands only are known as homoleptic carbonyl. Such types of compounds are formed by most of the transition metals. These metal carbonyls always have simple, well-defined structures. In metal carbonyls the metal - carbonyl bond possess both s and p.character. M-C-bond is sigma bond. It is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons of the carbonyl carbon into the vacant orbital of the metal. The M-C pi bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electron from a filled d orbital of a metal into the vacant antibonding? orbital of carbon monoxide. Such type of metal to ligand bonding creates a synergic effect which strengthens the bond between CO and metal.
Benefit of using NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5
Class 12 Coordination Compounds NCERT solutions benefits are as follows:
- Enhance the conceptual knowledge
- Improve problem solving skills
- Good for revision and practice
- Boost confidence in the students
NCERT Chemistry Chapter 5 Coordination Compounds – FAQs
Students can check Coordination Compounds ncert solution pdf faqs below.
Explore exams which ask questions on Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th
Select your preferred stream
Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 12th Exam
