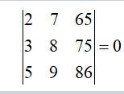
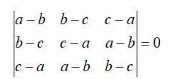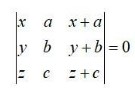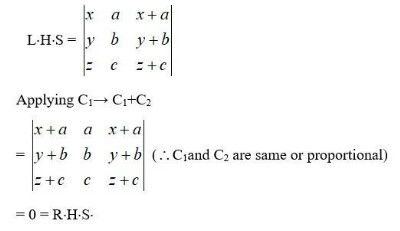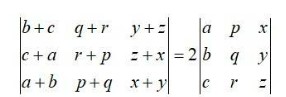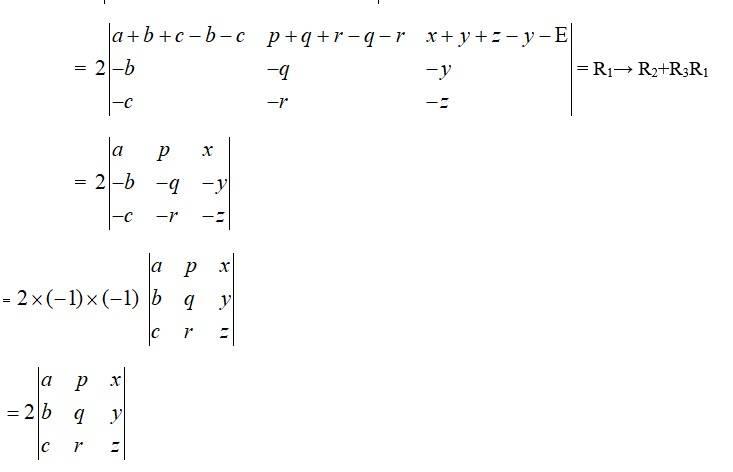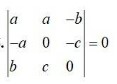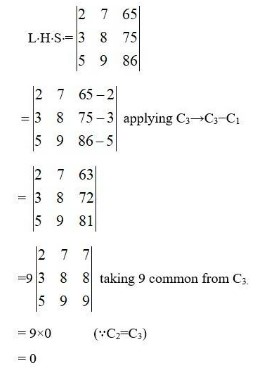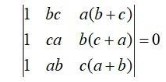Class 12 Determinants is an important chapter as it has a variety of applications in various fields including Social Science, Economics, Science, Engineering etc. Determinants Class 12 covers many properties of determinants, cofactors, minors and applications of determinants in finding inverse of a square matrix, adjoint, and area of a triangle, and inconsistency of system of linear equations. The chapter also covers finding the solution of linear equations in two or three variables using the inverse of a matrix.
The experts at Shiksha, with years of experience, have created the Class 12 determinants NCERT solutions to help students score well in their CBSE Board exam and other competitive exams like JEE Mains. It will help students to understand the concept better and know how to solve even the complex problems of the chapter. It offers step-by-step solutions to all the questions of this chapter in the NCERT textbook.
If you are looking for notes on all topics for Class 12 Maths with solved examples, PDF, and questions and answers, check Class 12 Maths Notes.
- Glance at Determinants Class 12
- Class 12 Math Determinants NCERT Solution PDF: Free Download
- Class 12 Math Determinants: Key Topics, Weightage
- Important Formulas of Class 12 Determinants
- Exercise-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Math Chapter 4 Determinants
- NCERT Class 12 Math Determinants Exercise 4.1 Solutions
Glance at Determinants Class 12
See below the quick summary of the Determinants Class 12 NCERT Solutions:
- The chapter includes many more such concepts and formulas.
Explore here the NCERT solutions of all three subjects - Chemistry, Physics, and Maths of Class 11 and Class 12. The subject matter experts at Shiksha have created all these solutions.
Class 12 Math Determinants NCERT Solution PDF: Free Download
Students can download the free Determinants Class 12 PDF from the link below. It will help them understand the concepts clearly and improve their exam preparation.
Class 12 Math Chapter 4 Determinants Solution: Free PDF Download
Related Links
| Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions | NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 | NCERT Class 12 Notes |
Class 12 Math Determinants: Key Topics, Weightage
In Class 12 Maths Chapter 4, the focus area of preparation for students should be determinants, their properties, and applications. To score well in the exams, the students should master the fundamental concepts and practice a variety of problems. The following topics are covered in this chapter:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 4.1 | Introduction |
| 4.2 | Determinant |
| 4.3 | Area of a Triangle |
| 4.4 | Minors and Cofactors |
| 4.5 | Adjoint and Inverse of a Matrix |
| 4.6 | Applications of Determinants and Matrices |
Class 12 Determinants Weightage in JEE Mains
| Exam | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| JEE Main | 2 questions | 6.6% |
Important Formulas of Class 12 Determinants
Determinants Important Formulae for CBSE and Competitive Exams
Students must learn important formulae and basic concepts of the Class 12 Determinants for a better grasp of the concepts. Students can also use these formulae to solve NCERT Determinants exercises.
Determinant of a Matrix: Students can check the formula to find the value of determinant for Matrix.
Determinant of a Matrix: Students can check the formula to find the value of determinant for Matrix.
Cramer's Rule:
Solution of
:
where
is the matrix obtained by replacing the
column of
with
.
Properties of Determinants:
-
-
-
- for an matrix.
-
-
Adjoint and Inverse:
Exercise-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Math Chapter 4 Determinants
Class 12 Determinants chapter deals with important topics such as finding determinants of square Matrices, findingarea of triangle with help of determinant, co-factors, minors, adjoint and inverse of a Matrix. consistency of linear systems. All exercise deals with different concepts, Class 12 Determinants exeercies 4.1 deals with the basics of determinants and finding the value. Class 12 Determinants Exercise 4.2 deals with finding the area of triangle. Class Determinants Exercises 4.3 deals with finding Minors and Co-factors. Class 12 Determinants Exercise 4.4 focuses on adjoints and inverse of Matrix. Class Determinants Exercise 4.5 deals with checking consistency of system of equations. Students can check Exercise-wise Class 12 Chapter 4 Determinants NCERT Solutions below;
NCERT Class 12 Math Determinants Exercise 4.1 Solutions
Ex 4.1 Class 12 Maths NCERT solutions discusses basic concept of determinants, starting with the calculation of determinants for and matrices. This exercise helps in building foundational blocks of the determinants. The Determinants Exercise 4.1 Solutions consist of 8 Questions including 2 Long, 5 Short Answers, 1 MCQ. Students can check complete solution of Exercuse 4.1 below;
Determinants Exercise 4.1 SolutionsQ1.Evaluate the determinants in Exercises 1 and 2.
|
| A.1. 2×(−1) – 4×(−5) = −2+20 = 18 |
| Q2.(i) (ii) |
| A.2. (i)
= cos²θ + sin²θ =1 (ii)
= + − − + +1 – + 1 = - + 2 |
| Q3.If , then show that | 2A | = 4 | A | |
| A.3.Given, A= So, 2A= 2 = . L.H.S. = = = 2×4 – 4×8 = 8−32 = −24 R.H.S. = 4 = 4 = 4(1×2 – 2×4) = 4[2 − 8] = 4[−6] = 24. LHS = RHS |
| Q4. If A= |
Commonly asked questions
16.
LHS
Multiplying R1, R2& R3 by x, y&z.
Taking xyz common from c3.
=
Expanding along c3 we get,
= 1
= (y-x)(z-x). Taking (yx) & (zx) common from R1 and R2.
= (y-x)(z-x). Taking (y-x) & (z-x) common from R1 and R2.
= (y-x)(z-x)[(y + x)(z2 + x2 + zx) - (z + x)(y2 + x2 + xy)]
= (y-x)(z-x)[yz2 + yx2 + xyz + xz2 + x3 + x2z-zy2-zx2-xyz-xy2-x3-x2y]
= y-x)(z-x)[yz2-zy2 + xz2-xy2]
= (y-x)(z-x)[yz (z-y) + x(z2-y2)]
= y-x)(z-x)(z-y)[yz + x (z + y)]
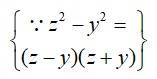
= (- 1)(x-y)(z-x)(- 1)(y-z)[yz+ 1 xz + xy]
= (x-y)(y-z)(z-x)(xy + yz + xz). = R.H.S
Kindly Consider the following
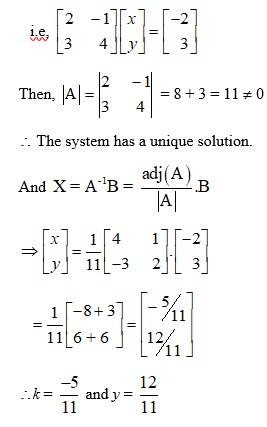
58.
The given system of eqn in matrix form is AK = B
10. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
=0=RHS
20.
LHS =
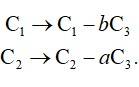
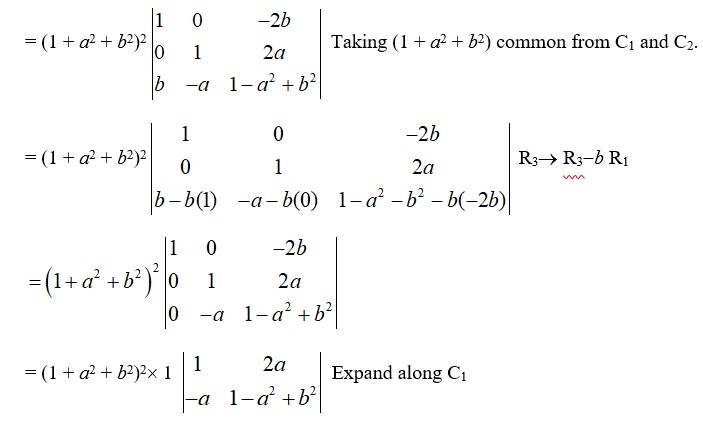
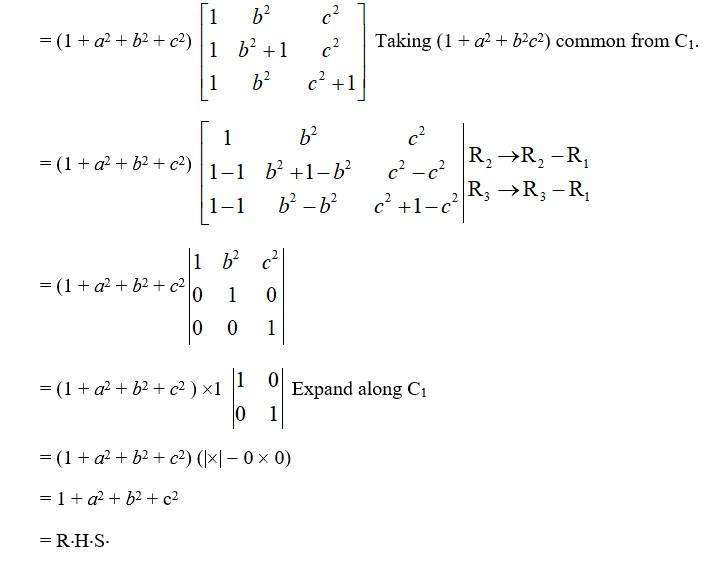
= (1 + a2 + b2)2 [(1 -a2 + b2) - 2a (-a)]
= (1 + a2 + b2)2 (1 -a2 + b2 + 2a2)
= (1 + a2 + b2)2 (1 + a2 + b2)
= (1 + a2 + b2)3 = R.H.S.
Using the property of determinants and without expanding in Exercises 1 to 7, prove that:
Kindly go through the solution
Kindly Consider the following
60.
The given system of equation in matrix form is
AK = B
67. Prove that the determinant 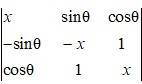 is independent of θ.
is independent of θ.
Kindly go through the solution
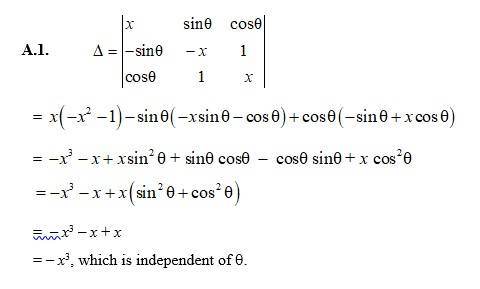
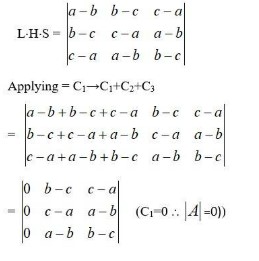
By using properties of determinants, in Exercises 8 to 14, show that:
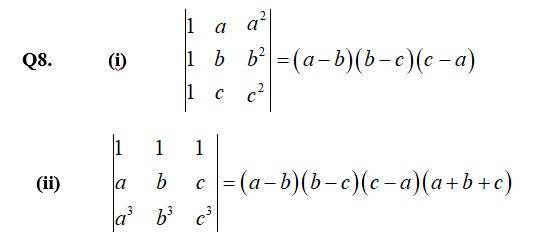
=(b-a)(c-a)[(c+a)-(b+a)]
=(b-a)(c-a)[(c+a – b – a)]
=(b-a)(c-a)(c-b)
=(-1)(a-b) ×(-1)(b-c)(c-a)
=(a-b)(b-c)(c-a).
= R.H.S.
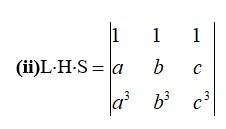
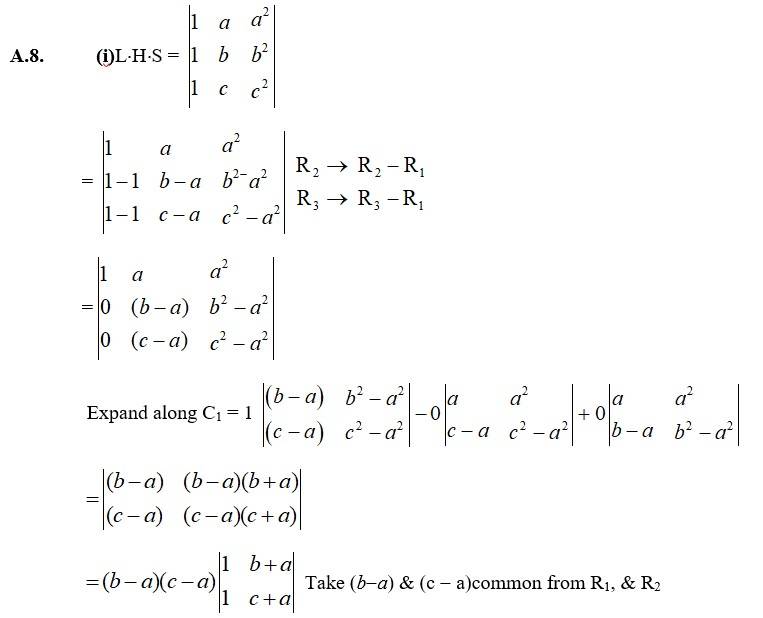
=
Expanding along R1
=
= (ba)(ca)
= (b-a)(c-a) {(c2 + a2 + ab)- (b2 + a2 + ab)}
= (b-a) (c -a) {c2 + a2 + ab-b2-a2-ab}
= (b-a) (c-a)(c2-b2 + ac-ab)
= (b-a)(c-a)(c-b)(c + b) + (c-b) a}
= (b-a)(c-a)(c-b)(a + c + b).
= (- 1)(a-b)(c-a)(- 1)(b-c)(a + c + b)
= (a-b)(b-c)(c-a)(a + c + b)
= R.H.S.
32. Using Cofactors of elements of third column, evaluate
Given,
Co-factor of elements of third column

∴ Δ = a13A13 + a23A23 + a33A33
= yz (z-y) + zx [- (z-x)] + xy (y-x)
= y z2-y2z-z2x+ zx2 + xy2-x2y.
= yz2-y2z+ (xy2-xz2) + (zx2-x2y)
= yz (z-y) + x (y2 – z2) -x2 (y-z)
= -yz (y-z) + x (y + z) (y-z) -x2 (y-z)
= (y-z) [-yz + x (y + z) -x2]
= (y-z) [-yz + xy + xz-x2]
= (y-z) [-y (z-x) + x (z-x)]
= (y-z) (z-x) (x -y)
17. (i)
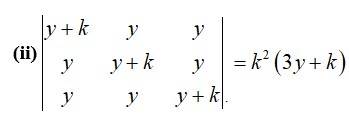
(i) LHS =
R1→R1 + R2 + R3
Taking (5x + 4) common from R1.
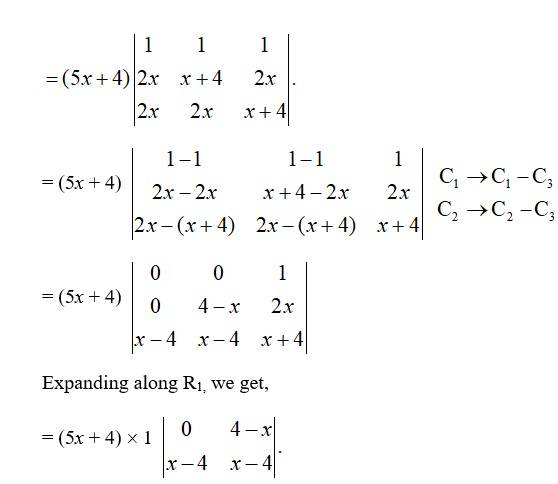
= (5x + 4)[0 - (4 -x)(x- 4)]
= (5x + 4)(4 -x)(4 -x)
= (5x + 4)(4 -x)2 = R.H.S.
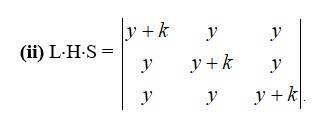
= R1→R1 + R2+ R3
= (3y + k)
65. solve the system of equations.
Kindly go through the solution
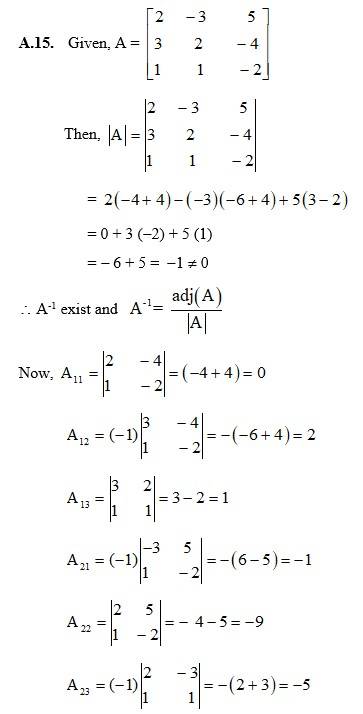
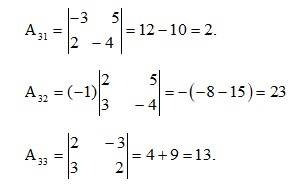
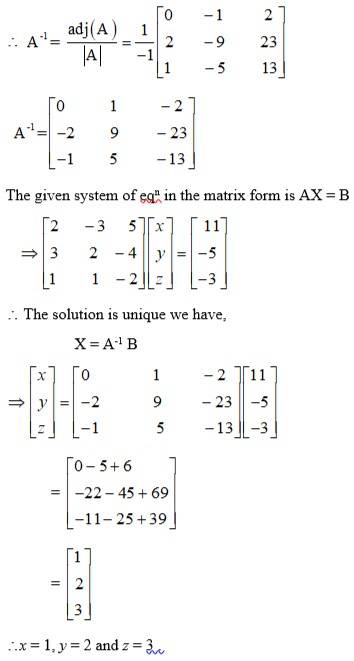
61.
The given system of solution in matrix form is AK = B.
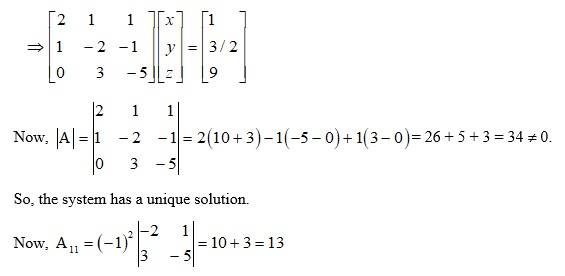
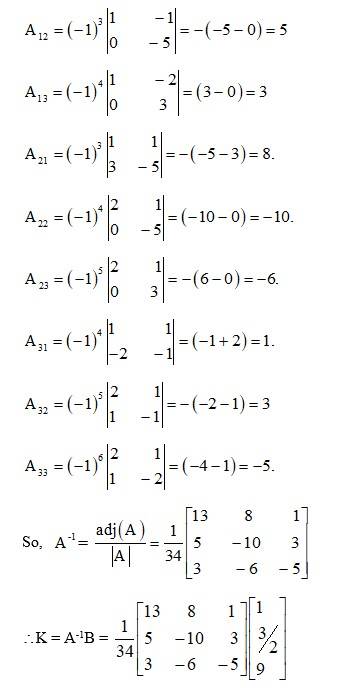
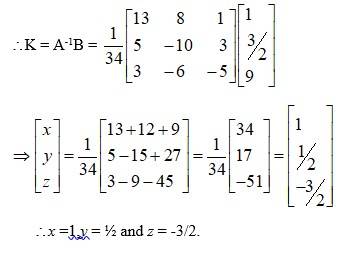
62.
The given system of eqn can be written in matrix form as AK = B.
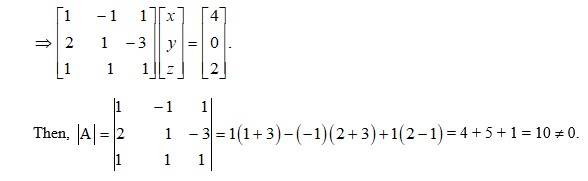
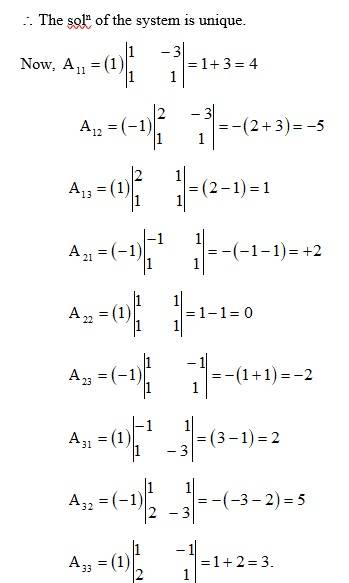
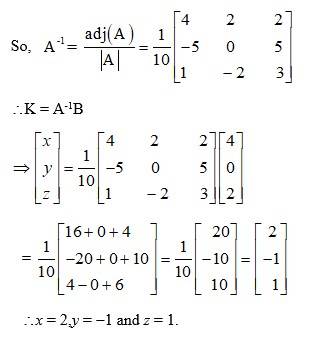
13. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
70. If a, b and c are real numbers and
Show that either a+b+c=0 or a=b=c=0
Taking 2(a + b + c) common from R1
Either i.e. a+b+c=0 or
and
Expanding along
Multiplying by -2
Either a+b+c=0 or a=b=c
28. If area of triangle is 35 sq units with vertices (2, – 6), (5, 4) and (k, 4). Then k is
(A) 12 (B) –2 (C) –12, –2 (D) 12, –2
Given,
Area of triangle = 35 sq. Units
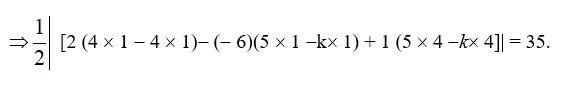
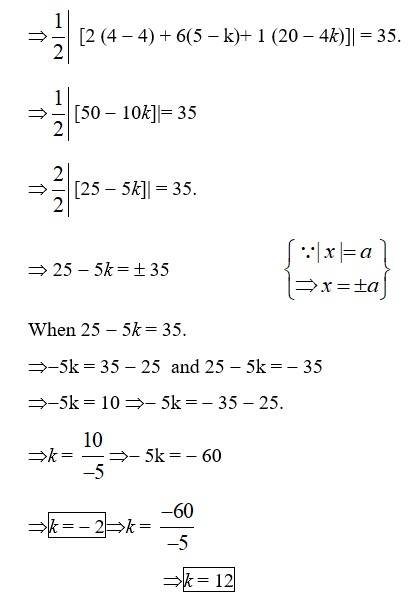
∴ Option D is correct.
Kindly Consider the following
42.
Kindly go through the solution
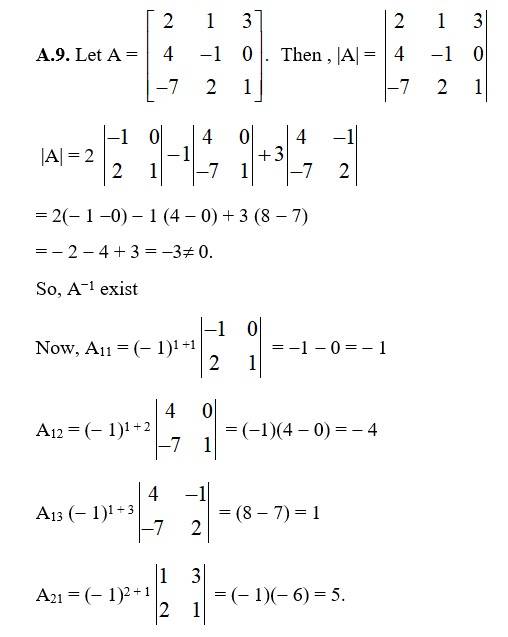
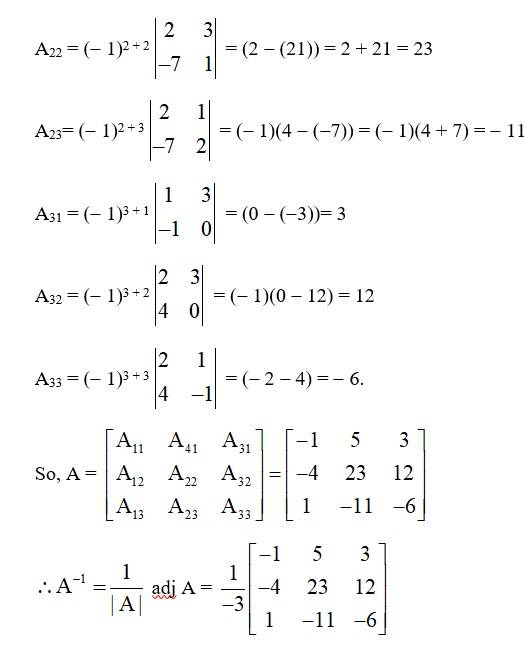
14. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution

=a2b2c2× (−2)
= a2b2c2× (−2)× (−2)
= 4a2b2c2
= R.H.S.
85. Let A = , where 0 ≤θ≤ 2. Then
(A) Det (A) = 0 (B) Det (A) (2, ∞)
(C) Det (A) (2, 4) (D) Det (A) [2, 4]
Kindly go through the solution
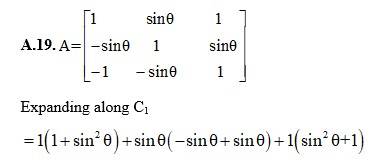
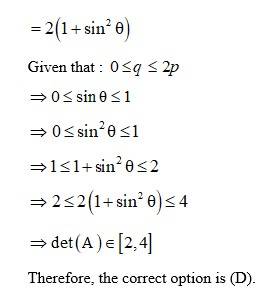
5. Evaluate the determinants
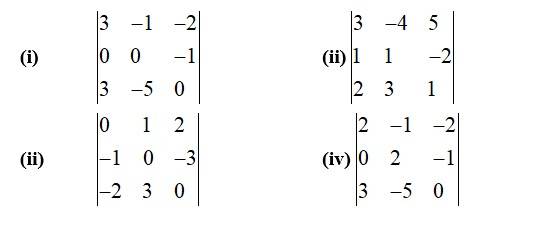
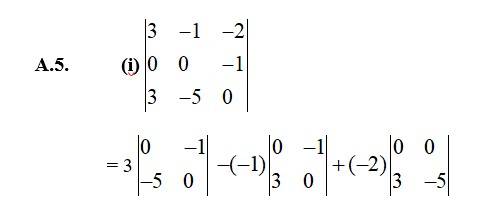
= 15 + 3
= 12
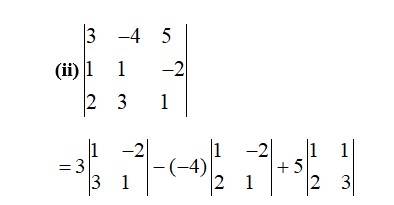
=3 [1×1− (−2)×3]+4 [1×1− (−2)×2]+5 [3×1−2×1]
= 3 [1+6]+4 [1+4]+5 (3−2)
= 3×7+4×5+5×1
= 21+20+5
= 46
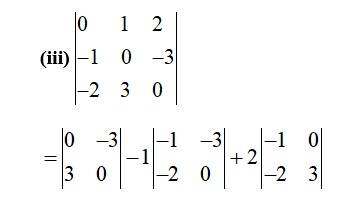
= 0 –1 [ − 1×0 – (−2)× (−3)] + 2 [−1×3 – (−2)×0]
= (− 1)× ( − 6)+2 (− 3)
= 6 – 6
= 0
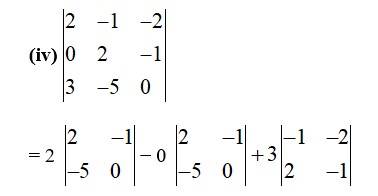
= 2 [2×0− ( − 5)× (−1)]+3 [ (−1)× (− 1) – (− 2)×2]
= 2 (−5)+3 (1+4)
= 2 (−5) + 3× (5)
= −10+15
= 5
33. If and is Cofactors of then value of is given by
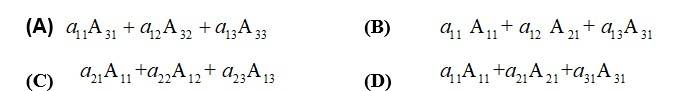
Option D is correct.
Kindly Consider the following
37.
Kindly go through the solution
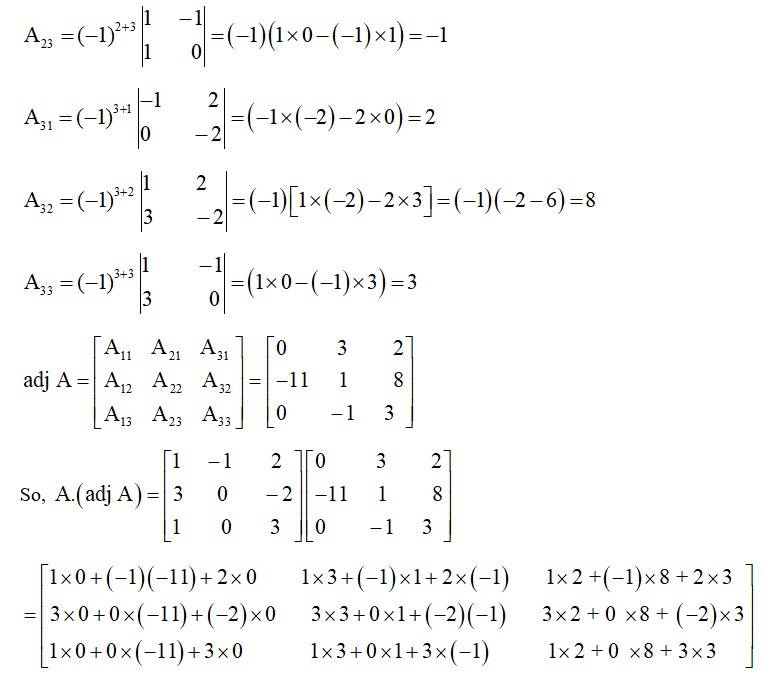
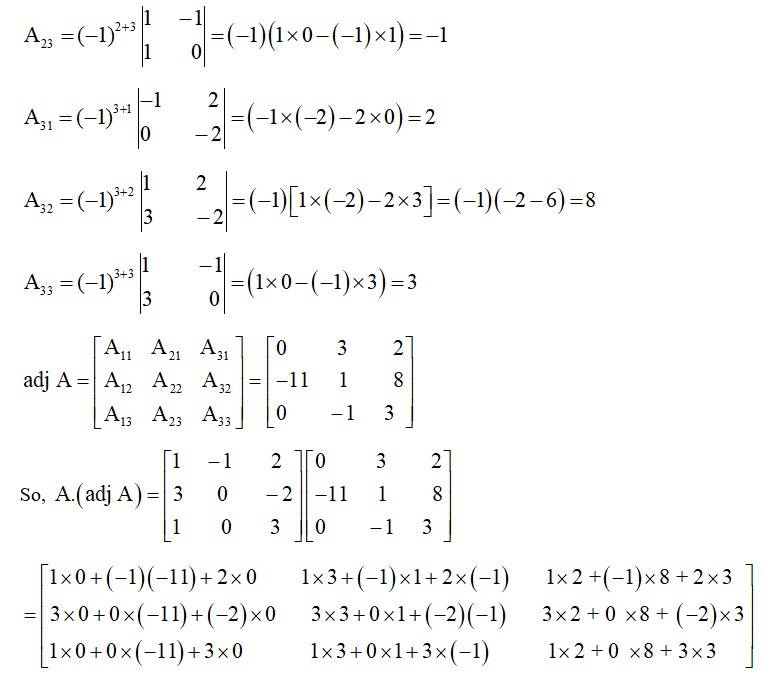
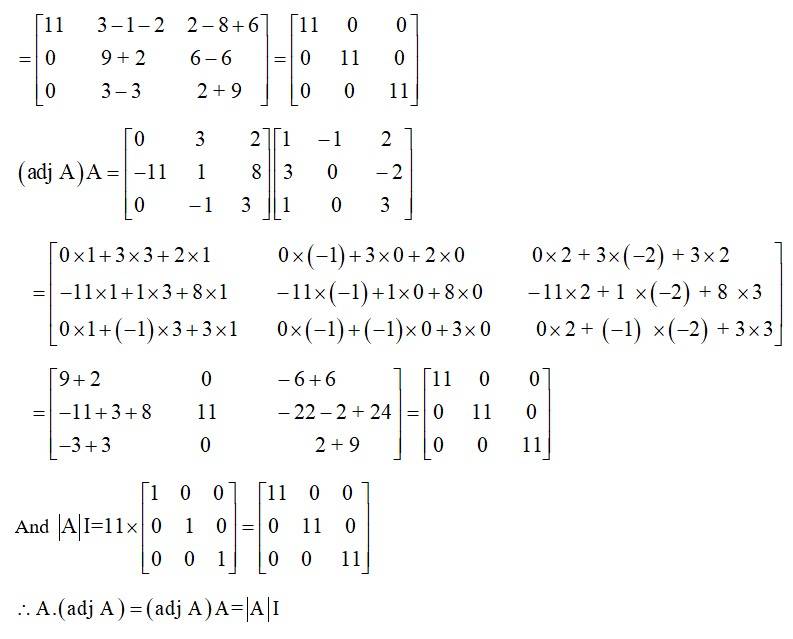
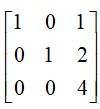
4. If A= ![]() ,then show that | 3 A | = 27 | A |
,then show that | 3 A | = 27 | A |
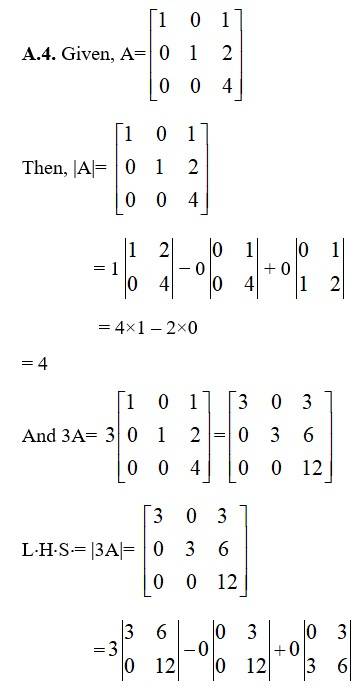
=3 [36 – 6×0]
= 108
RHS = 27. |A| = 27 4 = 108
∴ LHS = RHS
8. If 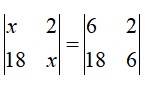 , then x is equal to
, then x is equal to
(A) 6 (B) ± 6 (C) – 6 (D) 0
Kindly go through the solution
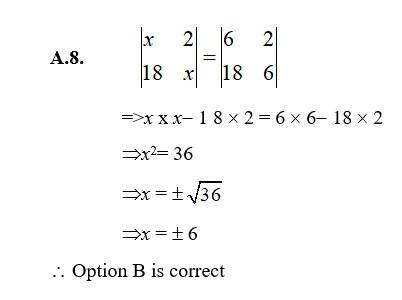
27. (i) Find equation of line joining (1, 2) and (3, 6) using determinants.
(ii) Find equation of line joining (3, 1) and (9, 3) using determinants
(i) Let P (x, y) be any point on line joining A (1, 2) & B (3, 6)
Then, area of triangle (ABP) = 0 {the point are collinear
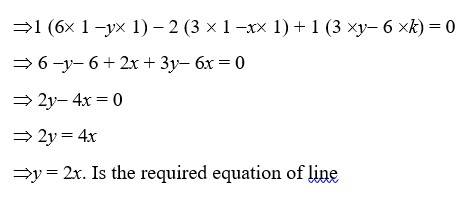
31. Using Cofactors of elements of second row, evaluate
Given,
Co-factors of elements of second row,
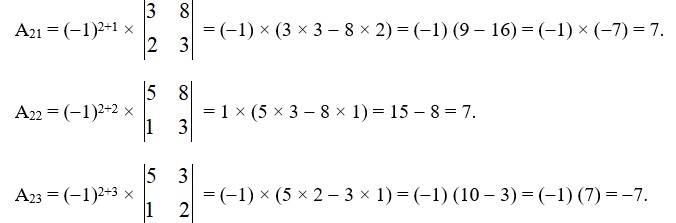
? ? = a21A21 + a22A22 + a23A23
= 2 * 7 + 0 * 7 + 1 * (-7) = 14 + 0 - 7 = 7.
Kindly Consider the following
69. Evaluate 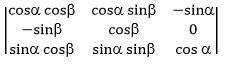
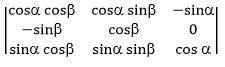
=1
76. Evaluate
Kindly go through the solution
21.
LHS =
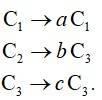
Taking a, b&c common from R1, R2&R3
C1→ C2 + C3.
Choose the correct answer in Exercises 15 and 16.
22. Let A be a square matrix of order 3 × 3, then | kA| is equal to
(A) k| A| (B) | A | (C) | A | (D) 3k | A |
Then, KA =
So, option c is correct.
Kindly Consider the following
38.
Kindly go through the solution
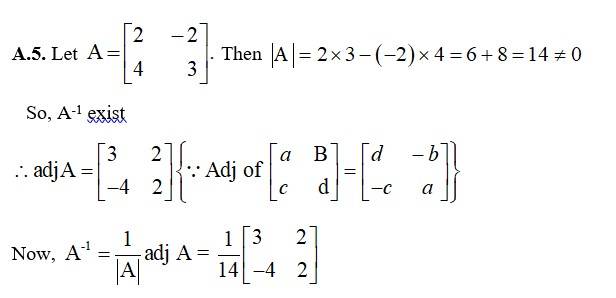
48. For the matrix A =
Given, A=
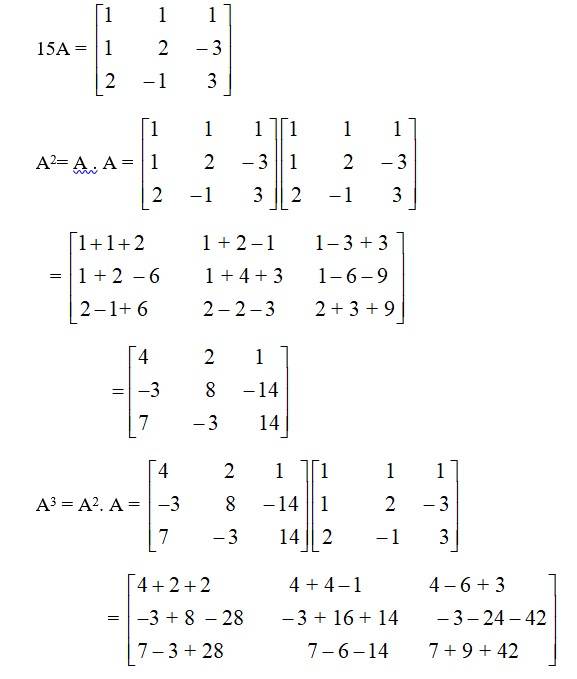

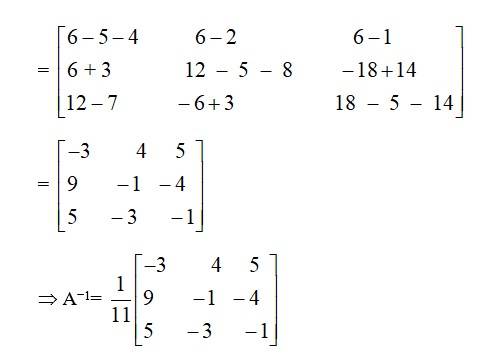
56.
The given system of eqn in matrix form is AK = B
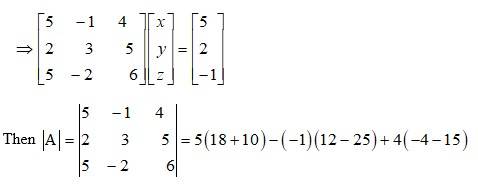
= 5 x 28 -13 + 4 x (-9)
= 140 - 13 - 76
= 51 ≠ 0 .
The given system of eqn are consistent
66. The cost of 4 kg onion, 3 kg wheat and 2 kg rice is `60. The cost of 2 kg onion, 4 kg wheat and 6 kg rice is `90. The cost of 6 kg onion 2 kg wheat and 3 kg rice is `70. Find cost of each item per kg by matrix method.
Let k, y and z be the cost per kg of onion, wheat and rice. Then, we form a system of equations as follows
4k + 3y + 2z = 60
2k + 4y + 6z = 90
6k + 2y + 3z = 70
In matrix form we can write,
AX = B
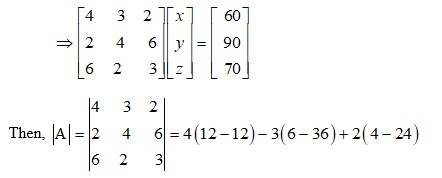
= 0 - 3 (-30) + 2 (-20)
= 90 - 40
= 50 ≠ 0.
∴ The system has a unique solution.
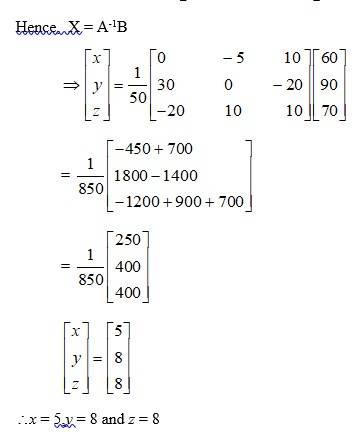

The cost of onion, wheat and rice per kg are? 5? 8 and? 8 respectively.
68. Without expanding the determinants, prove that
L.H.S.=
Multiplying R1, by a, R2 by b and R3 by c
Taking abc common from c3 =
Inter changing c1 and c3 =
Inter changing c2 and c3 =
Kindly Consider the following
41.
Kindly go through the solution

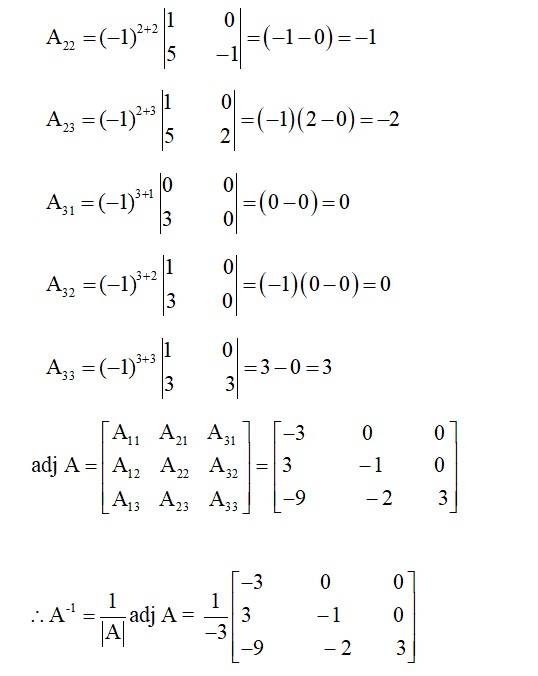
24. Find area of the triangle with vertices at the point given in each of the following:
(i) (1, 0), (6, 0), (4, 3)
(ii) (2, 7), (1, 1), (10, 8)
(iii) (–2, –3), (3, 2), (–1, –8)
(i) Area of triangle is given by,
Δ =
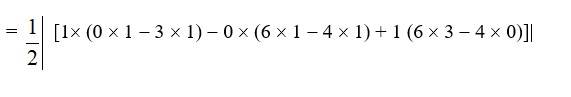
=7.5sq. units.
(ii) Area of the triangle is given by,
Δ =
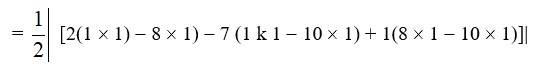
= =23.5 sq. units
(iii) Area of triangle is given by,
Δ =
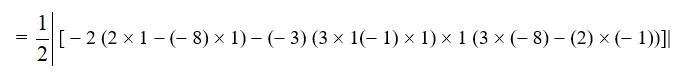
= 15 sq. units.
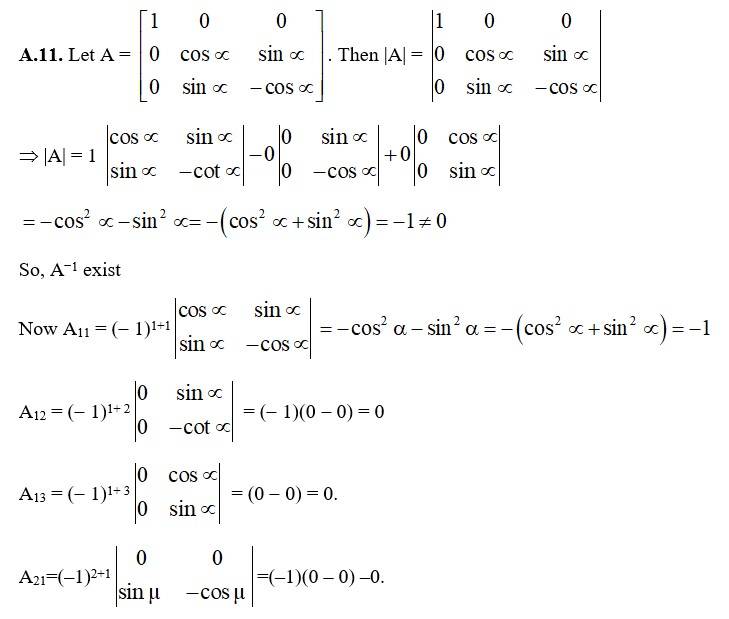
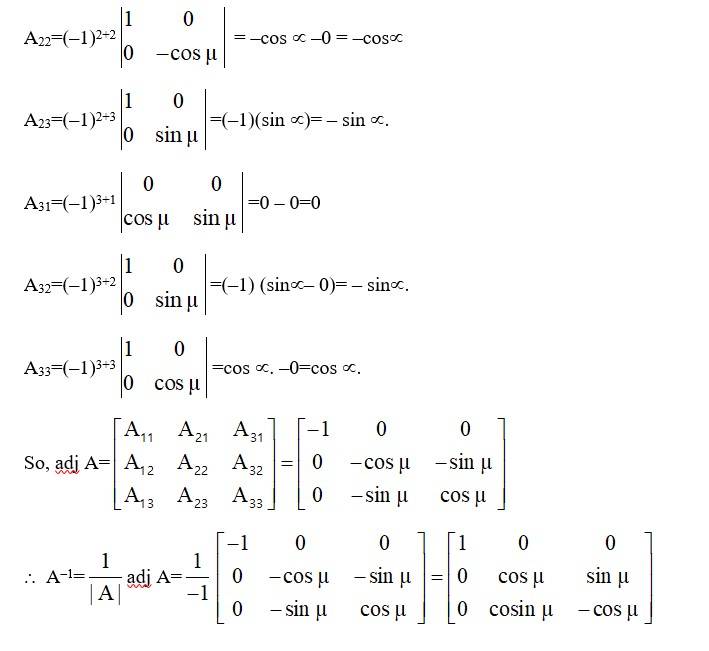
74. Let A =  . Verify that
. Verify that
(i) [adj A]-1 = adj (A-1) (ii) (A-1)-1 = A
Kindly go through the solution

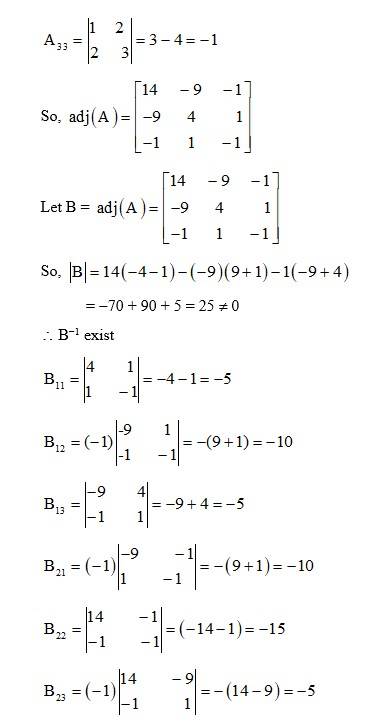
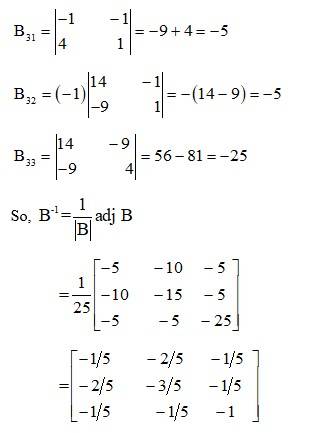


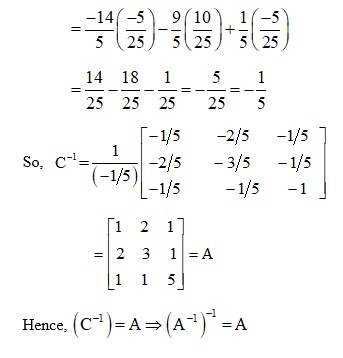
6. If A= 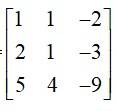 ,find | A |
,find | A |
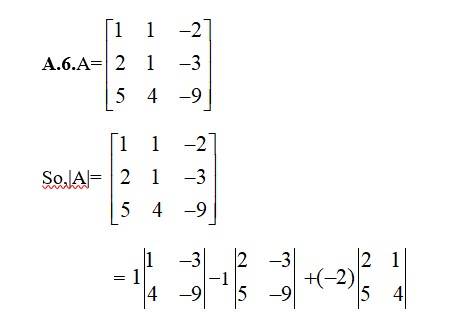
= 1 [1× (−9) – 4× (−3)]–1 [2× (–9)–5× (– 3)]– 2 [2×4 −5×1]
= 1 [− 9 + 12] −1 [− 18+15] − 2 [8 − 5]
= 3 + 3 −6
= 0
11. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
35.
We have,
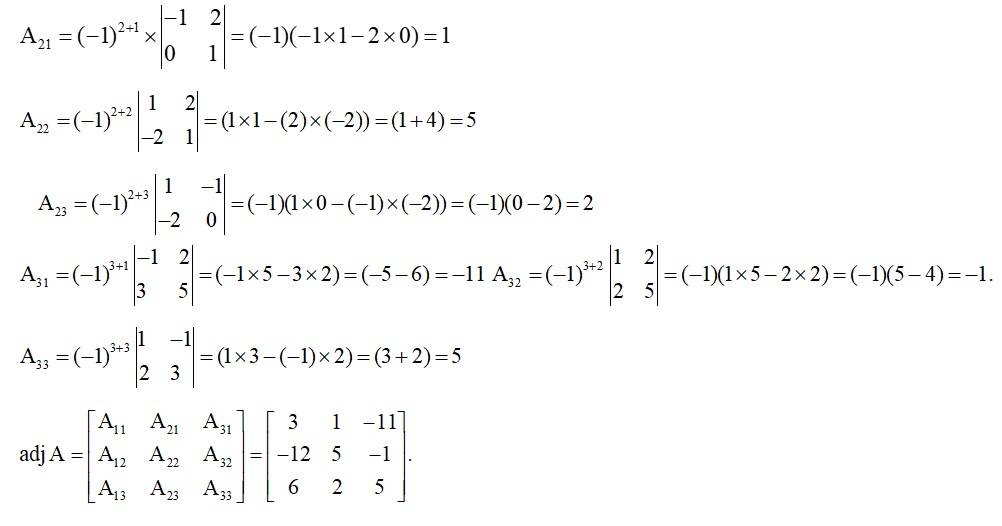
Kindly Consider the following
40.
Kindly go through the solution
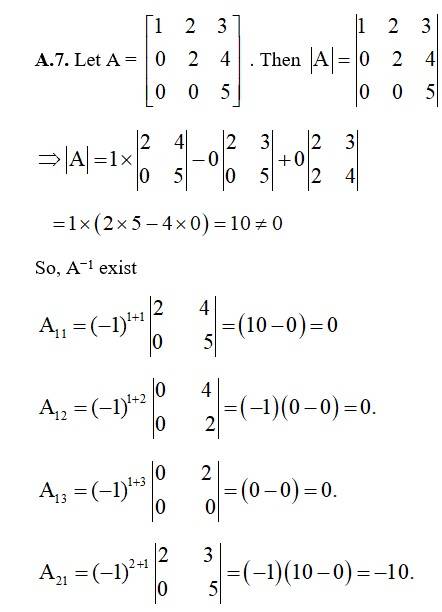
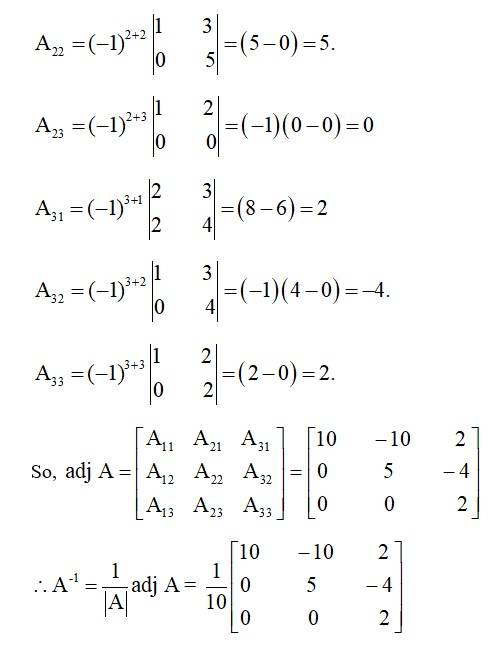
Kindly Consider the following
43.
Let A = Then |A| =
= (8 - 6) + (0 - (- 9) + 2 (0 - 6)
= 2 + 9 - 12 = - 1 ¹ 0
So, A-1 exist
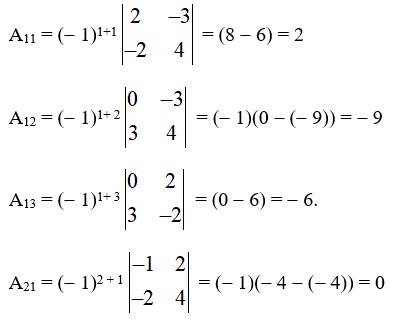
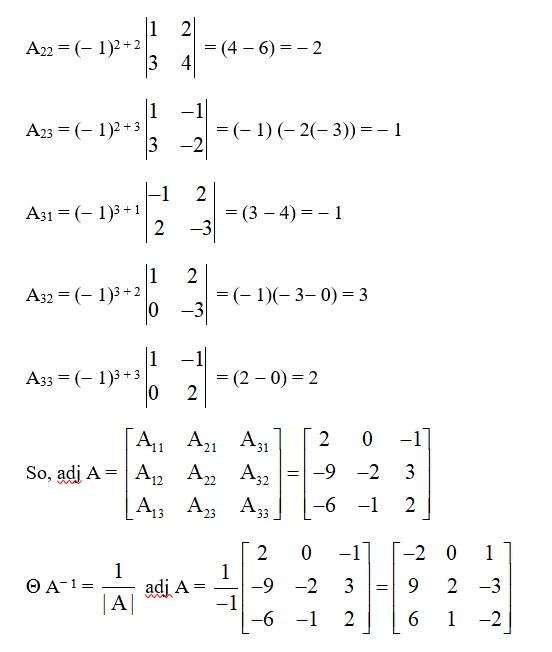
3. If , then show that | 2A | = 4 | A |
Given, A=
So, 2A= 2
= .
L.H.S. = = = 2×4 – 4×8 = 8−32 = −24
R.H.S. = 4 = 4 = 4 (1×2 – 2×4)
= 4 [2 − 8]
= 4 [−6] = 24.
LHS = RHS
1.Evaluate the determinants in Exercises 1 and 2.
2× (−1) – 4× (−5) = −2+20 = 18
7. Find values of x, if
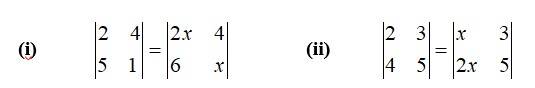
Kindly go through the solution
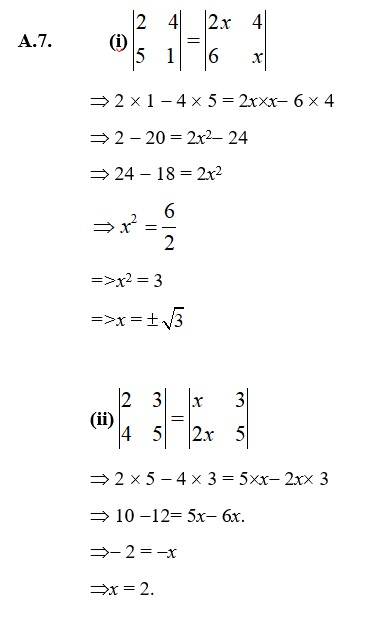
26. Find values of k if area of triangle is 4 sq. units and vertices are
(i) (k, 0), (4, 0), (0, 2) (ii) (–2, 0), (0, 4), (0, k)
(i) Area of the triangle = 4 sq. units (given)
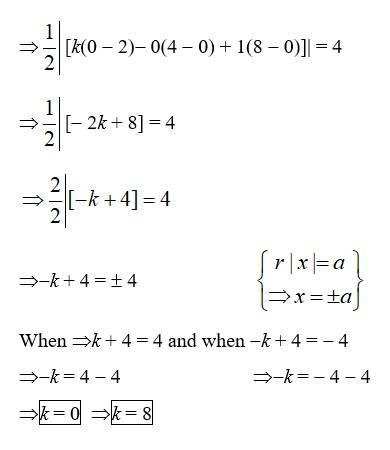
(ii) Area of the triangle = 4 sq units
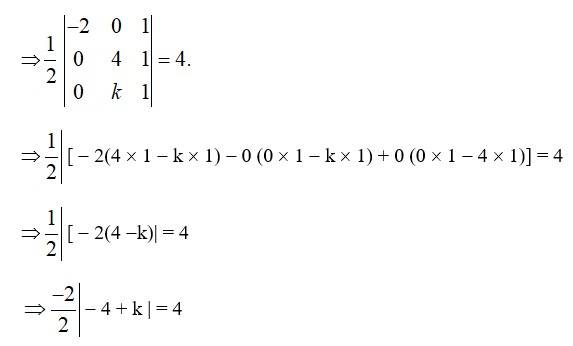
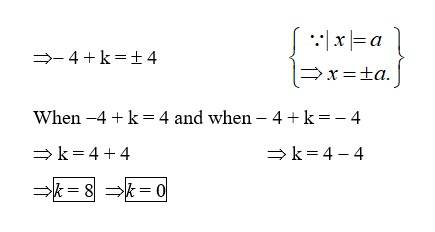
34.
We have,
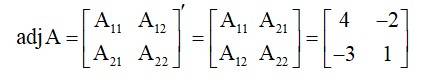
Kindly Consider the following
36.
Let
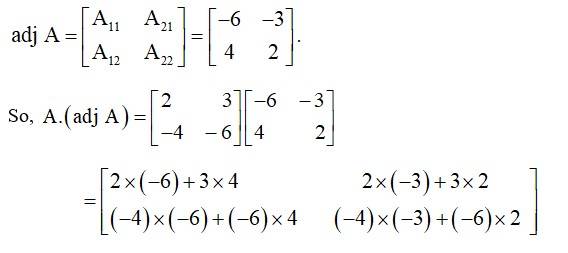
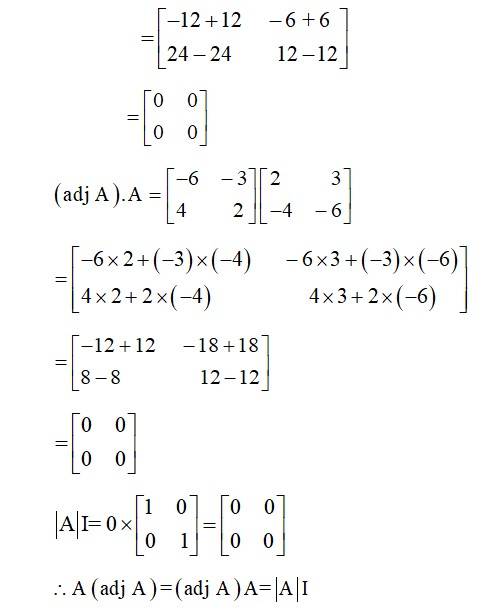
Kindly Consider the following
39.
Kindly go through the solution
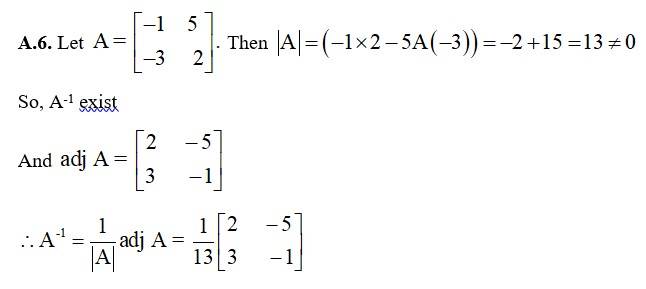
44.
Kindly go through the solution
Kindly Consider the following
49.
Kindly go through the solution
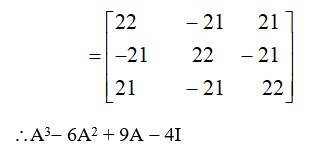

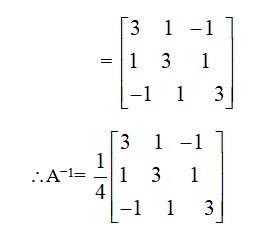
Kindly Consider the following
75. Evaluate 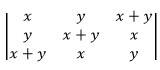
Expanding along C1
=
81.
Applying in
82. Solve the system of equations
= 4
= 1
= 2
Given equations are :-
This system of equation can be written, in matrix form, as AX= B, Where
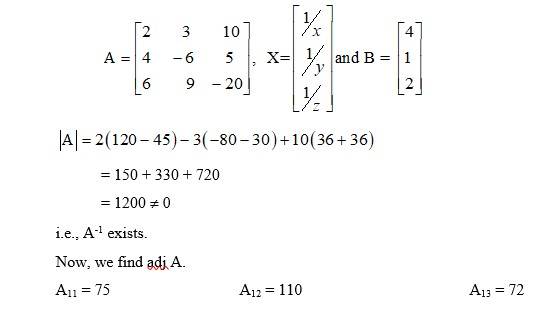
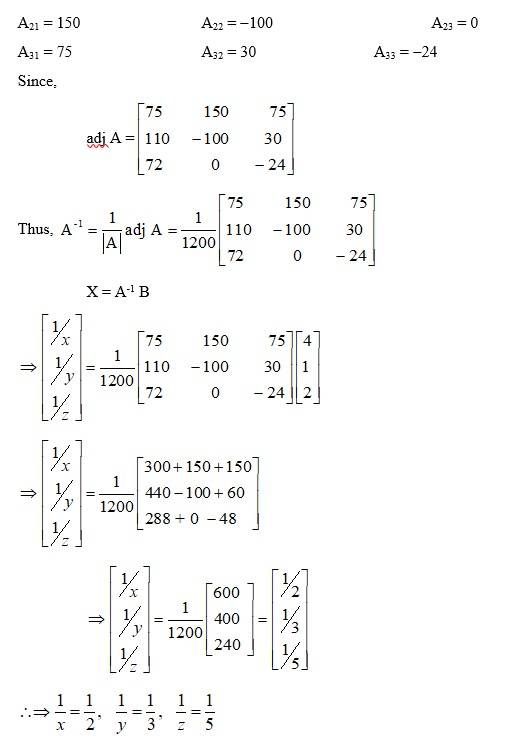
⇒ x = 2, y = 3, z = 5.
2. (i) (ii)
(i)
= cos²θ + sin²θ
=1
(ii)
= + − − + +1 – + 1
= - + 2
12. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
18. (i)
(i) LHS =
R1→ R1 + R2 + R3
= (a + b + c) Taking (a + b + c) common from R1
= (a + b+ c)
= (a + b + c)
= (a + b + c) × 1. Expand along R1
= (a + b + c){(a + b + c)2- 0}
= (a + b +c)3 = R.H.S
(ii) LHS =
C1→ C1 + C2 + C3.
= 2 (k + y + z) Taking 2
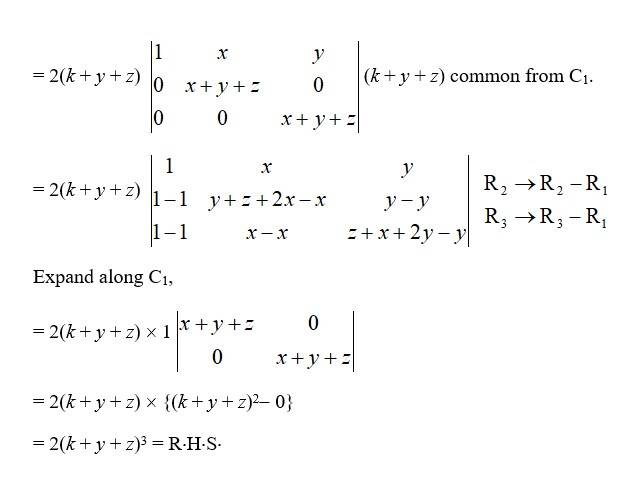
19.
LHS =
R1→ R1 + R2 + R3
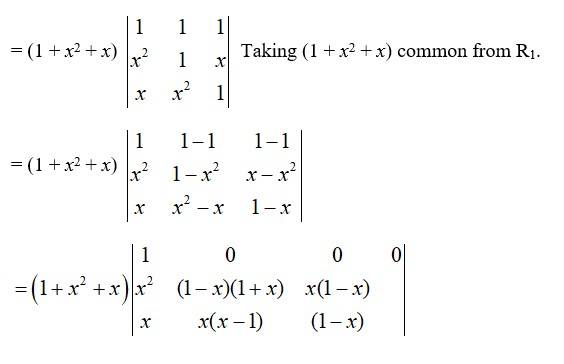
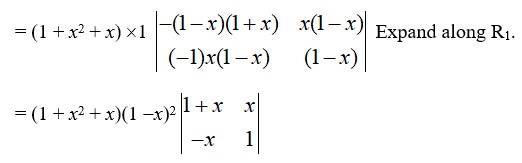
= (1 + x2 + x) (1 -x)2 [ (1 + x)× 1 - (-x) x].
= (1 + x2 + x) (1 -x)2 (1 + x + x2).
= { (1 + x2 + x) (1 -x)}2
= {1 -x + x2-x3 + x-x2}2
= (1 -x3)2 = R.H.S.
23. Which of the following is correct
(A) Determinant is a square matrix.
(B) Determinant is a number associated to a matrix.
(C) Determinant is a number associated to a square matrix.
(D) None of these
Option 'C' is correct as determinant is a number associated to a square matrix.
25. Show that points
A (a, b + c), B (b, c + a), C (c, a + b) are collinear.
The area of triangle from by the given points is area ( ΔABC) =
C1→ C1 + C2 + C3
Taking (a + b + c + 1) common from C1
= 0
Hence the points A, B C are collinear.
29. (i) (ii)
(i) We know that,
Minor of element aij is mij and its co-factor is Aij = (–1)i+j Mij
So,
M11 = 3 and A11 = (- 1)1 + 1 M11 = 1 * 3 = 3
M12 = 0 and A12 = (-1)1+2 M12 = -1 * 0 = 0
M21 = -4 and A21 = (-1)2+1 M21 = (-1) * (-4) = 4
M22 = 2 and A22 = (-1)2+2 M22 = 1 * 2 = 2
(ii) Given A =
So,
M11 = d and A11 = (-1)1+1 M11 = 1 * d = d
M12 = b and A12 = (-1)1+2 M12 = (-1) * b = -b
M21 = c and A21 = (-1)2+ 1 M21 = (–1) * c = –c
M22 = a and A22 = (-1)2+2 M22 = 1 * a = a
30. (i) (ii)
(i) Given, A =
So,
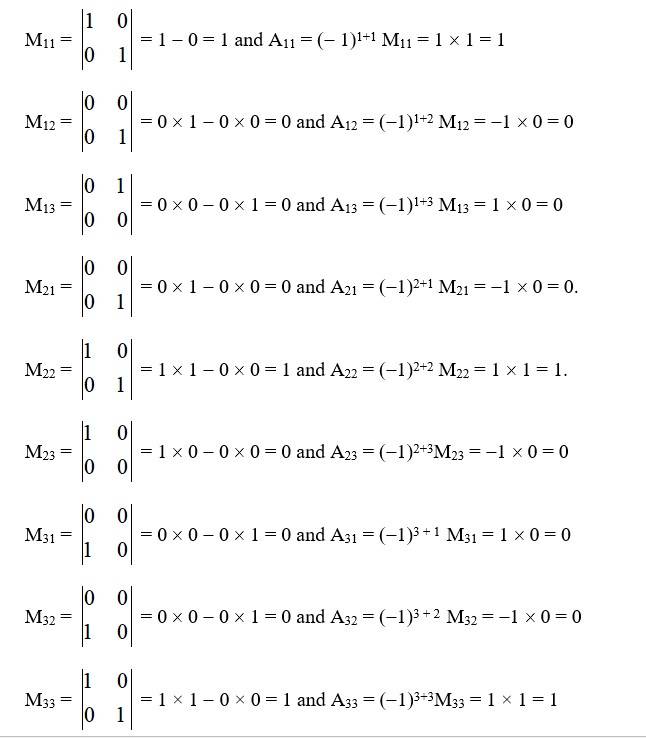
(ii)Given,
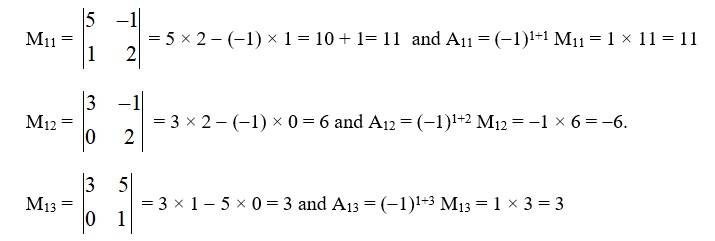
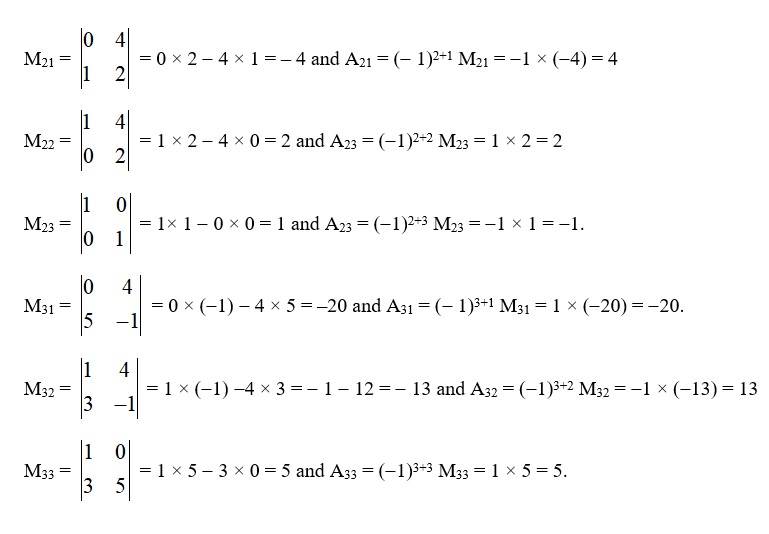
Kindly Consider the following
45.
Kindly go through the solution
Kindly Consider the following
46.
Given, A=
we have, A2 = A?A =
Hence, A2 – 5A+71=
Now, A2 – 5A+7I=0.
A?A – 5A= –7I.
A A(A–1)–5(AA–1)= –7I(A–1) (Multiplying by A-1on both sides)
AI – 5I= –7A–1
7A–1= –(AI – 5I)
A–1=
=
=
A–1=
Kindly Consider the following
47. 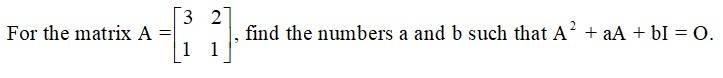
Kindly go through the solution
⇒ b = 1
Kindly Consider the following
50. 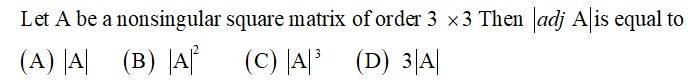
Given, A is an invertible matrix of order 2.
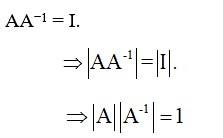
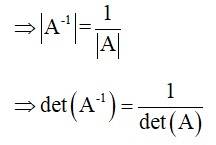
∴ Option (B) is correct.
51.
The given system of equation can be written in the form of AK = B
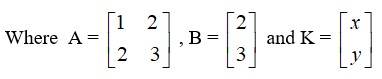
Now, = 3 × 1 - 2 × 2 = 3 - 4 = -1 ≠ 0.
∴ The system has unique soln and hence equation are consistent
Kindly Consider the following
52.
The given system of eqn can be written in the form AK = B where
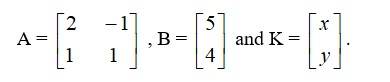
Now, = 2 – (-1) = 2 + 1 = 3 ≠ 0.
∴ The system of eqnis consistent.
Kindly Consider the following
53.
The given system of equation can be written in the form AK = B
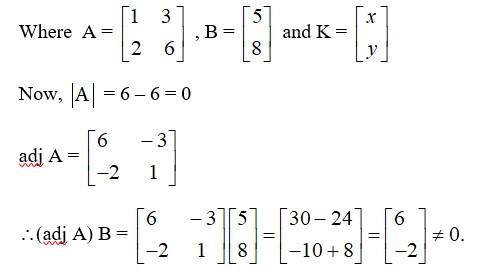
Hence the given system of eqn are inconsistent.
54.
The given system of eqn using matrix method can be expressed as
AK = B
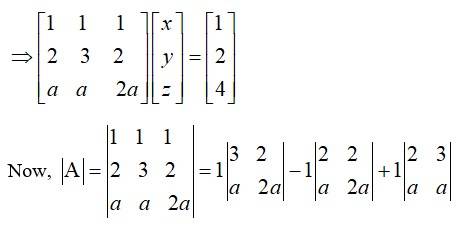
= 4a – 2a – a
= a ≠ 0.
Hence, the given system of eqn is consistent
55.
The given system of eqn using matrix form can be written as AK = B
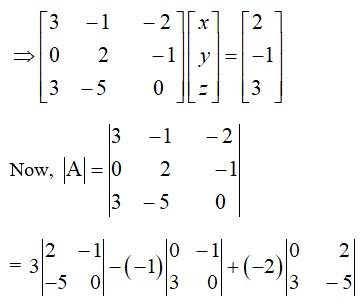
= -15 + 3 + 12
= -15 + 15
= 0
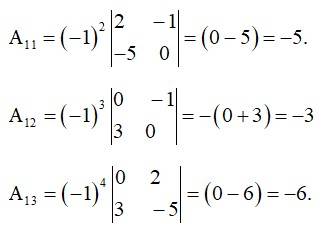
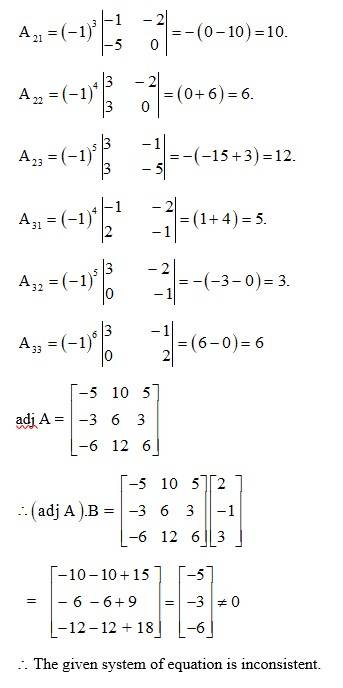
Kindly Consider the following
57.
The given system of eqn in matrix form is AK = B.
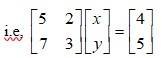
Then, |A| = 5 x 3 - 7 x 2 = 15 - 14 = 1 ≠ 0
∴ The system has a unique solution.
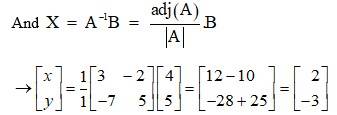
∴ k = 2 and y = -3
Kindly Consider the following
59.
The given system of eqn can be written in matrix form as
AK = B
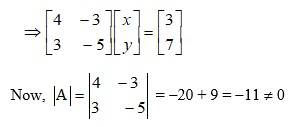
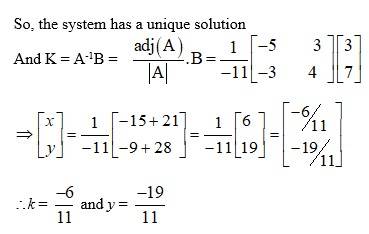
63.
The given system of equation can be represented in matrix form as AK = B
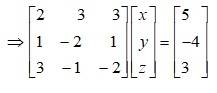


64.
The given system of eqn can be written in matrix form as
AK = B
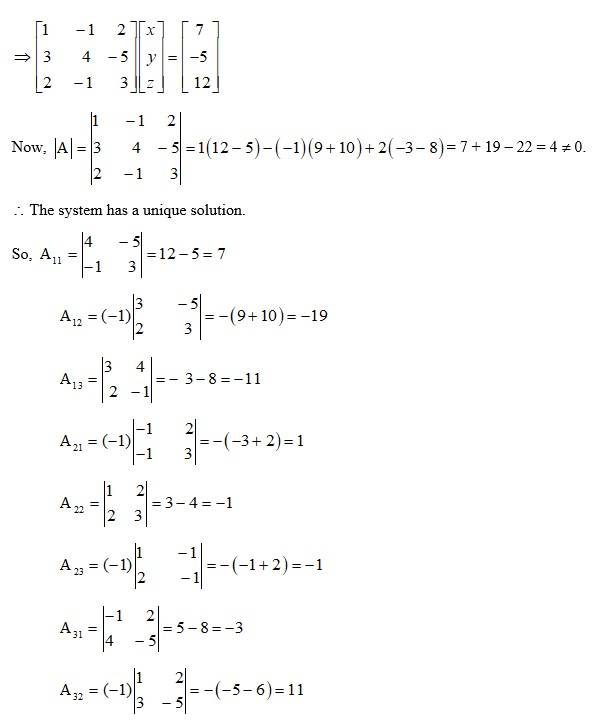
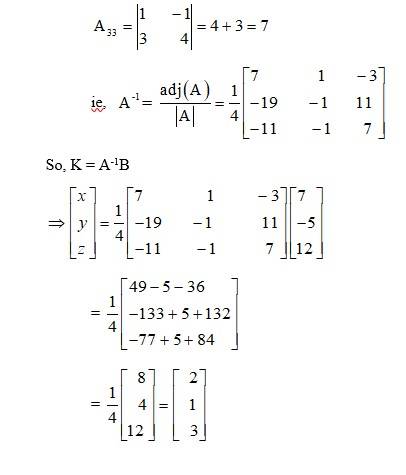
∴ x= 2, y = 1 and z = 3 .
71. Solve the equation
Taking 3x+a common from
Either
Or
Expanding along ,
is the only solution.
72. Prove that
Taking a, b, c common from c1, c2 and c3 respectively
Expanding along
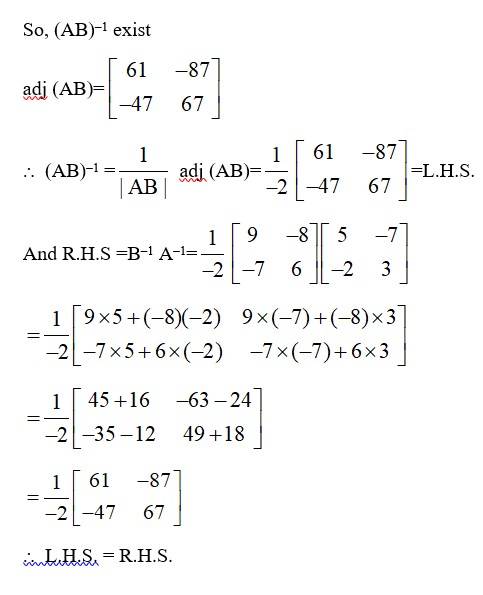
73. If A-1 = and B = find (AB)-1
Kindly go through the solution
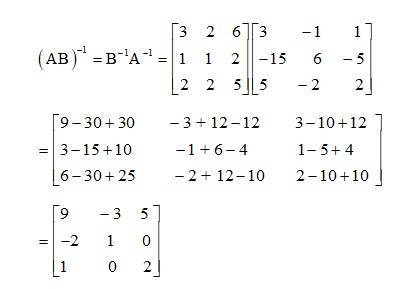
77.
and
Expanding along
78.
Putting value in (1)
and
Expanding along
Putting in (2)
79.
and
Expanding along
80. Using properties of determinants,
Prove that:
Expanding along
83. Choose the correct answer
If a, b, c are in AP, then the determinant
A. 0
B. 1
C. Z
D. 2x
A
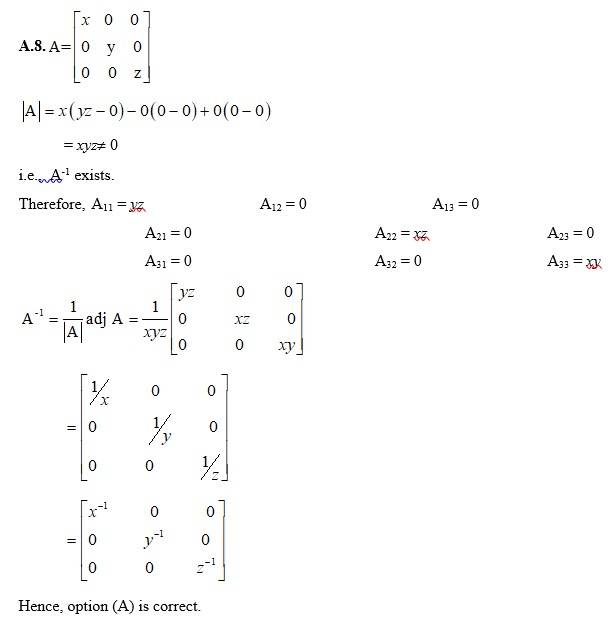
84. If x, y, z are nonzero real numbers, then the inverse of matrix A = is
(A) (B) xyz
(C) (D)
Kindly go through the solution
Maths Ncert Solutions class 12th Exam

 ,then show that | 3 A | = 27 | A |
,then show that | 3 A | = 27 | A |