- Coordination Compounds Questions and Answers
- JEE Main Solutions 2022
Coordination Compounds Questions and Answers
| 1. Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following: (i) [CoF6]3- ,[Co(H2O)6]2+ ,[Co(CN)6]3- |
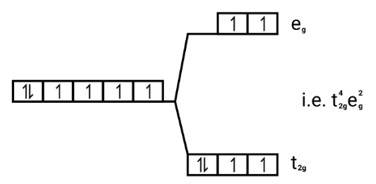
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: Electronic cnfiguration: Co3+ =[Ar]3d6 Energy level diagram: Magnetic moment: Number of unpaired electrons (n)=4 Magnetic moment = μ= = = = 4.9 BM [Co(H2O)6]2+ Electronic cnfiguration: Co2+=[Ar]3 d7 Energy level diagram: Magnetic moment: Since ,number of unpaired electrons (n)=3, therefore magnetic moment = = = 3.87BM
[Co(CN)6]3− Electronic configuration: [Ar]Co3+=3 d6 Energy level diagram: |
| (ii) [FeF6]3- ,[Fe(H2O)6]2 + ,[Fe(CN)6]4 - |
| Ans: [FeF6]3− Electronic configuration: Fe3+=[Ar]3 d5 Energy level diagram: Number of unpaired electrons = μ= = μ= = 5.95BM [Fe(H2O)6]2+ Fe2+=[Ar]3 d6 Energy level diagram: Magnetic moment Since, number of unpaired electrons (n)=4, therefore magnetic moment is- = = 4.9BM [Fe(CN)6]4− Electronic configuration: Fe2+=[Ar]3 d6 Energy level diagram Since CN− is strong field ligand, it forces all the electrons to get paired up Magnetic moment. In the absence of unpaired electrons it behaves as diamagnetic ( ie. no magnetic behaviour ). So magnetic moment = zero |
| 2. Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below: [Mn(CN)6]3- ,[Co(NH3)6]3+ ,[Cr(H2O)6]3+ ,[FeCl]4- (i) Type of hybridisation. (ii) Inner or outer orbital complex. (iii) Magnetic behaviour. (iv) Spin only magnetic moment value |
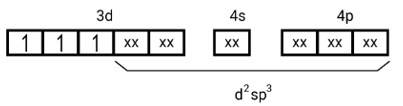
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: [Mn(CN)6]3− Electronic configuration is Mn3+=[Ar]3 d4 hence box electronic structure (i) Type of hybridisation d2sp3 (ii) Inner orbital complex (iii) paramagnetic, due to presence of three unpaired electrons. (iv) Spin only magnetic moment is calculated using the formula : n=2 in this case, we get spin only magnetic moment in BMas = = = 2.87BM
[Co(NH3)6]3+ Electronic configuration of Co3+=[Ar]3 d6 (i) Hyb As shown in the above box electronic structure the type of hybridisation is ........... d2sp3 (ii) Inner orbital complex (iii) Diamagnetic (iv) Zero( Since no unpaired electrons are present, as depicted above)
[Cr(H2O)6]3+ (i) type of hybridisation........ d2sp3 (ii) Inner orbital complex (iii) paramagnetic (iv) 3.87BM [Fe(Cl)6]4− electronic configuration is of Fe2+=[Ar]3 d6 (i) type of hybridisation will be sp3d2 (ii) Outer orbital complex (iii) Paramagnetic (iv) 4.9BM |
| 3. CoSO4Cl.5NH3 exists in two isomeric forms ‘A’ and ‘B’. Isomer ‘A’ reacts with AgNO3 to give white precipitate but does not react with BaCl2 . Isomer ‘B’ gives white precipitate with BaCl2 but does not react with AgNO3. Answer the following questions. (i) Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and write their structural formulas. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: ‘A’ is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl ‘B’ is [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 |
| (iii) Give the IUPAC name of ‘A’ and ‘B’. |
| Ans: IUPAC name of isomer ‘A’ is pentaaminesulphatocobalt(III)chloride IUPAC name of isomer ‘B’ is pentaaminechlorocobalt(III)sulphate |
| 4. What is the relationship between observed colour of the complex and the wavelength of light absorbed by the complex? |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: When light wavelengths from a specific part of the spectrum are absorbed by a substance, the result is a complimentary colour. When a complex absorbs a wavelength of light, it reflects a complementary colour. If a violent colour is absorbed, for example, yellow is conveyed. The CFSE value, often known as the colour definer for any complex, comes next. To determine the wavelength value in order to determine which colour absorbs the most energy. Δe= As λ has shorter wavelength. Low spin complexes absorb shorter wavelengths, while high spin complexes absorb longer ones. The colour theory, complex, and wavelength are all determined using this method. |
Commonly asked questions
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following:
(i) [CoF6]3- ,[Co(H2O)6]2+ ,[Co(CN)6]3-
(ii) [FeF6]3- ,[Fe(H2O)6]2 + ,[Fe(CN)6]4 -
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) Electronic cnfiguration: Co3+ =[Ar]3d6
Energy level diagram:
Magnetic moment:
Number of unpaired electrons (n)=4
Magnetic moment = μ= =
= = 4.9 BM
[Co(H2O)6]2+
Electronic cnfiguration: Co2+=[Ar]3 d7
Energy level diagram:
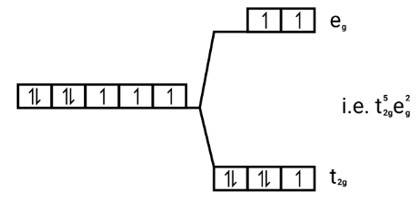
Magnetic moment: Since ,number of unpaired electrons (n)=3, therefore magnetic moment = = = 3.87BM
[Co(CN)6]3−
Electronic configuration: [Ar]Co3+=3 d6
Energy level diagram:
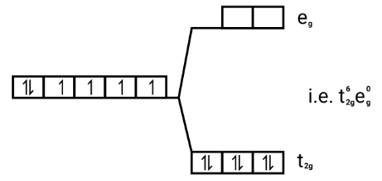
Ans: [FeF6]3−
Electronic configuration: Fe3+=[Ar]3 d5
Energy level diagram:
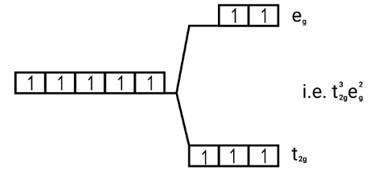
Number of unpaired electrons = μ= = μ= = 5.95BM [Fe(H2O)6]2+
Fe2+=[Ar]3 d6
Energy level diagram:
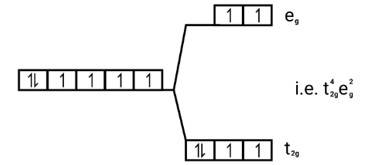
Magnetic moment
Since, number of unpaired electrons (n)=4, therefore magnetic moment is-
= = 4.9BM
[Fe(CN)6]4−
Electronic configuration: Fe2+=[Ar]3 d6
Energy level diagram
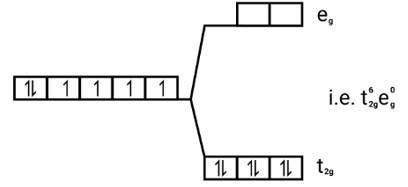
Since CN− is strong field ligand, it forces all the electrons to get paired up Magnetic moment.
In the absence of unpaired electrons it behaves as diamagnetic ( ie. no magnetic behaviour ).
So magnetic moment = zero
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
[Mn(CN)6]3- ,[Co(NH3)6]3+ ,[Cr(H2O)6]3+ ,[FeCl]4-
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
[Mn (CN)6]3−
Electronic configuration is Mn3+= [Ar]3 d4 hence box electronic structure
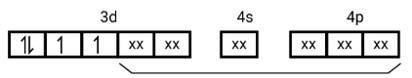
(i) Type of hybridisation d2sp3
(ii) Inner orbital complex
(iii) paramagnetic, due to presence of three unpaired electrons.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment is calculated using the formula : n=2 in this case, we get spin only magnetic moment in BMas = = = 2.87BM
[Co (NH3)6]3+
Electronic configuration of Co3+= [Ar]3 d6
(i) Hyb As shown in the above box electronic structure the type of hybridisation is . d2sp3
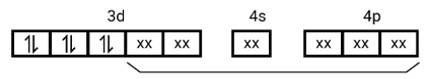
(ii) Inner orbital complex
(iii) Diamagnetic
(iv) Zero ( Since no unpaired electrons are present, as depicted above)
[Cr (H2O)6]3+
(i) type of hybridisation. d2sp3
(ii) Inner orbital complex
(iii) paramagnetic
(iv) 3.87BM
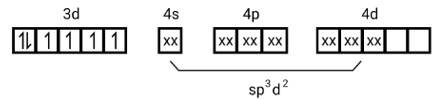
[Fe (Cl)6]4−
electronic configuration is of Fe2+= [Ar]3 d6

(i) type of hybridisation will be sp3d2
(ii) Outer orbital complex
(iii) Paramagnetic
(iv) 4.9BM
CoSO4Cl.5NH3 exists in two isomeric forms ‘A’ and ‘B’. Isomer ‘A’ reacts with AgNO3 to give white precipitate but does not react with BaCl2 . Isomer ‘B’ gives white precipitate with BaCl2 but does not react with AgNO3.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ and write their structural formulas.
(ii) Name the type of isomerism involved.
(iii) Give the IUPAC name of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) 'A' is [Co (NH3)5SO4]Cl
'B' is [Co (NH3)5Cl]SO4
(ii) Type of isomerism is ionisation isomerism
(iii) IUPAC name of isomer 'A' is pentaaminesulphatocobalt (III)chloride
IUPAC name of isomer 'B' is pentaaminechlorocobalt (III)sulphate
What is the relationship between observed colour of the complex and the wavelength of light absorbed by the complex?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: When light wavelengths from a specific part of the spectrum are absorbed by a substance, the result is a complimentary colour. When a complex absorbs a wavelength of light, it reflects a complementary colour. If a violent colour is absorbed, for example, yellow is conveyed. The CFSE value, often known as the colour definer for any complex, comes next. To determine the wavelength value in order to determine which colour absorbs the most energy.
Δe=
As λ has shorter wavelength.
Low spin complexes absorb shorter wavelengths, while high spin complexes absorb longer ones. The colour theory, complex, and wavelength are all determined using this method.
Why are different colours observed in octahedral and tetrahedral complexes for the same metal and same ligands?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The octahedral and tetrahedral splitting up of d orbitals is different.
Δt= ( )Δ0
Δt < Δ0
Δt= CFSE in tetrahedral field
Δ0= CFSE in octahedral field
Comparing CFSE with energy=
Arrange the following complexes in the increasing order of conductivity of their solution: [Co(NH3)3Cl3], [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl, [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Complexes with more number of ions show more conductivity.
[Co (NH3)3Cl3], [Co (NH3)4Cl2] < [Cr (NH3)5Cl]Cl2
A coordination compound CrCl3.4H2O precipitates silver chloride when treated with silver nitrate. The molar conductance of its solution corresponds to a total of two ions. Write structural formula of the compound and name it.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The solution CrCl3.4H2O molar conductance shows that it contains one positive and one negative ion.
An ion is present outside the complex when silver chloride is treated with silver nitrate chloride. Outside the complex, there are two ions and one chloride, hence the name of the complex will be
[Co (H2O)4Cl2]Cl, Tetraaquadichloridocobalt (III)chloride.
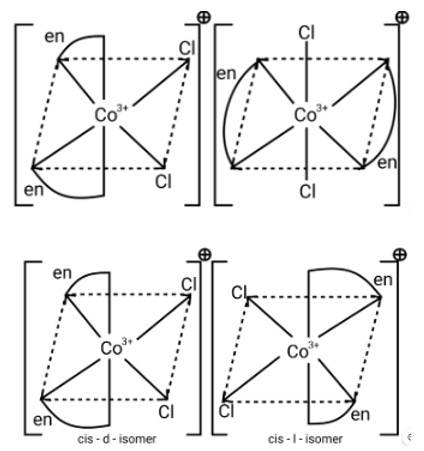
A complex of the type [M(AA)2X2]n + is known to be optically active. What does this indicate about the structure of the complex? Give one example of such a complex.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: [M (AA)2X2]n + is a bidentate ligand and %X is a monodentate ligand. It is an example of octahedral geometry as well as an ion. There are cis and trans isomers of this ion. Trans isomers are symmetrically active, while cis isomers are optically active.
Magnetic moment of [MnCl4]2- is 5.92 BM. Explain giving reason.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The existence of five unpaired electrons in the ion's mid-orbits Mn2+ equates to a magnetic moment of 5.92 BM. The number of hybridizations in this case is sp3. As a result, the magnetic moment value of the tetrahedral structure complex is 5.92 BM.
Based on crystal field theory explain why Co(III) forms a paramagnetic octahedral complex with weak field ligands whereas it forms a diamagnetic octahedral complex with strong field ligands.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Weak field ligands, Electronic configuration of Co (III) is t42g e0g, has 4 paired electrons and it is paramagnetic.
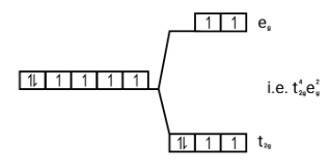
Strong field ligands, Electronic configuration of is Co (III) t62ge0g.

Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In a tetrahedral complex, the d-orbit splits too little compared to an octahedral complex. As a result, orbital energy alone are insufficient to couple. Low spin tetrahedral complexes do not form as a result.
Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes based on Crystal Field Splitting theory [CoF6]3-,[Fe(CN)6]4-and [Cu(NH3)6]2+
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The ligands can be grouped in ascending order of increasing field intensity according to spectrochemical series.
[CoF6]3−, Co3+ → (d6)→ t42g e0g
[FE (CN)6]4−, Fe2+→ (d6)→ t62g e2g
[Cu (NH3)6]2+, Cu2+→ (d9)→ t62g e2g
Explain why [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has magnetic moment value of 5.92 BM whereas [Fe(CN)6]3- has a value of only 1.74 BM.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: CN- is a strong ligand and [Fe (CN)6]3- has one paired electron
H2O is a weak ligand and [Fe (H2O)6]3+ has five paired electrons.
Arrange following complex ions in increasing order of crystal field splitting energy (Δ0)
[Cr(Cl)6]3- ,[Cr(CN)6]3- ,[Cr(NH3)6]3+
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: CFSE is higher when the complex contains strong field ligand. Thus, crystal field splitting energy increases in the order
[Cr (Cl)6]3−< [Cr (NH3)6]3+< [Cr (CN)6]3−.
Because according to spectrochemical series the order of field strength is
Cl−
Why do compounds having similar geometry have different magnetic moments?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Due to the presence of weak and strong field ligands in complexes, compounds with comparable geometry have distinct magnetic moments. The magnetic moment decreases when the CFSE increases, and vice versa.
Example: [Fe (CN)6]3- - Fe3+ ,3d5, CN- (strong field ligand, pairs electron)
[Fe (H2O)6]3- - Fe3+ ,3d5, H2O (weak field ligand, does not pair)
CuSO4.5H2O is blue in colour while CuSO4 is colourless. Why?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In CuSO4⋅5H2O, water acts as ligand and causes crystal field splitting. This makes d - d transitions possible. On the other hand, in CuSO4, splitting is not possible due to the lack of ligand in the crystal field. As a result, no colour is visible.
Name the type of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are attached to central metal ion. Give two examples of ambidentate ligands.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Ambidentate ligands are ligands which have two donating sites. Coordinating compounds containing ambidentate ligands show linkage isomerism due to two different binding positions. Linkage isomerism have same ligand and geometry attached to a central metal ion by different donating sites
Examples:
(i)
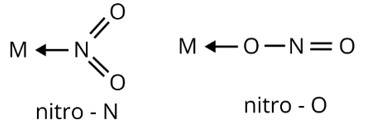
(ii) M←SCN
thiocyanato
M←NCS
isothiocyanato
Which of the following complexes formed by Cu2+ ions are most stable?
(i) Cu2+ + 4NH3⇌[Cu(NH3)4]2+,logK=11.6
(ii) Cu2+ + 4CN−⇌[Cu(CN)4]2−,logK=27.3
(iii) Cu2+ + 2en⇌[Cu(en)2]2+,logK=15.4
(iv) Cu2+ + 4H2O⇌[Cu(H2O)4]2+,logK=8.9
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct options: B
The bigger the value of constant, the better will be the stability.
Here, has the highest value of logk which corresponds to the highest value of k.
The colour of the coordination compounds depends on the crystal field splitting. What will be the correct order of absorption of wavelength of light in the visible region, for the complexes, [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Co(H2O)6]3+.
A: [Co(H2O)6]3+ > [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(H2O)6]3+ .
B: [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(H2O)6]3+ > [Co(CN)6]3-
C: [Co(H2O)6]3+ > [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(CN)6]3-
D: [Co(CN)6]3- > [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(H2O)6]3+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
Strong field ligands have five degenerate energy levels, which means they have more energy separation than weak field ligands.
Here, ΔE=
ΔE α
α
The wavelength decreases as the energy separation rises.
When 0.1 mol CoCl3(NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, 0.2 mol of AgCl are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to
A: 1:3 electrolyte
B: 1:2 electrolyte
C: 1:1 electrolyte
D: 3:1 electrolyte
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B
When 0.1 mol CoCl3 (NH3)5 is treated with excess of AgNO3, In the given reaction [CoCl3 (NH3)5]Cl2
then electrolytic solution must contain
[CoCl3 (NH3)5]Cl2+ and two Cl- ions.
Hence, it is 1:2 electrolyte.
When 1 mol [CrCl3(H2O)3]6H2O is treated with excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl are obtained. The formula of the complex is:
A: [CrCl3(H2O)3 ].3H2O
B: [CrCl2(H2O)4]Cl.2H2O
C: [CrCl2(H2O)5]Cl2H2O
D: [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: D
When 1 mol [CrCl3 (H2O)3]6H2O is treated with excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl is produced, i.e., [CrCl3 (H2O)3]6H2Ois dissociated in aqueous solution and all three chloride comes in solution.
[Cr (H2O)6]Cl3→ [Cr (H2O)6]3+ + 3Cl-
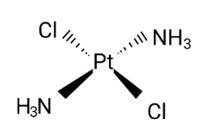
The correct IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is
(i) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (II)
(ii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (IV)
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (0)
(iv) Dichloridodiammineplatinum (IV)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
Diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) is also known as azane
A: [Fe(CO)5]
B: [Fe(CN)6]3-
C: [Fe(C2O4)3]3-
D: [Fe(H2O)6]3+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: C
The chelate effect is when a chelating ligand coordinates the stabilisation of a molecule. Any ligand that binds to metal forms a ring with 5 or 6 members, which is the most stable.
Here, CO, CN, H2O is monodentate ligand [Fe (C2O4)3]3- is an oxalate ligand.
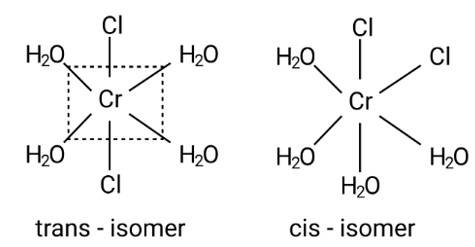
Indicate the complex ion which shows geometrical isomerism.
A: [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+
B: [Pt(NH3)3Cl]
C: [Co(NH3)6]3+
D: [Co(CN)5](NC)3-
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
This is due to the complex's octahedral structure and (cis-trans) isomerism. Two Cl ligands are next to each other in trans isomerism. Although these isomers have the same structure, they are not identical.
Possible isomers are:
The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4- is 18,000 cm−1. The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2- will be
A: 18,000 cm−1
B: 16,000 cm−1
C: 8,000 cm−1
D: 20,000 cm−1
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
CFSE for octahedral and tetrahedral complex is related as
Δt = Δ0
Where Δ0= CFSE for octahedral complex
Δ0= CFSE for tetrahedral complex
Δ0=1800 cm−1
Δt =49×18000=8000 cm−1
Due to the presence of ambidentate ligands coordination compounds show isomerism. Palladium complexes of the type [Pd(C6H5)2(SCN)2] and [Pd(C6H5)2(NCS)2] are
(A) Linkage isomers
(B) Coordination isomers
(C) Ionization isomers
(D) Geometrical isomers
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: (A)
Linkage isomerism arises in a coordination compound containing ambidentate ligand.
A simple example is by complexes containing the thiocyanate ligand, NCS-which may bind through the nitrogen to give M-NCS or through sulphur to give M-SCN.
The compounds [Co(SO4)(NH3)5] Brand [Co(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl represent
A: Linkage isomerism
B: Ionisation isomerism
C: Coordination isomerism
D: No isomerism
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: D
Two or more compounds with the same formula but distinct structures and characteristics are known as isomers.
So, in this case compounds
[Co (SO4) (NH3)5]Br and [Co (SO4) (NH3)5]Cl show no isomerism
A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?
A: Thiosulphato
B: Oxalato
C Glycinato
D: Ethane-1,2-diamine
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
A chelating agent binds to a single metal ion with two or more donor atoms. Oxaloto, Glycinato, and ethane-1,2-diamine all have two donor oxygen atoms. The gland Thiosulpato is ambidentate.
Which of the following species is not expected to be a ligand?
A: NO
B: NH4+
C: NH2CH2CH2NH2
D: CO
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B
Ligands are neutral ions that form a coordination complex with the central metal atom.
NH4+ does not have a lone pair of electrons to give.
What kind of isomerism exists between [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2⋅H2O (greyish-green)?
A: Linkage isomerism
B: Solvate isomerism
C: Ionisation isomerism
D: Coordination isomerism
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B
Hydrate isomerism is isomerism in which water is used as a solvent.
Coordination compounds with the same composition but varying ligand connectivity are known as linkage isomers.
Solvate isomerism has the same composition as free solvent but distinct solvent ligand molecules.
Except for the ligand that swaps places with the anion, ionisation isomers are identical isomers.
Coordination isomers are coordination compounds with distinct metal and ligand compositions.
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is
A: Platinum diaminechloronitrite
B: Chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II)
C Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
D Diamminechloronitrito-N-platinate (II)
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: C
[Pt (NH3)2Cl (NO2)] is a neutral molecule. Ligands are arranged alphabetically.
So, NH3 Diammine, chloride and the embedded linkage is nitrogen and last is the metal name.
Atomic numbers of Mn, Fe, and Co are 25, 26 and 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbital octahedral complex ions are diamagnetic?
A: [Co(NH3)6]3+
B: [Mn(CN)6]3-
C: [Fe(CN)6]4-
D: [Fe(CN)6]3-
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A and C
(i) Orbitals of Co3+ ion d2sp3 hybridised orbitals of Co3+ [Co (NH3)6]3+ (inner orbital or low spin complex)
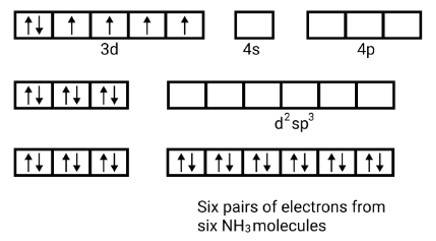
No. of unpaired electron =0
Magnetic property = diamagnetic, due to absence of unpaired electrons
(ii) Electronic configuration is 3 d6 orbitals of Fe2+ ion:
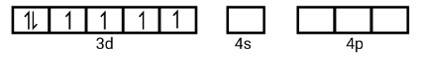

6 electron pairs from CN− ions occupy the six hybrid d2sp3 orbitals. Then,
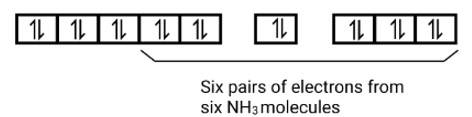
Hence, the geometry of the complex is octahedral and the complex is diamagnetic (as there are no unpaired electrons.
Atomic number of Mn, Fe, Co and Ni are 25, 26 27 and 28 respectively. Which of the following outer orbital octahedral complexes have same number of unpaired electrons?
A: [MnCl6]3-
B: [FeF6]3-
C: [CoF6]3-
D: [Ni(NH3)6]2+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A and C
The outer octahedral complexes are weak ligands, number of pairing electrons and high spinning potential.
[MnCl6]3- - electronic configuration of Mn = 3d5,4s2. Shifting the valence electrons become
Mn3+ ,3d4 and number of unpaired electrons is 4.
[FeF6]3- - electronic configuration of Fe = 3d6,4s2. Shifting the valence electrons become
Fe3+ ,3d5 and the number of unpaired electrons is 5.
[CoF6]3 - electronic configuration of Co = 3d7,4s2 shifting the valence electrons become
Fe3+ ,3d6 and the number of unpaired electrons is 4.
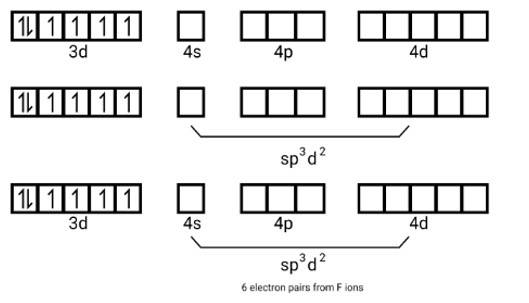
[Ni (NH3)6]2+ - electronic configuration of Ni = 3d8,4s2. Shuffling the valence electrons become
Ni2+ ,3d6 and the number of unpaired electrons is 2.
Which of the following options are correct for [Fe(CN)6]3 - complex?
A: d2sp3 hybridisation
B: sp3d2 hybridisation
C: Paramagnetic
D: Diamagnetic
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A and C
For answer at (A) Atomic number of Iron is 26 . In ferricyanide complex, iron is in oxidation state of 3+. The orbitals on the metal atom undergoes d2sp3 hybridizaion and hence the complex has octahedral shape.
Also it can be said that, [Fe (CN)6]3- has one unpaired electron which makes it weakiy paramagnetic. Therefore, option C is also correct.
An aqueous pink solution of cobalt (II) chloride changes to deep blue on addition of excess of HCl. This is because____________.
A: [Co(H2O)]2+ is transformed into [CoCl6]4-
B: [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl4]2-
C: Tetrahedral complexes have smaller crystal field splitting than octahedral complexes.
D: Tetrahedral complexes have larger crystal field splitting than octahedral complex.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B and C
[Co (H2O)6]2+ is increased when excess of HCl is added. Tetrahedral complexes have smaller crystal field splitting than octahedral complexes because Δt = Δ0
Which of the following complexes are homoleptic?
A: [Co(NH3)6]3+
B: [Co(NH3)4]+
C: 4[Ni(CN)4]2-
D: [Ni(NH3)4Cl2]
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct options: A, B and C
A homoleptic complex is one that has only one species or group as a ligand.
Option A, B, and C each have only one ligand, but option D has two.
Which of the following complexes are heteroleptic?
A: [Cr(NH3)6]3+
B: [Fe(NH3)4Cl]+
C: [Mn(CN)6]4-
D: [Co(NH3)6Cl2]
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B and D
Heteroleptic is a compound that contains many ligands of various sorts. NH3 and
Cl as a ligand or also called as donor groups, is a heteroleptic complex.
Identify the optically active compounds from the following.
A: [Co(en)3]3+
B: trans - [Co(en)2]+
C: cis - [Co(en)2Cl2]+
D: [Cr(NH3)5Cl]
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A and C
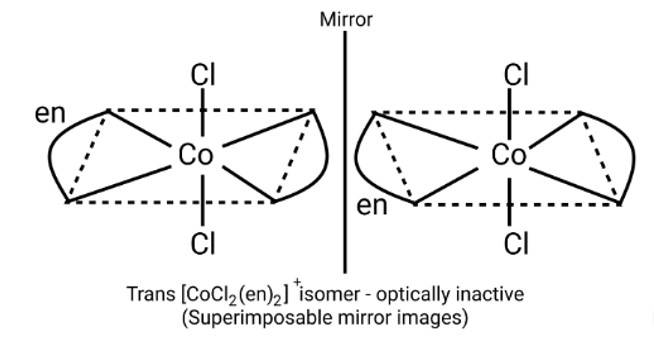
Optical compounds are highly imposable compounds that lack symmetry components. As a result, Option A and C are mirror reflections of each other.
Identify the correct statements for the behaviour of ethane-1, 2-diamine as a ligand.
A: It is a neutral ligand.
B: It is a didentate ligand.
C: It is a chelating ligand.
D: It is a unidentate ligand
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct options: A, B and C
Option A, B, and C describe that ethane-1, 2-diamine is a neutral ligand due to its lack of charge, a bidentate ligand due to the presence of two donor sites on one nitrogen atom, and a chelating ligand due to its ability to chelate with metal.
Which of the following complexes show linkage isomerism?
A: [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+
B: [Co(H2O)5]3+
C: [Cr(NH3)5SCN]2+
D: [Fe(en)5Cl2]+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: C
Coordination compounds with the same composition but varying ligand-metal connectivity are known as linkage isomerism.
[Co (NH3)5 (NO2)]2+ , NO2 has two donor sites N and O
[Cr (NH3)5SCN]2+ , S and N are two donor sites.
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the colours given in Column II and assign the correct code
|
Column I (Complex ion) |
Column II (Colour) |
|
A. [Co(NH3)6]3+ |
1. Violet |
|
B. [Ti(H2O)6]3+ |
2. Green |
|
C. [Ni(H2O)6]2+ |
3. Pale blue |
|
D. [Ni(H2O)4(en]2+ (aq) |
4. Yellowish orange |
|
5. Blue
|
Code
(i) A (1) B (2) C (4) D (5)
(ii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1)
(iii) A (3) B (2) C (4) D (1)
(iv) A (4) B (1) C (2) D (3)
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: (ii)
Match the coordination compounds given in Column I with the central metal atoms given in Column II and assign the correct code
|
Column I (Coordination Compound) |
Column II (Central metal atom) |
|
A. Chlorophyll |
1. Rhodium |
|
B. Blood pigment |
2. Cobalt |
|
C. Wilkinson catalyst |
3. calcium |
|
D. Vitamin B12 |
4. iron |
|
5. magnesium |
Code
(i) A (5) B (4) C (1) D (2)
(ii) A (3) B (4) C (5) D (1)
(iii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1)
(iv) A (3) B (4) C (1) D (2)
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: (i)
Match the complex ions given in Column I with the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons given in Column II and assign the correct code
|
Column I (Complex ion) |
Column II (Hybrisization, number of unpaired electrons) |
|
A. [Cr(H2O)6]3+ |
1. dsp2, 1 |
|
B. [Co(CN)4]2- |
2. sp3d2, 5 |
|
C. [Ni(NH3)6]2+ |
3. d2sp3, 3 |
|
D. [MnF6]4- |
4. sp3, 4 |
|
5. sp3d2, 2 |
Code
(i) A (3) B (1) C (5) D (2)
(ii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1)
(iii) A (3) B (2) C (4) D (1)
(iv) A (4) B (1) C (2) D (3)
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: (ii)
Match the complex species given in Column I with the possible isomerism given in Column II and assign the correct code
|
Column I (Complex species) |
Column II (Isomerism) |
|
A. [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ |
1. Optical |
|
B. cis - [Co(en)2Cl2]+ |
2. Ionisation |
|
C. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 |
3. Coordination |
|
D. [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] |
4. geometrical |
|
5. linkage |
Code :
(i) A (1) B (2) C (4) D (5)
(ii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1)
(iii) A (4) B (1) C (5) D (3)
(iv) A (4) B (1) C (2) D (3)
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: (iv)
Match the compounds given in Column I with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code.
|
Column I (Compound) |
Column II (Oxidation state of Co) |
|
A. [Co(NCS)(NH3)5(SO3)] |
1. + 4 |
|
B. [Co(NH3)4Cl2]SO4 |
2. 0 |
|
C. Na4[Co(S2O3)3] |
3. +1 |
|
D. [Co2(CO)8] |
4. +2 |
|
5. +3 |
Code
(i) A (1) B (2) C (4) D (5)
(ii) A (4) B (3) C (2) D (1)
(iii) A (5) B (1) C (4) D (2)
(iv) A (4) B (1) C (2) D (3)
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: (i)
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
A: Assertion and reason both are true, reason is correct of assertion.
B: Assertion and reason both are true, but reason is not the correct of assertion.
C: Assertion is true, reason is false.
D: Assertion is false, reason is true
1. Assertion: Toxic metal ions are removed by the chelating ligands.
Reason: Chelate complexes tend to be more stable.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
Toxic metal ions are removed by the chelating ligands. Chelate complexes tend to be more stable. When a solution of the chelating ligand is added to a solution containing toxic metals ligands chelates the metal ions by the formation of a stable complex.
Thus, EDT A (hexadentate ligand) forms a stable metal chelate and is used to remove toxic metal ions.
Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct for Assertion.
Hence, option A is correct.
Assertion : [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature.
Reason: Unpaired electrons are present in their d-orbitals.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B
[Cr (H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe (H2O)6]Cl2
Due to the creation of a more stable complex ion after obtaining ion, [Cr (H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe (H2O)6]Cl2 are reduced in nature. Both compounds have a coordination of 6 and so form an octahedral complex. The hybridisation state of is 3 and the oxidation state of is 2+. Hybridization is 3d4 and 3d6 is 2+. Both compounds have unpaired electrons and have weak field ligands. In both compounds, removing electrons is simple.
Assertion: Linkage isomerism arises in coordination compounds containing ambidentate ligand.
Reason: Ambidentate ligand has two different donor atoms.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: A
The term "linkage isomerism" refers to two molecules that have similar ligands but differ in the donating site of the ligand. Ambidentate is made up of two different types of donor atoms.
Example [Fe (NO2) (H2O)5]Cl2. NO2 is Ambidentate ligand as Nand O2 are donors.
As a result, linkage isomerism occurs in coordinations with ambidentate ligands. Reason and Assertion are both correct.
Assertion: Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism.
Reason: Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: B
From the Cis and Trans forms, geometrical isomerism forms compounds. All of the valences in the MX6 ligand are the same, resulting in an identical molecule. L is a distinct ligand in MX5L, and it can be replaced with any other valency in the structure to create an identical molecule; the molecule does not change. Because of the presence of symmetry, which is an essential prerequisite for revealing geometrical isomerism, complexes do not show geometrical isomerism.
Assertion: [Fe(CN)6]3- ion shows magnetic moment corresponding to two unpaired electrons.
Reason: Because it has d2sp3 type hybridisation.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: D
[Fe (CN)6]3- ion shows magnetic moment corresponding to one unpaired electron. (CN) is a ligand with a strong field that couples electrons, resulting in hybridisation. d2sp3 and it has one unpaired electron, it has the magnetic moment of one paired electron.
μ= = 1 (1 + 2)
= 3 = 1.73BM
JEE Main Solutions 2022
JEE Mains Solution 2022
Commonly asked questions
Which of the following pair of molecules contain odd electron molecule and an expanded octet molecule?
BCl3 – electron deficient molecule
SF6 – expanded octet molecule
NO – odd electron bond containing molecule
H2SO4 – expanded octet molecule
20g 5g
Consider the above reaction, the limiting reagent of the reaction and number of moles of NH3 formed respectively are:
t = 0 0
Here, N2 is the limiting reagent
and No of moles of NH3 = 2 × No of moles ofN2 reacted
100 mL of 5% (w/v) solution of NaCl in water was prepared in 250 mL beaker. Albumin from the egg was poured into NaCl solution and stirred well. This resulted in a/an:
This is the method of preparation of lyophilic solution as condition is given.
The first ionization enthalpy on Na, Mg and Si, respectively, are : 496, 737 and 786 kJ mol-1. The first ionization enthalpy (kJ mol-1) of Al is:
Following is the trends of I.E. of given metals
In metallurgy the term “gangue” is used for:
In ores/mineral available earthy and undesired impurities are gangue
The reaction of zinc with excess of aqueous alkali, evolves hydrogen gas and gives:
Following is the reaction of Zn with excess alkali,
Lithium nitrate and sodium nitrate, when heated separately, respectively, give:
Number of lone pairs of electrons in the central atom of SCl2, O3, ClF3 and SF6, respectively are:
SCl2 – 2 lone pair of central atom
O3 – 1 lone pair of central atom
ClF3 – 2 lone pair of central atom
SF6 – 0 lone pair of central atom
In following pairs, the one in which both transition metal ions are colourless is:
electron in last subshell
electron in last subshell
electron in last subshell
electron in last subshell
electron in last subshell
electron in last subshell
electron in last subshell
In neutral of faintly alkaline medium KMnO4 being a powerful oxidant can oxidize, thiosulphate almost quantitatively, to sulphate. In this reaction overall change in oxidation state of manganese will be:
Following is the reaction of KMnO4 in basic medium with thiosulphate anion.
Change = 7 – 4 = 3
Which among the following pairs has only herbicides?
The pair of herbicides is sodium chlorate and sodium arsinite
Which among the following is the strongest Bronsted base?
Due the absence of inversion and non resonating nature
Which of the following compounds is an example of hypnotic drug?
Drug used in the treatment of sleeping problems
Resistance of a conductivity cell (cell constant 129 m1) filled with 74.5 ppm solution of KCl is (labeled as solution 1). When the same cell is filled with KCl solution of 149 ppm, the resistance is (labeled as solution 2). The ratio of molar conductivity of solution 1 and solution 2 is i.e. The value of x is________. (Nearest integer)
Given cell constant
Ratio of ppm of two solution of KCl = Ratio of moles of per unit volume.
x = 1000
Ionic radii of cation A+ and anion B are 102 and 181 pm respectively. These ions are allowed to crystallize into an ionic solid. This crystal has cubic close packing for B. A+ is present in all octahedral voids. The edge length of the unit cell of the crystal AB is________ pm.
(Nearest integer)
Edge length of the unit cell AB = a = 2
The minimum uncertainty in the speed of an electron in an one dimensional region of length 2a0 (Where a0 = Bohr radius 52.9 pm) is__________ km s-1.
(Given: Mass of electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg, Planck’s constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainly principle
= 548273 ms-1
When 600 mL of 0.2 M HNO3 is mixed with 400 mL of 0.1 M NaOH solution in a flask, the rise in temperature of the flask is_________ × 10-2 °C.
(Enthalpy of neutralization = 57 kJ mol-1 and Specific heat of water = 4.2 JK-1 g-1)
(Neglect heat capacity of flask)
HNO3 + NaOH ® NaNO3 + H2O
t = 0, (600 × 0.2)meq (400 × 0.1)meq 40 meq 40 meq
120 meq 40 meq
t =
Total heat produced during neutralization ;
2280 = 1000 × 4.2 × q
If O2 gas is bubbled through water at 303 K, the number of millimoles of O2 gas that dissolve in 1 litre of water is______________. (Nearest integer)
(Given: Henry’s Law constant for O2 at 303 K is 46.82 k bar and partial pressure of O2 = 0.920 bar)
(Assume solubility of O2 in water in too small, nearly negligible)
According to Henry’s law
P = KH × mole fraction of solute
Mole of O2 = 1.09 × 10-3
If the solubility product of PbS is 8 × 10-28, then the solubility of PbS in pure water at 298 K is The value of x is__________. (Nearest integer)
[Given:
Or solubility of PbS = 282 × 10-16
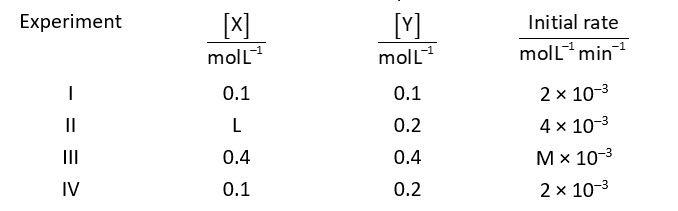
The reaction between X and Y is first order respect to X and zero order with respect to Y.
Examine the data of table and calculate ratio of numerical values of M and L (Nearest integer)
According to condition
Rate
By using experimental data I and II
And by using experimental data I and II
M = 8
Ratio of
In a linear tetrapeptide (Constituted with different amino acids), (number of amino acids) (number of peptide bonds) is_______________.
No. of Amino acid units are 4 and
No. of peptide bonds are 3
In tetrapeptide
In bromination of Propyne, with Bromine 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrabromopropane is obtained in 27% yield. The amount of 1, 1, 2, 2- tetrabromopropane obtained from 1g of Bromine in this reaction is_______________× 10-1g. (Nearest integer) (Molar mass: Bromine = 80g / mol)
Reaction is
Mass of product, 1, 2, 2- tetrobromopropane obtained
=
= 3.30375
= 3.0375 × 10-1
should be an inner orbital complex. Ignoring the pairing energy, the value of crystal field stabilization energy for this complex is (-) _________ (Nearest integer)
In complex
CN is the strong field ligand
CFSE value = 5 ×
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Nine Exam