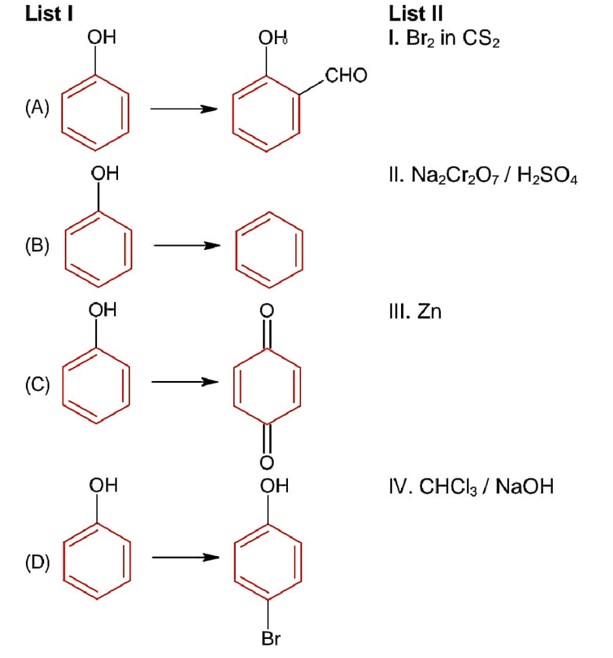
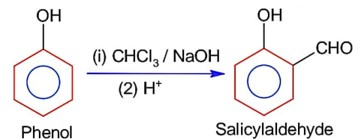
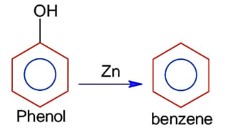
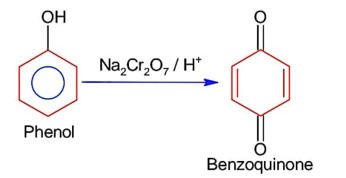
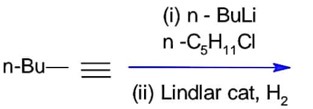- The D- And F- Block Element Questions and Answers
- JEE Main 27th June 2022 (Second Shift)
- JEE Mains Solutions 2022,27th june ,chemistry , first
- JEE Mains 2020
The D- And F- Block Element Questions and Answers
| 1. Identify A to E and explain reaction involves:
|
| Ans: CuCO3 (D) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O (E) CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2 clear sol. CuO + CuS (A) Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O (conc.) (B) Cu(NO3)2 + 4NH3 → [Cu(NH3)4](NO3)2 (C) blue solution |
| 2. When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water, a yellow solution of compound (B) is obtained. After treatment of this yellow solution with sulphuric acid, compound (C) can be crystallized from the solution. When compound (C) is treated with ���, orange crystals of compound (D) crystallise out. Identify A to D and also explain the reactions. |
| Ans: (A) = FeCr2O4 (B) = Na2CrO4 (C) = Na2Cr2O7 (D) = K2Cr2O7 4FeCrO4 + 8NaCO3 + 7O2 → 8Na2CrO4 + 2Fe2O3 + 8CO2 (A) (B) 2NaCrO4 + 2H + → Na2Cr2O7 + 2Na + + H2O Na2Cr2O7 + KCl→ K2Cr2O7 + 2NaCl (C) (D) |
| 3. When an oxide of manganese (A) is fused with KOH in the presence of an oxidizing agent and dissolved in water, it gives a dark green solution of compound (B). Compound (B) disproportionate in neutral or acidic solution to give purple compound (C). An alkaline solution of compound (C) oxidises potassium iodide solution to a compound (D) and compound (A) is also formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved. |
| Ans: (A) = MnO2 (B) = K2MnO4 (C) = KMnO4 (D) = KIO3 2MnO2 + 4KOH + O2 → 2K2MnO4 + 2H2O (A) (B) 3MnO42- + 4H+ → 2MnO4- + MnO2 + 2H2O (C) 2MnO42- + 2H2O + KI→ 2MnO2 + 2SO4- + KIO3 (A) (D) |
| 4. On the basis of lanthanoid contraction, explain the following: (a) Nature of bonding in La2O3 and Lu2O3. |
| Ans: As per fajan’s rule, smaller the size of ion, greater is its tendency to make covalent bonds as the positively charged cation strongly attract the negatively charged electron cloud. On moving from La to Lu in the lanthanoid series, the atomic size decreases so the covalent character increases. Hence, La2O3 is ionic and Lu2O3 is covalent. |
| (b) Trends in the stability of oxo-salts of lanthanoids from La to Lu. |
| Ans: The stability of Oxo salts is directly proportional to the size of atom, as we move from La to Lu, the size of the atom decreases and hence the stability of oxo salts also decreases. |
| (c) Stability of the complexes of lanthanides. |
| Ans: As we move along the lanthanide series, the atomic size decreases. As a result, the charge/size ratio increases and the stability of the complexes also increases. |
| (d) Radii of 4d- and 5d-block elements. |
| Ans: As an effect of lanthanide contraction, zirconium and hafnium have similar radius of 160pm and 159 pm respectively. Due to this similarity in their size, they show similar physical and chemical properties. Lanthanoid contraction: Because the elements in Row 3 have 4f electrons. These electrons do not shield good, causing a greater nuclear charge. This greater nuclear charge has a greater pull on the electrons and result in the decrease in their size and atomic radii. |
| (e) Trends in acidic character of lanthanide oxides. |
| Ans: Acidic or basic character of oxides is related to the nature of oxides. As we move along the lanthanide series from La to Lu, the covalent character increases. Therefore, their basic character decreases or acidic character increases. |
| 5. (A) Answer the following questions: (i) Which element of the first transition series has the highest second ionization enthalpy? |
| Ans: Out of all the elements of the first transition series copper has the highest second ionisation enthalpy. Electronic configuration of Copper is: 3d104s1 After the Loss of first electron from the 4s copper acquires 3d10 configuration which is stable. Therefore, removal of second electron from the field 3-D orbital is very difficult and requires high amount of energy. |
| 6. (ii) Which element of the first transition series has highest third ionization enthalpy? |
| Ans: Among the elements of first transition series zinc has the highest third ionisation enthalpy. Electronic configuration of zinc is: 3d104s2 After the loss of two electrons from 4s orbital, Z and +2 Ion acquires 3d10 fully filled configuration which is highly stable therefore removal of third electron from 3d 10orbital will be more difficult and requires a large amount of energy. |
| (iii) Which element of the first transition series has lowest enthalpy of atomization? |
| Ans: Zinc is the element of the first transition series that has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation. The electronic configuration of zinc is: 3d104s2.This is because it has filled 3d-subshell and filled 4s-subshell so no unpaid electron is available for metallic bonding. |
| (b) Identify the metal and justify your answer: (I) CarbonylmM(CO)5 |
| Ans: Fe(CO)5 as per EAN Rule. EAN Rule: Effective atomic number (EAN), number that represents the total number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of a metal atom in a metal complex. (II) MO3F Ans: The M in the given complex is in +7 O.S. Manganese is the only element in the first transition series that shows +7 oxidation state, therefore this compound is MnO3F. |
| 6. Mention the type of compounds formed when small atoms like H get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals. Also give physical and chemical characteristics of these compounds. |
| Ans: Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms like H, C and N get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals. Characteristics: They are hard and rigid in nature having high melting points. Like pure metals only, they are conductors. They can gain chemical inertness. |
| 8. (A) Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state. How does Fe(III) catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions? |
| Ans: 2I- + S2O82- →Fe(III) I2 + 2SO42- role of fe ions: 2Fe3+ + 2I- → 2Fe2+ + I2 2Fe2+ + S2O82- → 2Fe3+ + 2SO42- |
| (B) Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts. |
| Ans: 1. Fine powdered state of Nickel is used in the hydrogenation of oils into fats.
|
| 9. A violet compound of manganese (A) decomposes on heating to liberate oxygen and compounds (B) and (C) of manganese are formed. Compound (C) reacts with KOH in the presence of potassium nitrate to give compound (B). On heating compound (C) with conc. H2SO4 and NaCl, chlorine gas is liberated and a compound (D) of manganese along with other products is formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved. |
| Ans: KMnO4 (A) (B) (C) MnO2 + KOH → 2K2MnO4 + 2H2O MnO2 + 4NaCl + 4H2SO4→ MnCl2 + 2NaHSO4+2H2O + Cl2 (D) (A) = KMnO4 (B) = K2MnO4 (C) = MnO2 (D) = MnCl2
|
Commonly asked questions
65. Match the catalysts given in Column I with the processes given in Column II.
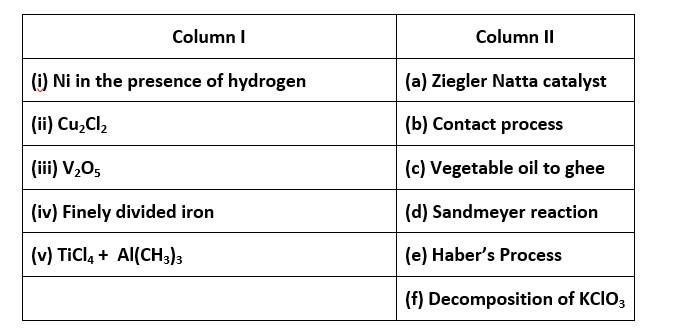
65. (i) - (c); (ii)- (d); (iii)- (b); (iv)- (e); (v)- (a)
1. Identify A to E and explain reaction involves:
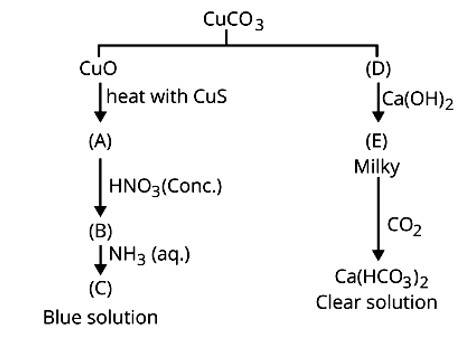
1. CuCO3 ![]() CuO + CO2
CuO + CO2
(D)
Ca (OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(E)
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca (HCO3)2
clear sol.
CuO + CuS ![]() 3Cu + SO2
3Cu + SO2
(A)
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu (NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
(conc.) (B)
Cu (NO3)2 + 4NH3 → [Cu (NH3)4] (NO3)2
(C) blue solution
2. When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water, a yellow solution of compound (B) is obtained. After treatment of this yellow solution with sulphuric acid, compound (C) can be crystallized from the solution. When compound (C) is treated with ???, orange crystals of compound (D) crystallise out. Identify A to D and also explain the reactions.
2. (A) = FeCr2O4
(B) = Na2CrO4
(C) = Na2Cr2O7
(D) = K2Cr2O7
4FeCrO4 + 8NaCO3 + 7O2 → 8Na2CrO4 + 2Fe2O3 + 8CO2
(A) (B)
2NaCrO4 + 2H + → Na2Cr2O7 + 2Na + + H2O
Na2Cr2O7 + KCl→ K2Cr2O7 + 2NaCl
(C) (D)
3. When an oxide of manganese (A) is fused with KOH in the presence of an oxidizing agent and dissolved in water, it gives a dark green solution of compound (B). Compound (B) disproportionate in neutral or acidic solution to give purple compound (C). An alkaline solution of compound (C) oxidises potassium iodide solution to a compound (D) and compound (A) is also formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved.
3. (A) = MnO2
(B) = K2MnO4
(C) = KMnO4
(D) = KIO3
2MnO2 + 4KOH + O2 → 2K2MnO4 + 2H2O
(A) (B)
3MnO42- + 4H+ → 2MnO4- + MnO2 + 2H2O
(C)
2MnO42- + 2H2O + KI→ 2MnO2 + 2SO4- + KIO3
(A) (D)
4. On the basis of lanthanoid contraction, explain the following:
(a) Nature of bonding in La2O3 and Lu2O3.
(b) Trends in the stability of oxo-salts of lanthanoids from La to Lu.
(c) Stability of the complexes of lanthanides.
(d) Radii of 4d- and 5d-block elements.
(e) Trends in acidic character of lanthanide oxides.
4. (a) As per fajan's rule, smaller the size of ion, greater is its tendency to make covalent bonds as the positively charged cation strongly attract the negatively charged electron cloud.
On moving from La to Lu in the lanthanoid series, the atomic size decreases so the covalent character increases. Hence, La2O3 is ionic and Lu2O3 is covalent.
(b) The stability of Oxo salts is directly proportional to the size of atom, as we move from La to Lu, the size of the atom decreases and hence the stability of oxo salts also decreases.
(c) As we move along the lanthanide series, the atomic size decreases. As a result, the charge/size ratio increases and the stability of the complexes also increases.
(d) As an effect of lanthanide contraction, zirconium and hafnium have similar radius of 160pm and 159 pm respectively. Due to this similarity in their size, they show similar physical and chemical properties. Lanthanoid contraction: Because the elements in Row 3 have 4f electrons.
These electrons do not shield good, causing a greater nuclear charge. This greater nuclear charge has a greater pull on the electrons and result in the decrease in their size and atomic radii.
(e) Acidic or basic character of oxides is related to the nature of oxides. As we move along the lanthanide series from La to Lu, the covalent character increases.
Therefore, their basic character decreases or acidic character increases.
5. (A) Answer the following questions:
(i) Which element of the first transition series has the highest second ionization enthalpy?
(ii) Which element of the first transition series has highest third ionization enthalpy?
(iii) Which element of the first transition series has lowest enthalpy of atomization?
(B) Identify the metal and justify your answer:
(i) CarbonylmM(CO)5
(ii) MO3F
5. (A) (i) Out of all the elements of the first transition series copper has the highest second ionisation enthalpy.
Electronic configuration of Copper is: 3d104s1
After the Loss of first electron from the 4s copper acquires 3d10 configuration which is stable. Therefore, removal of second electron from the field 3-D orbital is very difficult and requires high amount of energy.
(ii) Among the elements of first transition series zinc has the highest third ionisation enthalpy. Electronic configuration of zinc is: 3d104s2
After the loss of two electrons from 4s orbital, Z and +2 Ion acquires 3d10 fully filled configuration which is highly stable therefore removal of third electron from 3d 10orbital will be more difficult and requires a large amount of energy.
(iii) Zinc is the element of the first transition series that has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation. The electronic configuration of zinc is: 3d104s2.This is because it has filled 3d-subshell and filled 4s-subshell so no unpaid electron is available for metallic bonding.
(B) (i) CarbonylmM (CO)5
Ans: Fe (CO)5 as per EAN Rule.
EAN Rule: Effective atomic number (EAN), number that represents the total number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of a metal atom in a metal complex.
(ii) MO3F
Ans: The M in the given complex is in +7 O.S.
6. Mention the type of compounds formed when small atoms like H get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals. Also give physical and chemical characteristics of these compounds.
6. Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms like H, C and N get trapped inside the crystal lattice of transition metals.
Characteristics:
They are hard and rigid in nature having high melting points.
Like pure metals only, they are conductors. They can gain chemical inertness.
7. (A) Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state.
How does Fe(III) catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions?
(B) Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts.
7. (A) 2I- + S2O82- →Fe (III) I2 + 2SO42-
role of fe ions:
2Fe3+ + 2I- → 2Fe2+ + I2
2Fe2+ + S2O82- → 2Fe3+ + 2SO42-
(B) 1. Fine powdered state of Nickel is used in the hydrogenation of oils into fats.
2. Iron is used in the formation of ammonia in Haber’s process.
3. In contact process in manufacture of H2SO4, vanadium is used in its oxide form- V2O5.
8. A violet compound of manganese (A) decomposes on heating to liberate oxygen and compounds (B) and (C) of manganese are formed. Compound (C) reacts with KOH in the presence of potassium nitrate to give compound (B). On heating compound (C) with conc. H2SO4 and NaCl, chlorine gas is liberated and a compound (D) of manganese along with other products is formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved.
8. KMnO4 ![]() K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
(A) (B) (C)
MnO2 + KOH → 2K2MnO4 + 2H2O
MnO2 + 4NaCl + 4H2SO4→ MnCl2 + 2NaHSO4+2H2O + Cl2
(D)
(A) = KMnO4
(B) = K2MnO4
(C) = MnO2
(D) = MnCl2
9. Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
9. Copper lies below hydrogen in electrochemical series which means it has positive standard reduction potential i.e. + 0.34 V. and hence cannot liberate hydrogen from acids.
10. Why E? value for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected?
10. Mn has half-filled 3d5 electrons and Zn has fully-filled 3d10 electrons which give them extra stability and they both resist to lose electrons and get reduced.
The E? value also depends on the hydration enthalpy. More negative is the enthalpy of hydration, high is the E? value. This is the reason behind Mn, Ni and Zn are having higher E? value than expected
11. Why is the first ionization enthalpy of Cr lower than that of Zn?
11. Cr (24)= [Ar]3d54s2
Zn (30) = [Ar] 3d104s2
The stability of orbitals according to the electrons filled is in order:
Fully filled > half-filled > partially filled
As 3d10 is completely filled orbital of Zn is more stable than the 3d5 half-filled orbital of Cr . It is comparatively easy to remove electron from 3d5 than from 3d10.
Therefore, the first ionization enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn.
12. Transition elements show high melting points. Why?
12. Transition elements have the ability to involve their d-electrons along with their s-electrons in the process of bond formation. This results in formation of strong metal-metal bonds which makes their melting point high.
13. When Cu2+ ion is treated with KI, a white precipitate is formed. Explain the reaction with the help of a chemical equation.
13. 2Cu2+ + 4I- → Cu2I2 + I2
When Cu2+ reacts with potassium iodide white precipitate of Cu2I2 is formed.
14. Out of Cu2Cl2 and CuCl2, which is more stable and why?
14. Higher enthalpy of hydration provides extra stability to Cu2+ oxidation state than +1 oxidation state.
Enthalpy of hydration is described as the amount of energy released on dilution of one mole of gaseous ions.
15. When a brown compound of manganese
(A) Is treated with HCl, it gives a gas
(B) The gas taken in excess, reacts with NH3 to give an explosive compound
(C) Identify compounds A, B and C.
15. The reactions are explained as:
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
(A) (B)
3Cl2 + 2NH3 → NCl3 + 3HCl
(excess) (C)
16. Although fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen, the ability of oxygen to stabilize higher oxidation states exceeds that of fluorine. Why?
16. Fluorine - 1s22s22p5
Oxygen - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
As we can infer from the electronic configuration, fluorine only has one unpaired electron in its 2p-orbital which can be involved in formation of only one bond and fluorine lacks d-orbital.
While oxygen has d-orbitals in its configuration which allow the oxygen to form multiple bonds. Therefore, oxygen has greater stability to stabilise its oxidation states than fluorine.
17. Although Cr3+ and Co2+ ions have same number of unpaired electrons but the magnetic moment of Cr3+ is 3.87 BM and that of Co2+ is 4.87 BM. Why?
17. Magnetic moment of an electron/dipole moment is caused by its intrinsic properties of spin and electric charge. It depends upon the number of unpaired electrons in its valence shell. The more the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the value of magnetic moment.
Cr3+ = [Ar] 3d3 = 3 unpaired electrons
Co2+ = [Ar] 3d7 = 3 unpaired electrons
But as both the ions have the same no. of unpaired electrons, there’s one other factor called orbital contribution which also influences the magnetic moment. As, the three unpaired electronic configuration is symmetrical in Cr3+ this contributes zero orbital contribution but this is quite appreciable in case of Co2+ and hence it has larger value of Magnetic moment than Cr3+
18. Ionisation enthalpies of Ce, Pr and Nd are higher than Th, Pa and U. Why?
18. Ce, Pr and Nd belong to the lanthanide series whereas Th, Pa and U belong to the actinides family.
When electrons start accommodating the 4f and 5f orbitals, the 5f electrons penetrate less into the inner core. They are more effectively shielded nuclei in comparison to 4f-electrons in lanthanides. This leads to the fact that 5f-electrons experience reduced nuclear force of attraction and hence they have Lower ionisation enthalpies than lanthanoids.
19. Although Zr belongs to 4d and Hf belongs to the 5d transition series but it is quite difficult to separate them. Why?
19. As an effect of lanthanoid contraction, zirconium and hafnium have similar radius of 160 pm and 159 pm respectively. Due to this similarity in their size, they show similar physical and chemical properties.
Lanthanoid contraction: Because the elements in Row 3 have 4f electrons. These electrons do not shield good, causing a greater nuclear charge. This greater nuclear charge has a greater pull on the electrons and result in the decrease in their size and atomic radii.
20. Although +3 oxidation state is the characteristic oxidation state of lanthanoids but cerium shows +4 oxidation state also. Why?
20. Ce = 4f1 5d1 6s2
Ce3 + = 4f1 5d0 6s0
As in Ce3+ ,
4f has only single electron. Cerium holds the capacity to lose this electron also and attain 4f0 configuration which is more stable.
Ce4+ = 4f0 5d0 6s0
Hence it shows 4+ oxidation states.
21. Explain why does colour of KMnO4 disappear when oxalic acid is added to its solution in acidic medium?
21. 2MnO4- + 16H+ + 5C2O42- → 2Mn2 + + 8H2O + 10CO2
KMnO4 oxidises the oxalic acid to CO2 and reduces itself to Mn2+ state. Mn2+ is colourless that’s why it seems that KMnO4 has been disappeared.
22. When orange solution containing Cr2O72− ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when H+ ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why this happens?
22. This is due to the inter conversion of dichromate (orange) to chromate ion (yellow).
Cr2O72- CrO42-
(orange) (yellow)
23. A solution of KMnO4 on reduction yields either a colourless solution or a brown precipitate or a green solution depending on pH of the solution. What different stages of the reduction do these represent and how are they carried out?
23. KMnO4 act as an oxidising agent however it’s activity as oxidising agent is influenced by the pH of the solution i.e. acidic, basic or neutral solution.
K2Cr2O7 + 2KOH → 2K2CrO4 + H2O
(Orange) (yellow)
2K2CrO4 + H2SO4 → K2Cr2O7 + K2SO4 + H2O
(yellow) (orange)
24. The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain why?
24. As an effect of lanthanide contraction, the second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other. For example, zirconium and hafnium have similar radius i.e. 160pm and 159pm respectively. Due to this similarity in their size, they show similar physical and chemical properties.
Lanthanoid contraction: Because the elements in Row 3 have 4f electrons. These electrons do not shield good, causing a greater nuclear charge. This greater nuclear charge has a greater pull on the electrons and result in the decrease in their size and atomic radii.
25. E of Cu is +0.34V while that of Zn is −0.76V. Explain.
25. The sum of sublimation energy and ionisation enthalpy to oxidise cu (s) to Cu2+ is so highly that it is not compensated by the hydration enthalpy of Cu. Due to this, the Eof Cu is positive.
While in case if Zn, the E value is negative or more negative than the expected value because when the electrons are removed from the 4s-orbital. Zn acquires a stable 3d10 configuration state.
26. The halides of transition elements become more covalent with increasing oxidation state of the metal. Why?
26. As the positive charge of the ion increases or we can say that oxidation state of a transition element increases, its size decreases and as per Fajan's rule, more the charge on the metal ion, more is its tendency to form covalent compounds because positively charged cation attracts the electron cloud strongly towards itself.
27. While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s-orbital is filled before the 3d-orbital but reverse happens during the ionization of the atom. Explain why?
27. As per (n + l) rule, 4s has lower energy than 3d-orbital.
3d−n+l = 3+2 = 5
4s - n + l = 4 + 0 = 4
So, 4s are filled first.
After filling of electrons, 4s-orbital moves beyond 3d-orbital and 4s electrons are loosely held by the nucleus. Hence, electrons are removed first during the process of ionisation.
28. Reactivity of transition elements decreases almost regularly from Sc to Cu. Explain.
28. Ionisation enthalpies are the main factor that influence the reactivity of transition elements. Higher the ionisation enthalpy, lesser is the reacting of the transition element.
When we move along the period from Sc to Cu, a regular increase in the ionisation enthalpy is observed which results in the almost regular decrease in the reactivity of elements.
29. Electronic configuration of a transition element X in +3 oxidation state is [Ar]3d5. What is its atomic number?
(A) 25
(B) 26
(C) 27
(D) 24
29. (B) 26
Positive oxidation states indicate the loss of electrons from the atom. If X is in +3 oxidation state, then three electrons have been removed from it. Find the atomic number of the parent atom, we will add three in the given electronic number. i.e.
X3+ (Z = 23) = [Ar] 3d5
X = 23 + 3 = 26
30. The electronic configuration of Cu(II) is 3d9 whereas that of Cu(I)) is 3d10. Which of the following is correct?
(A) Cu(II) is more stable .
(B) Cu(II) is less stable
(C) Cu(I) and Cu(II) are equally stable
(D) Stability of Cu(II) and Cu(I) depends on the nature of copper salts.
30. (A) Cu (II) is more stable .
Electronic configuration of Cuis [Ar] 3d10 4s1
Cu (I) - [Ar] 3d10 4s0
Cu (II)- [Ar] 3d9 4s0
Despite the fact that Cu (I) has fully filled 3d-orbital but Cu (II) is more stable than Cu (I) due to the greater effective nuclear charge of Cu (II) as nucleus has to hold 17 electrons rather than 18 electrons like in Cu (I).
31. Metallic radii of some transition elements are given below. Which of these elements will have the highest density?
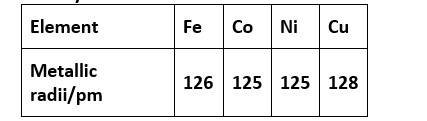
(A) Fe
(B) Ni
(C) Co
(D) Cu
31. (D) Cu
Density is mass by volume. As we move from left to right for a long period, the atomic radii decrease. Hence, volume decreases. Also, an increase in atomic masses is observed.
So overall the density increases out of the above option from iron to copper, copper will have the highest density.
32. Generally, transition elements form coloured salts due to the presence of unpaired electrons. Which of the following compounds will be coloured in solid-state?
(A) Ag2SO4
(B) CuF2
(C) ZnF2
(D) Cu2Cl2
32. (B) CuF2
(A) Ag2SO4 (Ag+ )→ 5d106s0
(B) CuF2 (Cu2+ )→ 3d94s0
(C) ZnF2 (Zn2+)→ 3d104s0
(D) Cu2Cl2 (Cu+)→ 3d106s0
Unpaired electrons present in any compound impart colour to the salt of transition metal. Only CuF2 has unpaired electrons in its 3d orbital that’s why it is white coloured in its solid-state while rest of the salts are colourless.
33. In addition to a small amount of KMnO4 to concentrate H2SO4, a green oily compound is obtained which is highly explosive in nature. Identify the compound from the following:
(A) Mn2O7
(B) MnO2
(C) MnSO4
(D) Mn2O3
33. (A) Mn2O7
2KMnO4 + 2H2SO4 (conc.) → Mn2O7 + 2KHSO4 + H2O
Manganese heptoxide is an acid anhydride of permanganic acid ( HMnO4). It is a dangerous oxidiser, volatile and highly reactive liquid.
34. The magnetic nature of elements depends on the presence of unpaired electrons. Identify the configuration of the transition element, which shows the highest magnetic moment.
(A) 3d7
(B) 3d5
(C) 3d8
(D) 3d2
34. (B) 3d5
Magnetic moment of an electron/dipole moment is caused by its intrinsic properties of spin and electric charge. It depends upon the number of unpaired electrons in its valence shell. The more the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the value of magnetic moment.
3d7 = 3 unpaired electrons
3d5 = 5 unpaired electrons
3d8 = 2 unpaired electrons
3d2 = 2 unpaired electrons
Out of all, 3d5 has five unpaired electrons that is maximum and hence it has the highest magnetic moment.
35. Which of the following oxidation states is common for all lanthanides?
(A) +2
(B) +3
(C) +4
(D) +5
35. (B)+3
Out of all +3 is the most common oxidation state for all the lanthanide elements.
36. Which of the following reactions are disproportionation reactions?
i. Cu+→ Cu2++ Cu
ii. 3MnO4− + 4H+→2MnO4− + MnO2 + 2H2O
iii. 2KMnO4→K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
iii. 2MnO4− + 3Mn2+ + 2H2O → 5MnO2 + 4H+
(A) i,ii
(B) i,ii,iii
(C) ii,iii,iv
(D) i,iv
36. (A)i, ii
Disproportionation/redox reaction is a reaction in which one compound is oxidised as well as reduced at the same time.
(A) Cu+ ? Cu2+ + Cu
( + 1) ( + 2) (0)
(B) 3MnO4- + 4H+ ? 2MnO4- + MnO2 + 2H2O
( + 6) ( + 7) ( + 4)
37. When KMnO4 solution is added to oxalic acid solution, the decolourisation is slow in the beginning but becomes instantaneous after some time because
(A) CO2 is formed as the product
(B) Reaction is exothermic
(C) MnO4 catalyses the reaction
(D) Mn2+ acts as auto catalyst
37. (D) Mn2+ acts as auto catalyst
Mn2+ formed in the reaction acts as an autocatalyst. Auto catalyst is a compound that is one of the products that are formed in the reaction itself catalyses the reaction.
Reaction: 2MnO4- + 16H+ + 5C2O42- → 2Mn2 + + 10CO2 + 8H2O
38. There are 14 elements in the actinide series. Which of the following elements does-not belong to this series?
(A) U
(B) Np
(C) Tm
(D) Fm
38. (C) Tm
In the periodic table, actinides lie from atomic number 90 to 103.
Thulium is not an actinide; it is a lanthanide.
11. KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent in acidic medium. The number of moles of KMnO4 that will be needed to react with one mole of sulphide ions in acidic solution is
(A) 25
(B) 35
(C) 45
(D) 15
39. (A) 25
2MnO4- + 5S2- + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5S + H2O
From the reaction,
For 5 moles of S, two moles of KMnO4 were required.
Therefore, for one mole of S, the number of moles of KMnO4 required will be = 25.
40. Which of the following is amphoteric oxide?
Mn2O7, CrO3, Cr2O3, CrO, V2O5, V2O4
(A) V2O5, Cr2O3
(B) Mn2O7, CrO3
(C) CrO,V2O5
(D) V2O5, V2O4
40. (A) V2O5, Cr2O3
Oxides in the lower oxidation state are basic and in the higher oxidation state they are acidic. They are amphoteric in the intermediate oxidation state. Therefore, V2O5, Cr2O3 are amphoteric in nature.
41. Gadolinium belongs to the 4f series. Its atomic number is 64. Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration of gadolinium?
(A) [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
(B) [Xe] 4f6 5d2 6s2
(C) [Xe] 4f8 6d2
(D) [Xe] 4f9 5s1
41. (A) [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
Gadolinium belongs to the 4f series; it has atomic no.= 64. It has extra stability due to a half-filled 4f subshell.
Gd (Z=64) ? [Xe] 4f6 5d2 6s2
42. Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are trapped inside the crystal lattice of metals. Which of the following is not the characteristic property of interstitial compounds?
(A) They have high melting points in comparison to pure metals
(B) They are very hard
(C) They retain metallic conductivity
(D) They are chemically very reactive.
42. (D) They are chemically very reactive.
Interstitial compounds/alloys are substances that are formed when a small atom like carbon, hydrogen, boron, nitrogen can occupy space in their lattices. All the properties mentioned above are true for interstitial compounds except (D), they are chemically inert.
43. The magnetic moment is associated with its spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. Spin only magnetic moment value of Cr3+ion is
(A) 2.87 B.M.
(B) 3.87 B.M.
(C) 3.47 B.M.
(D) 3.57 B.M.
43. (B) 3.87 B.M.
Cr → (Z = 24)
Cr3 + → (Z = 21)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s0
n = 3 ( 3 unpaired electrons )
μ =
μ =
μ =
μ =
= 3.87 B.M.
44. KmNO4 acts as an oxidizing agent in alkaline medium. When alkaline KmNO4 is treated with KI, iodide ion is oxidized to
(A) I2
(B) IO−
(C) IO3−
(D) IO4−
44. (C) IO3-
Iodide is oxidised to iodate.
2KMnO4 + KI + H2O → 2KOH + 2MnO2 + KIO3
iodide iodate
45. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(A) Copper liberates hydrogen from acids
(B) In its higher oxidation states, manganese forms stable compounds with oxygen and fluorine
(C) Mn3+ and CO3+ are oxidizing agents in aqueous solution
(D) Ti2+ and Cr2+ a re reducing agents in aqueous solution
45. (A) is incorrect.
Copper lies below hydrogen in electrochemical series and hence cannot liberate hydrogen from acids.
Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
46. When acidified K2Cr2O7 solution is added to Sn2+ salts Sn2+ changes to
(A) Sn
(B) Sn3+
(C) Sn4+
(D) Sn+
46. (C) Sn4+
Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 3Sn2+ → 2Cr3 + + 3Sn4+ + 7H2O
In the above redox reaction, oxidation of Sn2+ is taking place. It gets converted to Sn4+ whereas, reduction of chromium is occurring from +6 oxidation state to +3.
47. Highest oxidation state of manganese in fluoride is +4 (MnF4)but highest oxidation state in oxides is +7 (Mn2O7) because
(A) Fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen
(B) Fluorine does not possess d-orbitals
(C) Fluorine stabilizes lower oxidation state
(D) In covalent compounds fluorine can form single bond only while oxygen forms double bond
47. (D) in covalent compounds fluorine can form single bond only while oxygen forms double bond
Oxygen has the capacity to form multiple bonds which enables it to form a variety of covalent compounds.
In (Mn2O7) also, 6 oxygen are doubly bonded to two manganese atoms and one oxygen is forming bridge between two.
While in (MnF4), four fluorine atoms are singly bonded to manganese atom giving it a +4 oxidation state.
Therefore, due to capability of oxygen to have multiple bonds in covalent compounds, manganese is having higher oxidation state of +7 in (Mn2O7) .
48. Although zirconium belongs to 4d transition series and hafnium to 5d transition series even then they show similar physical and chemical properties because
(A) Both belong to d-block
(B) Both have same number of electrons
(C) Both have similar atomic radius
(D) Both belong to the same group of the periodic table
48. (C) both have similar atomic radius
As an effect of lanthanide contraction, zirconium and hafnium have similar radii of 160 pm and 159 pm respectively. Due to this similarity in their size, they show similar physical and chemical properties.
Lanthanide contraction: Because the elements in Row 3 have 4f electrons. These electrons do not shield well, causing a greater nuclear charge. This greater nuclear charge has a greater pull on the electrons and results in the decrease in their size and atomic radii.
49. Why is HCl not used to make the medium acidic in oxidation reactions of KMnO4 in acidic medium?
(A) Both HCl and KMnO4 act as oxidizing agents.
(B) KMnO4 oxidises HCl into Cl2 which is also an oxidizing agent.
(C) KMnO4 is a weaker oxidizing agent than HCl.
(D) KMnO4acts as a reducing agent in the presence of HCl.
49. (B) KMnO4 oxidises HCl into Cl2 which is also an oxidizing agent.
HCl is not used in titrations involving KMnO4 as it produces unsatisfactory results. When HCl is added to KMnO4, it itself acts as reducing agent and coverts HCl to Cl2.
50. Generally, transition elements and their salts are coloured due to the presence of unpaired electrons in metal ions. Which of the following compounds are coloured?
(A) KMnO4
(B) Ce(SO4)2
(C) TiCl4
(D) Cu2Cl2
50. (A) & (B)
Due to charge transfer phenomenon, which can be understood, for an instant, an electron is transferred from oxygen to the central metal atom, where oxidation state of metal is reduced by one and oxygen gets converted from O- to O2- .
This transfer imparts Colour to the compound.
51. Transition elements show magnetic moments due to spin and orbital motion of electrons. Which of the following metallic ions have almost the same spin only magnetic moment?
(A) CO2+
(B) Cr2+
(C) Mn2+
(D) Cr3+
51. (A) & (D)
The magnetic moment of an electron/dipole moment is caused by its intrinsic properties of spin and electric charge. It depends upon the number of unpaired electrons in its valence shell. The more the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the value of the magnetic moment.
Co2+ and Cr3+ have same unpaired electrons i.e. 3 unpaired electrons. Hence they have the same spin only magnetic moment.
52. In the form of dichromate, Cr(VI) is a strong oxidizing agent in acidic medium but Mo (VI) in MoO3 and W (VI) in WO3 are not because
(A) Cr(VI) is more stable than Mo (VI) and W (VI)
(B) Mo (VI) and W (VI) are more stable than Cr (VI)
(C) Higher oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable
(D) Lower oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable.
52. (B) and (C)
For the heavier metals of d-block, higher oxidation state is more favourably stable than the lower oxidation state. For example: Mo (VI) and W (VI) are more stable than Cr (VI). For lighter d-block elements like chromium, +3 oxidation state is more stable. So, Cr (VI) in dichromate act as a strong oxidising agent by reducing itself from +6 to +3 oxidation states While Mo (VI) and W (VI) does not.
53. Which of the following actinoids show oxidation states up to +7?
(A) Am
(B) Pu
(C) U
(D) Np
53. (B) & (D)
Actinides show a variety of oxidation states like +3, +5, +6 and +7.
From the given option, plutonium and neptunium show all oxidation states up to +7
54. General electronic configuration of actinides is (n−−2)f1−14(n−−1)d0−2ns2. Which of the following actinoids have one electron in 6d orbital?
(A) U (Atomic no. 92)
(B) Np (Atomic no. 93)
(C) Pu (Atomic no. 94)
(D) Am (Atomic no. 95)
54. (A) and (B)
Electronic configuration:
92U - 5f3 6d1 7s2
93Np - 5f4 6d1 7s2
55. Which of the following lanthanoids show +2 oxidation state besides the characteristic oxidation state +3 of lanthanides?
(A) Ce
(B) Eu
(C) Yb
(D) Ho
55. (B) and (C)
Ce (Z = 57) = [Xe] 4f5 5d0 6s2 , O.S. = + 3, + 4
Eu (Z = 63) = [Xe] 4f7 5d0 6s2, O.S. = + 2, + 3
Yb (Z = 70) = [Xe] 4f14 5d0 6s2, O.S. = + 2, + 3
Ho (Z = 67) = [Xe] 4f11 5d0 6s2, O.S. = + 3
56. Which of the following ions show higher spin only magnetic moment value?
(A) Ti3+
(B) Mn2+
(C) Fe2+
(D) Co3+
56. (B) and (C)
Magnetic moment of an electron/dipole moment is caused by its intrinsic properties of spin and electric charge. It depends upon the number of unpaired electrons in its valence shell. The more the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the value of magnetic moment.
Electronic configuration:
Ti3+ = 3d1 = 1 unpaired electron
Mn2+ = 3d5 = 5 unpaired electrons
Fe2+ = 3d6 = 4 unpaired electrons
Co2+ = 3d7 = 3 unpaired electrons
Out of all given options, Mn2+ and Fe2+ have unpaired electrons in number of five and four respectively. Hence, have higher spin only magnetic moment.
57. Transition elements form binary compounds with halogens. Which of the following elements will form MF3 type compounds?
(A) Cr
(B) Co
(C) Cu
(D) Ni
57. (A) and (B)
Cr and Co form tri halide compounds.
58. Which of the following will not act as oxidizing agents?
(A) CrO3
(B) MoO3
(C) WO3
(D) CrO42−
58. (B) and (C)
A compound act as oxidising agent when it's central atom is reduced to its lower oxidation state. This occurs only when the lower oxidation state of metal is more stable than the higher oxidation states.
In metal WO3 and CrO42- , both W and Cr are stable in their higher oxidation state and won't get reduced to their lower oxidation state. Therefore, will not act as oxidising agents.
59. Although +3 is the characteristic oxidation state for lanthanide but cerium also shows +4 oxidation state because
(A) It has variable ionization enthalpy
(B) It has a tendency to attain noble gas configuration
(C) It has a tendency to attain f? configuration
(D) It resembles Pb4+
59. (B) and (C)
Electronic configuration of cerium:
Ce - 4f1 5d1 6s2
Ce4+? 4f0 5d0 6s0
Lead has the tendency to lose its four outer electrons to attain Noble gas configuration and this removal of electrons corresponds to the f? configuration and cause it to be stable in +4 oxidation state
60. Assertion (A): Cu2+ iodide is not known.
Reason (R): Cu2+ oxidises I to iodine.
60. All halogens combine with copper to form copper halides except iodine. The reason behind this is that Cu2+ oxidises iodide (-1) to iodine (0). Therefore, Cu2+ iodide does not exist .Both the statements assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
61 Assertion (A): Separation of Zr and Hf is difficult.
Reason (R): Because Zr and Hf lie in the same group of the periodic table.
61. Although Zr and Hf lie in same group but As an effect of lanthanide contraction, zirconium and hafnium have similar radius of 160pm and 159 pm respectively. Due to this similarity in their size, they show similar physical and chemical properties. As a result, Zr and Hf are difficult to separate. Both the statements assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
62. Assertion (A): Actinoids form relatively less stable complexes as compared to lanthanoids.
Reason (R): Actinoids can utilize their 5d orbitals along with 6d orbitals in bonding but lanthanoids do not use their 4f orbital for bonding.
62. Actinoids are more reactive than lanthanoids as they involve their 5d-orbital in the bond formation process while due to effectively shielded and greater nuclear charge 4f-orbitals are not available for bonding. Thus, lanthanoids comparatively form less complexes than actinoids.
Assertion is not true but reason is true.
63. Assertion (A): Cu cannot liberate hydrogen from acids .
Reason (R): because it has positive electrode potential.
63. Cu lies below hydrogen in electrochemical series and has positive electrode potential. hence cannot liberate hydrogen from acids.
Both the statements assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
64. Assertion (A): The highest oxidation state of osmium is +8.
Reason (R): Osmium is a 5d-block element.
64. Osmium has the capacity to expands its octet by utilising all the electrons from its 6s and 5d orbitals this results it to attain an oxidation state of +8.
Both the statements assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. The correct option is B.
66. Match the compounds/elements given in Column I with uses given in Column II
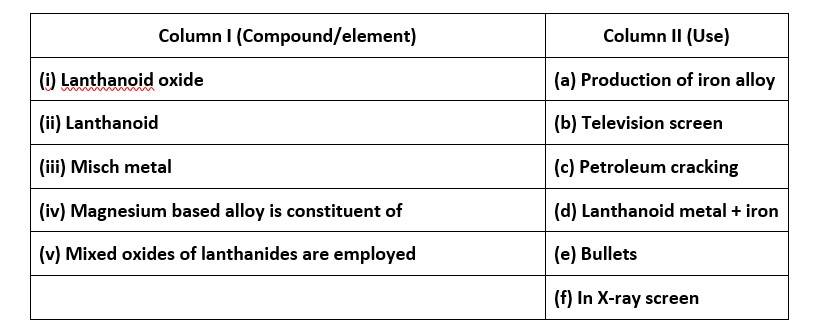
66. (i) - (b); (ii)- (a); (iii)- (d); (iv)- (e); (v)- (c)
67. Match the properties given in Column I with the metals given in Column II.
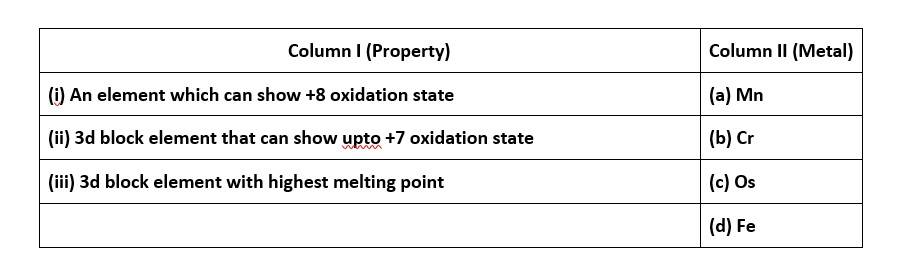
67. (i) - (c); (ii)- (a); (iii)- (b)
68. Match the statements given in Column I with the oxidation states given in Column II.

68. (i) - (c); (ii)- (a); (iii)- (e); (iv)- (b)
69. Match the solutions given in Column I and the colours given in Column II.

69. (i) - (d); (ii)- (a); (iii)- (b); (iv)- (e); (v)- (f)
70. Match the property given in Column I with the element given in Column II.
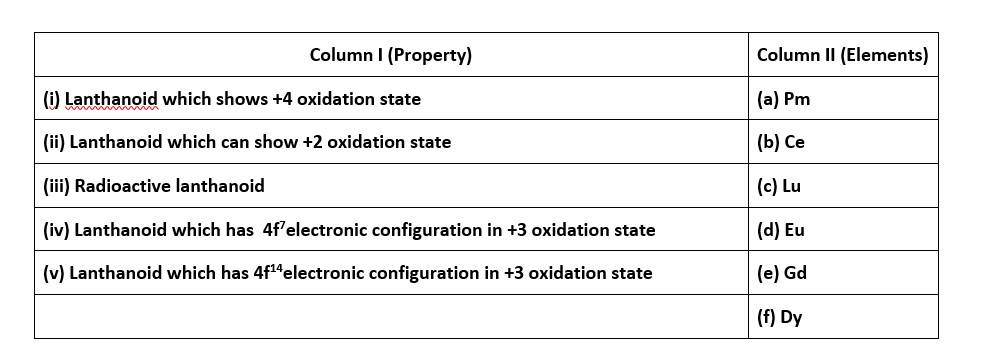
70. (i) - (b); (ii)- (d); (iii)- (a); (iv)- (e); (v)- (c)
71. Match the properties given in Column I with the medals given in Column II.

71. (i) - (c); (ii)- (d); (iii)- (b); (iv)- (e)
JEE Main 27th June 2022 (Second Shift)
JEE Main 27th June 2022 (Second Shift)
Commonly asked questions
Identify the incorrect statement for PCl5 from the following
Structure PCl5 is trigonal bipyramidal,
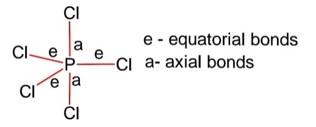
Hybridization of P is sp3d
Equatorial bonds lie in a plane
Axial bonds are longer than equatorial bonds so axial bonds are weaker than equatorial bonds.
The gas produced by treating an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride with sodium nitride is
Hence, N2 gas is produced.
Arrange the following coordination compounds in the increasing order of magnetic moments (Atomic numbers: Mn = 25; Fe = 26)
(A) (B) (C) (high spin) (D)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A.
Fe3+ - 3d54s0
F- is weak field ligand, so no pairing of electrons :
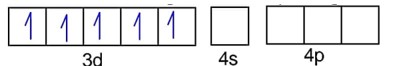
Number of unpaired electrons, n = 5
B.
CN- is strong field ligand, so pairing of electrons takes place.
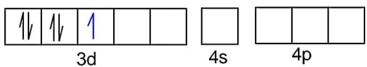
Number of unpaired electrons, n = 1
C.
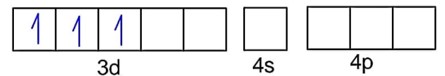
Number of unpaired electrons, n = 3
D.
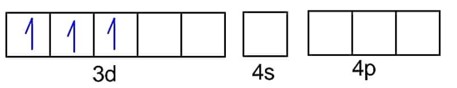
Number of unpaired electrons, n = 3
Higher the number of unpaired electrons. Then higher be the magnetic moment as;
Magnetic moment,
Hence, order of magnetic moment is ;
B < D = C < A
Match List I with List II
0.25g of an organic compound containing chlorine gave 0.40g of silver chloride in Carius estimation. The percentage of chlorine present in the compound is___________. [ in nearest integer]
(Given: Molar mass of Ag is 108 g mol-1 and that of Cl is 35.5 g mol-1)
Moles of chlorine in the given compound = Moles of chlorine in AgCl
= moles of AgCl
Mass of chlorine =
= 0.098 g
Which amongst the given plots is the correct plot for pressure (p) vs density (d) for an ideal gas?
For ideal gas using ;
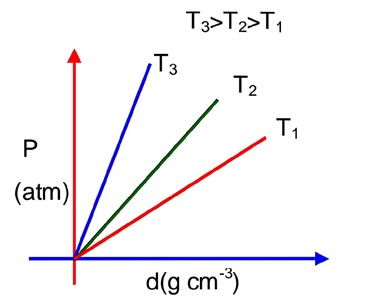
PM = dRT
Comparing with y = mx + C
Slope, m =
Slope
So; higher the slope higher the T
Hence, T3 > T2 > T1
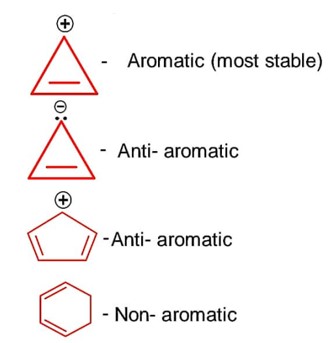
Which of the following is most stable?
Aromatic species are most stable, here
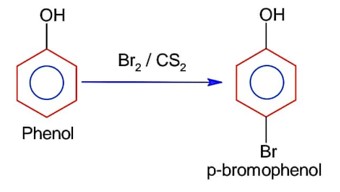
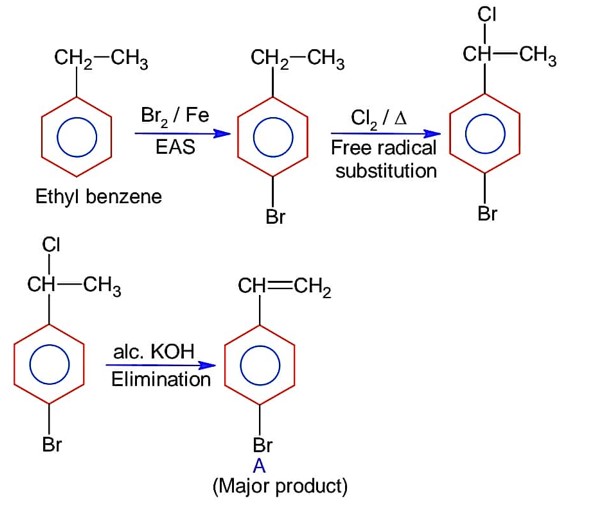
Product ‘A’ of following sequence of reaction is
Statement I: Leaching of gold with cyanide ion in absence of air / O2 leads to cyano complex of Au(III)
Statement II: Zinc is oxidized during the displacement reaction carried out for gold extraction.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer form the options given below.
Leaching involves the given reaction,
Here, O2 is required for formation of Au (l) cyanide complex but no complex in absence of O2.
In above displacement reaction, Zn is oxidized.
The correct order of increasing intermolecular hydrogen bond strength is
Higher the E.N. difference between hydrogen and other atom then higher be the strength of intermolecular H-bond
Here, order of difference in E.N is
O - H > N – H > C - H
Hence, correct order of H bond strength is,
CH4 < HCN < NH3
The correct order of increasing ionic radii is
For isoelectronic species
Hence, correct order of ionic radii is;
Given below are two statements: one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labeled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Flourine forms one oxoacid.
Reason R: Flourine has smallest size amongst all halogens and is highly electronegative.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Fluorine forms only one oxoacid which is hypofluorous acid HOF because it shows only – 1 oxidation state. Which is due to its the smallest size among halogens & the highest electronegativity.
In 3d series, the metal having the highest M2+ / M standard electrode potential is
In 3d-series, all metals except Cu have negative value of
The ‘f’ orbitals are half and completely filled, respectively in lanthanide ions
[Given: Atomic no. Eu, 63; Sm, 62; Tm, 69; Tb, 65; Yb, 70; Dy, 66]
Electronic configuration of the given ions is :
Hence, Eu2+ and Tb4+ have half | filled f-orbitals and Yb2+ have completely filled f-orbitals.
On the surface of polar stratospheric clouds, hydrolysis of chlorine nitrate given A and B while its reaction with HCl produces B and C.A, B and C are, respectively.
Chlorine nitrate as hydrolysis gives hypohalous acid and nitric acid as,
Chlorine nitrate on reaction with HCl produces Cl2 and HNO3 as,
Decarboxylation of all six possible forms of diaminobenzoic acid yields three product A, B and C. Three acids give a products ‘A’ two acids gives a products ‘B’ and one acids give a products ‘C’. The melting point of product ‘C’ is
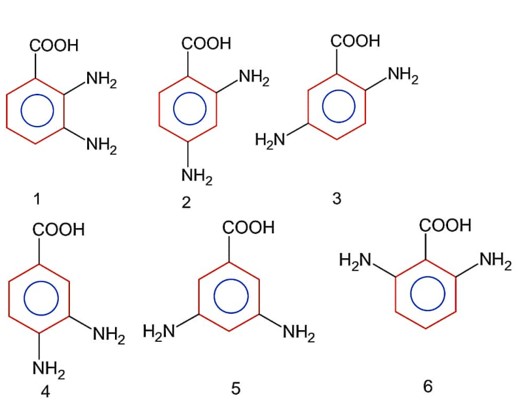
Above are the six possible forms of diaminobenzoic acid.
On decarboxylation we get;
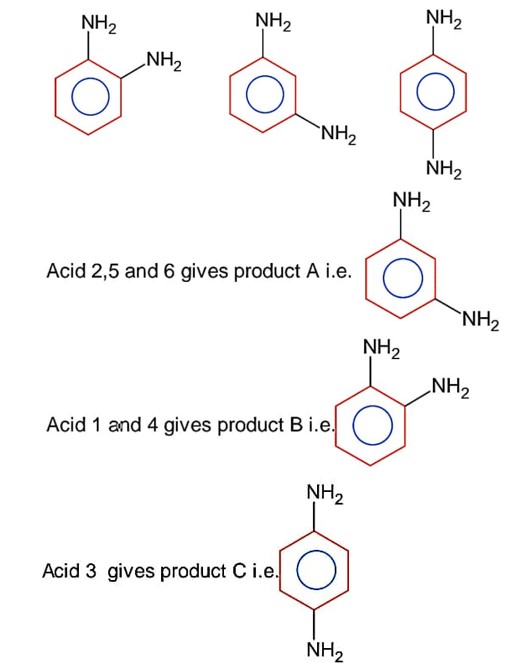
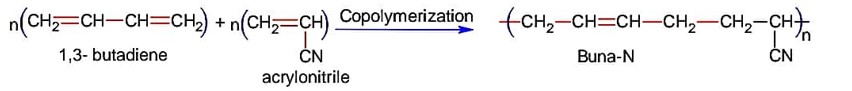
Which is true about Buna-N
Buna-N is obtained by copolymerization of 1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile,
Given below are two statements.
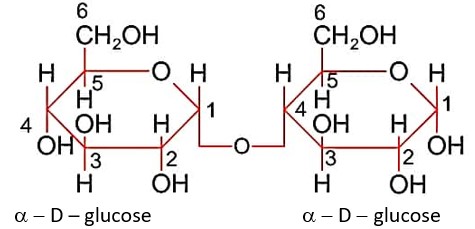
Statements I: Maltose has two a-D-glucose units linked at C1 and C4 and is a reducing sugar:
Statements II: Maltose has two manosaccharides: a-D-glucose and b-D-glucose linked at C1 and C6 and its is a non-reducing sugar.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
In maltose, two units of a-D-glucose are linked by glycosidic linkage at C1 and C4 as shown.
a - D – glucose a - D - glucose
Maltose has hemiacetal link so it is reducing sugar.
Match List I with List II
List I List II
A. Antipyretic I. Reduces pain
B. Analgesic II. Reduces stress
C. Tranquilizer III. Reduces fever
D. Antacid IV. Reduces acidity (stomach)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A. Antipyretic reduces fever.
B. Analgesic reduces pain.
C. Tranquilizer reduces stress.
D. Antacid reduces acidity of stomach.
Match List I with List II
|
List I |
List II |
||
|
(Anion) |
(gas evolved on reaction with dil H2SO4) |
||
|
A. |
CO32- |
I. |
Colourless gas which turns lead acetate paper black |
|
B. |
S2- |
II. |
Colourless gas which turns acidified potassium dichromate solution green |
|
C. |
SO32- |
III. |
Brown fumes which turns acidified Kl solution containing starch blue.
|
|
D. |
NO2- |
IV. |
Colourless gas evolved with brisk effervescence, which turns lime water milky |
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
A.
CO2 is colourless gas with brisk effervescence and turns lime water milky
B.
H2S + (CH3COO)2Pb →
C.
SO3 is colourless gas which turns acidified potassium dichromate solution green as
D.
I2 + starch → Blue colour complex.
116 g of a substance upon dissociation reaction yields 7.5 g of hydrogen 60 g of oxygen and 48.5 g of carbon. Given that the atomic masses of H, O and C are 1, 16 and 12, respectively. The data agrees with how many formulae of the following?
(a) CH3COOH (b) HCHO (c) CH3OOCH3 (d) CH3CHO
Determining empirical formula of the given compound.
Mass Moles Simplest ratio
C 41.8g
H 6.5 g
O 51.7 g
Ratio of moles of C, H and O is 1 : 2 : 1
A. CH3COOH ⇒ C : H : O = 2 : 4 : 2 = 1 : 2 : 1
B. HCHO ⇒ C : H : O = 1 : 2 : 1
C. CH3OOCH3 ⇒ C : H : O = 2 : 6 : 2 = 1 : 3 : 1
D. CH3CHO ⇒ C : H : O = 2 : 4 : 1
So, CH3COOH and HCHO formulae agree with the given data
Consider the following set of quantum numbers.
|
|
n |
|
|
|
A. |
3 |
3 |
-3 |
|
B. |
3 |
2 |
-2 |
|
C. |
2 |
1 |
+1 |
|
D. |
2 |
2 |
+2 |
The number of correct sets of quantum numbers is____________.
n = 1, 2, 3 …….;
A. n = 3 is incorrect as
B. n = 3 = -2 is correct set.
C. n = 2 = +2 is incorrect set as
So; correct set of quantum numbers is B and C.
BeO reacts with HF in presence of ammonia to give [A] which on thermal decomposition produces [B] and ammonium fluoride. Oxidation state of Be in [A] is____________.
here, oxidation state of be in A is +2.
When 5 moles of He gas expand isothermally and reversibly at 300K from 10 litre to 20 litre, the magnitude of the maximum work obtained is___________J. (nearest integer)
[Given: R=8.3 JK-1mol-1 and log2 = 0.3010]
Number of moles, n = 5 mol
Temperature, T= 300 K
Initial volume, V1 = 10L
Final volume, V2 = 20 L
Using;
Work done; w = -2.303 nRT log10
= -8630 J
So, magnitude of work done is 8630 J.
A solution containing 2.5 × 10-3 kg of solute dissolved in 75 × 10-3 kg of water boils at 373.535 K. The molar mass of the solute is_________g mol-1. (nearest integer)
[Given Kb(H2O) = 0.52 K kg mol-1 and boiling point of water = 373.15 K)
Mass of solute ; wB = 2.5 × 10-3 kg
Mass of solvent,
Boiling point of solution ;
Boiling point of water ;
So, elevation in boiling point,
Using ;
Molar mass of solute ; MB = 45 g/mol
pH value of 0.001 M NaOH solution is___________.
0.001 M NaOH solution has [OH-] = 0.001 M = 10-3 M
Using ; pOH =
=
pOH = 3
pH = 14 – pOH
pH = 14 – 3
pH = 11
For the reaction taking place in the cell:
The value of is________________kJ mol-1 (in nearest integer)
For the given cell, net redox reaction is as;
n = 2
Using;
Now, for the reaction
n = 1
So;
=
It has been found that for a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 9K the rate constant gets doubled. Assuming a reaction to be occurring at 300 K, the value of activation energy is found to be________ kJ mol-1. (in nearest integer)
(Given: In 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1, log2 = 0.30)
Initial temperature ; T1 = 300 K
Final temperature ; T2 = 309 K
Rate constant gets doubled i.e K2 = 2K1
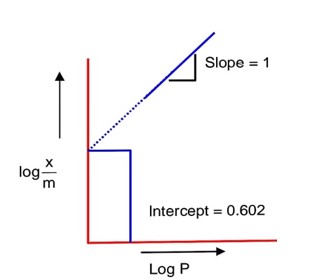
If the initial pressure of a gas is 0.03 atm, the mass of the gas adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent is____________× 10-2g.
Using, Freundlich adsorption isotherm ;
………………. (i)
Comparing with y = mx + C
Slope =
Intercept, log k = 0.602
log k = log 4
k = 4
from equation (i)
= 0.12
= 12 × 10-2
So, 12 × 10-2 g of gas is adsorbed per gram of adsorbent,
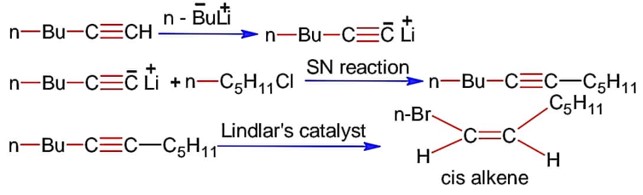
What will be the major product of following sequence of reactions?
Lindlar's catalyst reduces alkynes to cis-alkene.
Lindlar's catalyst reduces alkynes to cis-alkene.
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,27th june ,chemistry , first
JEE Mains Solutions 2022,27th june ,chemistry , first
Commonly asked questions
Metal deficiency defect in shown by Fe0.93O. In the crystal, some Fe2+ cations are missing and loss of positive charge is compensated by the presence of Fe3+ ions. The percentage of Fe2+ ions in the Fe0.93O crystals is___________.
In Fe0.93O
Let us suppose that fraction of Fe2+ is x and fraction of Fe3+ is (1 – x)
If the uncertainty in velocity and position of a minute particle in space are, 2.4 × 10-26(ms-1) and 10-7(m) respectively. The mass of the particle in g is __________.
(Given: h = 6.626 × 10-34g)
And
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty
Or 21.98 gm
Or 22 gm in the nearest integer.
2g of a non-volatile non-electrolyte solute is dissolved in 200g of two different solvents A and B whose ebullioscopic constant are in the ratio of 1:8. The elevation in boiling points of A and B are in the ratio The value of y is __________. (Nearest integer)
or
In an experiment 2.0 mole of NOCl was placed in a non-litre flask and the concentration of NO after equilibrium established, was found to be 0.4 mol/L. The equilibrium constant at 30°C is__________× 10-4
t = 0 2 mol/Lit 0 0
teq 2 – x x x/2
The limiting molar conductivities of Nal, NaNO3 and AgNO3 are 12.7, 12.0 and 13.3 mS m2 mol-1, respectively (all at 25°C). The limiting molar conductivity of Agl at this temperature is_________mS m2 mol-1.
of NaNO3 = 12.0 m Sm2 mol-1
of AgNO3 = 13.3 mSm2 mol-1
= (13.3 + 12.7) - 12.0 = 14.0 m Sm2 mol-1
The rate constant for a first order reaction is given by the following equation Ink = 33.24 -
The activation energy for the reaction is given by ___________kJ mol-1 (In nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.3JK-1mol-1)
According to Arrhenius equation ;
Here lnk = 33.24
The Number of statement(s) correct from the following for Copper (At no. 29) is / are__________.
(a) Cu(II) complexes are always paramagnetic
(b) Cu(I) complexes are generally colourless
(c) Cu(I) is easily oxidized
(d) In Fehling solution, the active re agent has Cu(I)
Cu+ Paramagnetic due to unpaired e-
Cu+ Colourless from due to 3d10
Cu+ acts as readucing agent
Cu+ it's a product form of Fehling's solution
Acidified potassium permanganate solution oxidizes oxalic acid. The spin only magnetic moment of the manganese product formed from the above reaction is_______________B.M.
Following is the reaction for oxidation of oxalic acid by KMnO4
Here, Mn2+ ion is in product form
Having 5 unpaired electron
Magnetic moment =
Two elements A and B which 0.15 moles of A2B and AB3 type compounds. If both A2B and AB3 weight equally, then the atomic weight of A is _______times of atomic weight of B
Mol wt A2B = Mol wt of AB3
Hence (2A + B) = (A + 3B)
Atomic wt of A is two times of atomic wt of B.
Total number of possible stereoisomers of dimethyl cyclopentatne is_____________.
Following are the possible isomers of dimethyl cyclopentane.
JEE Mains 2020
JEE Mains 2020
Commonly asked questions
The number of molecules with energy greater than the threshold energy for a reaction increases five fold by a rise of temperature from 27°C to 42°C. Its energy of activation in J/mol is (Take in 5 = 1.6094; R = 8.314 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹)
k = Ae? Ea/RT
ln (K? /K? ) = (Ea/R) [1/T? - 1/T? ]
ln (5) = (Ea/8.314) [1/300 - 1/315]
1.6094 = (Ea/8.314) [15 / (300 × 315)]
Ea = 84297 J
Consider the following equations :
2Fe²⁺ + H₂O₂ → xA + yB (in basic medium)
2MnO₄⁻ + 6H⁺ + 5H₂O₂ → x'C + y'D + z'E (in acidic medium)
The sum of the stoichiometric coefficients x, y, x', y' and z' for products A, B, C, D and E, respectively, is
(i) 2Fe²? + H? O? → 2Fe³? + 2OH?
(ii) 2MnO? + 5H? O? + 6H? → 2Mn²? + 5O? + 8H? O
So sum of (x + y + x¹ + y¹ + z¹) = 2 + 2 + 2 + 5 + 8 = 19
The number of chiral centres present in threonine is
Threonine has two chiral carbon atoms.
A 100 mL solution was made by adding 1.43 g of Na₂CO₃ · xH₂O. The normality of the solution is 0.1 N. The value of x is (The atomic mass of Na is 23 g/mol )
Equivalent of solute = 0.1 × 0.1
Mole of solute (Na? CO? ·xH? O) = [0.1 × 0.1]/2
Mass of Na? CO? ·xH? O = ( [0.1 × 0.1]/2) × [106 + 18x] = 1.43
⇒ 106 + 18x = 286
18x = 180
x = 10
The osmotic pressure of a solution of NaCl is 0.10 atm and that of a glucose solution is 0.20 atm. The osmotic pressure of a solution formed by mixing 1 L of the sodium chloride solution with 2 L of the glucose solution is x × 10⁻³ atm. x is (nearest integer)
Π = iCRT = I (n/V)RT
Πfinal = (Π? V? + Π? V? )/ (V? + V? )
Πfinal = [ (0.1 × 1) + (0.2 × 2)]/3
= (0.1 + 0.4)/3 = 0.5/3 = (500/3) × 10? ³ atm
so X = 167
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eight Exam